
로지스틱 회귀(Rogistic Regression)란?
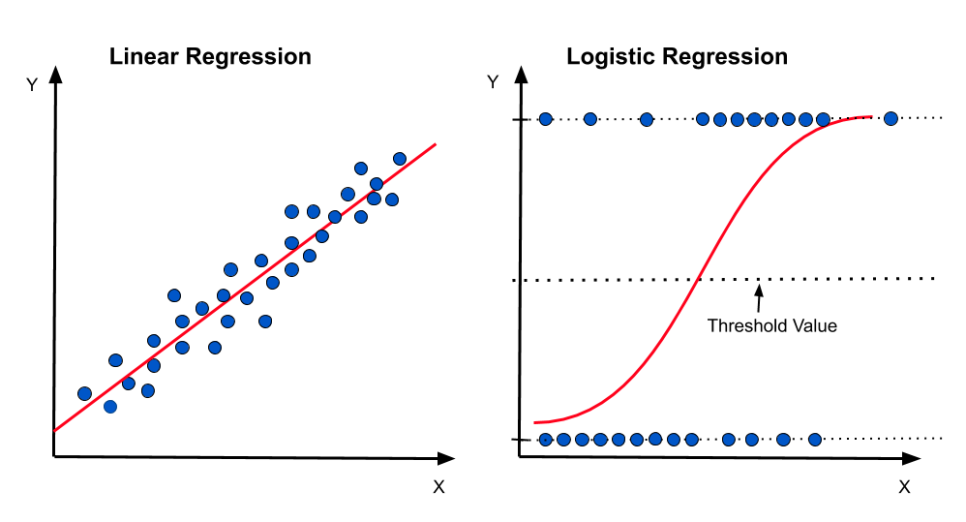
대표적인 분류 알고리즘이다.
-
작동원리: 데이터를 보고 특정 클래스에 속할 확률을 계산한다. 확률이 0.5보다 크면 1, 작으면 0으로 판정한다.
-
특징: 결과가 직선이 아니라 S자 곡선(Sigmoid 함수) 형태로 나타나며, 0과 1사이로 값을 가둔다.
혼동 행렬(Confusion Matrix)
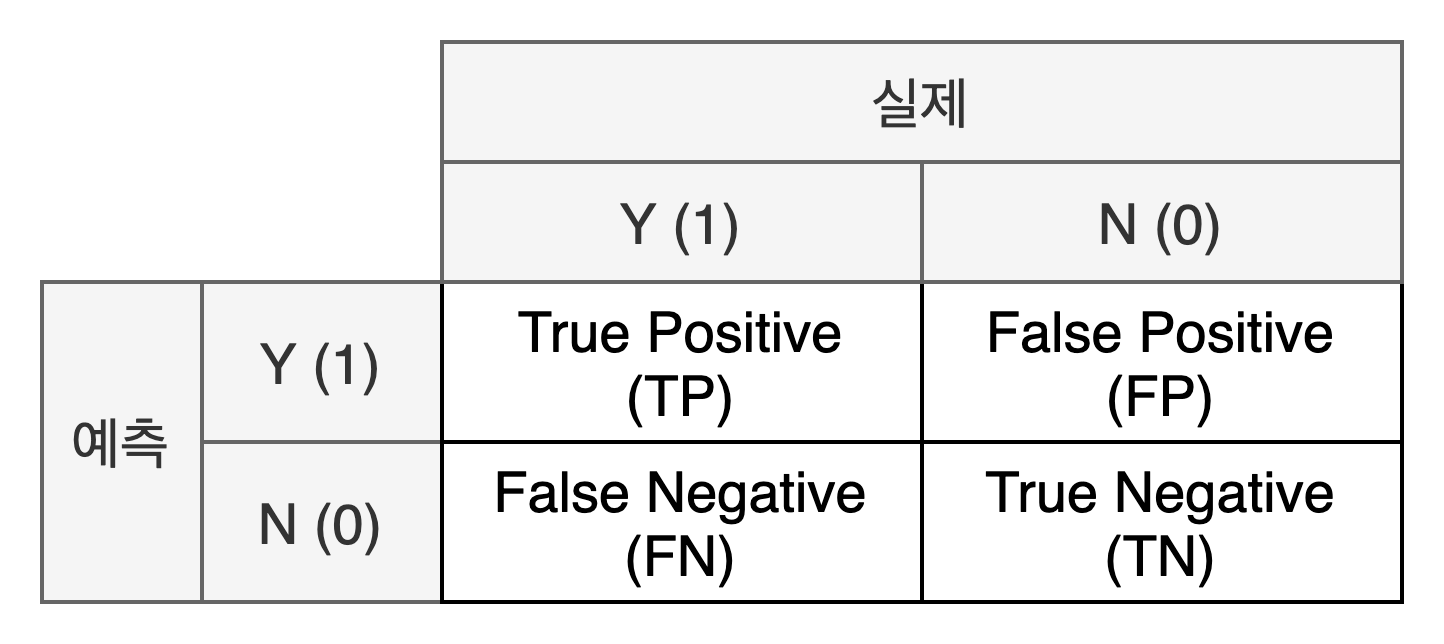
분류 모델의 성적표는 대신 '정확도(Accuracy)'와 '혼동 행렬'을 본다.
- 정확도: 전체 748명 중 AI가 수료 여부를 몇 명이나 맞혔는가?
- 혼동 행렬: "수료인데 미수료라고 예측한 경우"와 "미수료인데 수료라고 예측한 경우"를 표로 나누오 분석한다.
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LogisticRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score, confusion_matrix, classification_report
class FinalClassificationPredictor:
def __init__(self, file_path: str):
self.df = pd.read_csv(file_path)
self.features = ['time_input', 'total_class_count', 'job']
self.target = 'completed'
self.df = self.df[self.features + [self.target]].dropna()
def run_classification(self):
encoded_df = pd.get_dummies(self.df, columns=['job'])
X = encoded_df.drop(columns=[self.target])
y = encoded_df[self.target]
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test = train_test_split(X, y, test_size=0.2, random_state=42)
model = LogisticRegression(max_iter=1000)
model.fit(X_train, y_train)
y_pred = model.predict(X_test)
acc = accuracy_score(y_test, y_pred)
print(f"--- 분류 분석 결과 (Logistic Regression) ---")
print(f"전체 정확도(Accuracy): {acc:.4f}")
print("\n[혼동 행렬(Confusion Matrix)]")
print(confusion_matrix(y_test, y_pred))
# --- 실행부 ---
predictor = FinalClassificationPredictor('train.csv')
predictor.run_classification()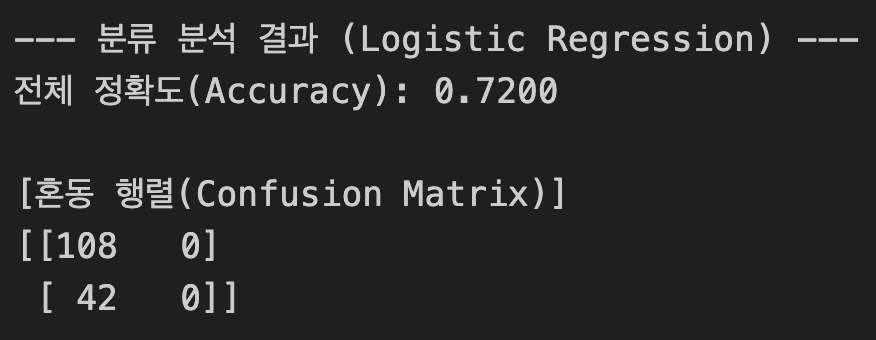
클래스 불균형(Class Imbalance) 문제
