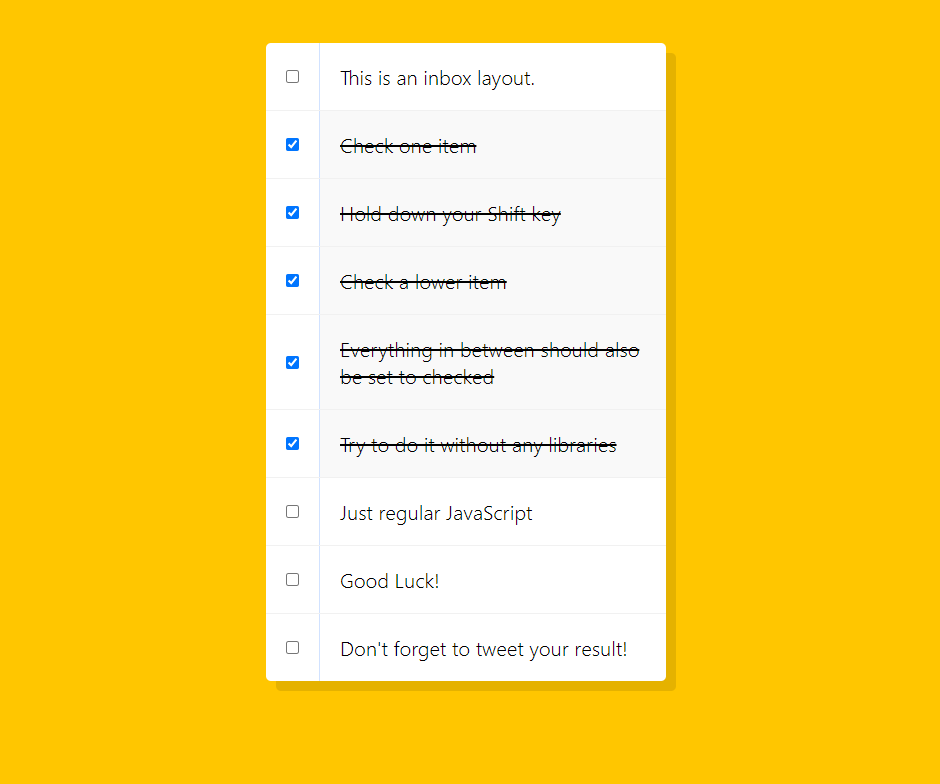
1. Hold Shift to Check Multiple Checkboxes
- 첫번째 체크박스를 클릭한다.
- SHIFT 키 누른 후 두 번째 체크박스 클릭 시, 중간에 포함 된 모든 체크박스들이 체크 된다.
2. 전체 코드
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html lang="en">
<head>
<meta charset="UTF-8">
<title>Hold Shift to Check Multiple Checkboxes</title>
</head>
<body>
<style>
html {
font-family: sans-serif;
background: #ffc600;
}
.inbox {
max-width: 400px;
margin: 50px auto;
background: white;
border-radius: 5px;
box-shadow: 10px 10px 0 rgba(0, 0, 0, 0.1);
}
.item {
display: flex;
align-items: center;
border-bottom: 1px solid #F1F1F1;
}
.item:last-child {
border-bottom: 0;
}
input:checked+p {
background: #F9F9F9;
text-decoration: line-through;
}
input[type="checkbox"] {
margin: 20px;
}
p {
margin: 0;
padding: 20px;
transition: background 0.2s;
flex: 1;
font-family: 'helvetica neue';
font-size: 20px;
font-weight: 200;
border-left: 1px solid #D1E2FF;
}
</style>
<!--
The following is a common layout you would see in an email client.
When a user clicks a checkbox, holds Shift, and then clicks another checkbox a few rows down, all the checkboxes inbetween those two checkboxes should be checked.
-->
<div class="inbox">
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>This is an inbox layout.</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Check one item</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Hold down your Shift key</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Check a lower item</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Everything in between should also be set to checked</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Try to do it without any libraries</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Just regular JavaScript</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Good Luck!</p>
</div>
<div class="item">
<input type="checkbox">
<p>Don't forget to tweet your result!</p>
</div>
</div>
<script>
const checkboxes = document.querySelectorAll('.inbox input[type="checkbox"]')
let lastChecked;
function handleCheck(e) {
let inBetween = false;
if (e.shiftKey && this.checked) {
checkboxes.forEach(checkbox => {
console.log(checkbox);
if (checkbox === this || checkbox === lastChecked) {
inBetween = !inBetween;
console.log('Starting to check them in between!');
}
if (inBetween) {
checkbox.checked = true;
}
});
}
lastChecked = this;
}
console.log(checkboxes)
// checkboxes.forEach(checkbox => checkbox.addEventListener('click', handleCheck));
const checkboxArray = Array.from(checkboxes);
checkboxArray.map((checkbox) => checkbox.addEventListener('click', handleCheck));
</script>
</body>
</html>3. 동작 순서
[1] 처음 클릭 시
1. checkbox의 addEventListenr를 통해 click 동작 감지 , handleCheck 함수를 호출한다.
2. handleCheck() 함수에서 처음 클릭한 checkbox를 lastChecked로 세팅한다.
[2] 두번째 클릭 시 (shift키 함께 누름)
1. checkbox의 addEventListenr를 통해 click 동작 감지 , handleCheck 함수를 호출한다.
2. (shift키가 눌렸는지 여부) + (해당 체크박스 체크 여부)를 만족하면
2-1 전체 체크박스에 대해 다음의 반복문을 수행한다.
2-1-1 checkbox === lastChecked (처음 선택한 체크박스 인지) 이거나 checkbox === this ( 두번 째 찍은 체크박스 인지) 일때
2-1-2 inBetween 변수를 컨트롤 하여 체크박스 체크표시를 한다.
4. HTML, CSS
5. JAVASCRIPT
nodeList
NodeList: 일반적으로 element.childNodes와 같은 속성(property)과 document.querySelectorAll 와 같은 메서드에 의해 반환되는 노드의 콜렉션.- 유사배열이다.
==> Array의 함수를 이용할 수 없어 해당 함수를 사용하기 위해선 Array.from()으로 변환이 필요하다.const checkboxes = document.querySelectorAll('.inbox input[type="checkbox"]') // checkboxes 가 nodeList이므로 map 적용 불가 / forEach로 반복문 실행 checkboxes.forEach(checkbox => checkbox.addEventListener('click', handleCheck)); //Array로 변환가능. const checkboxArray = Array.from(checkboxes); checkboxArray.map((checkbox) => checkbox.addEventListener('click', handleCheck));
this
this: 자신이 속한 객체 또는 자신이 생성할 인스턴스를 가리키는 자기 참조 변수- this 바인딩(this에 바인딩될 값)은 함수 호출 방식, 즉 함수가 어떻게 호출되었는지에 따라 동적으로 결정된다.
- 일반 함수 호출
==> 일반 함수로 호출하면 함수 내부의 this에는 전역 객체가 바인딩된다.- 메서드 호출
==> 메소드 내부의 this는 해당 메소드를 소유한 객체, 즉 해당 메소드를 호출한 객체에 바인딩- 생성자 함수 호출
==> 생성자 함수 내부의 this에는 생성자 함수가 생성할 인스턴스가 바인딩- 화살표 함수 내부의 this
==> 화살표 함수 내부의 this는 상위 스코프의 this를 가리킨다
