Abstract
Monocular video로부터 새로운 카메라 각도에서의 영상을 생성해내는 작업에 있어 dynamic NeRFs와 같은 현 SOTA 모델들은 번지거나 부정확한 rendering 결과를 보임. 기존 image-based rendering framework의 prior를 활용하여 카메라 경로에 제약을 받지 않는 모델 제안.
1. Introduction
-
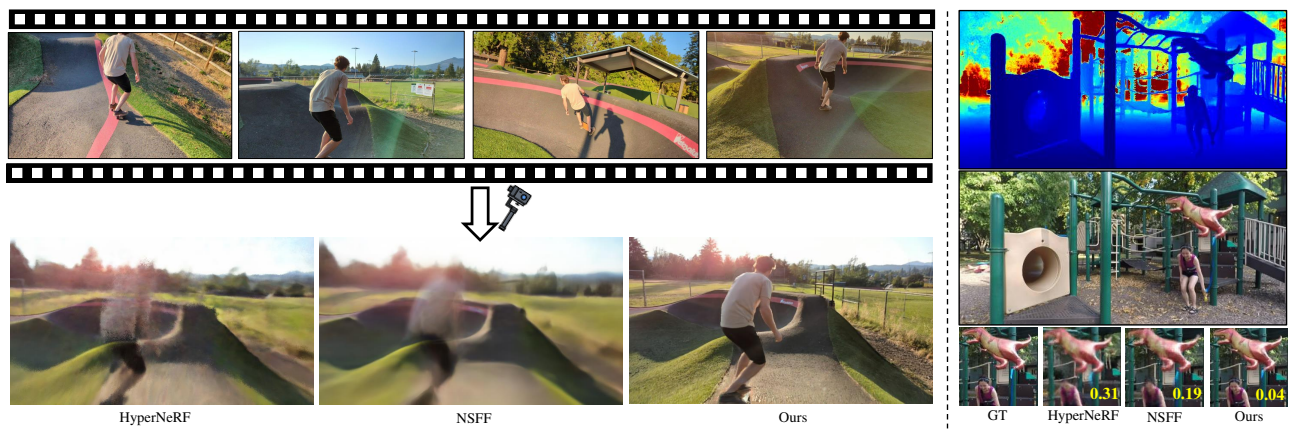
3D scene에 대한 novel view synthesis보다 monocular video에 대한 작업이 더 어려움. 이를 수행하는 HyperNeRF, Neural Scene Flow Fields와 같은 dynamic NeRF 는 물체의 움직임이 복잡하거나 영상의 길이가 긴 경우 제 성능을 발휘하지 못함.
-
1) Long time duration, 2) unbounded scene, 3) uncontrolled camera trajectories, 4) fast & complex object motion의 영상에 적용 가능한 접근 방식 제안. View-dependent한 volumetric scene representation의 prior를 leverage하며, static & dynamic scene content에 대한 rendering fidelity를 높임.
-
고정된 장면에 대해 epipolar line 상의 nearby view를 aggregate하여 novel image를 생성하는 모델(aggregation-based methods)을 dynamic scene에 대해 scale up. Scene motion-adjusted ray space 상에서 feature를 aggregate.
-
1) 학습된 basis function으로 표현되어 여러 frame을 span하는 motion trajectory field로 영상의 움직임을 모델링. 2) 새로운 temporal photometric loss를 도입하여 temporal coherence 유지. 3) IBR-based motion segmentation technique로 장면을 static component와 dynamic component로 분리.
2. Related Work
(생략)
3. Dynamic Image-Based Rendering
-
의 frame과 의 camera parameters로 구성된 영상에 대해, reconstruction을 위한 optimization을 먼저 진행한 뒤, 해당 모델로 임의 시간에서의 novel view synthesize 수행.
-
IBR 아이디어를 volumetric rendering framework에 도입하여, volumetric representation으로 scene geometry 모델링.
3.1. Motion-Adjusted Feature Aggregation
-
-th frame에 대한 novel view frame을 생성하기 위해, 시간 상으로 인접한 번째 frame에 대한 camera parameter 와 shared convolutional encoder network에서 출력된 2D feature map 으로 tuple 을 구성하여 사용.
-
정적 장면의 경우, 주변 view의 epipolar line이 target ray에 해당하기 때문에 epipolar lines를 sampling하여 합산할 수 있음. 하지만 동적 장면은 epipolar 제약을 거스르기에 움직임이 고려되지 않는다면 inconsistent feature aggregation으로 이어짐. Motion-adjusted feature aggregation 제안.
-
MLP로 각 픽셀에 대한 scene flow field를 estimate하는 것은 computationally infeasible. Learned basis functions 기반의 motion trajectory fields 구성. Time 에서의 ray 상에 놓이는 3D point 에 대해, positional encoding 와 motion trajectory를 출력하는 MLP 로 결정되는 basis coefficients 은 아래와 같음.
-
또한 fixed DCT basis의 한계점을 보완하고자 global learnable motion basis 도입.
-
앞선 estimated motion trajectory 로 time 에서의 3D point 를 계산. Camera parameters 로 source view 에 projection.
