이 포스팅은 ACL 2020에서 발표한 Open-Domain Question Answering 를 참고하여 작성하였습니다. 실제 Tutorial 발표 영상을 보고 싶다면, T8: Open-Domain Question Answering로 이동하세요.
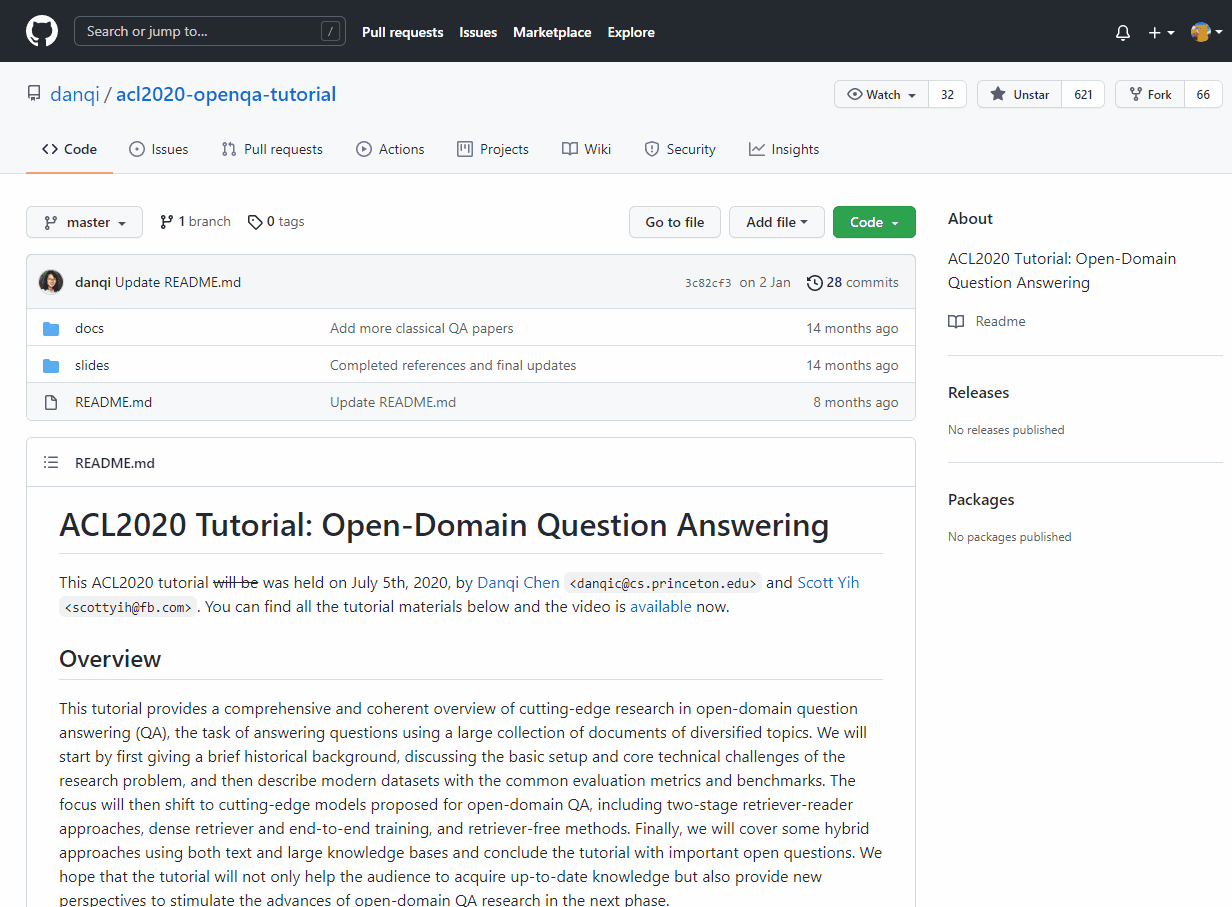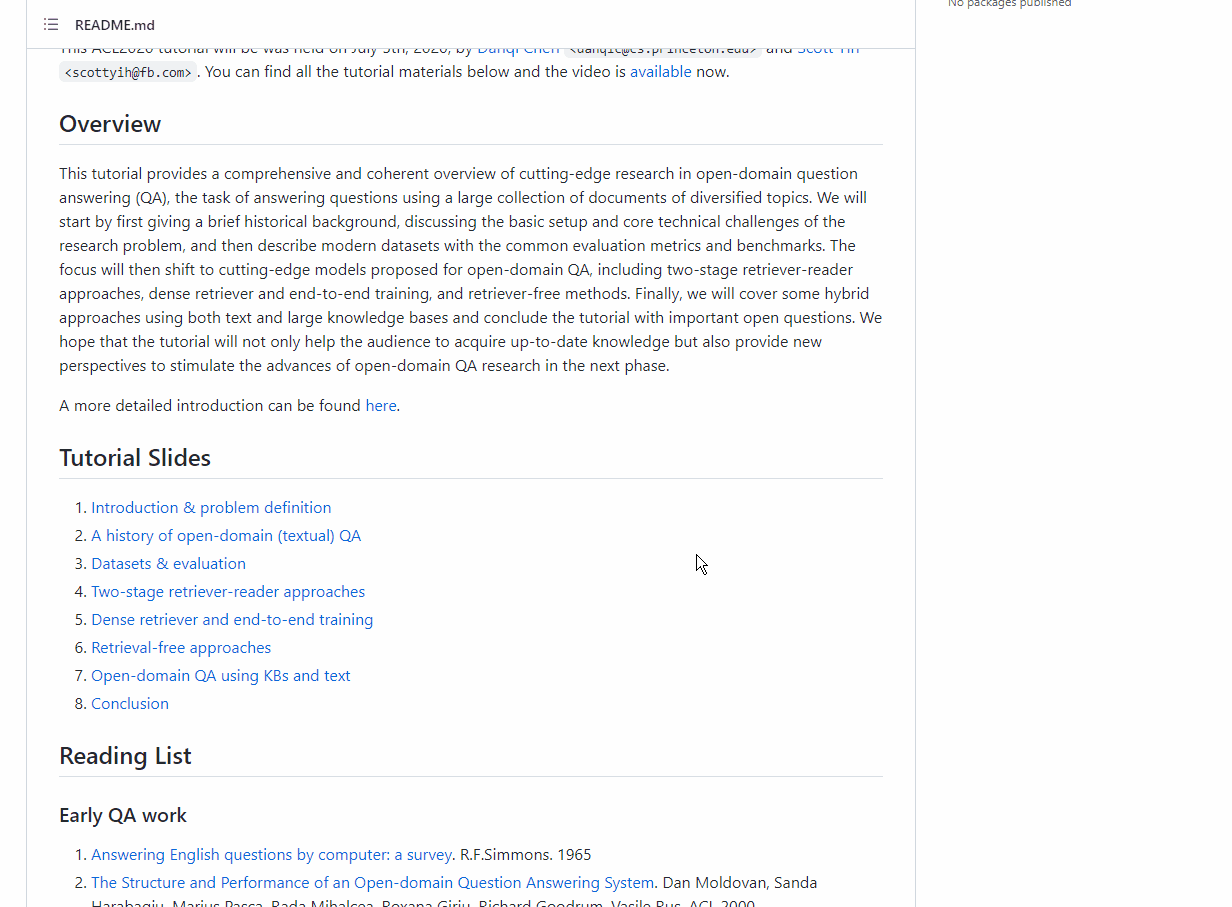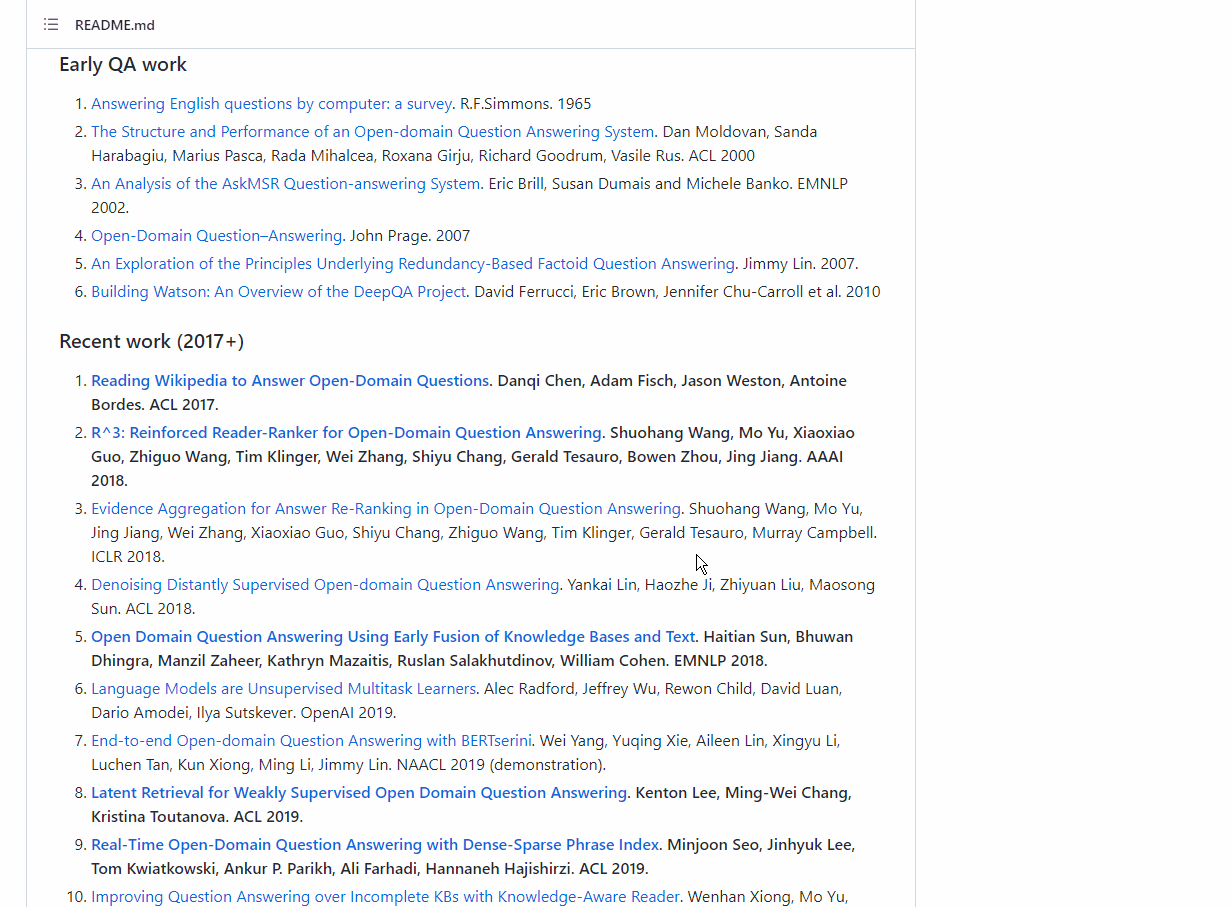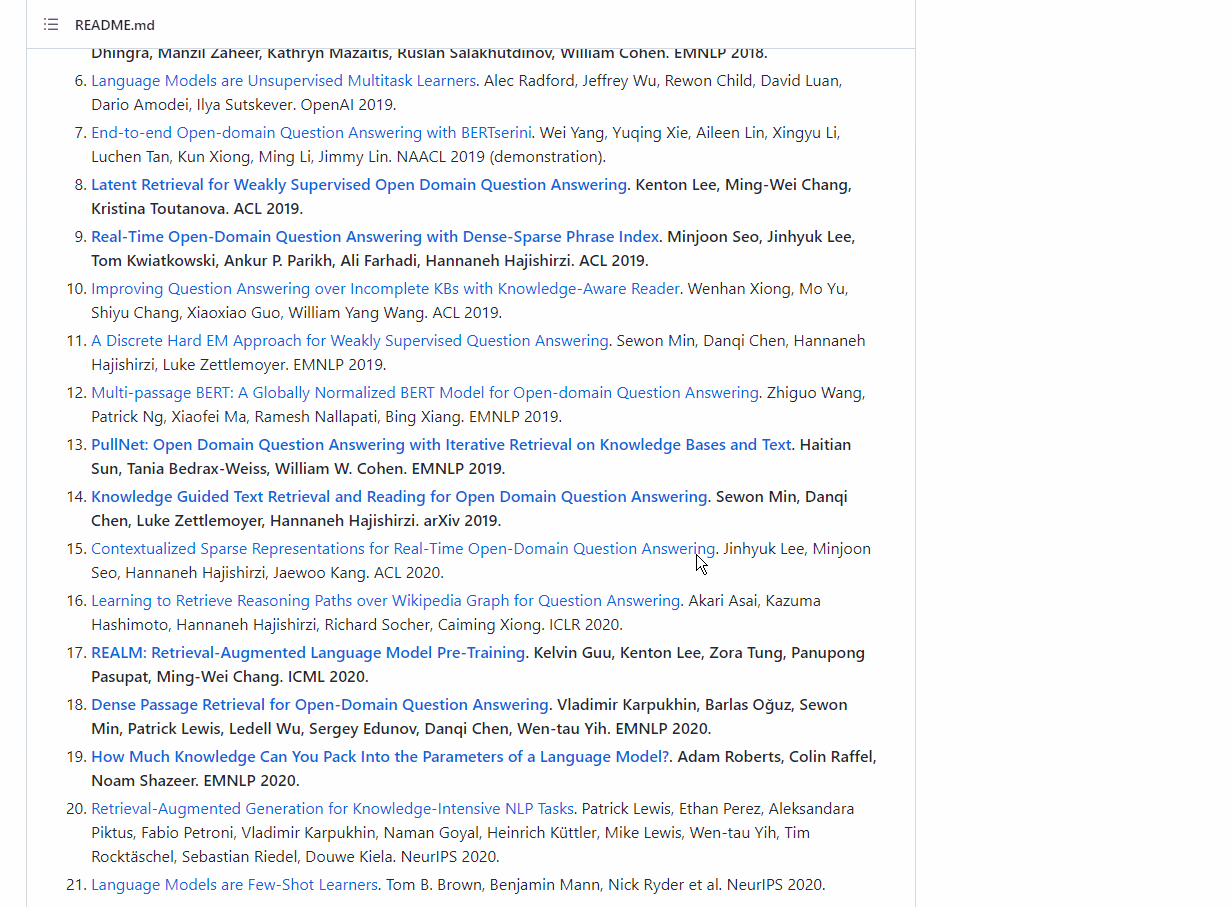
📌 Description
Open-domain Question Answering은 다양한 주제의 대량의 문서 집합을 사용한 질의응답에 관한 task이다. Open-domain QA는 NLP, information retrieval(IR)에서 오래된 문제이다 [1].
전통적인 QA 시스템은 일반적으로 question processing, document/passage retrieval, answering processing으로 이루어진 pipeline으로 구성되었다.
급격한 인공신경망의 발전으로 [2], 현대의 open-domain QA 시스템은 기존의 IR 기술과 AI 모델[3]과의 결합으로 재구성되거나 또는 end-to-end fahsion[4]으로 구현되었다. Open-domain QA에 대한 간략한 배경지식을 설명하고 연구 문제에 대한 기본 구성과 핵심 기술 변화에 대해 논의한다. highly-modulated pipeline systems부터 현대의 깊은 인공신경망 end-to-end 학습까지 지난 수십 년간 그 분야가 어떻게 발전해 왔는지에 대한 관점을 제공한다.
open-domain QA를 위해 제안된 최첨단 모델에 초점을 둔다. 3개의 메인 카테고리들로 기존 모델들을 구분한다: Two-stage retriever-reader approaches, Dense retriever and end-to-end training, and Retriever-free approaches.
Two-stage retriever-reader approaches.
-
Retriever : 대량의 문서 집합에서 answer이 포함된 문서를 찾는 것
- TF-IDF이나 BM25 같은 전통적인 sparse vector space methods 사용
-
Reader : 주어진 문단이나 문서에서 answer를 찾는 것
- 인공신경망 모델을 사용 -
multi-passage training [5], passage reranking [6], denoising distantly-supervised data [7]
Dense retriever and end-to-end training.
- 기존의 IR 기법 대신 dense representations를 대체하여 retriever를 학습하는 방법에 중점을 둠
- Learning and searching in dense vector space이 어떻게 기존 모델에 의해 달성되었는가에 깊이 논의함
- 새로운 pre-training methods [8], carefully-designed learning algorithms [9], hybrid approach using dense and sparse representations [10]
Retriever-free approaches
- 암시적 KB으로서 대규모 pre-trained models에만 의존하는 방식 [11]
- 추론 시간 동안 텍스트 데이터에 접근할 필요가 없다
- retriever가 필요하지 않다. 그래서 retriever-free approaches라고 함.
- 이러한 pre-trained 모델은 zero-shot manner [12] 식으로 질문에 즉시 답하거나 질문-응답 쌍을 사용하여 fine-tuned되는 데 사용된다.
👩🏫 미리보기
-
문제 정의, 동기 부여, 응용
-
간략한 히스토리
2-1. 초기 AI 도전 중 하나
2-2. TREC QA tracks
2-3. IBM Watson Deep QA
2-4. MRC
-
QA의 최신 개발론
- open-domain QA를 학습 및 평가를 위한 유명한 dataset
- Retriever+Reader : DrQA, 2017
- Dense retriever and end-to-end training : ORQA, 2019
- Retrieval-free : T5, 2020.
-
KBs과 텍스트를 사용한 Open-domain QA
4-1. KBs를 사용한 open-domain QA 소개
entity 중심 지식 베이스의 속성, open-domain QA에서 KB의 장단점
4-2. text와 KBs 둘 다 사용에 대한 최근 연구
-
Open problems and future directions
-
🔥 Hot topic : the two open-domain QA 대표적인 예시
암시적 context 검색 vs. 모델에 인코딩된 지식 -
완전한 사용자 경험
답변을 뒷받침한 근거와 증거, answer triggering, 서술형 질문과 긴 형식의 답변 -
user interaction과 grounding
대화형 QA, 다중 모드 상호작용
구체적인 튜토리얼 리뷰는 ACL2020 Tutorial: Open-Domain Question Answering ver2에서 이어집니다.
[1] Ellen M Voorhees et al. 1999. The TREC-8 question answering track report. In Trec, volume 99, pages 77–82. Citeseer.;
Dan Moldovan, et al. 2000. The structure and performance of an open-domain question answering system. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 563–570.;
Eric Brill, et al. 2002. An analysis of the AskMSR question-answering system. In Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 257–264.;
David Ferrucci, et al. 2010. An overview of the DeepQA project. AI magazine, 31(3):59–79.
[2] Danqi Chen. 2018. Neural Reading Comprehension and Beyond. Ph.D. thesis, Stanford University;
[3] Danqi Chen, et al. 2017. Reading Wikipedia to answer open-domain questions. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 1870–1879;
Wei Yang, et al. 2019. End-to-end open-domain question answering with bertserini. In North American Association for Computational Linguistics (NAACL), pages 72–77;
Sewon Min, et al. 2019a. A discrete hard EM approach for weakly supervised question answering. In Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP).
[4] Kenton Lee, et al. 2019. Latent retrieval for weakly supervised open domain question answering. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 6086–6096;
Minjoon Seo, et al. 2019. Real-time open-domain question answering with dense-sparse phrase index. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 4430–4441;
Kelvin Guu, et al. 2020. REALM: Retrieval-augmented language model pre-training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08909;
Adam Roberts, et al. 2020. How much knowledge can you pack into the parameters of a language model? arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08910.
[5] Clark and Gardner. 2018. Simple and effective multi-paragraph reading comprehension. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 845–855.;
Wang et al. 2019. Multi-passage bert: A globally normalized bert model for open-domain question answering. In Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing (EMNLP), pages 5881–5885;
[6] Wang et al. 2018. Rˆ3: Reinforced reader-ranker for open-domain question answering. In Conference on Artificial Intelligence (AAAI).
Nogueira and Cho. 2019. Passage re-ranking with BERT. arXiv preprint arXiv:1901.04085;
[7] Yankai Lin, et al. 2018. Denoising distantly supervised open-domain
question answering. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 1736–1745
[8] Lee et al., 2019;
Guu, et al. 2020. REALM: Retrieval-augmented language model pre-training. arXiv preprint arXiv:2002.08909
[9] Karpukhin, et al. 2020. Dense passage retrieval for open-domain question answering. arXiv preprint arXiv:2004.04906
[10] Seo, et al. 2019. Real-time open-domain question answering with dense-sparse phrase index. In Association for Computational Linguistics (ACL), pages 4430–4441
[11] Radford, et al. 2018. Improving language understanding by generative pre-training. Technical report, OpenAI Devlin et al., 2018;
Liu, et al. 2019. RoBERTa: A robustly optimized BERT pretraining
approach. arXiv preprint arXiv:1907.11692.
