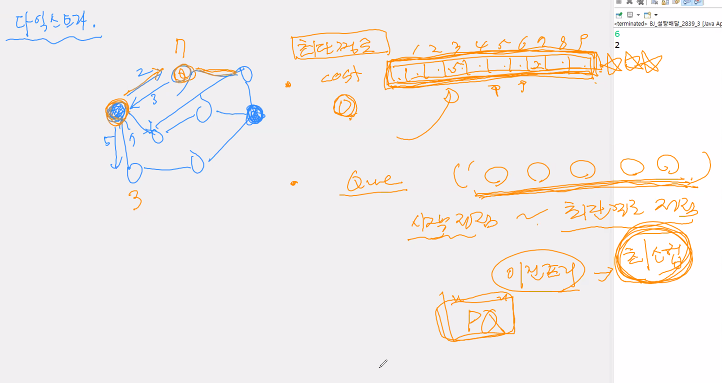
그래프 최단경로
- 비용, 거리, 무게
한 정점에서 다른 정점 탐색
가중치, 비용이 없다, 비용이 같다
-> bfs로 풀면 됨(코드 더 간결)
-> 몇단계 거쳐가는지만 체크하면 됨
-> 다른 알고리즘은 복잡
-> 5번에 갈 수 있다 이러면 bfs는 그걸 반드시 보장해줌
가중치, 비용이 있다
-> 다익스트라, 플로이드워셜
-> bfs에 가중치를 같이 끌고 가면? - 완탐형태가 됨 - 시간초과가 남
다익스트라
한 정점에서 다른 정점으로 갈 때 중간에 거쳐가는 정점도 모두 최단경로가 되어야 함
한 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로 가는 최단 경로를 구함
O(N log N)
플로이드워셜
그래프에 있는 모든 정점에서 다른 모든 정점으로 가는 최단 경로(한 정점이 아님)
dp, 완탐 느낌
O(N^3)
다익스트라
시작 정점에서 최종 정점으로 가는 최소 비용을 관리하는 자료구조가 필요하다.
-
배열
거리가 가장 작은 값을 찾기 위해 모든 원소를 순차탐색해야 하므로 효율적이지 못함 -
큐
PriorityQueue, 이진트리, 최소힙 등
-> 최소힙(PriorityQueue 사용 - 정렬 조건을 주면 됨)
우선순위 큐
우선순위가 가장 높은 데이터를 가장 먼저 삭제
첫번째 원소를 기준으로 우선순위가 설정됨
최소힙: 값이 낮은 데이터가 먼저 삭제
최대힙: 값이 큰 데이터가 먼저 삭제
-> 탐색할 필요 없이 거리가 가장 작은 것을 먼저 처리하기 때문에 더 빠름
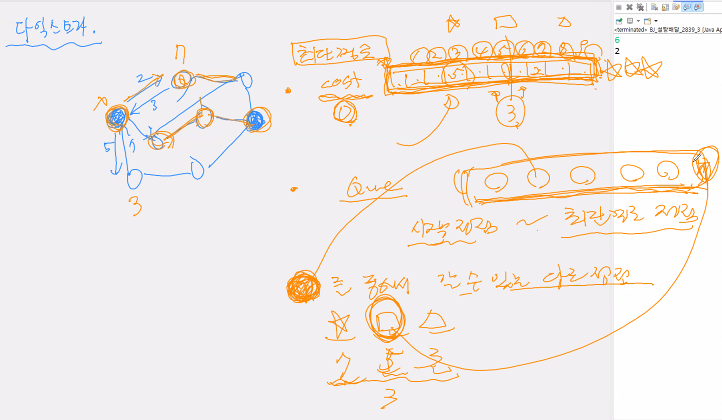
단계
-
단계마다 방문하지 않은 노드 중에서 최단 거리가 가장 짧은 노드를 선택하기 위해 매 단계마다 배열의 모든 원소를 순차탐색(O(V))
-> 우선순위 큐(힙)으로 담으면 더 빠름(O(ElogV)) -
노드와 연결된 노드 중에 방문하지 않은 노드들의 최단 거리를 계산한다. (시작~현 노드의 거리+현 노드~연결노드의 거리)
-
이 노드 거리가 우선순위 큐 값보다 작으면 갱신해준다.
(거리, 노드)의 형식으로 저장 -
우선순위 큐에 있는 노드 거리가 제일 작은 노드를 뽑아 위 과정을 반복한다.
-
모든 과정을 거친 후 최단 거리 테이블에 남아있는 각 노드의 값이 최단 경로이다.
인접행렬
package _240701; // 인접행렬 풀이
import java.beans.ExceptionListener;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.Arrays;
import java.util.PriorityQueue;
import java.util.StringTokenizer;
// 그래프 자료구조(인접행렬, 인접리스트)
// 비용관리 배열(시작점으로부터 각 정점까지의 최소비용(최단거리)
// 고려하는 큐에 담긴 정점 중 시작점에서부터 최소 비용의 정즘을 찾는 우선순위 큐
// 최소 비용으로 고려했던 정점 관리 visit
// 우선순위 큐에 담을 Vertex(Node) 클래스 (정점번호 , 시작점으로부터의 비용)
public class Dijkstra_PQ {
static class Node{
int v; // 정점 번호
int c; // 시작 정점에서부터의 거리
Node(int v, int c){
this.v = v;
this.c = c;
}
}
static int V, start, end;
static int[][] matrix; // 한 정점에서 다른 정점으로 가는 비용, 0은 연결x
static int[] cost; // 시작점으로부터 각 정점까지의 최소비용
static boolean[] visit;
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // cost 배열 초기화
static PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((n1, n2) -> n1.c - n2.c);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
V = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
start = 0;
end = V - 1;
matrix = new int[V][V];
cost = new int[V];
visit = new boolean[V];
// 입력 -> matrix 구성
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
for(int j=0;j<V;j++){
matrix[i][j] = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken()); // 비용 i -> j
}
}
// 비용 테이블 충분히 큰 값으로 초기화
Arrays.fill(cost, INF);
// 다익스트라
cost[start] = 0;
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(start, 0)); // 시작 정점을 pq에 넣고 다익스트라 진행
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){ // 전체를 모두 끝내면 모든 정점에 대한 최단 경로(최소비용)이 완성됨
Node node = priorityQueue.poll();
if(visit[node.v]) continue; // 이미 방문한 정점 스킵
visit[node.v] = true;
// 모든 정점이 아니라 목표하는 정점만 따질 경우
if(node.v == end){
break;
}
// 꺼낸 정점으로부터 갈 수 있는 곳 찾기
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
// 꺼낸 node.v 정점 ~~> i 고려
if(matrix[node.v][i] == 0) continue; // 연결 안되어있는거
// 아직 방문하지 않은 (최소비용노드로 확정되지 않은)
// i번 정점 고려중
// 현재 cost[i]는 시작점 ~~~> i 정점까지 최소 비용이 기록
// 만약 꺼낸 node.v 정점을 거쳐서 i로 가면 cost[i]가 줄어들 수 있나를 따지기
if(cost[i] > node.c + matrix[node.v][i]) {
cost[i] = node.c + matrix[node.v][i]; // 최소 비용 갱신
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(i, cost[i]));
}
}
}
System.out.println(cost[end]);
}
}
/*
5
0 2 2 5 9
2 0 3 4 8
2 3 0 7 6
5 4 7 0 5
9 8 6 5 0
==> 8
4
0 94 53 16
79 0 24 18
91 80 0 98
26 51 92 0
==> 16
7
0 2 8 5 9 15 20
2 0 5 4 7 10 16
8 5 0 7 6 4 10
5 4 7 0 15 8 9
9 7 6 15 0 11 13
15 10 4 8 11 0 6
20 16 10 9 13 6 0
==> 14
*/인접리스트
package _240701; // 인접 리스트
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
// 그래프 자료구조(인접행렬, 인접리스트)
// 비용관리 배열(시작점으로부터 각 정점까지의 최소비용(최단거리)
// 고려하는 큐에 담긴 정점 중 시작점에서부터 최소 비용의 정즘을 찾는 우선순위 큐
// 최소 비용으로 고려했던 정점 관리 visit
// 우선순위 큐에 담을 Vertex(Node) 클래스 (정점번호 , 시작점으로부터의 비용)
public class Dijkstra_PQ_2 {
static class Node{
int v; // 정점 번호
// 인접리스트에 Node를 사용할 경우: 인접리스트 정점 ~> v 정점까지의 비용(거리)
// 우선순위큐에 Node 를 사용할 경우 : 시작 정점으로부터의 최소 비용(거리)
int c;
Node(int v, int c){
this.v = v;
this.c = c;
}
}
static int V, E, start, end;
static List<List<Node>> adjList = new ArrayList<>(); // 한 정점에서 다른 정점으로 가는 비용, 0은 연결x
static int[] cost; // 시작점으로부터 각 정점까지의 최소비용
static boolean[] visit;
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE; // cost 배열 초기화
static PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((n1, n2) -> n1.c - n2.c);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
V = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
E = Integer.parseInt(bufferedReader.readLine());
start = 0;
end = V - 1;
cost = new int[V];
visit = new boolean[V];
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
adjList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
// 입력 E개 -> 인접리스트 구성
for(int i=0;i<V;i++){
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
int v1 = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int v2 = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
adjList.get(v1).add(new Node(v2, c)); // v1 정점에서 갈 수 있는 다른 정점 정보를 가져와 v2, c 넣기
}
// 비용 테이블 충분히 큰 값으로 초기화
Arrays.fill(cost, INF);
// 다익스트라
cost[start] = 0;
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(start, 0)); // 시작 정점을 pq에 넣고 다익스트라 진행
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){ // 전체를 모두 끝내면 모든 정점에 대한 최단 경로(최소비용)이 완성됨
Node node = priorityQueue.poll();
if(visit[node.v]) continue; // 이미 방문한 정점 스킵
visit[node.v] = true;
// 모든 정점이 아니라 목표하는 정점만 따질 경우
if(node.v == end) {
break;
}
// 꺼낸 정점으로부터 갈 수 있는 곳 찾기
for(Node n : adjList.get(node.v)){
if(visit[n.v]) continue;
if(cost[n.v] > cost[node.v] + n.c) { // n.c는 리스트에서 꺼낸거,
// node.v는 큐에서 뽑은거 cost[node.v] = node.c 같음
cost[n.v] = cost[node.v] + n.c; // 최소 비용 갱신 (n.v)
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(n.v, cost[n.v]));
}
}
}
System.out.println(cost[end]);
}
}
/* (노드, 목표, 비용)
5
20
0 1 2
0 2 2
0 3 5
0 4 9
1 0 2
1 2 3
1 3 4
1 4 8
2 0 2
2 1 3
2 3 7
2 4 6
3 0 5
3 1 4
3 2 7
3 4 5
4 0 9
4 1 8
4 2 6
4 3 5
==> 8
4
12
0 1 94
0 2 53
0 3 16
1 0 79
1 2 24
1 3 18
2 0 91
2 1 90
2 3 98
3 0 26
3 1 51
3 2 92
==> 16
*/플로이드 워셜
현재 A->B로 가는 최소값과 A->K->B를 모두 고려, 비교
A->B를 갱신해나가는 방법
3중 for문 사용하게 됨
for 모든 k -> for 모든 a -> for 모든 b
2차원 배열에 최단 거리 정보 저장
백준 파티 골드3
https://www.acmicpc.net/problem/1238

다익스트라 문제다.
여러 마을에서 도착점까지 가는 거리와 도착점에서 그 마을로 가는 거리를 구해야 한다.
도착점에서 하나의 마을로 가는 방법은 구하기 쉬운데 모든 노드에서 도착점으로 가는 것은 다익스트라를 N-1번 사용해야 한다.
따라서 역방향 그래프를 만들어 모든 노드에서 도착점으로 가는 최단 거리를 구한다.
https://jow1025.tistory.com/114
package _240701;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.InputStreamReader;
import java.util.*;
public class BOJ_파티 {
static class Node{
int v, c;
Node(int v, int c){
this.v = v;
this.c = c;
}
}
static List<List<Node>> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
static List<List<Node>> r_arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
static final int INF = Integer.MAX_VALUE;
static int N, M, X;
static PriorityQueue<Node> priorityQueue = new PriorityQueue<>((n1, n2) -> n1.v - n2.v);
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
BufferedReader bufferedReader = new BufferedReader(new InputStreamReader(System.in));
StringTokenizer stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
N = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
M = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
X = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
for(int i=0;i<=N;i++){
arrayList.add(new ArrayList<>());
r_arrayList.add(new ArrayList<>());
}
for(int i=0;i<M;i++){
stringTokenizer = new StringTokenizer(bufferedReader.readLine());
int v1 = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int v2 = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
int c = Integer.parseInt(stringTokenizer.nextToken());
arrayList.get(v1).add(new Node(v2, c));
r_arrayList.get(v2).add(new Node(v1, c));
}
int d1[] = dijkstra(arrayList);
int d2[] = dijkstra(r_arrayList);
int max = Integer.MIN_VALUE;
for(int i=1;i<=N;i++){
max = Math.max(max, d1[i] + d2[i]);
}
System.out.println(max);
}
static int[] dijkstra(List<List<Node>> arrayList){
int cost[] = new int[N+1];
boolean visit[] = new boolean[N+1];
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(X, 0));
Arrays.fill(cost, INF);
cost[X] = 0;
while(!priorityQueue.isEmpty()){
Node node = priorityQueue.poll();
if(visit[node.v]) continue;
for(Node n : arrayList.get(node.v)){
if(visit[node.v]) continue;
if(cost[n.v] > node.c + n.c)
{
cost[n.v] = node.c + n.c;
priorityQueue.offer(new Node(n.v, cost[n.v]));
}
}
}
return cost;
}
}