Coursera - Foundations of Project Management

Week 3. The project management life cycle and methodologies
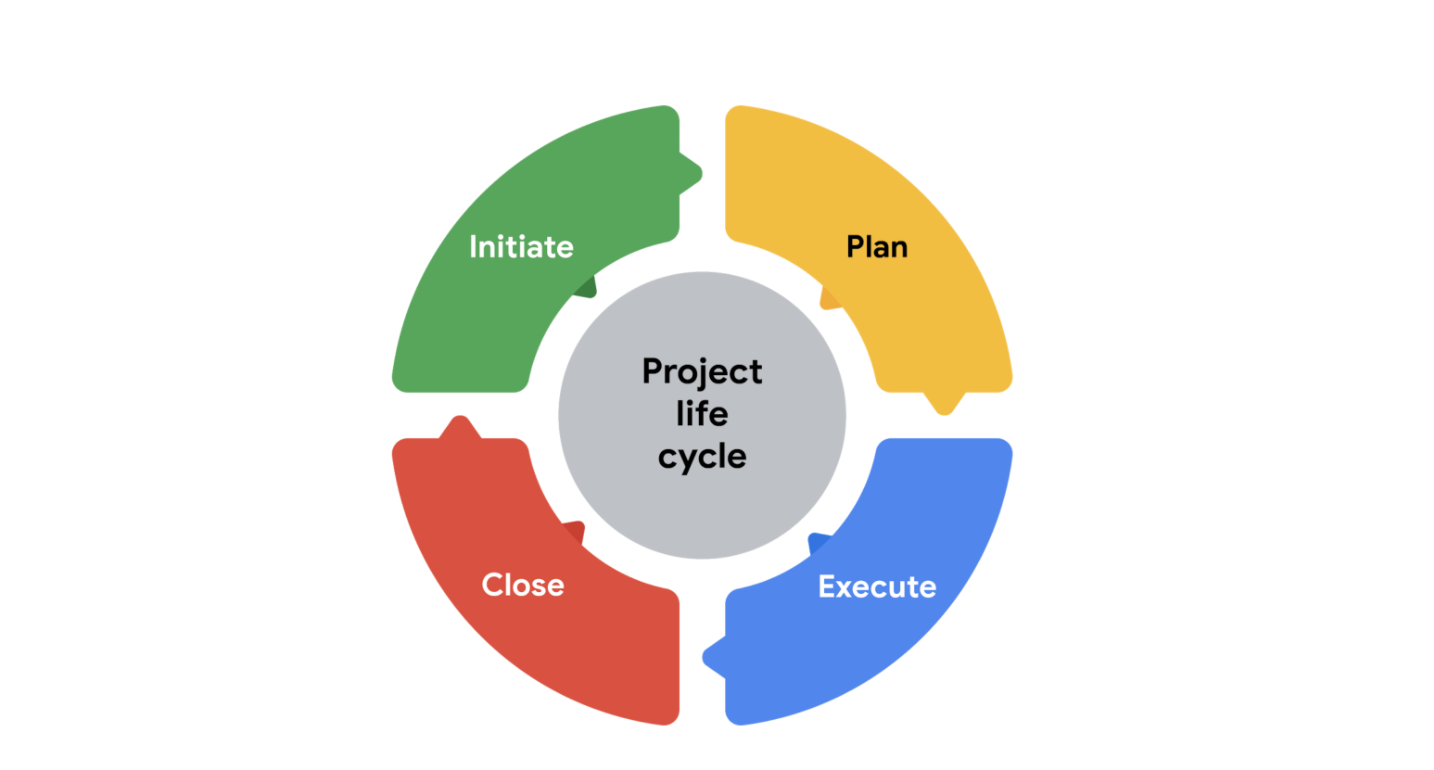
Phases of the project life cycle
1. Initiate the project
- Define project goals and deliverables
- Identify budget, resources, people involved,and any other details
- Document in one place to showcase the project's value
2. Make a plan
- Budget
- Breakdown of all the tasks that you need to be completed
- Ways to communicate team roles and responsibilities
- Schedule
- Resources
- What to do in case your project encounters problems or needs to change
3. Execute & complete tasks
- Monitor progress and keep your team motivated
- Remove any obstacles that might come up
4. Close the project
Closing the project is also a chance to evaluate how the project went
Specifics of each phases
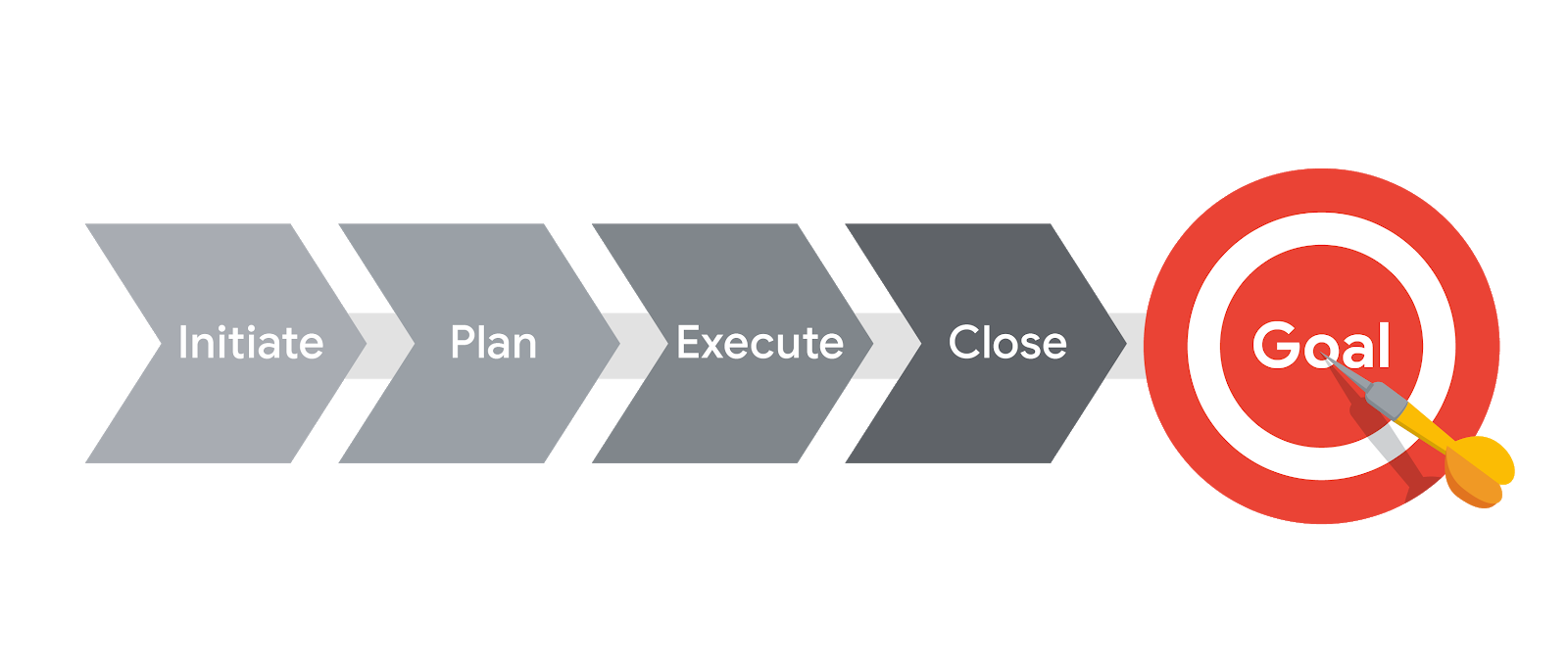
1. Initiating
Organize all of the information you have available to you about your project
- Define project goals
- Determine resources, people, and other project details
- Get project approval
2. Planning
- Create a budget
- Set the project schedule
- Establish the team
- Determine each person's roles and responsibilities
- Plan for risk and change
- Establish communications
3. Executing & Completing Tasks
Oversee team's efforts and make sure everyone understands what's expected of them, what tasks need to be done, and how and when to complete those tasks
- Manage the progress
- Communicate
- Make adjustments
4. Closing
- Ensure all tasks have been completed
-- Any outstanding invoices have been paid,
-- Resources are returned and accounted for
-- Project documentation has been submitted- Confirm acceptance of the project outcome
- Reflect on lessons learned -> Retrospective
Retrospective is a chance to note best practices and learn how to manage a project more effectively the next time.
- Communicate results with stakeholders
- Celebrate completing the project
Project management methodologies
A set of guiding principles and processes for owning a project through its life cycle
1. Linear
2. Iterative
Linear
Previous phase or task has to be completed before the next can start
Using linear project management approach, completing each step in order and sticking to the agreed upon specific results and being able to deliver just what the client ordered
Iterative
More flexible approach where some of the phases in tasks will overlap or happen at the same time that other tasks are being worked on
- Able to test out parts of the project to make sure they work before the final result is delivered
- Deliver parts of the project as they are completed
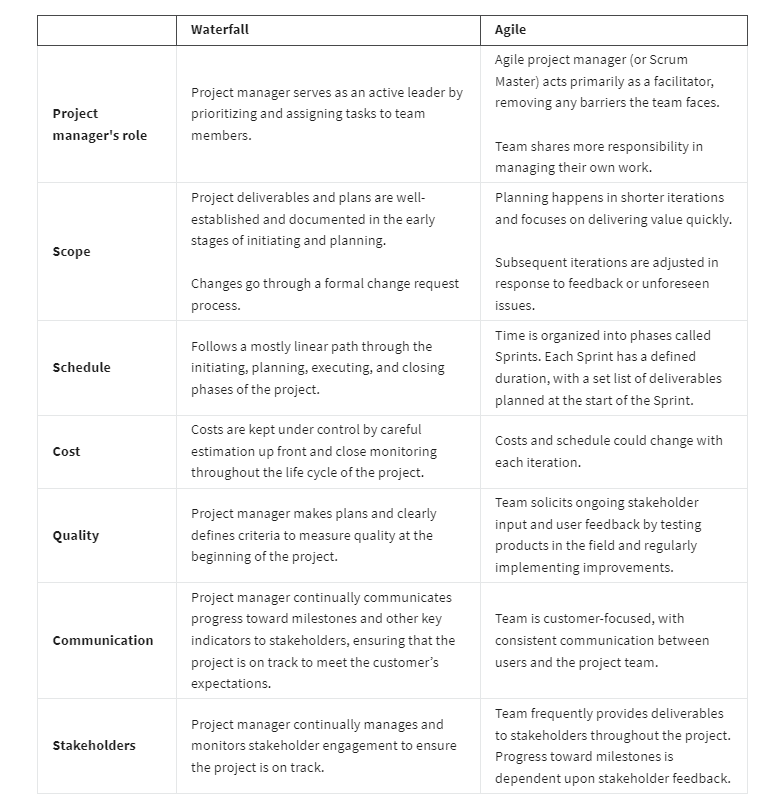
Waterfall and Agile
1. Waterfall - Linear approach
When to use waterfall?
- When the phases of the project are clearly defined
- When there are tasks to complete before another can begin
- When changes to the project are very expensive to implement once it's started
2. Agile - Iterative approach
Able to move quickly and easily.
Flexibility - being willing and able to change and adapt
Done in pieces
Agile project phases overlap and tasks are completed in iterations, which in Scrum, are called sprints
When to use Agile?
Where the client has an idea of what they want but doesn't have a concrete picture in mind, or they have a set of qualities they'd like to see in the end result, but aren't as concerned with exactly what it looks like
Waterfall vs Aglie
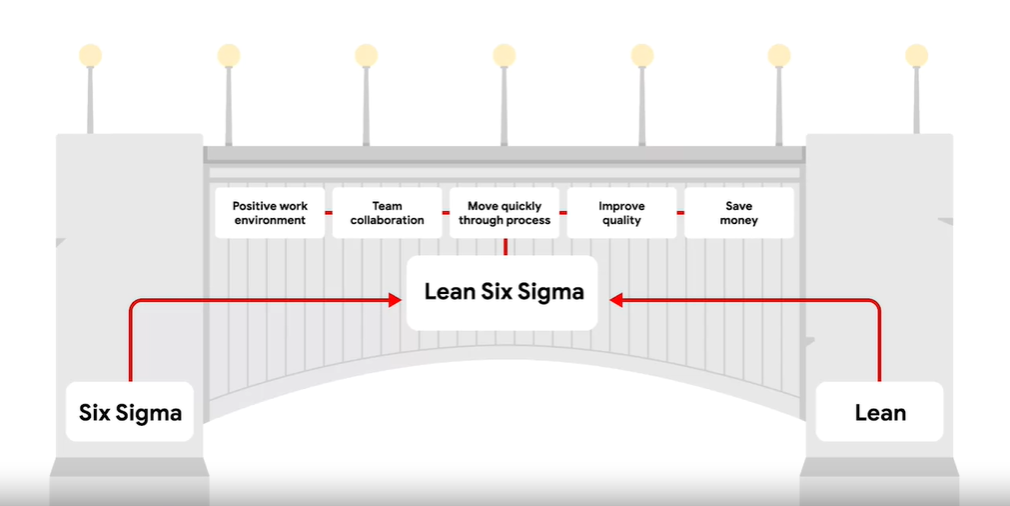
Lean Six Sigma
5 phases of Six Sigma

Define
Define the project goal and talk to stakeholders about expectations for the project
Measure
Map out the current process and locate exactly where the problems are and what kind of effect the problems have on the process
Analyze
Identify gaps and issues
Improve
Present your findings and get ready to start making improvements
Should only be made after a careful analysis
Control
Learning from the work you did up front to put new processes and documentation in place and continue to monitor so the company doesn't revert back to the old, inefficient way of doing things

So what is Lean and Six Sigma?
1. Lean
Removal of waste within an operation
Lean Manufacturing methodology recognizes eight types of waste within an operation
Defects, Excess processing, Overproduction, Waiting, Inventory, Transportation, Motion, and Non-utilized talent
Attributed to issues such as
- Lack of proper documentation
- Lack of process standards
- Not understanding the stakeholders’ needs
- Lack of effective communication
- Lack of process control
- Inefficient process design
- Failures of management
When to use?
When you want to use limited resources, reduce waste, and streamline processes to gain maximum benefits.
5S method
Cleaning up and organizing the workplace to achieve the smallest amount of wasted time and material
1. Sort
Remove all items not needed for current production operations and leave only the bare essentials
2. Set in order
Arrange needed items so that they are easy to use.
Label items so that anyone can find them or put them away
3. Shine
Keep everything in the correct place.
Clean your workspace every day
4. Standardize
Perform the process in the same way every time.
5. Sustain
Make a habit of maintaining correct procedures and instill this discipline in your team.
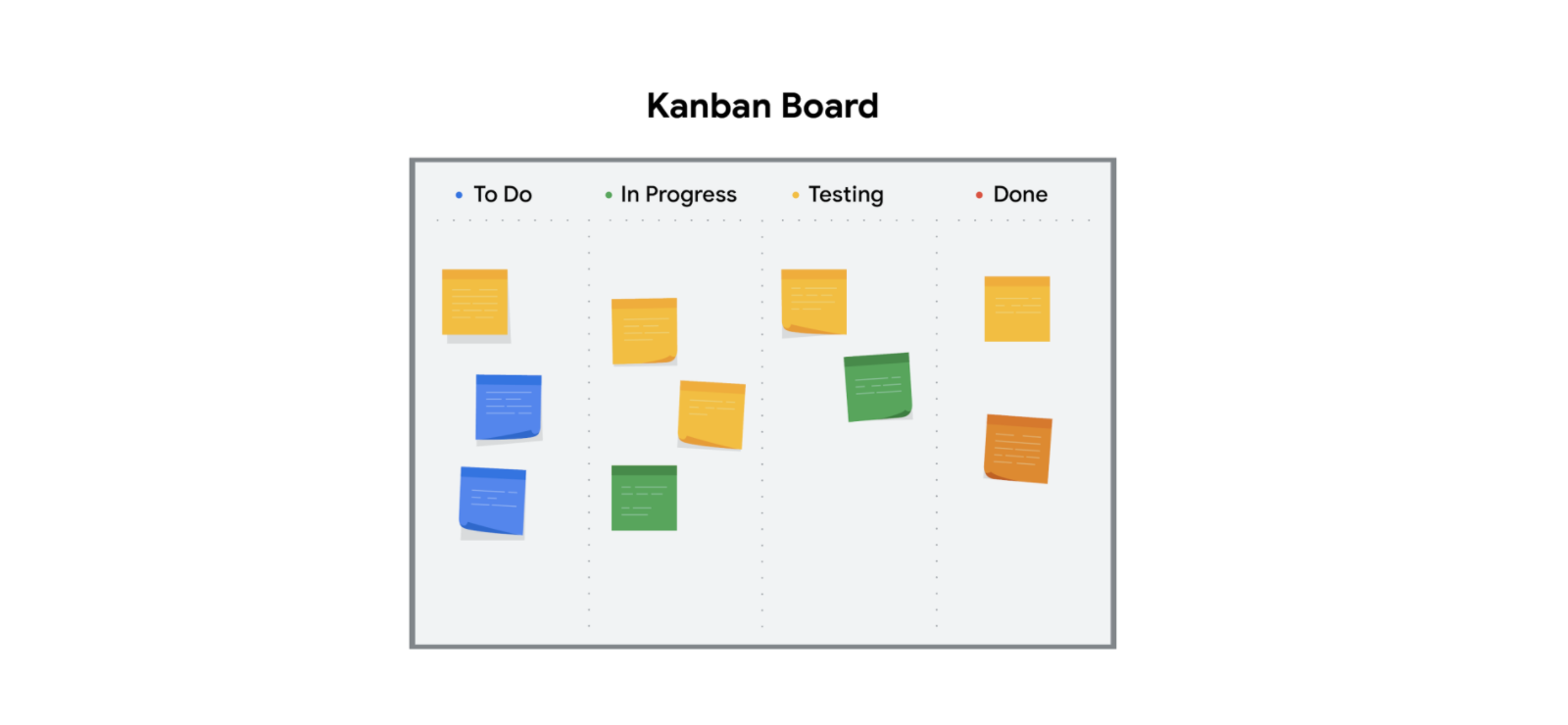
Kanban Board
A visualization tool that enables you to optimize the flow of your team’s work
2. Six Sigma
A methodology used to reduce variations by ensuring that quality processes are followed every time
7 key principles
1. Always focus on the stakeholders.
2. Identify and understand how the work gets done.
3. Make your processes flow smoothly.
4. Reduce waste and concentrate on value.
5. Stop defects by removing variation.
6. Involve and collaborate with your team.
7. Approach improvement activity in a systematic way.
Common project management approaches and how to select one
Popular project management approaches
1. Waterfall is a traditional methodology in which tasks and phases are completed in a linear, sequential manner, and each stage of the project must be completed before the next begins. The project manager is responsible for prioritizing and assigning tasks to team members. In Waterfall, the criteria used to measure quality is clearly defined at the beginning of the project.
2. Agile involves short phases of collaborative, iterative work with frequent testing and regularly-implemented improvements. Some phases and tasks happen at the same time as others. In Agile projects, teams share responsibility for managing their own work. Scrum and Kanban are examples of Agile frameworks, which are specific development approaches based on the Agile philosophy.
3. Scrum is an Agile framework that focuses on developing, delivering, and sustaining complex projects and products through collaboration, accountability, and an iterative process. Work is completed by small, cross-functional teams led by a Scrum Master and is divided into short Sprints with a set list of deliverables.
4. Kanban is both an Agile approach and a tool that provides visual feedback about the status of the work in progress through the use of Kanban boards or charts. With Kanban, project managers use sticky notes or note cards on a physical or digital Kanban board to represent the team’s tasks with categories like “To do,” “In progress,” and “Done.”
5. Lean uses the 5S quality tool to eliminate eight areas of waste, save money, improve quality, and streamline processes. Lean’s principles state that you can do more with less by addressing dysfunctions that create waste. Lean implements a Kanban scheduling system to manage production.
6. Six Sigma involves reducing variations by ensuring that quality processes are followed every time. The Six Sigma method follows a process-improvement approach called DMAIC, which stands for define, measure, analyze, improve, and control.
7. Lean Six Sigma is a combination of Lean and Six Sigma approaches. It is often used in projects that aim to save money, improve quality, and move through processes quickly. Lean Six Sigma is also ideal for solving complex or high-risk problems. The 5S quality tool, the DMAIC process, and the use of Kanban boards are all components of this approach.
5개의 댓글
Creative teams have always had a tough time selecting good project management software for their work. Most of the software programs are for software development teams. This project management software for creative https://krock.io/project-management-for-creative-teams/ has appeared recently and meets all the requirements for comfortable work. But you can also add a client to the project and show him your work all the time.
Hi what is the best way to do resource planning in Jira. We are currently transitioning to this project management system. It is therefore very important to get to grips with everything quickly.
Resource scheduling in Jira https://activitytimeline.com/how-to-do-capacity-planning-in-jira can be done by creating a resource calendar, assigning resources to tasks, and using plugins to automate scheduling. Resource calendars can be used to track the availability of team members or other resources, while assigning resources to tasks enables teams to track who is working on what. Jira plugins can provide additional features such as workload management, scheduling, and capacity planning. By using these tools, teams can effectively manage resources and optimize project timelines.
Another good tool for creative teams is https://storyboardhero.ai/
They provide a mix of traditional software, AI and human assistance.



Hi, we have a team of only designers, can you advise me normal software for project management, so that it takes into account the work of the creative teams.