Bibtex 인용
@inproceedings{kong2020semantic,
title={Semantic graph based place recognition for 3d point clouds},
author={Kong, Xin and Yang, Xuemeng and Zhai, Guangyao and Zhao, Xiangrui and Zeng, Xianfang and Wang, Mengmeng and Liu, Yong and Li, Wanlong and Wen, Feng},
booktitle={2020 IEEE/RSJ International Conference on Intelligent Robots and Systems (IROS)},
pages={8216--8223},
year={2020},
organization={IEEE}
}요약
- 3d 포인트 클라우드에서 Occulsion 및 viewpoint변화, place recognition에 강인한 descriptortor를 생성하는것이 어려움
- 대부분 로컬 아니면 글로벌 아니면 통계적 특징을 사용함
- 이 페이퍼에서는 human perspective에 ㄱㅣ반해서 semantric한 레벨을 목표로함
- semantic object를 인식하고 그래프 기반 접근 방식을 제시
- 장소 인식을 그래프 기반의 매칭 문제로 치환
- 코드는 여기.
인트로
- 누적된 주행 drift error를 제거하는 가장 효과적인 방법은 loop closing을 하는 방법임
- 현재의 place recognition 전략은 대부분 descriptor 생성과 feature distance measurement에 기반함
- 라이다 기반 방법에서 많이 쓰이는거는 raw data에 neural network 혹은 handcrafted design기반으로 local or global descriptor를 뽑는거임
- 이렇게 하면 보통 low level의 feature를 얻게됨 ex) local structure, distributing characteristic
- 이런거 occlusion 이나 rotation에 sensitive하고 segment사이의 관계들이 무시되는데 그게 scene expression에 치명적일 수 있음
- 이 논문에서는 point cloud data를 semantic information을 aggregate해서 만든 novel graph representation을 사용함
- 이런 graph based reperesentation은 topological relation을 고려하므로 포인트클라우드를 더 efficient and comprehensible하게 만들어줌
기여
- 3d point cloud에 대한 semantic graph representation을 제시함
- capture semantic information and model topological relations between objects
- loop closure detection에 사용될 수 있는 graph similarity matching 네트워크를 제시함
- semantic kitti로 테스트해서 reverse loop closure detection과 occlusion 및 viewpoint변화에 대한 robustness에 SOTA임을 보임
Methodology
- key insight는
- human perspective사용
- semantic level의 descriptor사용
- encoding relations among semantic object
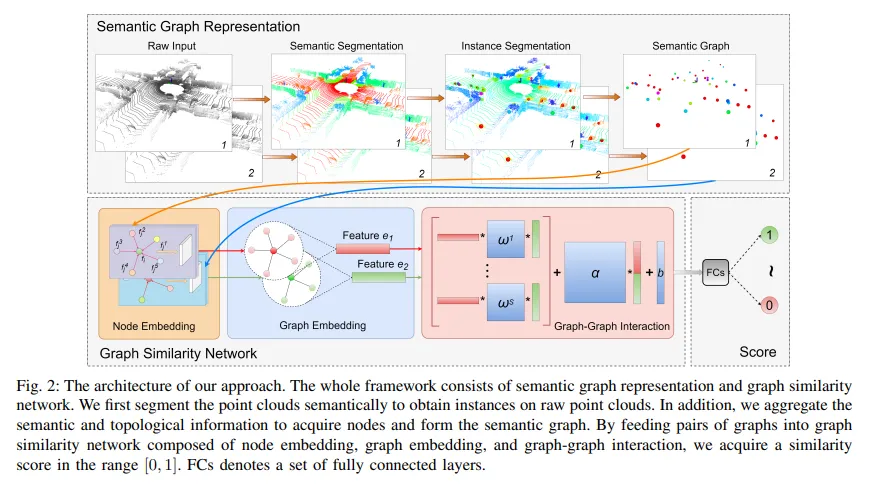
- raw 포인트에 대해서 semantic segmentation을 통해 instance 및 semantic information topological information을 취득하여 semantic graph를 구성함
- 그 이후에 raw point cloud들을 topological semantic graph로 변환하여서 place recognition문제를 그래프 매칭 문제로 바꿈
A. Semantic Graph Representation
Semantic Segmentation for Point Clouds
- RangeNet++이랑 Semantic KITTI사용해서 semantic object detection을 하는데, 이 과정에서 몇개의 클래스들을 합치고 지워서 12개의 카테고리만 사용함
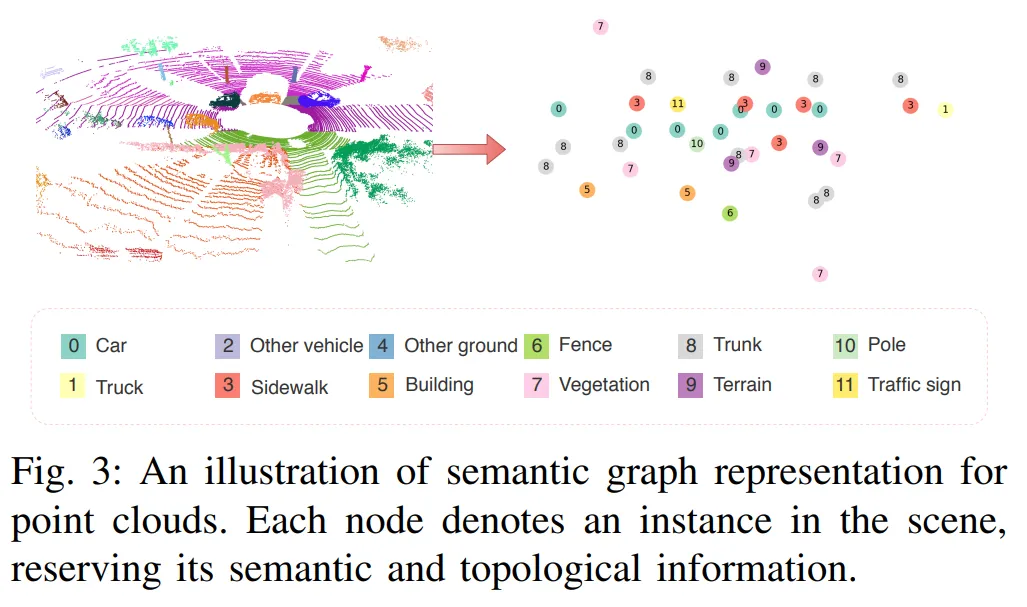
- 각 카테고리에 따라서 클러스터링 반경을 다르게 설정하고 , 유클리디안 클러스터링을 통해서 semantic instance를 취득
Semantic Graph Constriction
- 64채널 라이다가 보통 한 프레임 당 10만개 이상의 포인트를 capture하는데, 이거 너무 redundant함
- 줄이기위해서 down sampling이나 2D평면에 투영하는데, 우리는 topological semantic graph를 사용함
- concise하고 meaningful하며 semantic information과 topological relation이 잘 보존됨
- 각 semantic instance들은 one hot encoding되어서 사용되고 유클리디안 디스턴스 기반으로 나타남
- 그 그래프가 scene에 대한 representation임 그래서 이제 similarity measurement problem으로 두 그래프를 비교할 수 있음
B. Graph Similarity Network
- 보통 그래프 similarity metric으로 Graph Edit Distance(GED), Maximum Common Subgraph(MCS)를 사용하는데 이거 NP-complete라서 정확한 distance를 구하기 힘듦
- 그리고 loop closing을 위한 place recognition이기때문에 permutation invarient해야하고 rotation invariant해야함
- 위의 조건을 만족시키면서 원래의 similarity 산출방식을 사용하면 reasonable한 시간 안에 도출이 불가능
- 그래서 propseg한다, graph matching을 위한 graph similarity network inspired by SimGNN
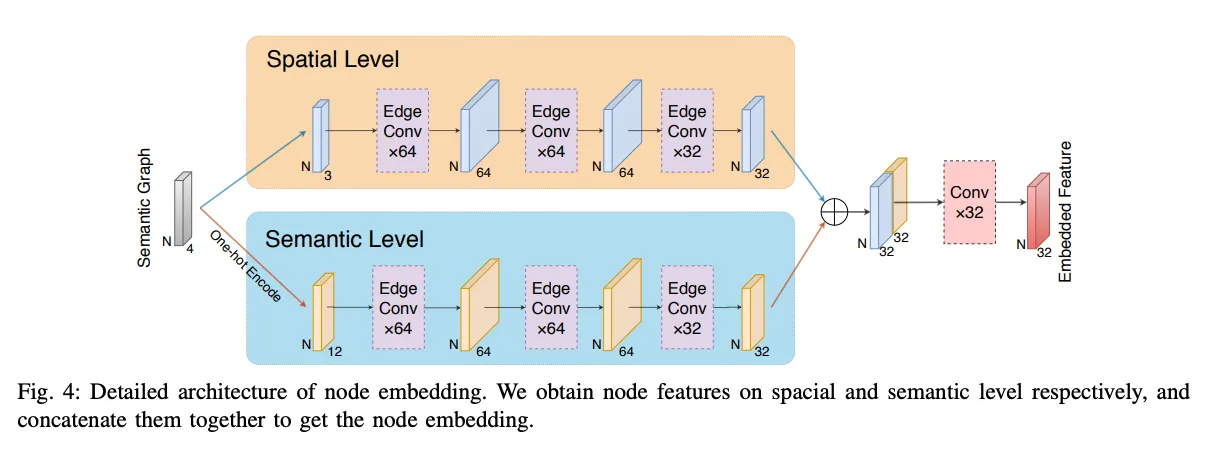
Node Embedding
- Graph Convolutional Network는 노드간의 relation을 기반으로 feature를 aggregate하지만, adjacency matrix를 미리 정의해야함
- 따라서 point cloud를 처리할떄는 dynamic하게 graph를 구성하는 것이 나음
- EdgeConv 사용, Dynamic Graph CNN(DGCNN)에서 제안되었음
- EdgeConv는 local geometry information을 capture하고 permutation invariance를 보장함
- dynamic하게 업데이트되는 그래프이기때문에 semantic grouping에 용이함
- EdgeConv layer
- kNN search를 통해 각 노드에 대해 feature space와 euclidean space에서 가장 가까운 k개의 이웃 찾음
- 각 노드 feature는 centroid information과 semantic label(one-hot encoded)로 initialize됨
- edge function은 와 같이 정의됨
- 는 학습 가능한 파라미터 집합, 는 global information을 포함하고 저거 뺀거는 local 관계 정보를 포함함
- multimodal feature aggregation을 위해 spatial and semantic level에서 독립적인 convolution을 수행하고 embedding진행 후 concat
Graph Embedding
- usually node enbedding은 weighted or unweighted average를 사용해서 생성
- 여기에서는 SimGNN에 영감을 받아 attention module을 활용해 각 node에 대해 학습가능한 가중치 행렬을 추정
- neural network가 어떤 노드가 graph를 대표하는데에 더 적합한지 학습
- Global Graph Context 는 각 노드에 대해서 node embedding 의 평균을 구한후 써서 계산함 →
- 는 그래프의 전체 구조 및 feature information을 제공하고 학습하면서 가중치 업데이트
- global context와 유사한 node가 더 높은 attention을 받음
- attention은 global context와 node embedding을 내적하고 를 사용해서 범위에 있도록함
- 그래서 이거 weighted sum사용해서 최종 graph embedding계산
Graph-Graph Interation
- graph level embedding에서 두 그래프의 관계 추정에 neural tensor network(NTN)사용
- NTN은 linear layer 대신 bilinear layer를 사용해서 두 벡터간 관계를 학습하는거 → 내적보다 나음
- relation between graph level embedding은 아래식대로
- 이게 뭐냐면 첫 항이 bilinear tensor연산으로 두 그래프 간의 관계를 학습하는거
- 두 번째 항이 두 embedding을 concat해서 linearize한다음에 추가적인 feature를 학습하는거
- 세 번째 항은 그냥 bias
Graph Similarity
- similarity 계산을 위해서 FC layer를 사용
- 최종적으로 범위의 score를 출력하고 이것을 통해 binary classification problem으로 치환해서 풀어냄
- similarity는 그냥 NTN에서 얻은 feature vector를 FC layer에 통과시켜서 단일 스칼라값(score)를 뽑아내고 여기에 사용해서 정규화
- 손실함수는 BCE사용 GT label이 이진수라서 그냥 이렇게 계산하면됨
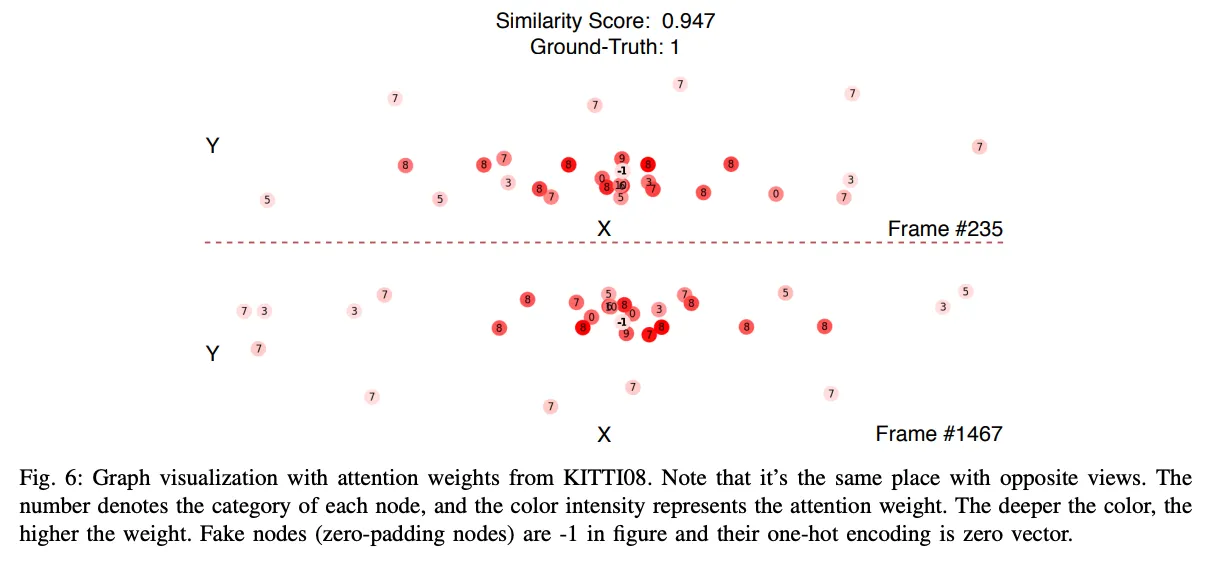
Experiment
- 암튼 잘 됐다 같은 느낌인데 확실히 recall은 좋음
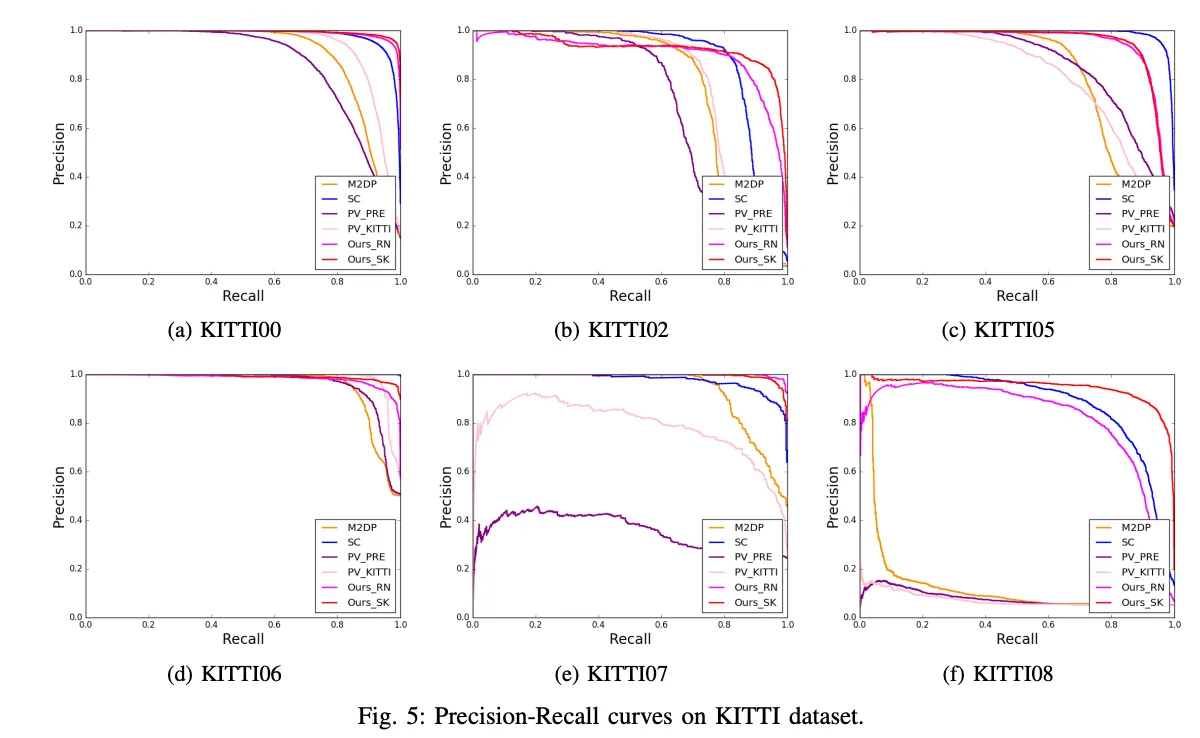
- 근데 이제 precision은 좀 낮은 시퀀스도 있긴함 근데 결과보면 무난히 좋아보인달까
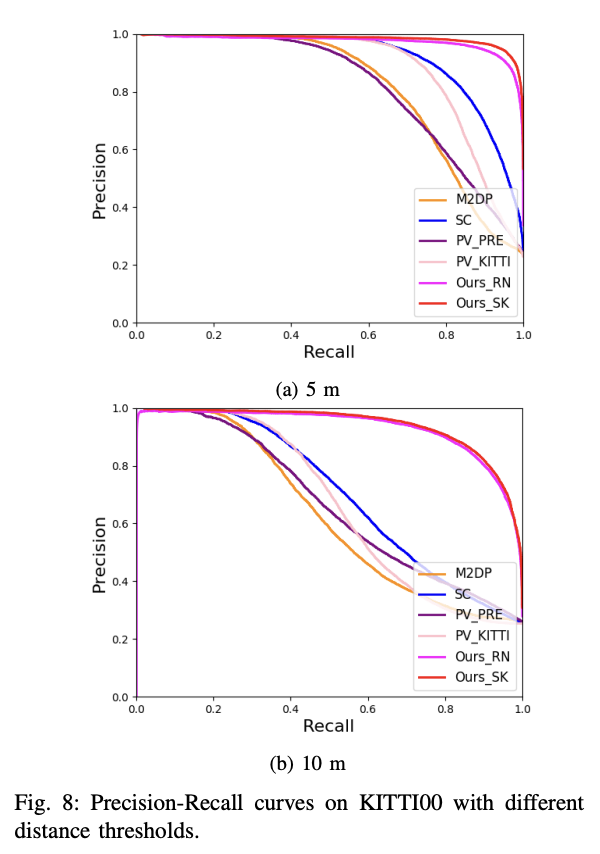
- threshold distance를 두고 잘 찾는지 보는데 아무튼 잘된다같은 느낌
- 뭐 다 그런 내용이었다 성능은
