A survey of model compression strategies for object detection
Lyu, Z., Yu, T., Pan, F. et al. A survey of model compression strategies for object detection. Multimed Tools Appl 83, 48165–48236 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11042-023-17192-x
Abstract
-
this paper presents a survey of object detection model compression techniques in recent years.
-
Firstly, these compression techniques were divided into six categories:
- network pruning
- lightweight network design
- neural architecture search (NAS)
- low-rank decomposition
- network quantization
- Knowledge distillation (KD) methods
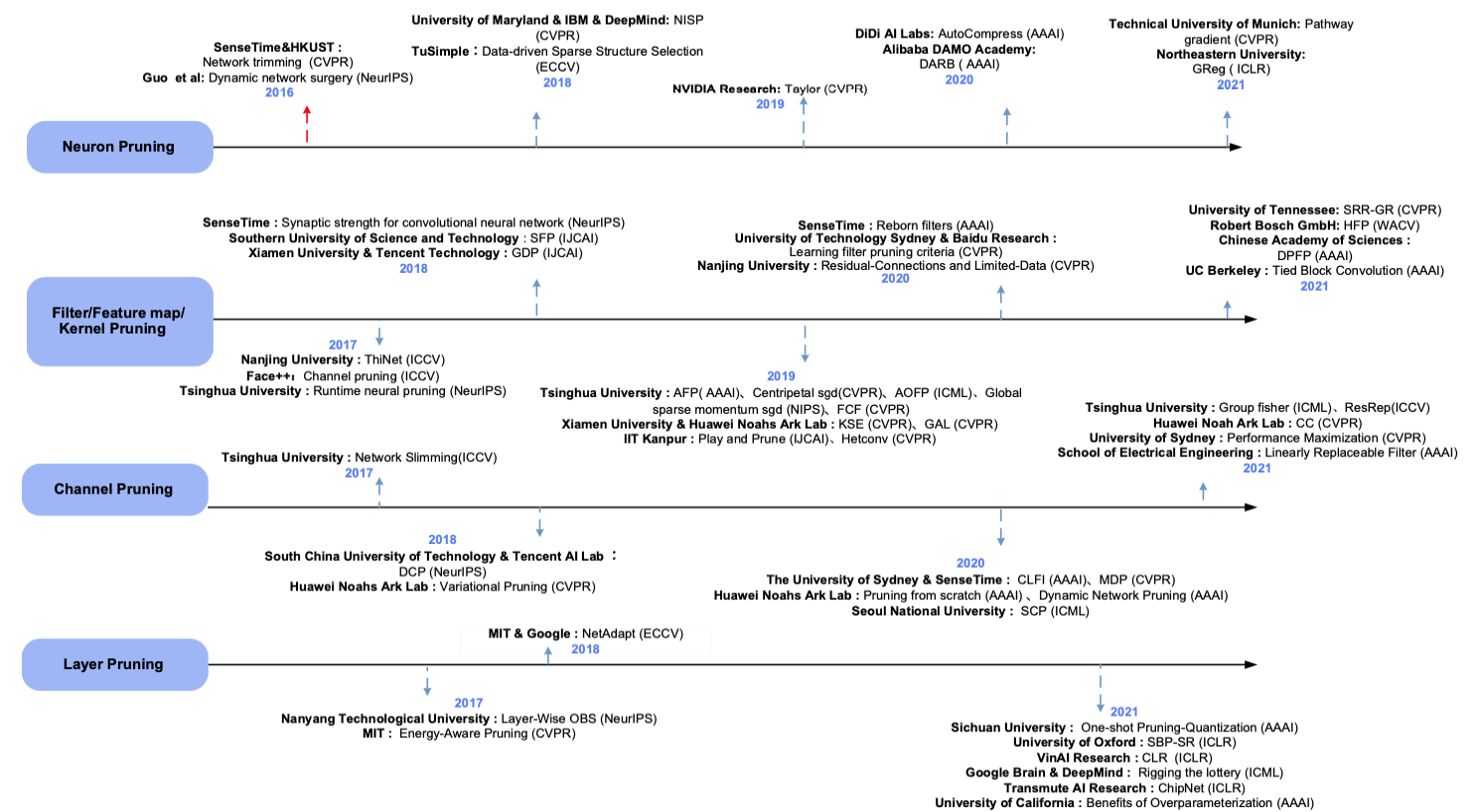
2. Model compression strategies
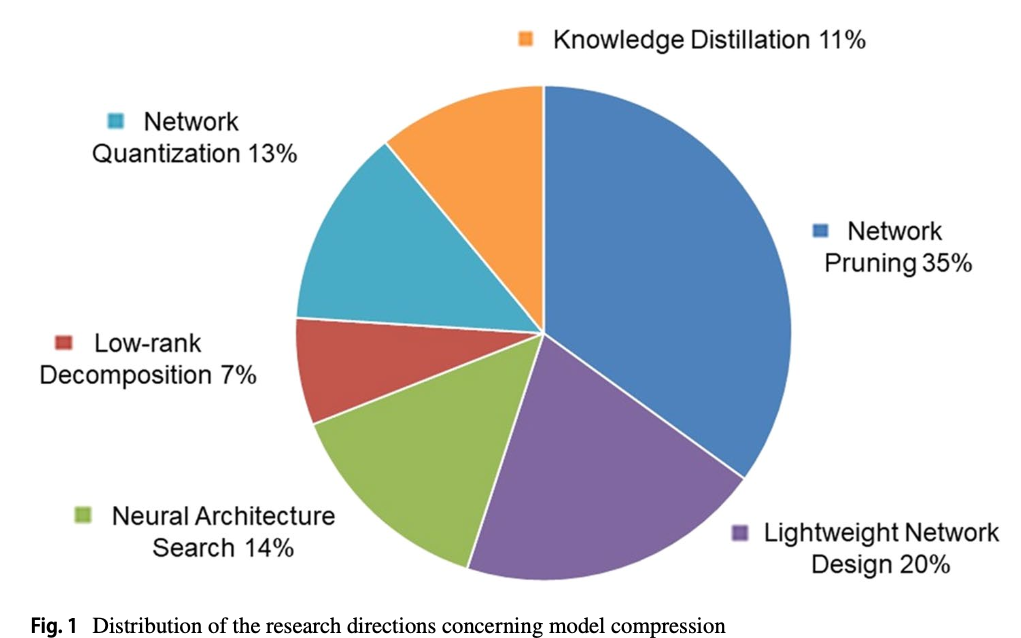
- 2014년부터 2021년까지 8년 동안 modle compression methods의 연구 방향 비율
2.1. Network pruning
-
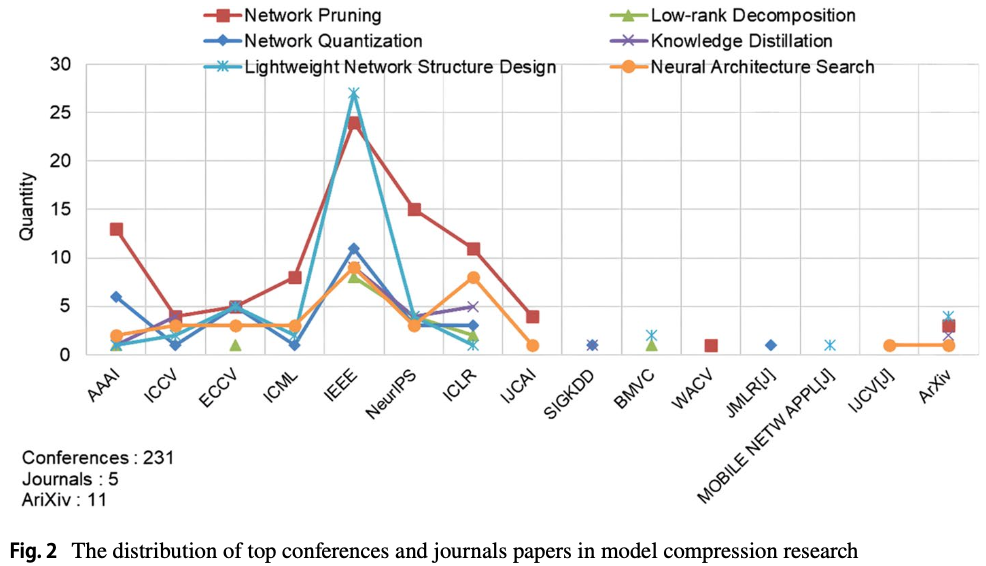
최근 top conferences에서 object detection에서 model compression methods는 a very important research hostpot이다.
-
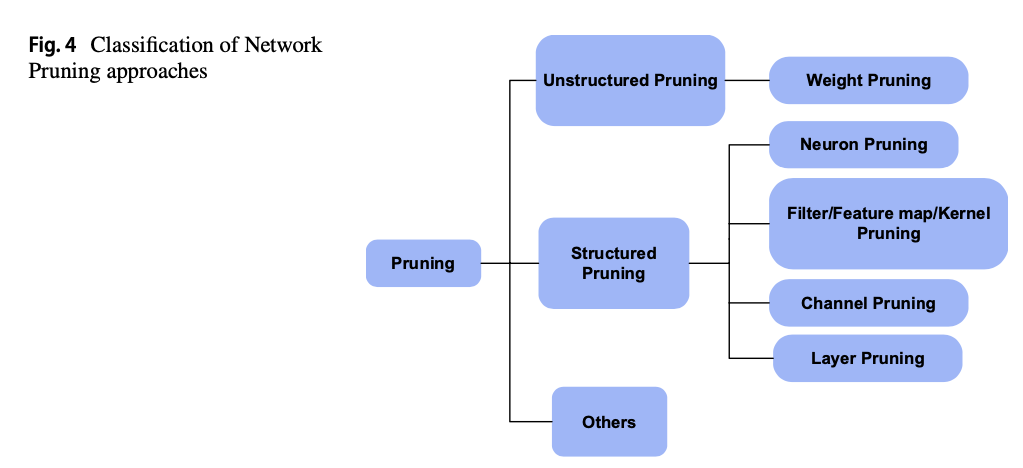
Classification of Network Pruning approaches
2.1.1. Unstructured pruning
-
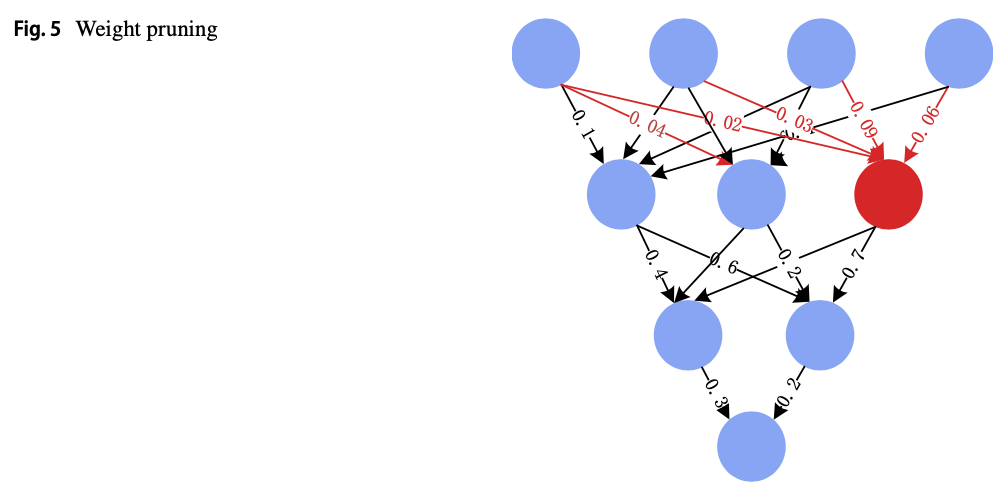
unstructured weight pruning의 원리는 Fig.5.에 있다.
unimportant weight edges of the given network는 pruned되어진다.
-
Stanford Univ.의 Han Song team은 model compression에 많은 발전을 이끌었다.
Han Son team과 NVIDIA team은 공동으로 첫 pruning weights 를 제안했다.
이를 뒤이어 Tsinghua Univ와도 함께 3-stage pipeline-based deep compression method, which combines pruning, training quantization and Huffman coding을 제안했다. -
각 layer 마다 thresholds를 제공함으로써 weights를 pruning하는 방법을
layer-wise magnitude-based pruning(LMP)라고도 부른다.
이 접근법에도 많은 연구들이 있었다.
threshold adjustment method는 manual operation으로 사용되었다.
하지만 전문 지식이 없는 사람들의 사용 편의성을 위해 많은 연구가 진행되었다. (자동적으로 threshold를 정해주는)- the Anhui Province Key Lab of Big Data Analysis and Application [16] proposed an approach called optimization based LMP (OLMP) to automatically adjust the pruning threshold of LMP.
- Lee et al. [20] proposed an importance score for global pruning by studying layered sparsity, namely, the layer-adaptive magnitude-based pruning (LAMP) score, and their approach did not require any hyper parameter tuning or heavy computation.
-
Many scholars are still exploring other methods of
judging the importance of model weightsinstead of using their magnitude as the importance evaluation metric.- The teams at Peking University and Microsoft Research [21] proposed a dynamic pruning scheme in the frequency domain by using spatial correlation.
- Carreira-Perpinán et al. of the University of California [22] proposed an algorithm called learning compression. They used the quadratic regularization term of a training model to periodically update the weight set and a Lagrange multiplier to find the most appropriate weight, not just the largest weight.
- Mallya et al. of Microsoft Research [23] proposed an algorithm called Packnet.
They packaged "multiple tasks" into a single network by performing iterative pruning and network retraining to solve the catastrophic forgetting problem in weight pruning. - The Samsung Research and Harvard University teams [24] proposed a sparse quantization neural network method for weight representation based on fine-grained and unstructured pruning.
Threshold pruning 방법은 LMP로부터 spatial correlation에 의한 dynamic weight welection, 그리고 최근에는 random initialization-based pruning method가 좋은 결과를 내고 있다.
structural position에 관계없이 unstructured pruning은 전체 model accuracy에 매우 작은 영향을 주고 high sparsity rate를 제공할 수 있다.
하지만, 우리는 이러한 unstructured pruning이 야기하는 irregular memory access에 주의를 기울여야 한다.
2.1.2 Structured pruning
-
structured pruning의 개념은 unstructured pruning의 한계점을 기반으로 제안되었다.
Structural pruning은 DNN 전체에서 unimportant structures를 제거함으로써 이루어진다.
(unstructured pruning은 weight를 pruning하여 layer 내부 연산이 불규칙하지만, stuctural pruning은 layer 자체를 pruning해버림.) -
structural pruning은 다음과 같이 세분화 가능
- neuron pruning
- filter/feature map/kernel pruning
- channel pruning and layer pruning
(1) Neuron Pruning
Neuron pruning은 weight pruning과 유사함.
weight pruning은 weight edges를 pruning하는 반면,
neuron pruning은 weight edges가 만들어낸 neuron을 pruning함.- The University of Maryland, Deepmind, IBM, Jingdong and other teams [28] jointly proposed applying feature ranking technology to measure the importance of each neuron in the "final response layer"
(FRL) and removing the least important neurons. - TuSimple Team [29] introduced a new parameter-scale factor to scale the output of a specific structure to achieve data-driven and end-to-end pruning.
- The NVIDIA team [30] repeatedly deleted neurons with small scores by estimating the contributions of neurons to the final loss.
- Khakzar [31] of the Technical University of Munich proposed a pathway selection method based on neuron contributions, and a feature attribution approach, (the “pathway gradient”), that reveals the input features associated with features encoded in the critical pathways.
- The University of Maryland, Deepmind, IBM, Jingdong and other teams [28] jointly proposed applying feature ranking technology to measure the importance of each neuron in the "final response layer"
- 몇몇 학자들은
structured weight pruning또한 연구하고 있다.- Last year, the DiDi AI research team [33] proposed an automatic structured pruning framework called Auto-Compress based on the alternating direction method of multipliers (ADMM).
- ...
neuron pruning에 대한 연구는 주로 neuron의 contribution rates와 importance levels 평가에 집중되어 있으며,
일부 연구에서는 이 주제를 structural weight pruning과 결합하여 다루고 있다.
전반적으로 neuron pruning을 다루는 연구는 많지 않다.
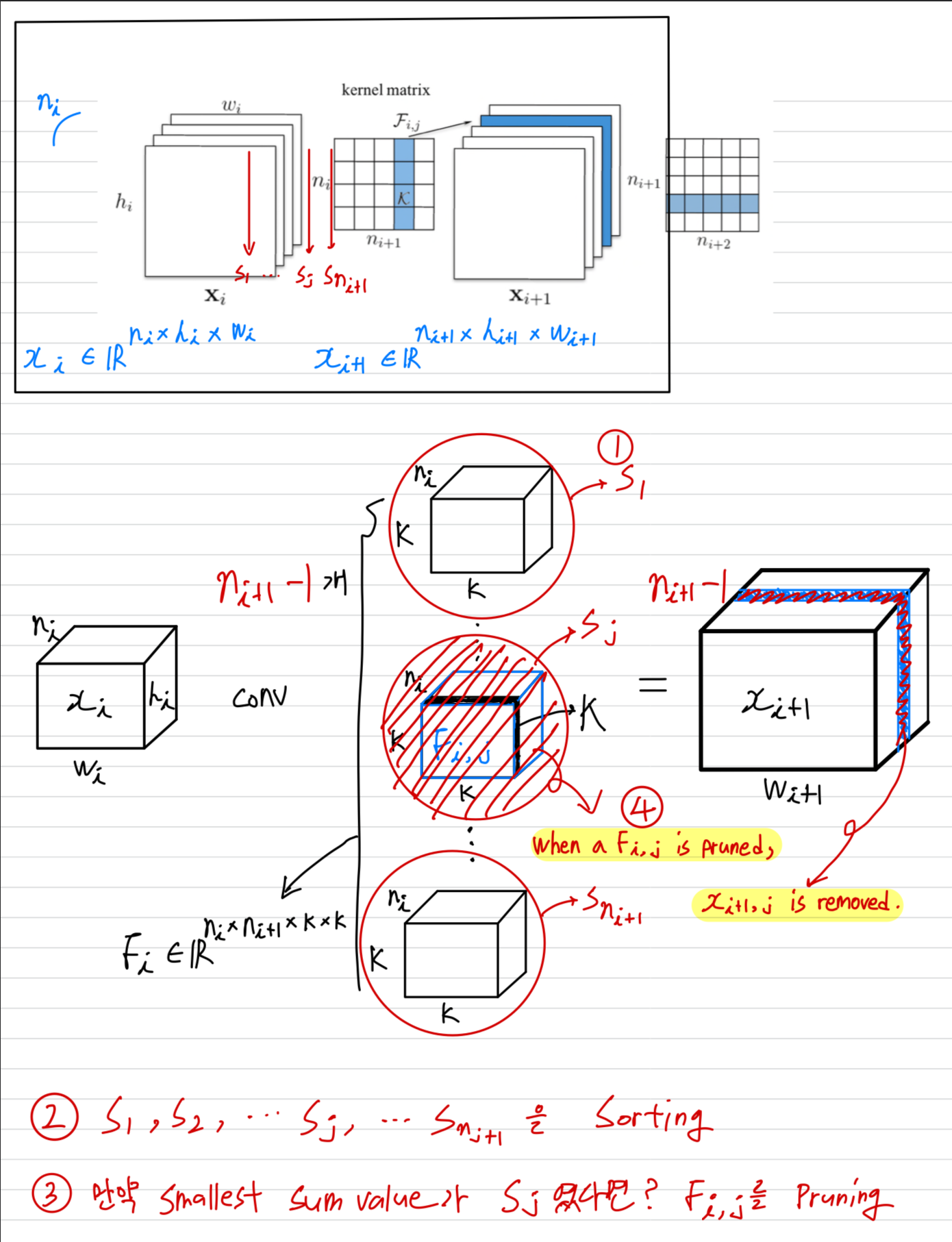
(2) Filter/Feature Map/Kernel Pruning
-
CNN에서는 서로 다른 filters and feature maps 사이에 상당한 redundancy가 있다.
feature map은 network의 output이며, filter는 network parameter이다.
feature maps과 filters는 corresponding relationships을 갖는다.
만약 feature map이 제거된다며, 연결되어 있는 filter도 제거된다. -
filter pruning과 neuron pruning은 약간의 차이점이 있다.
filter pruning은 개별 connection이나 neuron 수준이 아니라 filter 수준에서 CNN을 pruning한다.
filter pruning은 structured pruning 방법 중에서 가장 중요한 방법이다.
Methods based on Sparse Constraint Regularization
- sparse structures를 얻기 위해,
많은 연구자들은 network parameter regularization methods based on group sparsity to penalize unimportant parameters를 연구해오고 있다.- The University of Pittsburgh [36] used group least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression for regularization specification to explore the sparsities of different structure levels, and the
works in [37, 38] were similar. - Yoon and Hwang [39] also studied group sparse regularization, by using the correlations between the features in the examined network for pruning.
- A team at the University of Maryland and NEC Labs America [40] proposed a structural sparse CNN regularization and acceleration method, which can greatly reduce the cost of computation by removing all the filters and their connected feature maps in the network that have little impact on the output accuracy.
- Megvii Technology and Xi’an Jiaotong University [42] proposed a channel selection strategy based on the LASSO and a least-squares reconstruction algorithm to prune filters.
- ...
- The University of Pittsburgh [36] used group least absolute shrinkage and selection operator (LASSO) regression for regularization specification to explore the sparsities of different structure levels, and the
Methods based on adaptive and dynamic pruning
- 많은 연구자들은 adaptive and dynamic filter pruning을 달성하기 위해 몇가지 방법들을 제안했다
- In 2017, Lin et al. of Tsinghua University [50] considered that input samples should not be treated equally because of the different computational quantities required by different tasks. Therefore, they proposed a runtime neural pruning (RNP) framework that retains all the capabilities of the original network, and adaptively conducts pruning according to the input image and current feature map.
- In 2018, the Ding team of Tsinghua University proposed an auto-balanced filter pruning (AFP) method [51], which prunes some weak filters together with the corresponding feature maps.
- Ji Rongrong’s team of Xiamen University cooperated with Tencent Technology and other institutions [53] to propose a global and dynamic training algorithm to prune non-salient filters.
- A team at the University of Sydney and Baidu [54] proposed the learning filter pruning criterion (LFPC) by considering cross-layer filter distribution diversity, this approach adaptively selects the appropriate pruning criteria for different functional layers.
(3) Channel Pruning
- filter pruning과 channel pruning 방법은 모두 coarse-grained pruning methods로, 방법이 유사하다.
하지만 channel pruning은 filter purning의 dimensional mismatch 문제를 해결할 수 있다.
channel pruning의 main idea는 network의 conv layer로부터 나오는 channels 전체를 즉시 제거하는 것이다.
pruning 이후에, model은 즉시 higher compression ratio와 shorter computing time을 얻을 수 있다.- The team of Tsinghua University [76] proposed applying L1 regularization to channels
by pushing the value of the BN scaling factor to zero to identify and delete insignificant
convolution channels. - In 2021, the team [77] also proposed a layer grouping algorithm to automatically find coupled channels, and derived a unified metric based on Fisher information to evaluate the importance of a single channel and coupled channels.
- Ding’s team [78] at Tsinghua University proposed ResRep, a novel method for lossless channel pruning,
which slims down a CNN by reducing the widths (numbers of output channels) of convolutional layers. - Zhao et al. [82] introduced a variational technique to estimate the saliency distribution of the parameter channels, and removed redundant channels from the original model.
- ...
- The team of Tsinghua University [76] proposed applying L1 regularization to channels