🐢0.개요
Gazebo Plugin이란? Gazebo 시뮬레이션 환경에서 다양한 사물의 움직임을 구현하거나, 기능을 구현하는데 사용된다.
로봇의 센서,엑추에이터, 컨트롤러를 구현하는데 활용할 수 있다. Python이나 C++로 작성 될 수 있으며,
이번시간에서 C++로 Plugin을 직접 작성해보면서 Plugin의 역할을 알아보자.
🔌1.Plugin 작성 과정
이번 실습에는 Gazebo의 사물을 정사각형 모양을 그리면서 움직이는 모형을 만들어 볼 예정이다.
아래의 순서대로 진행해보자.
1.1 CMakeList.txt 작성하기
프로젝트의 의존성을 추가하기 위한 CMakeList를 작성한다.
gazebo_plugins,gazebo_ros,roscpp package를 추가해주고 아래와 같이 코드를 작성한다.
⛰️ CMakeList.txt
cmake_minimum_required(VERSION 3.0.2)
project(writing_plugins)
find_package(gazebo REQUIRED)
find_package(catkin REQUIRED COMPONENTS
gazebo_plugins
gazebo_ros
roscpp
)
catkin_package()
include_directories(
# include
${catkin_INCLUDE_DIRS}
)
include_directories(${GAZEBO_INCLUDE_DIRS})
link_directories(${GAZEBO_LIBRARY_DIRS})
list(APPEND CMAKE_CXX_FLAGS "${GAZEBO_CXX_FLAGS}")
add_library(a_model_plugin SHARED src/a_model_plugin.cc)
target_link_libraries(my_gazebo_plugin ${GAZEBO_LIBRARIES})add_library 라인에 본인이 작성한 플러그인 파일 (a_model_plugin.cc)을 넣어준다.
아래에서 .cc파일을 확인해보자
1.2 .CC 파일 작성
.cc파일에서는 Gazebo의 모델을 컨트롤할 코드를 작성해준다.
Load 함수는 플러그인이 로드 될 때 실행되는 함수이다. 클래스의 변수를 초기화 하여 Gazebo에 알려주는 역할을 한다.
여기에서는 물체의 속도 및 움직이는 시간을 입력하였다.
입력되는 변수가 없다면 초기에 선언한 값을 사용 할 수 있다.
OnUpdate 함수는 Gazebo 시뮬레이션에서 각 타임스탭에서 호출되는 함수이다.
아래와 같이 정사각형으로 움직이게 하기 위해 +x -> +y -> -x -> -y 순으로 동작하게 작성하였다.
🗒a_model_plugin.cc
#include <functional>
#include <gazebo/common/common.hh>
#include <gazebo/gazebo.hh>
#include <gazebo/physics/physics.hh>
#include <ignition/math/Vector3.hh>
namespace gazebo {
class AModelPlugin : public ModelPlugin {
public:
void Load(physics::ModelPtr _parent, sdf::ElementPtr _sdf) {
// Store the pointer to the model
this->model = _parent;
this->iterations = 10 * 1000;
if (_sdf->HasElement("iterations")) {
this->iterations = _sdf->Get<int>("iterations");
}
this->linear_vel = 0.1;
if (_sdf->HasElement("linear_vel")) {
this->linear_vel = _sdf->Get<double>("linear_vel");
}
// Listen to the update event. This event is broadcast every simulation
// iteration.
this->updateConnection = event::Events::ConnectWorldUpdateBegin(
std::bind(&AModelPlugin::OnUpdate, this));
}
// Called by the world update start event
public:
void OnUpdate() {
// Apply a small linear velocity to the model.
if ((counter / iterations) % 4 == 0) {
this->model->SetLinearVel(
ignition::math::Vector3d(this->linear_vel, 0, 0));
} else if ((counter / iterations) % 4 == 1) {
this->model->SetLinearVel(
ignition::math::Vector3d(0, this->linear_vel, 0));
} else if ((counter / iterations) % 4 == 2) {
this->model->SetLinearVel(
ignition::math::Vector3d(-this->linear_vel, 0, 0));
} else if ((counter / iterations) % 4 == 3) {
this->model->SetLinearVel(
ignition::math::Vector3d(0, -this->linear_vel, 0));
}
counter++;
}
// Pointer to the model
private:
physics::ModelPtr model;
private:
double linear_vel;
int iterations;
int counter;
// Pointer to the update event connection
private:
event::ConnectionPtr updateConnection;
};
// Register this plugin with the simulator
GZ_REGISTER_MODEL_PLUGIN(AModelPlugin)
} // namespace gazebo1.3 .world
world 에서 물체의 속성과 적용할 플러그인을 선언하였다.
.cc의 변수를 plugin tag 내에 삽입하여 해당 값을 사용 할 수 있게 한다.
🌍model.world
...
<model name="a_barrier">
<pose>2 2 0.5 0 0 0</pose>
<static>false</static>
<include>
<uri>model://person_walking</uri>
</include>
<!-- import plugin -->
<plugin name="liba_model_plugin" filename="liba_model_plugin.so">
<linear_vel>0.2</linear_vel>
<iterations>2500</iterations>
</plugin>
</model>
...1.4 Plugin 경로 설정
Gazebo에 사용할 Plugin의 경로를 알려주기 위해 터미널에 아래와 같이 입력한다.
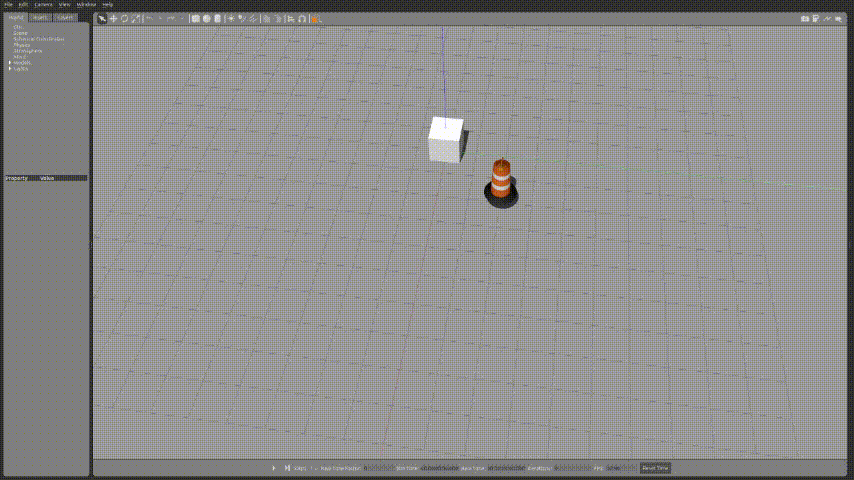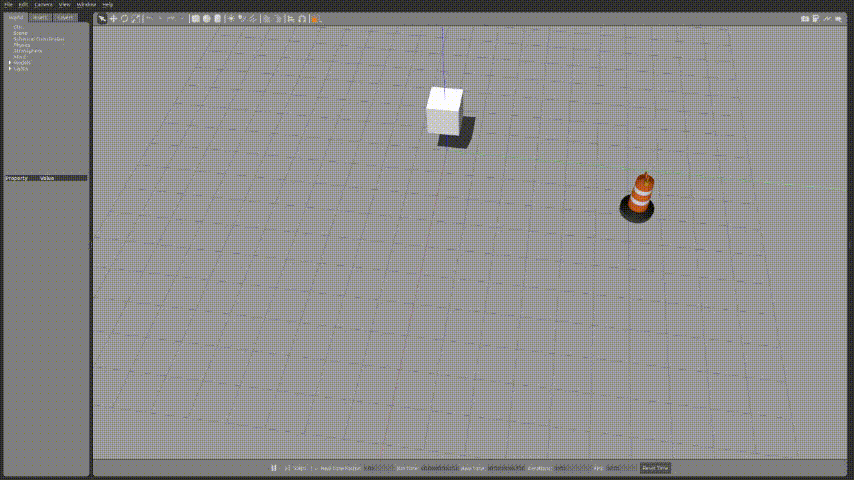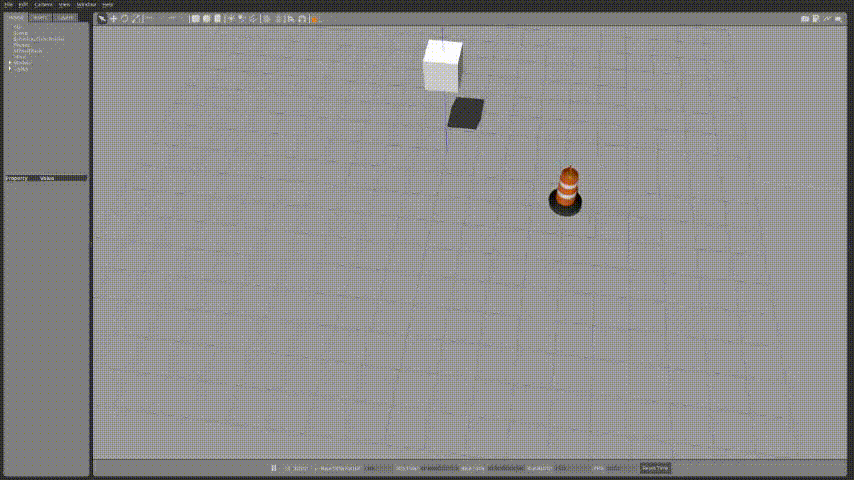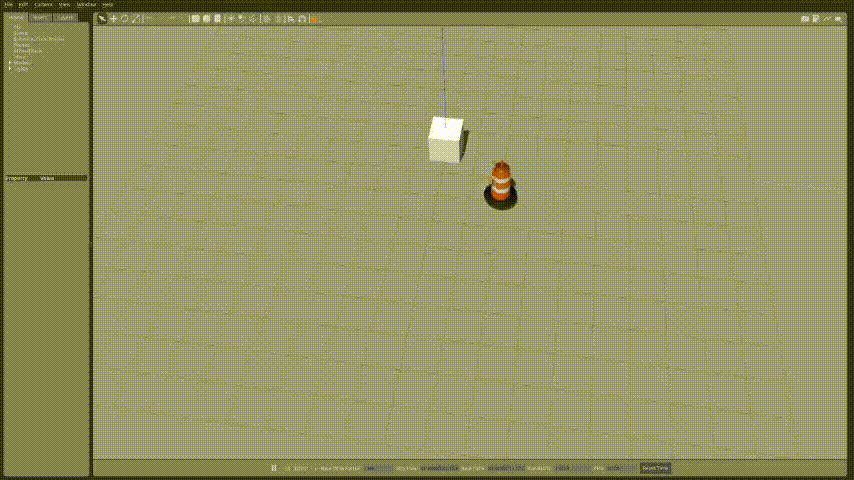
export GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH=${GAZEBO_PLUGIN_PATH}:~/sim_ws/devel/lib🚗2.실행화면
launch파일을 작성하여 실행화면을 확인해보자.
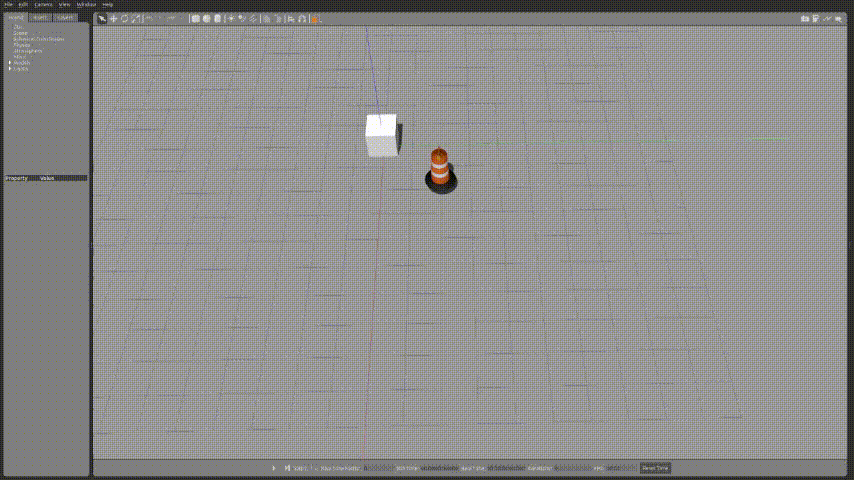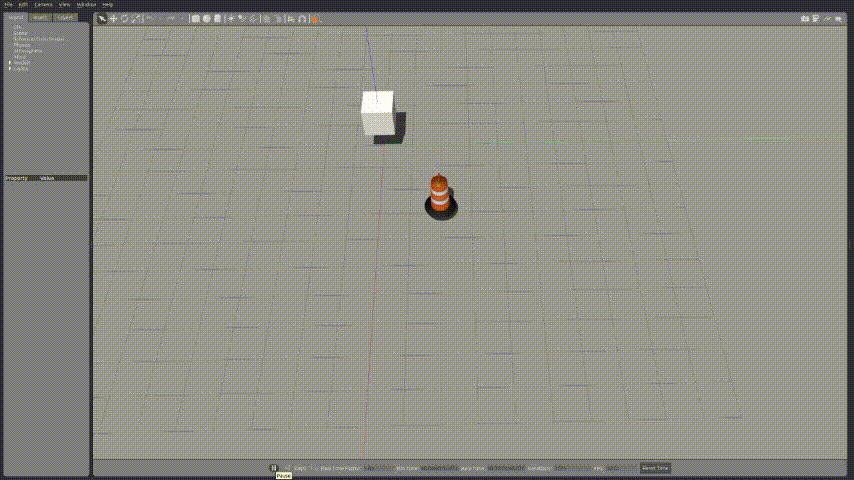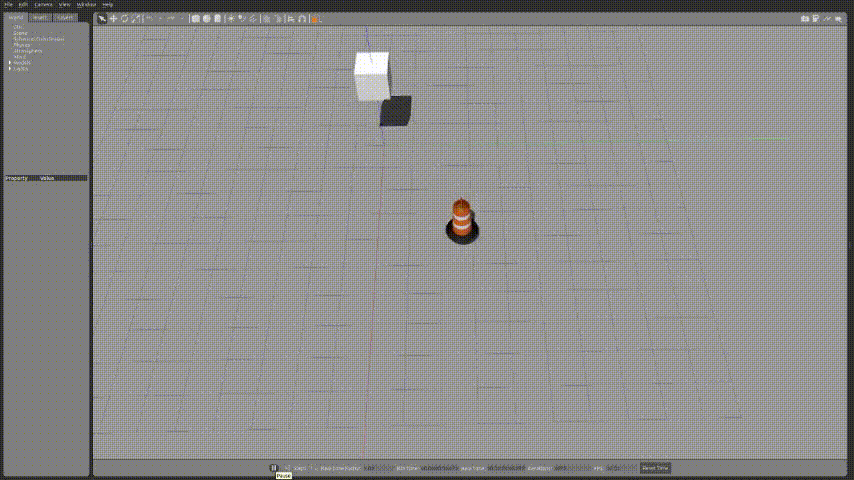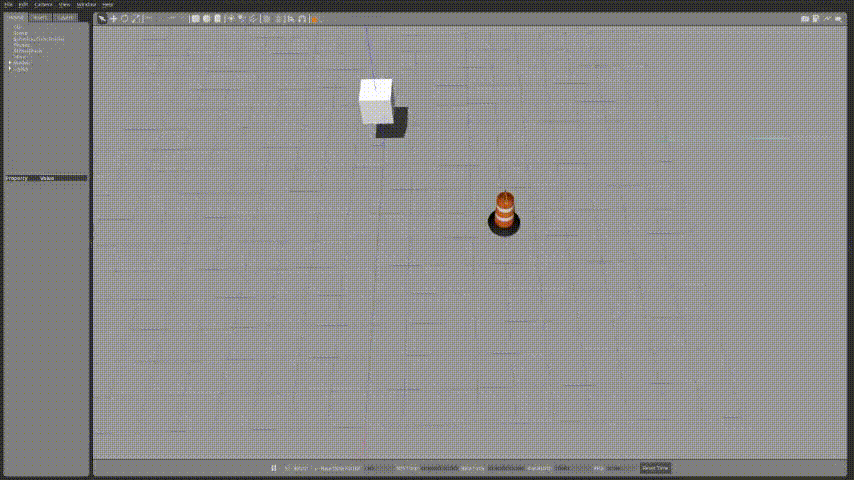
조금 속도가 느리지만 정사각형 형태를 그리면서 잘 동작하는 것을 확인 할 수 있다.
속도가 많이 느려서 아래와 같이 조정하였다.
linear_vel = 5.0 값 iterations = 1000
🌍model.world
...
<linear_vel>5.0</linear_vel>
<iterations>2500</iterations>
...
아래와 같이 코드를 수정하여 물체를 사람으로 변경하여 움직이게 할 수 있다.
🌍model.world
...
<model name="human">
<pose>2 2 0.5 0 0 0</pose>
<static>false</static>
<include>
<uri>model://person_walking</uri>
</include>
<!-- import plugin -->
<plugin name="liba_model_plugin" filename="liba_model_plugin.so">
<linear_vel>5.0</linear_vel>
<iterations>1000</iterations>
</plugin>
</model>
...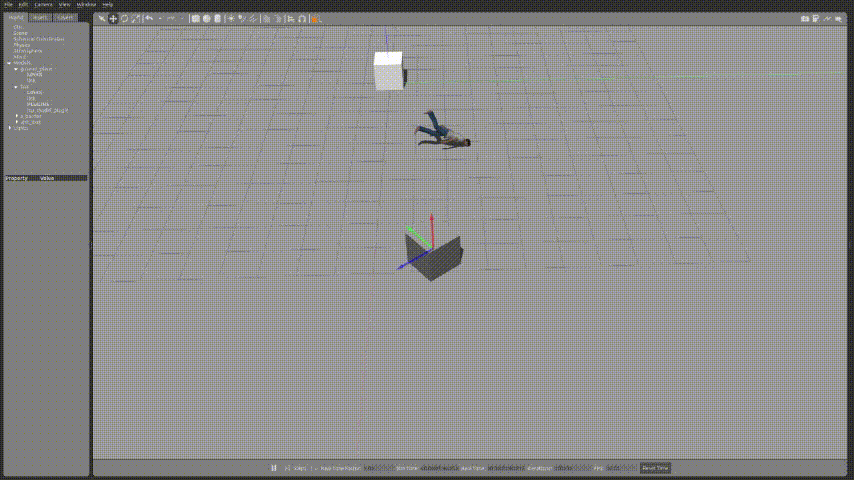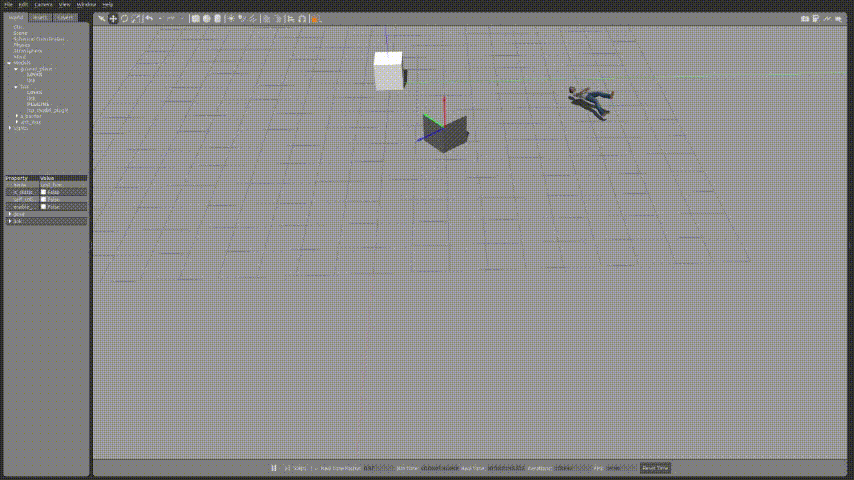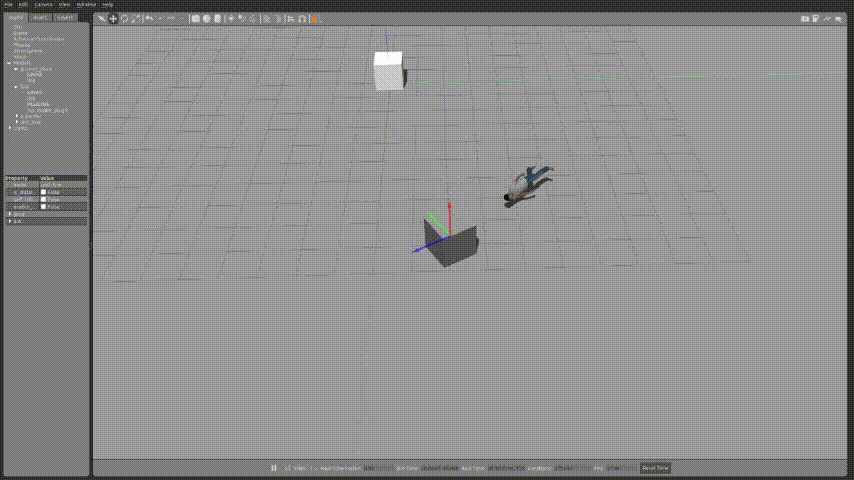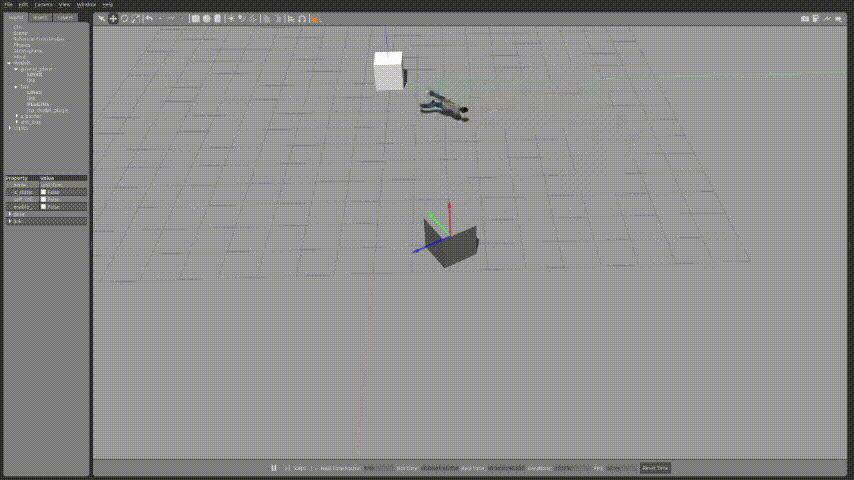
box객체를 밀어내는 사람의 모습을 확인 할 수 있었다.