Sequence를 이용한 Custom DataLoader를 만드는 방식에 대해 공부해볼 것이다.
Custom DataLoader with Sequence
CNN을 공부하다보면 Input Image Data 개수가 기본으로 1만 이상인걸 알 수 있다. Data가 너무 많기 때문에 우리는 Data를 효율적으로 Model에 load해줘야한다. 그리고 이렇게 load하는 과정에서 augmentation/preprocess를 적용할 수 있다.
이런 과정을 가능하게 해주는게 Sequence를 이용한 DataLoader를 만드는 것이다.
tensorflow 2.0에서 tensorflow.keras.utils.Sequence를 이용해 Custom Class를 구현할 수 있다.
Custom DataLoader 구현하기
def __init__()
__init__()는 class를 불러올 때 가장 먼저 실행되는 메소드다.
'컨스트럭터'라고 불린다.(초기화 함수)
이를 이용하여 처음에 사용자가 값을 입력한다.
ex) "파일 절대경로", "각 파일의 정답 값", "이미지 사이즈(nXn)", "배치 사이즈(Model에 넣을 사이즈)" ...
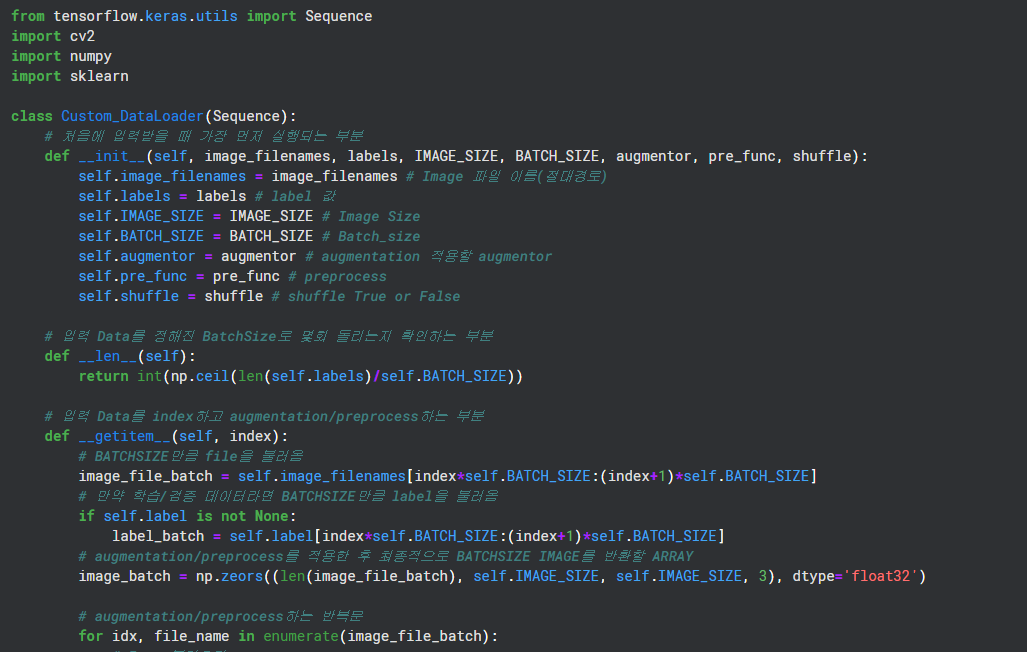
from tensorflow.keras.utils import Sequence
class Custom_DataLoader(Sequence):
# 처음에 입력받을 때 가장 먼저 실행되는 부분
def __init__(self, image_filenames, labels, IMAGE_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE, augmentor, pre_func, shuffle):
self.image_filenames = image_filenames # Image 파일 이름(절대경로)
self.labels = labels # label 값
self.IMAGE_SIZE = IMAGE_SIZE # Image Size
self.BATCH_SIZE = BATCH_SIZE # Batch_size
self.augmentor = augmentor # augmentation 적용할 augmentor
self.pre_func = pre_func # preprocess
self.shuffle = shuffle # shuffle True or Falsedef __len__()
길이함수인 __len__()은 Data를 한 epoch당 정해진 BathSize로 돌리면 몇 번 돌릴 수 있는지 알려주는 메소드다.
예를 들어 50000개의 Image고, BatchSize가 50이라면 한 epoch당 1000번 돌게된다.
# 입력 Data를 정해진 BatchSize로 몇회 돌리는지 확인하는 부분
def __len__(self):
return int(np.ceil(len(self.labels)/self.BATCH_SIZE))def __getitem__()
__getitem__()은 index값에 따라 Data를 반환하는 메소드다.
Model에 Data를 넣을때는 iteration마다 호출되는 메소드라고 생각할 수 있다.
단순히 Image를 BatchSize만큼 반환하는 방법도 있겠으나, __getitem__메소드에서 Image를 BatchSize만큼 가져온 후 augmentation/preprocess후 return할 수 있다.
Custom DataLoader에서 가장 중요한 부분이다.
# 입력 Data를 index하고 augmentation/preprocess하는 부분
def __getitem__(self, index):
# BATCHSIZE만큼 file을 불러옴
image_file_batch = self.image_filenames[index*self.BATCH_SIZE:(index+1)*self.BATCH_SIZE]
# 만약 학습/검증 데이터라면 BATCHSIZE만큼 label을 불러옴
if self.label is not None:
label_batch = self.label[index*self.BATCH_SIZE:(index+1)*self.BATCH_SIZE]
# augmentation/preprocess를 적용한 후 최종적으로 BATCHSIZE IMAGE를 반환할 ARRAY
image_batch = np.zeors((len(image_file_batch), self.IMAGE_SIZE, self.IMAGE_SIZE, 3), dtype='float32')
# augmentation/preprocess하는 반복문
for idx, file_name in enumerate(image_file_batch):
# Image불러오기
image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(file_name), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# augmentor 적용
image = self.augmentor(image=image)
# preprocess가 있다면 적용
if self.pre_func is not None:
image = self.pre_func(image)
# batch에 넣어주기
image_batch[idx] = image
return image_batch, label_batchdef on_epoch_end()
on_epoch_end()는 한 epoch가 끝날때마다 실행하는 함수다.
이 함수는 없어도 상관없지만 Overfitting을 방지하기 위해 Data를 섞는 경우에 사용된다.
# epoch가 끝날때마다 shuffle해주는 부분
def on_epoch_end(self):
# 만약 섞는다고 사용자가 지정하면 섞기
if self.shuffle:
self.image_file_batch, self.label = sklearn.utils.shuffle(self.image_file_batch, self.label)최종 코드
from tensorflow.keras.utils import Sequence
import cv2
import numpy
import sklearn
class Custom_DataLoader(Sequence):
# 처음에 입력받을 때 가장 먼저 실행되는 부분
def __init__(self, image_filenames, labels, IMAGE_SIZE, BATCH_SIZE, augmentor, pre_func, shuffle):
self.image_filenames = image_filenames # Image 파일 이름(절대경로)
self.labels = labels # label 값
self.IMAGE_SIZE = IMAGE_SIZE # Image Size
self.BATCH_SIZE = BATCH_SIZE # Batch_size
self.augmentor = augmentor # augmentation 적용할 augmentor
self.pre_func = pre_func # preprocess
self.shuffle = shuffle # shuffle True or False
# 입력 Data를 정해진 BatchSize로 몇회 돌리는지 확인하는 부분
def __len__(self):
return int(np.ceil(len(self.labels)/self.BATCH_SIZE))
# 입력 Data를 index하고 augmentation/preprocess하는 부분
def __getitem__(self, index):
# BATCHSIZE만큼 file을 불러옴
image_file_batch = self.image_filenames[index*self.BATCH_SIZE:(index+1)*self.BATCH_SIZE]
# 만약 학습/검증 데이터라면 BATCHSIZE만큼 label을 불러옴
if self.label is not None:
label_batch = self.label[index*self.BATCH_SIZE:(index+1)*self.BATCH_SIZE]
# augmentation/preprocess를 적용한 후 최종적으로 BATCHSIZE IMAGE를 반환할 ARRAY
image_batch = np.zeors((len(image_file_batch), self.IMAGE_SIZE, self.IMAGE_SIZE, 3), dtype='float32')
# augmentation/preprocess하는 반복문
for idx, file_name in enumerate(image_file_batch):
# Image불러오기
image = cv2.cvtColor(cv2.imread(file_name), cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB)
# augmentor 적용
image = self.augmentor(image=image)
# preprocess가 있다면 적용
if self.pre_func is not None:
image = self.pre_func(image)
# batch에 넣어주기
image_batch[idx] = image
return image_batch, label_batch
# epoch가 끝날때마다 shuffle해주는 부분
def on_epoch_end(self):
# 만약 섞는다고 사용자가 지정하면 섞기
if self.shuffle:
self.image_file_batch, self.label = sklearn.utils.shuffle(self.image_file_batch, self.label)참고자료
[딥러닝] Tensorflow에서 커스텀 데이터로더 만들기(Custom Dataloader)
[python] python의 self와 __init__의 이해
딥러닝 CNN 완벽가이드 - 권철민