Any-Precision LLM: Low-Cost Deployment of Multiple, Different-Sized LLMs
Park, Yeonhong, et al. "Any-Precision LLM: Low-Cost Deployment of Multiple, Different-Sized LLMs." arXiv preprint arXiv:2402.10517 (2024).
Abstract
-
최근, Large Language Models(LLMs)을 compressing하기 위한 상당한 노력들이 제시되고 있는데, 그들의 large sizes 때문에 상당한 deployment costs가 필요하다.
반면에, 다양한 크기의 multiple LLMs을 deploy하는 데 드는 비용을 완화(mitigating)하는 데에는
그 practical significance에도 불구하고 훨씬 적은 관심이 주어졌다. -
따라서 이 논문에서는 any-precision DNN의 개념을 LLM으로 확장한 any-precision LLM을 소개한다.
any-precision LLM의 과제를 해결하기 위해, 우리는 post-training quantization framework를 활용한 lightweight method 제안하고,
이를 효율적으로 서비스할 수 있는 specialized software engine을 개발했다. -
그 결과, 다양한 bit-widths(3, 4, .., n bits)로 quantized된 LLM을 overlaying(중첩)하여
single -bit LLM과 유사한 memory footprint로 different-sized LLMs을 deploy하는 데 드는 high cost를 줄일 수 있었다.
다양한 bit-withds로 지원되는 모든 LLMs은 SOTA의 model quality and inference throughput을 보여주며,
multiple, different-sized LLMs에 deployment를 위한 compelling(유망한) option임을 입증했다.
내가 이해한 내용>
PTQ(Post-Training Quant.)를 활용해서 any-precision LLM을 만들겠다.
그래서 LLM 내부에서 다양한 bit-widths로 quantized된 model은 single n-bit로 quantized된 model과 유사한 memory footprint를 갖기 때문에 실제 deploy 하는 데에 비용을 줄일 수 있다.
다양한 bit-widths로 quantized될 수 있기 때문에 different-sized LLMs을 deployment하기 위해서 좋은 방법이 될 수 있다.
1. Introduction
-
LLMs의 deployment 비용을 줄이기 위한 많은 연구들이 있었다.
특히, parameter size가 efficient deployment의 주요 obstacle이기 때문에
LLMs을 compressing하기 위한 pruning or quantization과 같은 techniques에 더욱 큰 집중이 있었다. -
(문제 제기 1)
한편, 다양한 sizes의 multiple LLMs을 deploying하는 것은 실용적으로 중요한데도 불구하고
관련한 costs를 완화하기 위한 discussion은 제한되어 왔다.
Real-world scenarios에서는 multiple LLMs의 dynamic adaptation의 수요가 자주 있으며,
각 distinct model은 quality/inference latency trade-offs가 있다.
이 접근법은 다양한 latency constraints에서 queries를 효과적으로 handling하는 것을 가능하게 한다.
게다가, 이 접근법은 a popular generation acceleration technique: speculative decoding을 지원한다.
이러한 장점들이 있음에도 불구하고, 다양한 sizes의 multiple LLMs을 deploying하는 것은 challenges로 남아있다.- 첫째, 이는 LLM deployment에서 이미 높은 memory cost를 더욱 악화시킨다(exacerbates).
- 둘째, 원하는 크기의 model이 open-source로 이용하지 못할 경우 여러 model version을 학습해야 한다.
-
(사전 지식 : Any-precision DNN?)
Any-precision LLM은 any-precision DNN (Yu et al., 2021)의 개념을 LLM에 확장한 것으로, 다양한 크기의 LLM을 저비용으로 배포할 수 있는 유망한 해결책이다.
Any-precision DNN은 n-bit로 quantized된 model이 Most Significant Bits(MSB)만을 사용하여 더 낮은 bit quatlized model((n-1)-bit, (n-2)-bit, ...))을 생성할 수 있는 model을 의미한다.
이 개념을 LLM에 적용하면, memory에 only a single large LLM(n-bit model)만 저장하면서 추가적으로 여러 LLM을 학습하는 overhead를 피할 수 있다. -
(문제 제기 2)
하지만, any-precision LLM의 effective implementation을 위해 풀어야 할 두 가지 challenges가 있다.- 첫째, LLM의 any-precision quantization을 위한 practical method가 필요하다.
DNN에 존재하는 any-precision quantization method는 model을 scratch부터 training하는 것이 필요한데, 이는 LLMs에 적용하는 데에 한계가 있다. - 둘째, quantized matrix-vector multiplication을 위한 새로운 GPU kernel이 필요하다.
새로운 GPU kernel은 any-precision LLM에서 감소된 bit-widths를 shorter inference times으로 변환할 수 있도록 한다.
현재의 quantized matrix-vector multiplication을 위한 kernel들은 각 quantized weight value's bit-vector 중 일부만 load하는 기능이 없다.
그 결과, 기존의 kernel을 사용하면 더 낮은 bit-width를 선택해도 memory bandwidth usage가 줄어들지 않는다.
- 첫째, LLM의 any-precision quantization을 위한 practical method가 필요하다.
-
(논문의 contribution)
따라서 본 논문에서는 위에서 언급한 두 가지 문제를 해결함으로써 any-precision LLM에 대한 strong case를 제시한다.- 첫째, 우리는 LLM의 any-precision quantization을 위한 lightweight method를 만들었다.
이는 post-training quantization(PTQ) framework를 활용하여 low-bit model을 생성한 후,
점진적으로 이를 더 higher bit-widths로 확장하여 any-precision property를 보존한다. - 둘째, 우리는 any-precision 지원을 전문으로 하는 새로운 SW engine을 개발하여
weight의 memory layout을 변경함으로써 any-precision LLMs을 제공하는 데 필요한 memory bandwidth를 효과적으로 절약한다.
- 첫째, 우리는 LLM의 any-precision quantization을 위한 lightweight method를 만들었다.
-
our extensive experimental sutdies는 우리의 방법이 여러 다른 크기의 LLM deployment를 위한 강력한 접근 방식임을 보여주며, 다음과 같은 결과를 달성했다:

2. Background
2.1. GPU Basics
GPU Architecture Fundamentals.
- LLM을 실행하는 사실상 standard platform인 GPU는 Streaming Multiprocessors (SM)라고 불리는 다량의 처리 processing elements로 구성되어 있다.
GPU는 종종 multi-level on-chip SRAM caches를 포함한다.
L1 cache의 일부는 shared memory로 구성할 수 있어 programmer가 직접 제어할 수 있는 memory space를 제공한다.
Execution Model.
- GPUsms kernels이라고 알려진 작업을 실행하기 위한 다량의 threads를 사용한다.
thread는 thread blocks으로 구조화되며, 이 thread block 내의 모든 thread는 동일한 shared memory space를 공유한다.
각 thread block 내에서, thread는 a set of warps로 조직되며, 각 warp는 32개의 연속적인 thread로 구성되어 있다.
(thread blocks == a set of warps == a set of 32 consecutive threads)
warp 내의 모든 thread들은 동시에 동일한 instruction을 실행한다.
2.2. LLM Quantization
-
이 section에서는 PTQ에 중점을 두고 LLM Quantization의 최근 발전을 논의한다.
LLM에서는 주로 weight만 quantization하려는 경향이 뚜렷해지고 있으며,
이는 inference throughput에서 주요 bottleneck이 computational requirements가 아닌 weight parameters의 크기에 의해 제한된 memory constraint 때문이다.
또한, PTQ는 실용성 덕분에 LLM Quantization에 선호되는 방법이 되었다.
QAT는 일반적으로 더 나은 성능을 내지만, high training expense로 인해 impractical하다. -
GPTQ(Frantar et al., 2023)는 LLM을 위한 weight-only PTQ의 선구적 연구로,
quantization을 layer-wise weight reconstruction problem으로 공식화한다.
GPTQ는 반복적으로 각 channel을 체계적으로 quantization하며,
동시에 not-yet-quantized weights를 조정하여 quantization-induced errors를 보정한다.
AWQ(Lin et al., 2023)는 preprocessing 단계로서 salient(두드러진) weight의 작은 부분을 보호하기 위해 per-channel scaling을 수행한다.
유사하게, QuIP(Chee et al., 2023)는 quantization에 더 적합하도록 weight를 preprocessing하여 2-bit precision에서도 인상적인 결과를 도출한다.
그러나 이는 상당한 runtime overhead를 유발하기 때문에 실용적인 유용성에 대한 의문이 제기된다. -
앞서 언급한 방법들은 uniform quantization을 사용하는 반면, non-uniform quantization을 weight distributions을 보다 잘 포착하므로 more effective alternative가 될 수 있다.
SqueezeLLM(Kim et al., 2023b)은 각 weight의 sensitivity를 고려한 clustering-based LLM quantization을 제안한다.
이전의 연구들과는 다소 다르게 주로 rounding shceme에 초점을 맞추는 것과는 별개로,
더 많은 bits를 sensitive weights에 할당하는 방법으로 mixed precision을 사용하는 제안도 있었다.(Kim et al., 2023b; Dettmers et al., 2024; Lee et al., 2024).
3. Motivation
3.1. Need for Deploying Multiple, Different-sized LLMs
-
서로 다른 크기의 LLM을 deploying하는 것은 상당한 pratical advantages를 제공한다.
이는 다양한 latency requirement를 가진 queries를 효과적으로 처리함으로써 user experience를 향상시킨다.
user와 application의 특정 요구에 따라, 일부 queries는 quick response를 필요로 하는 반면,
다른 queries는 slower response times을 허용할 수 있다.
여러 서로 다른 작업을 동시에 수행할 때 latency requirements는 더욱 다양해지며, 이는 LLM의 일반적인 사용 사례이다.
예를 들어, chatbot과 같은 interactive 작업에 대한 queries는 대부분 latency-senstive인 반면,
document analysis와 같은 작업은 종종 background에서 처리되어 more relaxed response times을 허용한다. -
서로 다른 크기의 여러 LLM이 필요한 또 다른 시나리오는 speculative decoding이다.
이 인기 있는 기술은 하나 이상의 더 작은 draft model을 추가적으로 활용함으로써 a large model의 throughput을 증가시킨다.(Leviathan et al., 2023; Chen et al., 2023; Kim et al., 2023d; Miao et al., 2023).
Challenges of Deploying Multiple, Different-sized LLMs
Challenge 1: Memory Overhead.
- LLM은 크기가 크기 때문에 추가적인 작은 model을 유지하는 데 large memory capacity overhead가 발생하며, 이로 인해 상당한 비용이 발생한다.
예를 들어, 세 가지 크기의 LLM(large, half-sized, quater-sized)을 배포하면 총 memory requirement가 거의 두 배로 증가한다.
Challenge 2: Training Costs.
-
training cost와 관련하여, 다양한 크기의 LLMs을 확보하는 것이 어렵고, 대부분의 open-source LLM이 제한된 variants만 제공한다.
원하는 크기의 model이 없을 경우 사용자가 직접 model을 만들어야 하며, LLM training은 high computational needs and large corpus requirement로 인해 매우 비싸다.
large model을 small model로 distillation하는 방법이 있지만, 적절한 training data와 hyperparameters를 찾는 것도 여전히 힘들다. -
개인 platform에서 LLM을 실행할 때 이러한 challenges가 특히 두드러지며, 본 논문은 on-device inference를 위한 다양한 크기의 LLM을 deploy하는 문제를 해결하는 데 중점을 둔다.
3.3. Our Solution: Any-Precision LLM
Concept.
-
Any-precision quantization은 다양한 크기의 LLMs을 deploying하는 비용을 줄이기 위한 유망한 해결법이다.
Figure 1.은 any-precision quantization의 concept을 시각화했다.
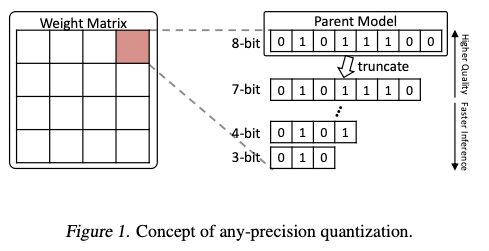 핵심은 large model(8-bit quantized model)에서 parameters의 상위 bits만 사용하여 smaller model(7-bit, 6-bit quantized model, ...)을 유도하는 것이다.
핵심은 large model(8-bit quantized model)에서 parameters의 상위 bits만 사용하여 smaller model(7-bit, 6-bit quantized model, ...)을 유도하는 것이다.
이 large model을 parent model이라고도 부른다.
물론, parent model의 parameter의 prefixes(접두어 = 앞부분?)만을 사용하더라도 quality drops이 심각하지 않도록 하기 위해 any-precision quantization을 위한 special method가 필요하다.
any-precision approach는 highly memory-efficient하며,
1) parent model의 quantized weight와 2) 지원되는 각 bit-width에 관련된 quantization parameters(e.g. centroid values)(이 parameter들은 상대적으로 크기가 작다.)를
memory에 저장함으로써 다양한 bit-width models을 활용할 수 있게 해준다.
또한 여러 model을 train할 필요가 없다. -
Table 1에서 any-precision LLM의 memory saving에 대한 quantitative analysis(정량적 분석)와
LLM에 대한 any-precision quantization을 제공한다.
any-precision quantization이 없을 경우, 서로 다른 bit-width model을 적응적으로 사용하려면 각각의 memory space를 차지하는 개별 model을 deploy해야 한다.
우리는 이를 separate deployment라고 부른다.
Llama-2-7B model을 사용하여 서로 다른 bit-width set이 필요한 다양한 시나리오에 대해 seperate deployment가 필요한 memory space를 any-precision LLM과 비교했다.
(내가 이해한 내용 : Separate Deployment = 3-bit Precision LLM + 6-bit Precision LLM)

Challenges of Any-Precision LLM.
- 위에서 Concept 자체는 매력적이지만, CNN model에 바로 적용했던 것 처럼 LLM에서도 바로 적용하면 문제가 생긴다.
- 첫째, 이는 QAT scheme이므로, model을 scratch로 training해야 한다.
training 중에 forward pass에서 parameter를 다양한 bit-widths로 quantize하여
resulting model이 any-precisoin quantization에 robust하게 된다.
하지만 LLM의 경우, training은 대부분의 users들이 감당할 수 없는 수준이다. - 둘째, 이 작업은 memory bandwidth saving에 대한 고려가 없다.
parent model의 전체 n-bit parameters가 memory에 Load된 후 필요에 따라 bit-shifting을 통해 낮은 bit-width weights로 추가적으로 quantized된다.
이 전략은 일반적으로 compute-bound(계산 집약적인) CNN model에는 적합하지만,
on-device에서의 LLM inference는 lower arithmetic intensity(더 낮은 산술 밀도)로 인해 매우 memory-bound(memory 집약적)이다.
따라서 weight parameters의 memory load는 single primary performance bottleneck 현상이다.
따라서 원래 방법이 LLM에 그대로 적용되면 낮은 bit-widths에서 operating하더라도 parent model에 비해 inference latency improvements가 미미할 수 있다.
따라서 LLM을 위해서는 low-cost any-precision quantization method와 reduced precision inference가 실제 속도 향상으로 직접 이어지는 specialized SW engine을 통합하는 새로운 방법이 필요하다.
- 첫째, 이는 QAT scheme이므로, model을 scratch로 training해야 한다.
따라서 가중치 매개변수의 메모리 로드는 단일 주요 성능 병목 현상입니다(Kim et al., 2023c). 따라서 원래 방법이 LLM에 그대로 적용되면 낮은 비트 너비에서 운영하더라도 부모 모델에 비해 추론 지연 시간 개선이 미미할 수 있습니다. 따라서 LLM을 위해서는 저비용의 모든 정밀도 양자화 방법과 낮은 정밀도 추론이 실제 속도 향상으로 직접 이어지는 특화된 소프트웨어 엔진을 통합하는 새로운 솔루션이 필요합니다.
4. Any-Precision Quantization for LLM
4.1. Incremental Upscaling
- 우리는 LLM의 any-precision quantization에 대한 새로운 접근법인 incremental upscaling을 제안한다.
Figure 2는 incremental upscaling을 활용한 any-precision quantization의 두 단계 flow를 보여준다.
a list of candidate bit-widths 을 가정할 때,
initial step은 minimum supported bit-width ()으로 quantize하며, 이를 seed model이라고 부른다.
그 후, 우리는 seed model을 한 번에 하나의 bit씩 점진적으로 upscale하여 최종 -bit parent model을 얻을 때까지 진행한다.
-bit model에서 model로의 각 incremental upscale 과정에서,
-bit model의 모든 parametersrk -bit model에 상속되며, 각 parameters의 끝에 하나의 추가 비트가 추가된다.

4.2. Non-uniform Quantization-based Incremental Upscaling
-
우리의 any-precision quantization의 incremental upscaling-based approach를 위해,
seed model 생성과 그 다음 upscaling process에 대한 기본 quantization 방법이 정해져야 한다.
이 목적을 위해 아무런 PTQ 방법을 사용할 수 있지만, expensive training process를 포함하지 않기 위해 QAT 방법은 제외한다.
다양한 PTQ 방법 중에서, 다음이 optimal choice가 될 것이다.
1) quality seed model 생성을 위한 SOTA quantization 결과를 보여주고
2) incremental upscaling process에 원활하게 확장하기 -
이를 위해 우리는 SOTA clustering-based non-uniform quantization scheme인 SqueezeLLM을 기본 방법으로 활용한다.
이 방법은 SOTA 결과를 제공하며 incremental upscaling과의 호환성이 뛰어나다.
clustering-based quantization 방법을 통한 incremental upscaling은 간단하다.
SqueezeLLM에서 quantization은 parameters를 clustering하는 과정으로, 각 cluster 내의 값들은 해당 centroid 값으로 rounded(반올림)된다
이러한 맥락에서 incremental upscaling은 각 cluster를 두 개의 sub-clusters로 나누는 방식으로 이루어질 수 있다.
구체적으로, 각 cluster 값에 대해 weighted K-means clustering을 수행하여 두 개의 sub-clusters를 생성한다.
clustering 과정에서 원래 방법과 유사하게 approximated second-order derivative에 기반한 sensitivity metric이 사용된다. -
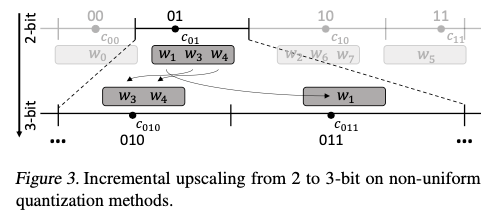
Figure 3은 clustering-based non-uniform quantization 방법을 사용하여 2-bit model에서 3-bit model로 변환하는 upscaling 과정을 시각화했다.
이 경우, 처음에 cluster 01에 할당되었던 세 개의 weight parameters()는 이전의 centroid 으로 rounded되었다.
이제 이들은 각각의 centroid 과 을 가진 두 개의 새로운 sub-clusters인 010과 011로 나누어진다.
동일한 과정이 나머지 세 개의 cluster(00, 10, 11)에도 적용되어 최종적으로 총 8개의 sub-clusters가 생성된다.
 clustering-based 방법과 대조적으로, SOTA uniform quantization method는 종종 weight reconstruction 및 per-channel scaling과 같은 복잡한 mechanism을 포함하여 incremental upscaling과의 호환성이 낮다.
clustering-based 방법과 대조적으로, SOTA uniform quantization method는 종종 weight reconstruction 및 per-channel scaling과 같은 복잡한 mechanism을 포함하여 incremental upscaling과의 호환성이 낮다.
예를 들어, Table 2는 3-bit model을 seed model로 사용하여 두 가지 SOTA uniform 방법(AWQ, GPTQ)에 incremental upscaling을 적용한 결과를 제시한다.
기존 uniform quantization 방법에 incremental upscaling을 적용하는 데 따른 도전 과제와 추가 실험 결과에 대한 심도 있는 논의는 Appendix E.에 있음.
(clustering-based 방법이 더 효과적이라는 것을 보여줬다...)

5. Specialized Software Engine
(skip)
몰랐던 것
-
any-precision DNN?
inference 동안 numerical precision이 유연하게 적용될 수 있도록 새로운 학습 방법을 통해 any-precision DNN이 제안되었다.
요약하면, 어떠한 precision에서든 효과적인 inference하도록 학습시키는 것

-
speculative decoding? (이해를 참고한 글 : https://ostin.tistory.com/402)
기존의 decoder에서 bottleneck이었던 autoregressive 방식의 문제점을 개선하기 위해,
여러 개의 token을 병렬로 계산하여 더 빠르게 sampling하는 Speculative Decoding.
efficient model 가 token sequence를 생성하고, target model 가 해당 sequence를 평가하여
token을 수용하고 거부하며 대안을 생성한다.
 K개의 token을 생성할 때, K번의 큰 model을 호출하지 않고 작은 model을 K번 호출한다.
K개의 token을 생성할 때, K번의 큰 model을 호출하지 않고 작은 model을 K번 호출한다.
결과적으로 큰 model은 한 번만 호출하여 병렬로 평가를 수행할 수 있기 때문에 빠르다.