Recap
Basic of Reinforcement Learning
- Input
given environment which provides numerical reward signal, and agent which act inside of that environment - Outputs
let agent learn how to take actions(policy) in order to maximize reward
policy는 goal을 달성하기 위한 strategy or skill - Goal
learn how to take actions in order to maximize reward - Design RL
Objective, State, Action, Reward
objective : goal, state : description of the world로 이해하면 됨
Design RL예시
-
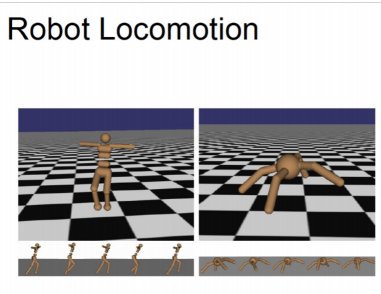
- objective : 로봇이 앞으로 움직이도록 만들기
- state : joints의 각도와 위치
- action : joints에 apply될 torques
- reward : 1 at each time step upright + forward movement
-
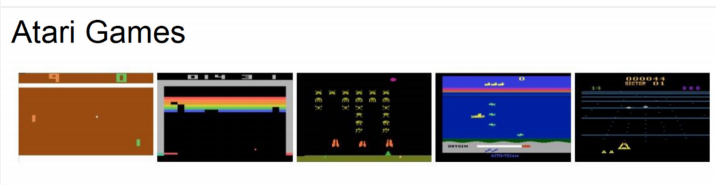
- objective : complete the game with the highest score
- state : raw pixel inputs of the game state
- action : game controls (e.g. left, right, up, down)
- reward : score increase/decrease at each time step
-
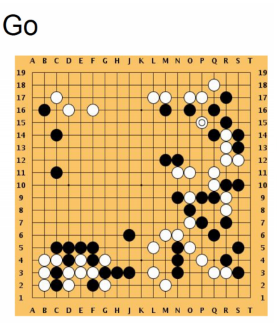
- objective : 바둑 우승
- state : 각 바둑돌들의 위치
- action : 다음 돌을 어디에 놓을지
- reward : 승리 시 1, 패배 시 0
Key Concepts in RL
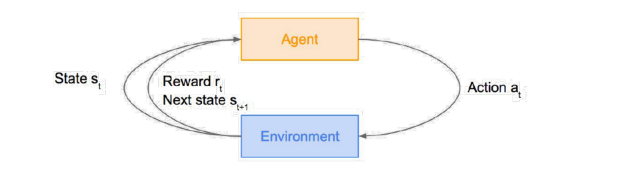
State ()
A complete description of the state of the world(environment)
Action ()
Agent take action on the environment
주어진 환경에서 가능한 액션의 집합을 action space으로 부름 (discrete/ continuous)
Reward ()
The agent also perceives a reward signal from the environment, a number that tells it how good or bad the current world state is.
Trajectories ()
world에서 state와 action, reward의 시퀀스
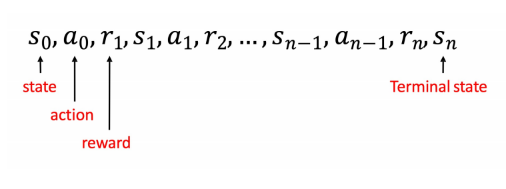
Meaning of Life for RL Agent
: Maximize Reward
주어진 trajectory
- Future reward:
Markov property를 따라 이미 일어난 일은 고려 안함 → future reward를 maximize하고자 함 - Discounted future reward:
는 discount factor - agent의 좋은 strategy는 언제나 (discounted) future reward를 최대화하는 action을 선택하는 것
- Why "discounted"?
- analyze convergence를 돕는 수학적 트릭
- environment stochasticity의 불확실성
미래는 멀수록 더 불확실해지므로 갈수록 리워드를 적게 고려하는 가중치를 곱하는 것
RL이 directly or indirectly 학습하려는 것
Policy
agent's behavior function
Value function
how good is each state and/or action
Model
agent's representation of the environment
Model Policy
각각에 대해 조금 더 깊이 알아보자면
Policy
- Agent's behavior function : A rule used by an agent to decide what actions to take
- Deterministic Policy:
only one action is correct to take - Stochastic Policy:
여러 action 가능- Categorical policies: discrete actions
- Gaussian policies: continuous actions
Value Function
- 각 state and/or action이 얼마나 좋았는지에 대한 점수
- the expected cumulative return if you start in the state or state-action pair
해당 state 또는 state-action pair에서 시작하는 경우의 예상 누적 수익률 - 거의 모든 RL algorithm에서 어떤 식으로든(one way or another) 사용 됨
Given Trajectory
Expected cumulative reward:
- Value Function ()
state 에서 시작하고 언제나 policy 를 따라 행동하는 경우의 예측값
간단하게 생각한다면, 현재 state 상황에서 가질 수 있는 future reward의 합이라고 생각하면 됨 - Action-Value Function ()
state 에서 action a를 하며 시작하고 언제나 policy 를 따라 행동하는 경우의 예측값
에서 를 취할 때 expected reward의 합
The RL Problem
RL의 목표는 agent가 따라 행동했을 때 expected cumulative reward를 최대화시키는 policy를 고르는 것
- 이 주어진 경우 → : Value function (V)
- 이 주어진 경우 → : Q function (Q)
self-consistent Bellman Function을 통해 policy를 수치적으로 최적화(numerically optimize)시킬 수 있음