📒 Gradient Descent
Bias가 없는 간단한 식으로 경사하강법을 이해해본다.
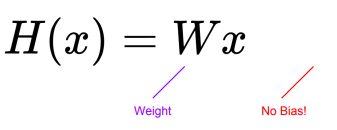
📝 Dummy Data
| Hours(x) | Points(y) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 1 |
| 2 | 2 |
| 3 | 3 |
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([1], [2], [3]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([1], [2], [3]])- H(x) = x가 정확한 모델이다. ( W = 1 이 가장 좋은 숫자이다.)
📝 Cost function
- W = 1 일 때 cost = 0이며, 1에서 멀어질수록 높아진다.
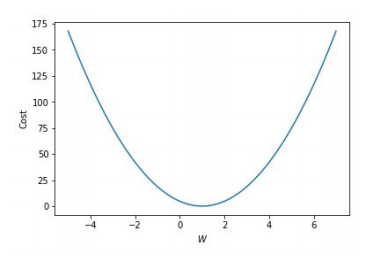
- Mean Squared Error(MSE)로 오차를 구한다.
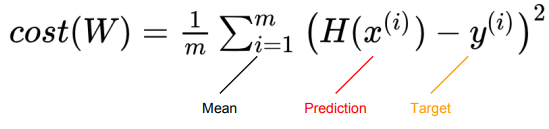
cost = torch.mean((hypothesis - y_train) ** 2)📝 Gradient descent
- 기울기가 양수면 W를 줄이고, 음수이면 W를 늘려야된다.
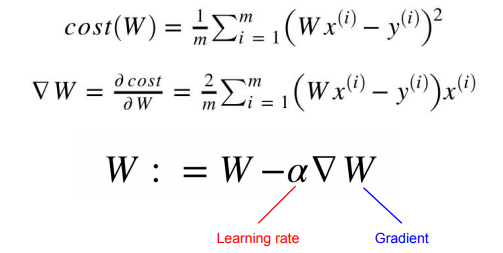
gradient = 2 * torch.mean((W * x_train - y_train) * x_train)
lr = 0.1
W -= lr * gradient📝 Full code
import torch
# 데이터
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1], [2], [3]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1], [2], [3]])
# 모델 초기화
W = torch.zeros(1)
# learning rate 설정
lr = 0.1
nb_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
# H(x) 계산
hypothesis = x_train * W
# cost gradient 계산
cost = torch.mean((hypothesis - y_train) ** 2)
gradient = torch.sum((W * x_train - y_train) * x_train)
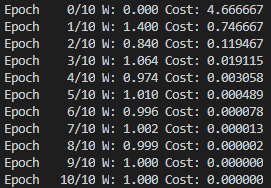
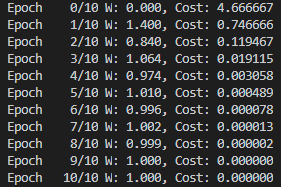
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} W: {:.3f}, Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, W.item(), cost.item()))
# cost gradient로 H(x) 개선
W -= lr * gradient- 점점 Cost가 줄어드는 모습을 확인할 수 있다.
📝 Full code with torch.optim
- torch.optim 으로 경사 하강법을 더 쉽게 구현할 수 있다.
import torch
# 데이터
x_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1], [2], [3]])
y_train = torch.FloatTensor([[1], [2], [3]])
# 모델 초기화
W = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
# optimizer 설정
optimizer = torch.optim.SGD([W], lr=0.15)
nb_epochs = 10
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
# H(x) 계산
hypothesis = x_train * W
# cost 계산
cost = torch.mean((hypothesis - y_train) ** 2)
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} W: {:.3f} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, W.item(), cost.item()))
# cost로 H(x) 개선
optimizer.zero_grad() # gradient를 0으로 초기화
cost.backward() # gradient 계산
optimizer.step() # 경사하강법(W에 적용)- 역시 1에 수렴하는 W와 줄어드는 cost를 확인할 수 있다.