Artificial Neural Networks
Computational models inspired by the human brain
- Artificial Neurons
- Network 를 구성하는 단위
- A connection point in an artificial neural network
- Typically taking the form of non-linear function
Neuron in the brain
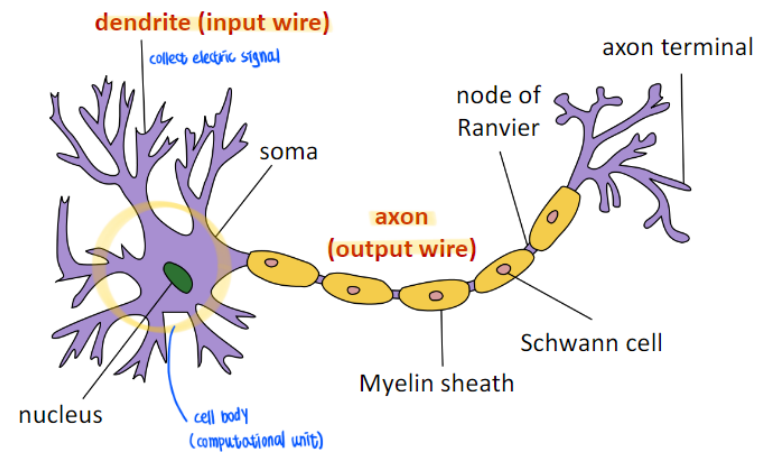
- Dendrites convey electrical signals from neuron to the cell body
- Resultant electrical signals are sent along the axon to other neurons.
Artificial Neurons
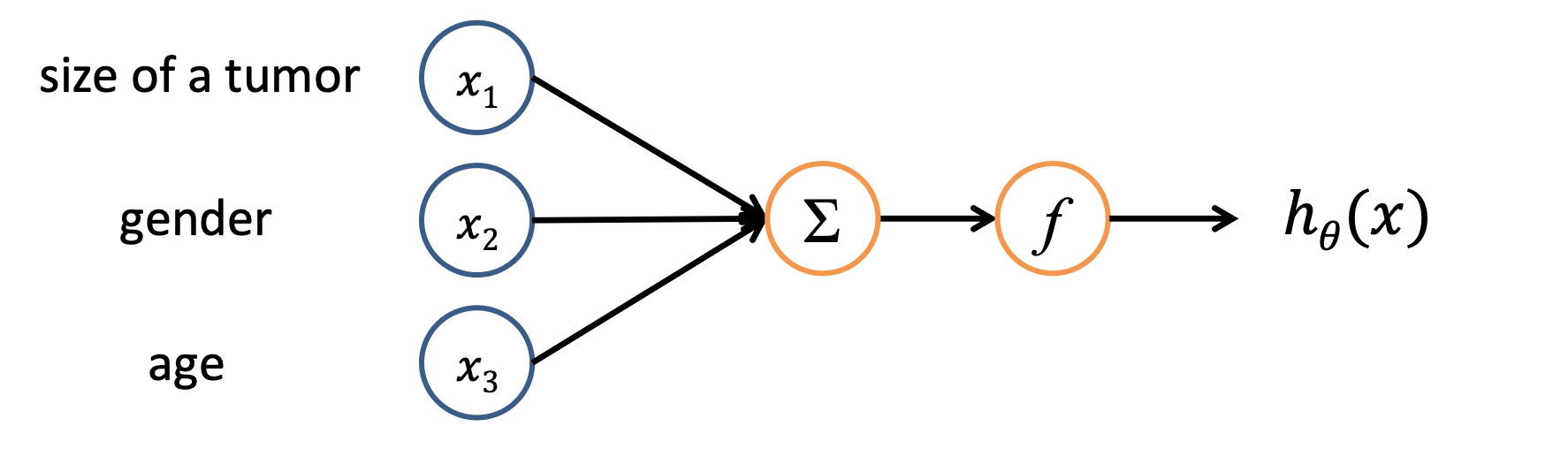
주황색 부분이 neuron임
- Inputs are translated into numerical values → by one-hot encoding
- Inputs are summed and passed to an activation function
- Value computed by the activation function is sent to other neurons.
Bias Units
- Always has a value of one(X_0 = 1)
- 하나의 뉴런으로 입력된 모든 Input을 더한 값에 더해지는 상수
- Increase the flexibility of the model to fit the data
- 최종으로 출력되는 값을 조절하는 역할 (함수를 좌우로 움직임)
Weight
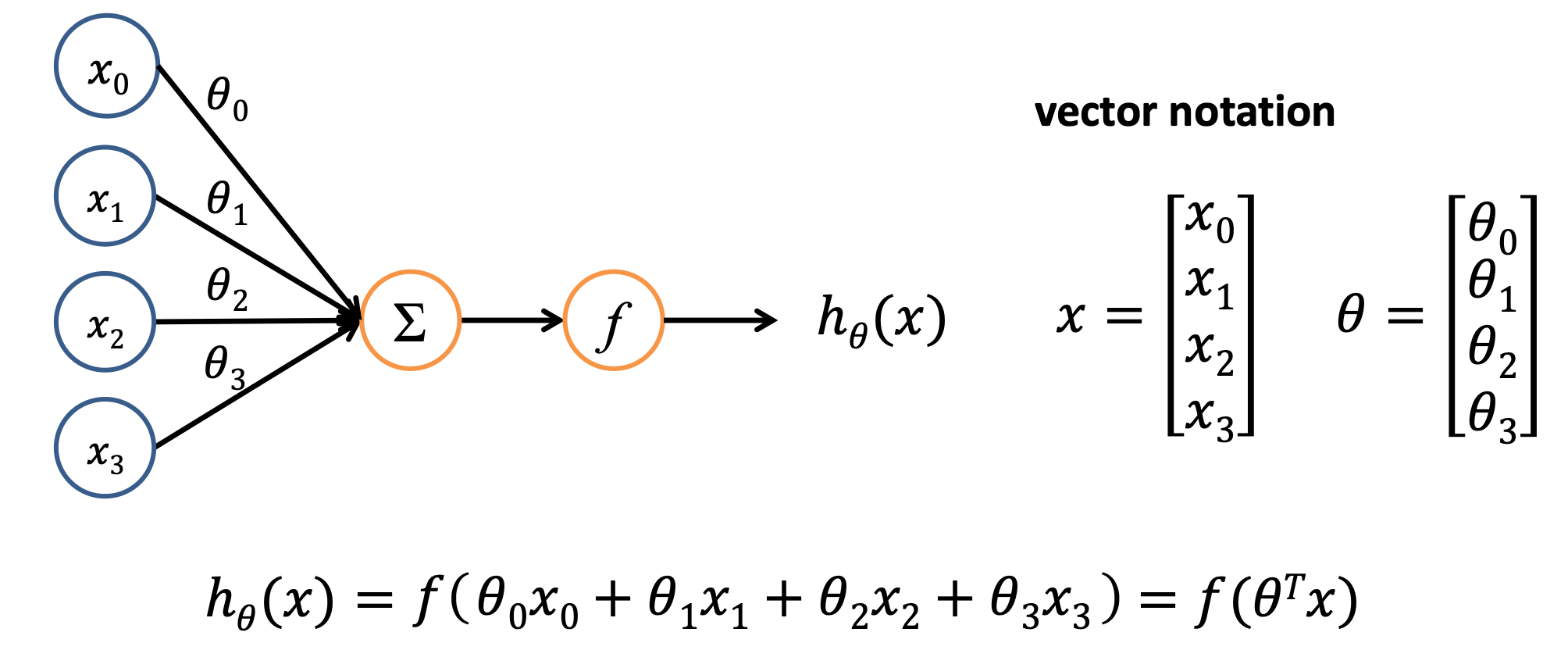
weights are assigned to the input ~ connection strength
Activation Function
데이터를 비선형으로 바꾸기 위해서 사용한다.
→ 비선형 시스템은 은닉층의 수가 많아져 연산 횟수가 줄어든다.
아무리 layer을 계속 추가시킨다 한들, activation function은 결국 같은 linear한 성격만 갖게 된다. 즉, 아무리 Hidden layer을 추가한들, Multi-layer Perceptron또한 linear한 문제만 풀수 밖에 없다.
f(x) = ax + b, h(x) = cx → y(x) = h(h(h(x))) = cccx = c^3x 결과론적으로는 1차 함수이다. 이런식.
-
Logistic(sigmoid) units
Artificial neurons that use the sigmoid (logistic) function as their activation function.
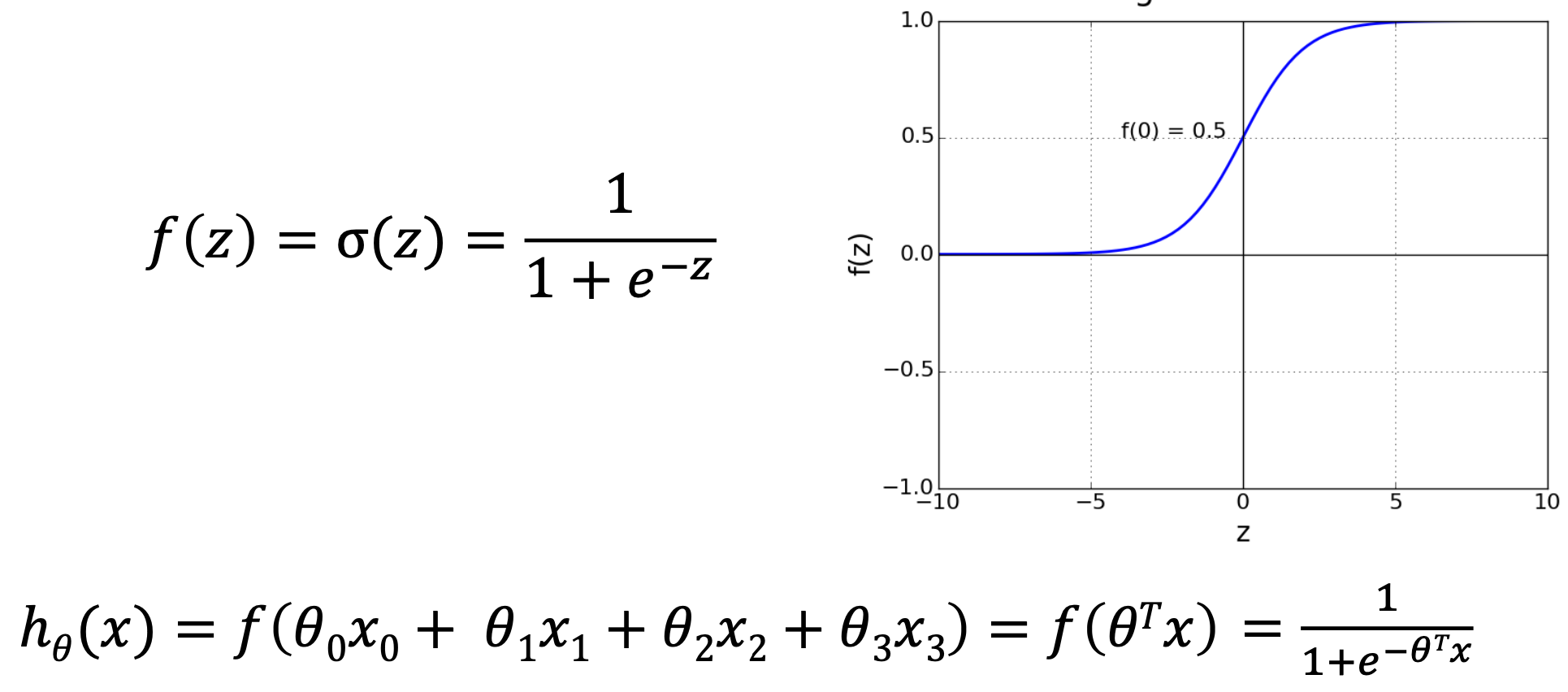
보통 분류 문제에서 많이 쓰임.
출력값이 0과 1 사이의 값일때 → 해당 class에 속할 확률로써 해석가능하다.
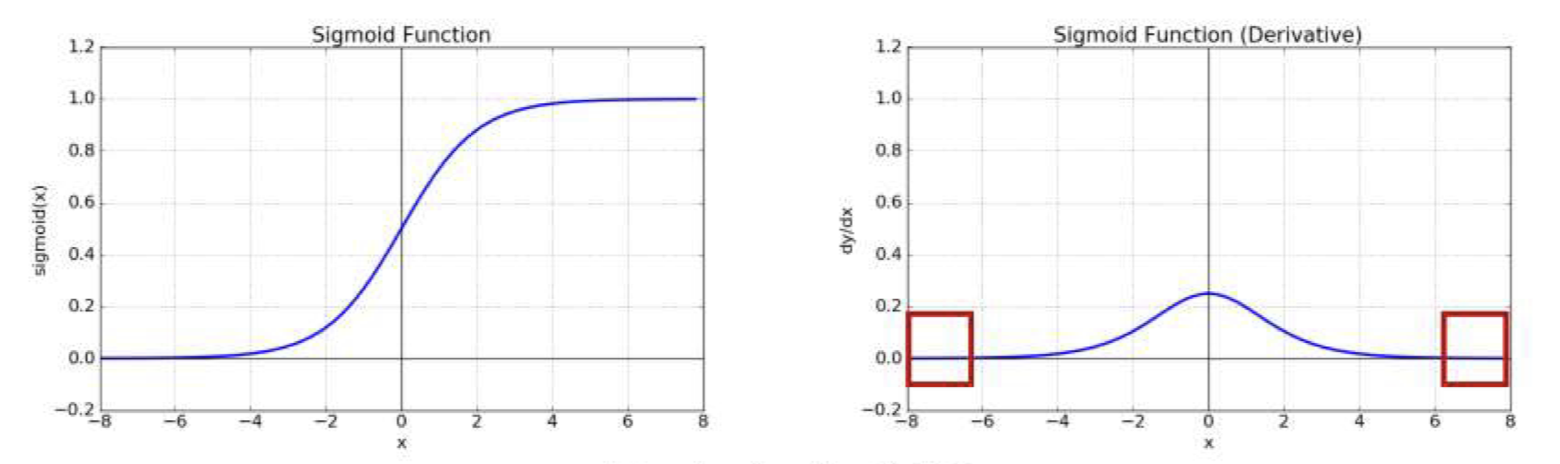
그러나 이런 sigmoid 함수는 Gradient Vanishing 문제가 있는데, 이는 Sigmoid 함수의 미분 함수는 |x|가 커질 수록 0에 수렴하는 형태이다. 따라서 역전파가 진행될수록, 기울기 값이 0에 수렴하게 되고, 가중치가 갱신되지 않는 문제점이 발생한다.
-
Tanh Units
artificial neurons that use the hyperbolic tangent function as their activation function
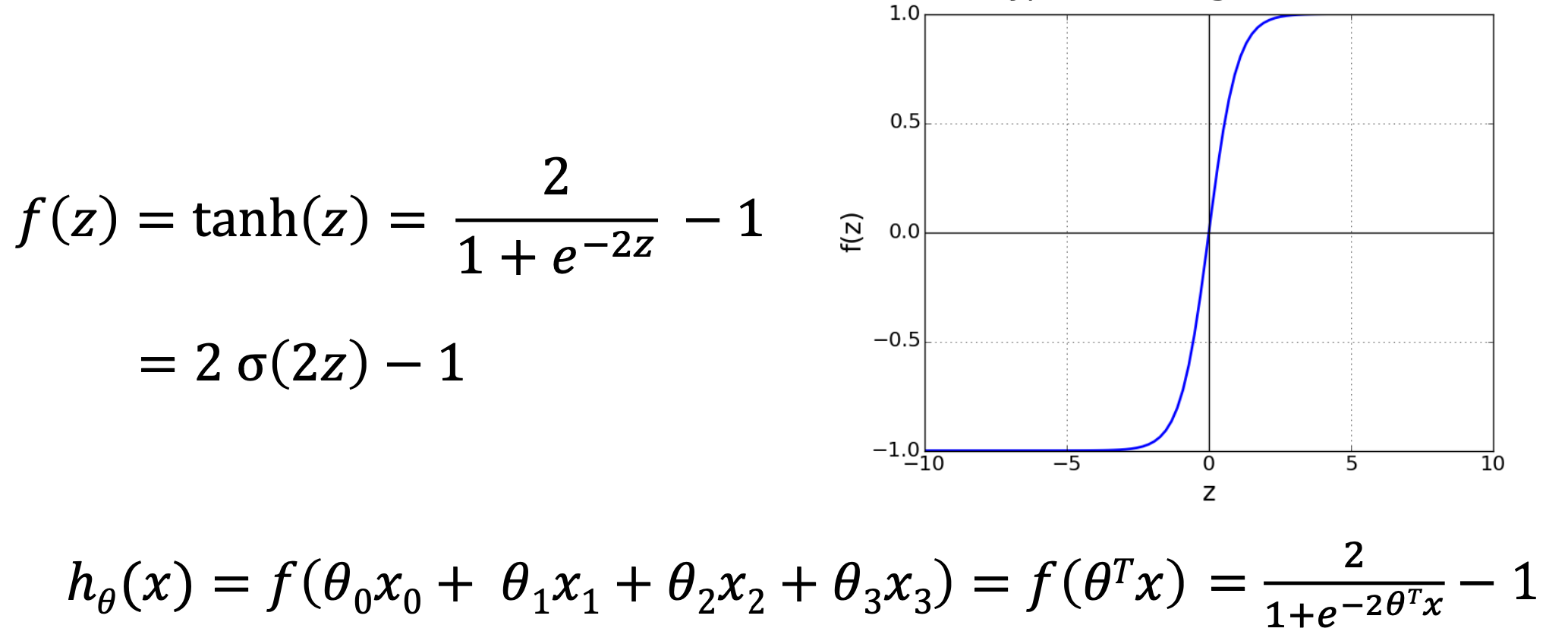
Summary: Hypotheses
- Linear regression(univariate) - 선형, Machine Learning
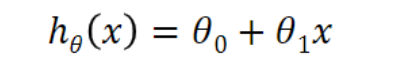
- Neural network(Logistic units) - Deep Learning
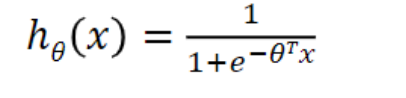
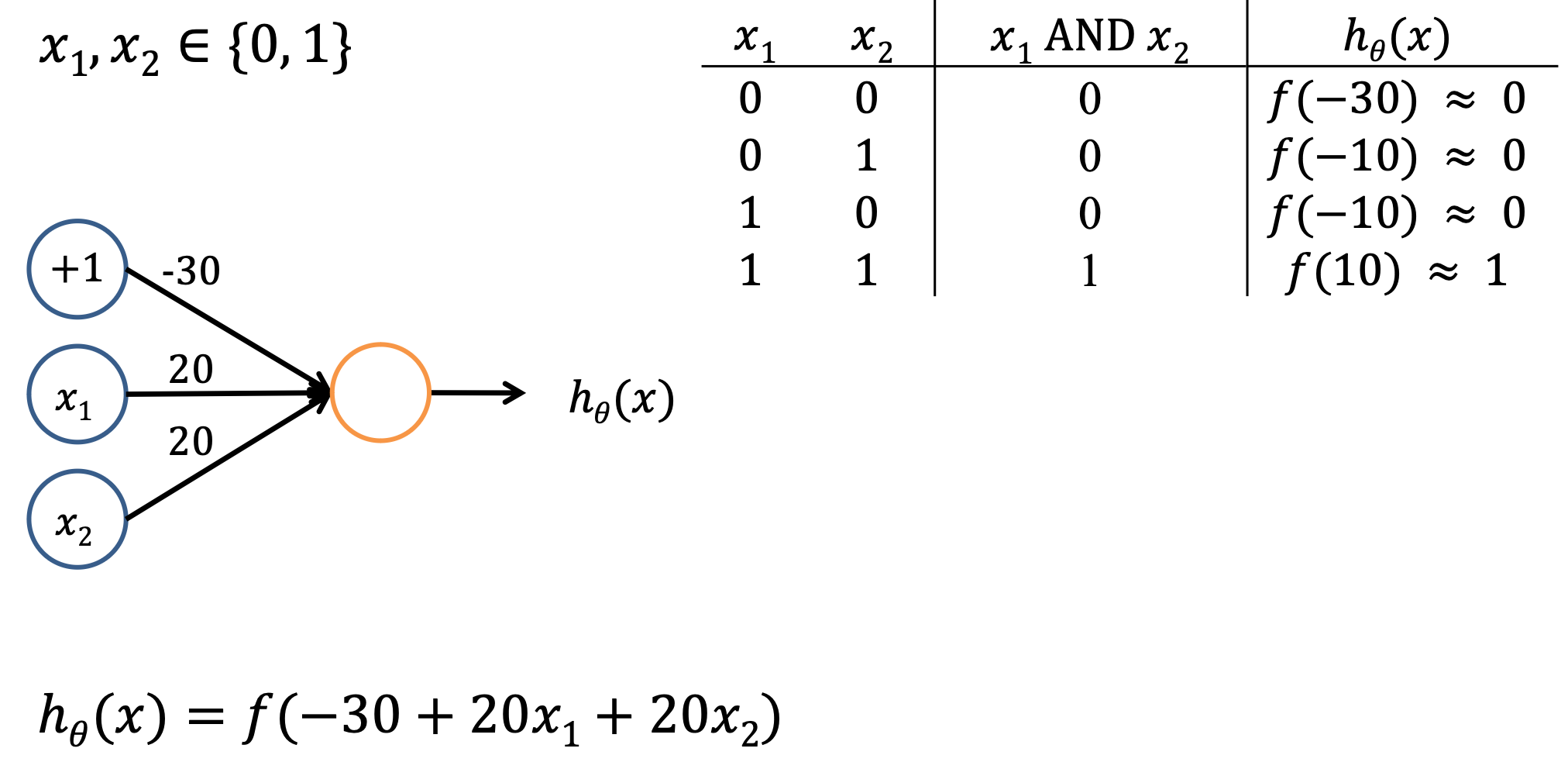
- Neural networks(tanh units) - Deep Learning
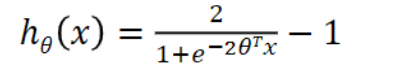
Functional Completeness and Universality
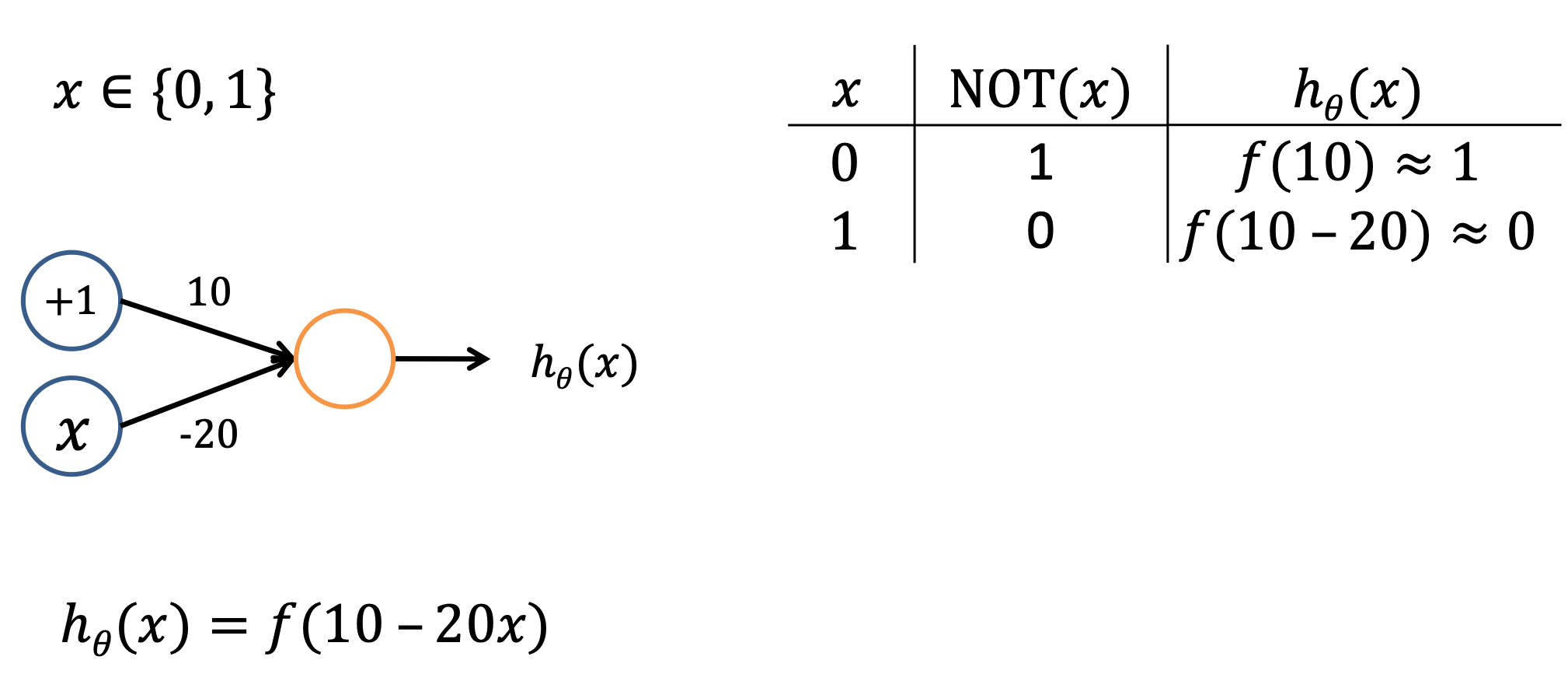
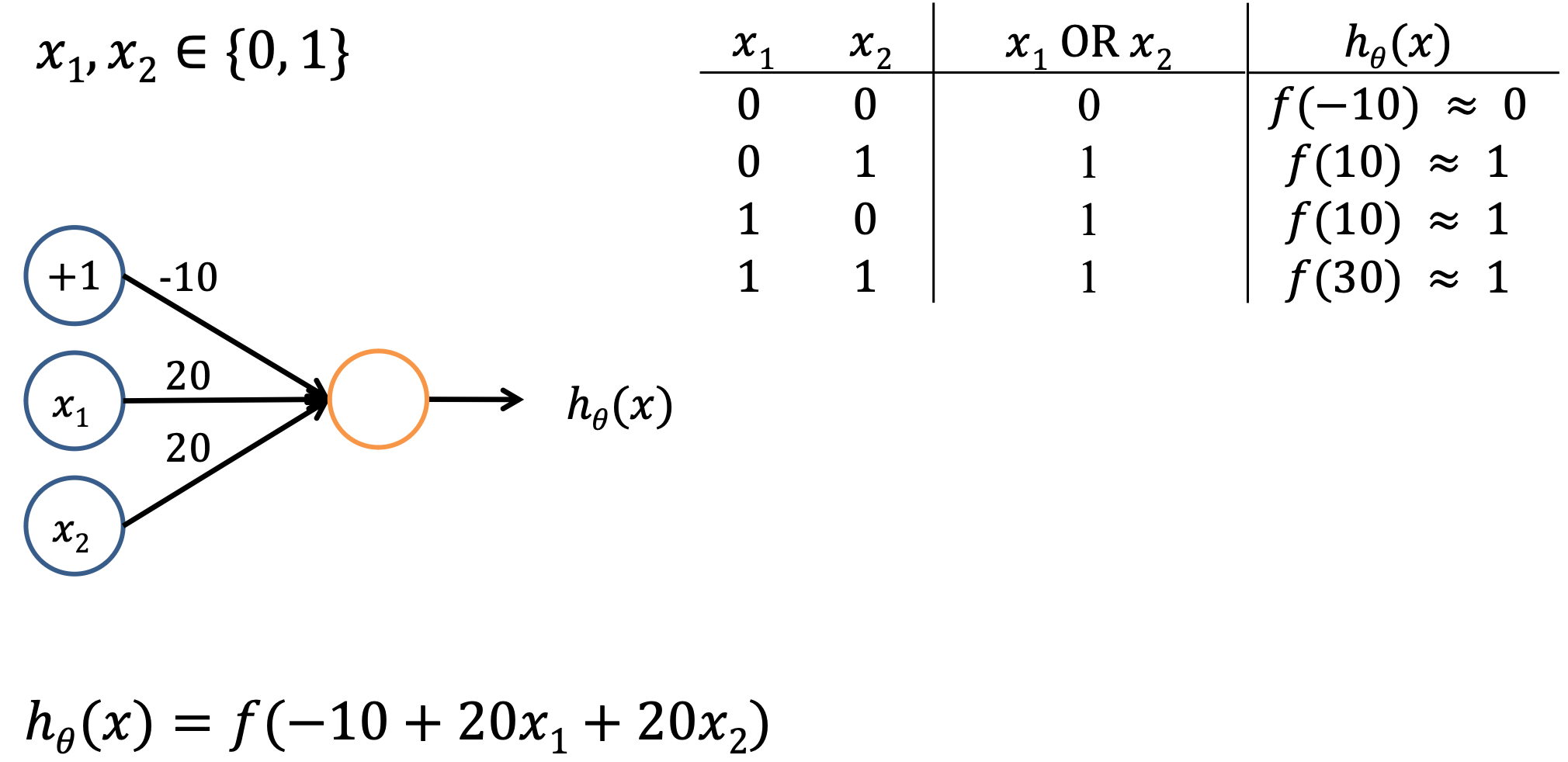
The support for the NOT and AND operator makes artificial neural networks functional complete
- Can be used to express all possible truth tables.
NOT과 AND는 논리연산자로서, 인공 신공망은 어떤 논리적 판단도 표현하고 계산할 수 있게 된다. 인공 신경망은 이러한 논리 연산자를 이용해 입력 데이터 사이의 복잡한 관계를 학습하고, 판별할 수 있게 되는 것.
Universal approximation theorem
artificial neural networks can be used to approximate any continuous function with an arbitrary precision
한 개 이상의 은닉층을 가진 인공 신경망이 임의의 연속 함수를 임의의 정밀도로 근사할 수 있다는 것을 의미한다. 어떤 연속적인 함수를 가지고 있다고 할 때, 그 함수가 어떠한 복잡한 형태를 가지고 있더라도 적절히 훈련된 인공 신경망을 이용하면 그 함수를 정확하게 근사할 수 있다는 것이다
임의의 개수 neuron을 포함하고, activation function이 sigmoid이면서, 1 Hidden layer을 가진 artificial neural networks는 적절한 Weight만 주어진다면, 어떤 함수들 근사화 할 수 있다.
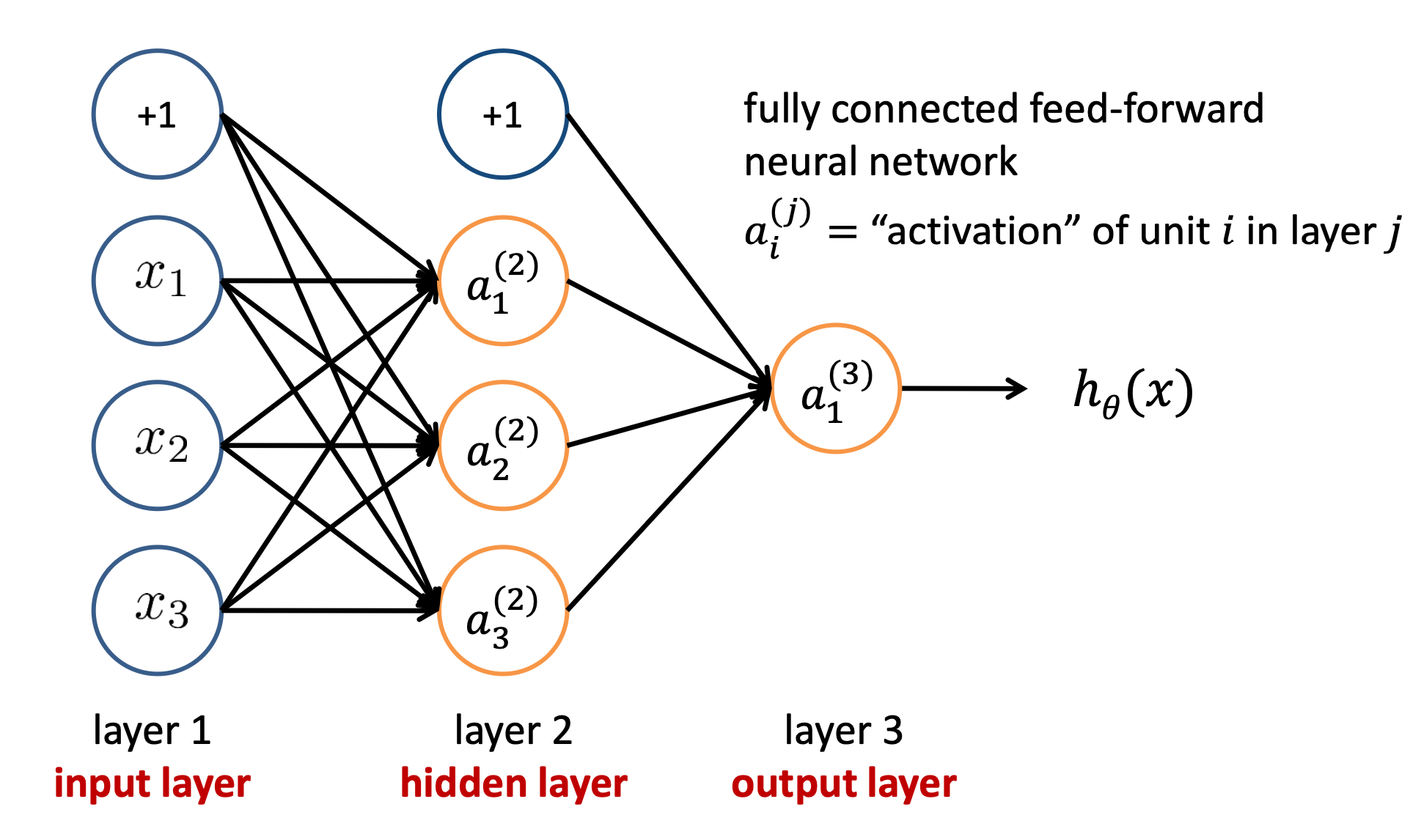
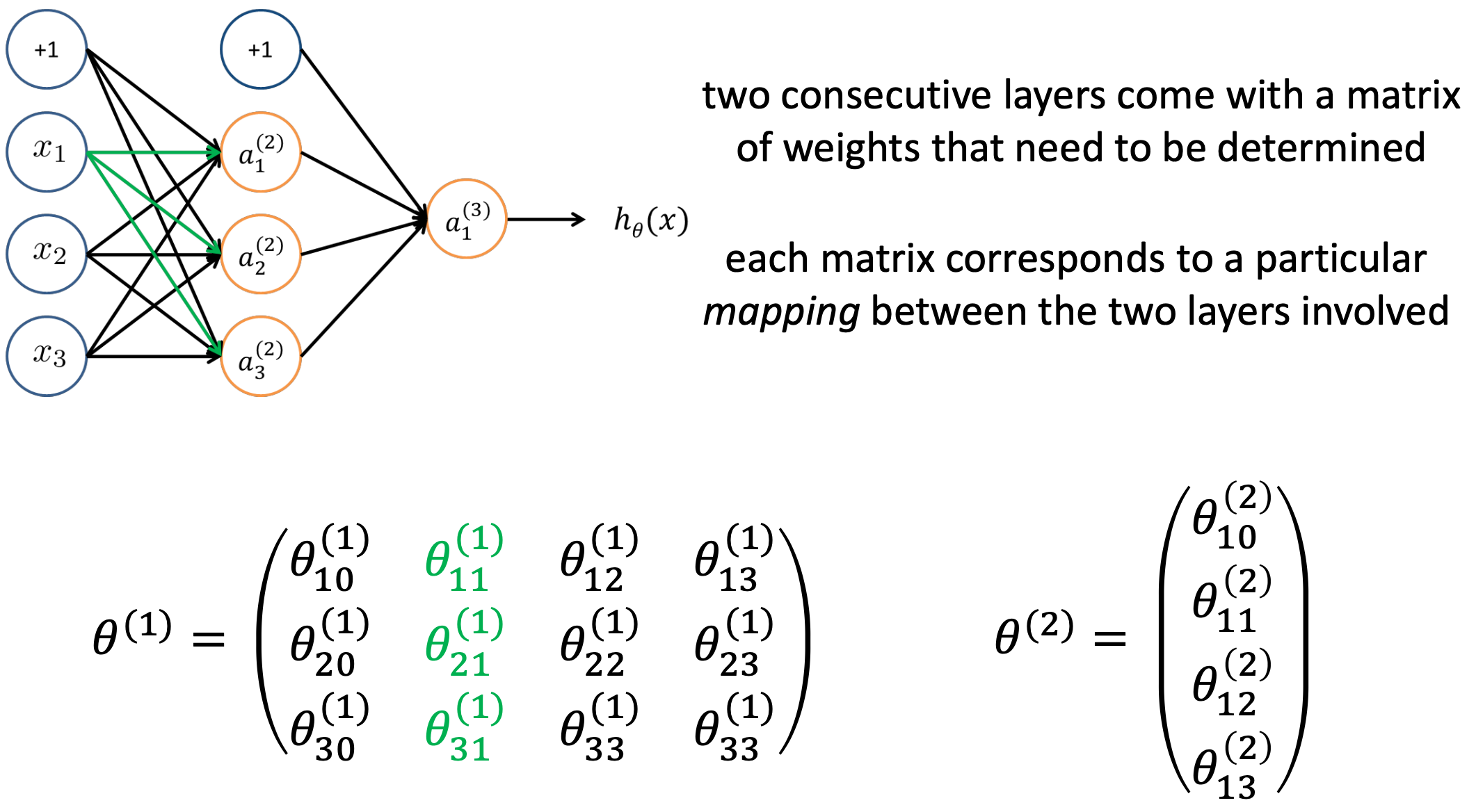
→ Matrix of weight between input layer and hidden layer
→ Matrix of weight between hidden layer and output layer

theyr are propagated through the computational graph
Automatic Computation of Weight
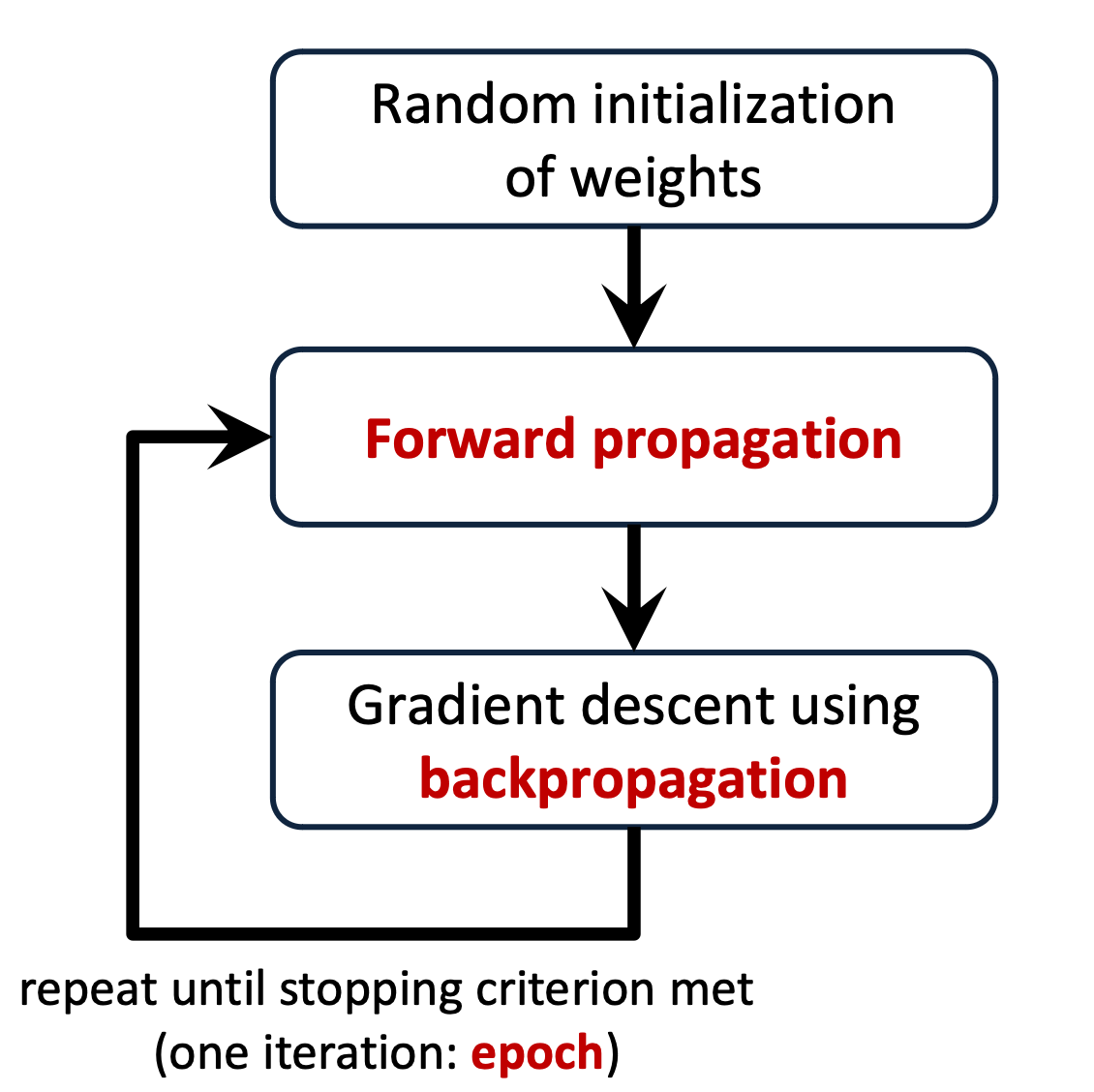
- compute overall prediction error for all training examples
- update weights so to minimize the overall prediction error
backpropagation: mathematical procedure to efficiently compute the many partial derivatives of the cost function.
Integration of artificial neural network
- Pick a network architecture (neuron connectivity pattern)
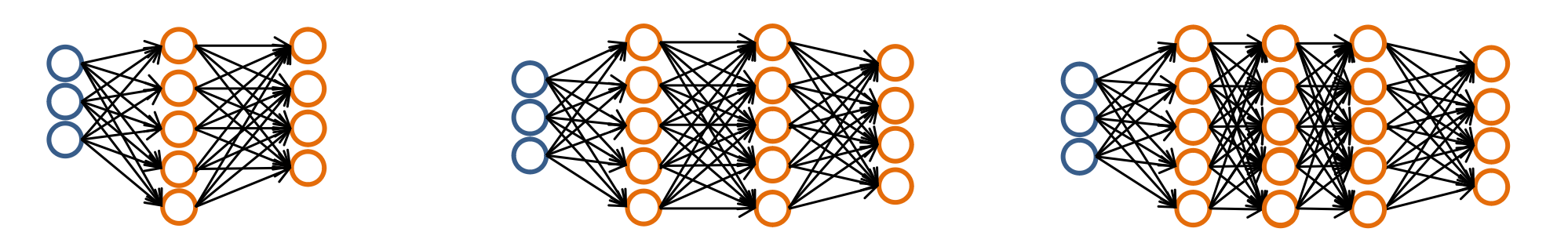
- input layer 개수: dimension of input
- output layer 개수: number of class
- Hidden layer 개수: when using more than one hidden layer, then have the same number of hidden units in every layer
- Train the neural network
- 뉴럴 네트워크를 training을 하여 hypothesis(trend line)을 만들기
- construct a data set of labeled examples
- perform random initialization of weights
- execute forward propagation and gradient descent using backpropagation in an iterative manner.
- Validate the neural network
- apply forward propagation to labeled examples not used during training, in order to check for overfitting.
(Training에 쓰지 않는 labeled example을 Forward propagation시키기)
- Test the neural network
- Apply forward propagation to unseen test examples.
Gradient Descent 종류
-
Batch Gradient Descent
weights are updated after having seen the whole training set
→ 시간이 너무 걸림 -
Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
weights are updated after having seen a single training example
→ 비교적 빠름 -
Mini-batch Stochastic Gradient Descent
weights are updated after having seen multiple training examples -
Downpour Stochastic Gradient Descent
large-scale distributed training (cluster)
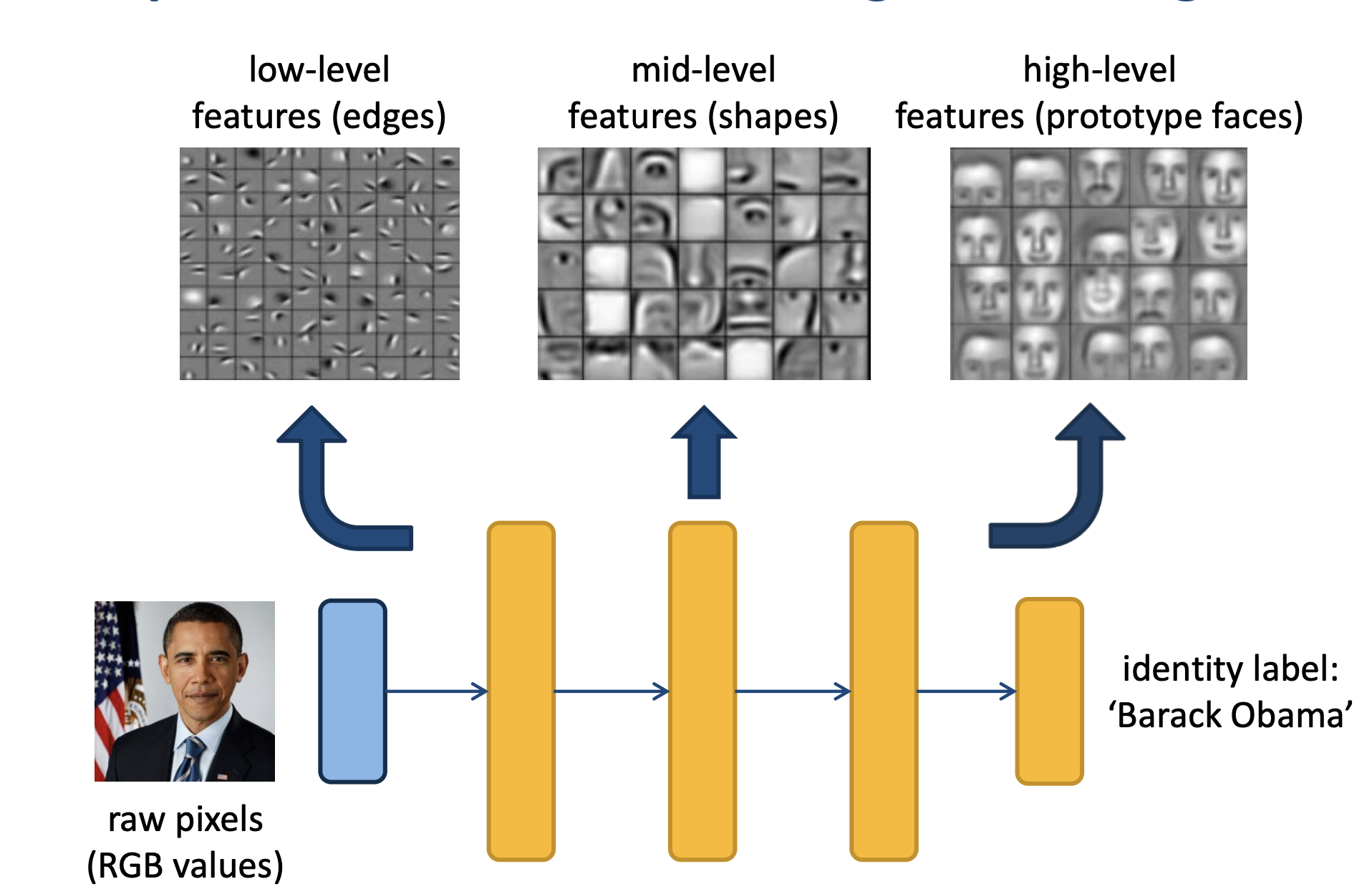
Deep Learning
Automatic Feature Learning → Automatically learn features from labeled (raw) input data in hidden layer. Typically through the use of multi-layered artificial neural network.
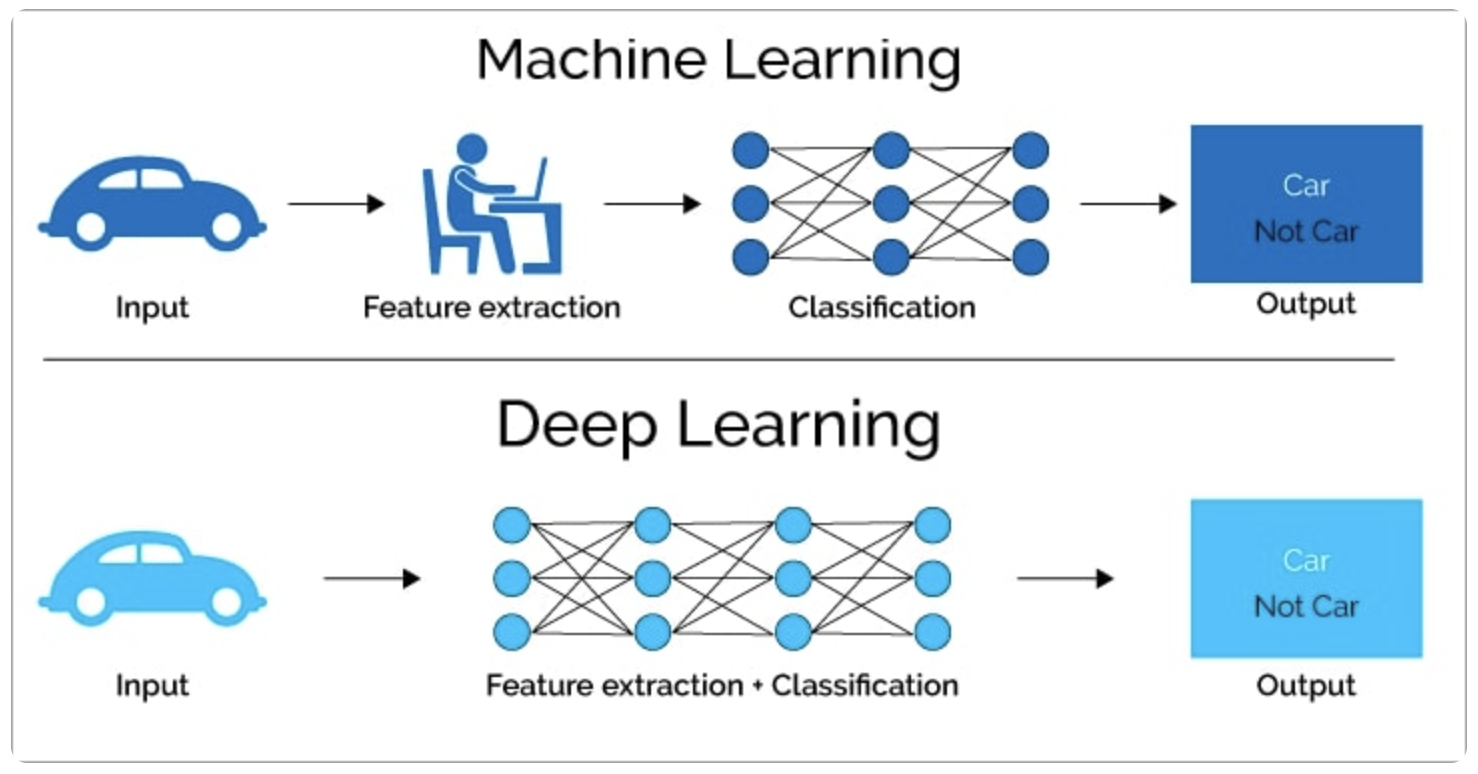
- Traditional (Shallow) machine learning
- Deep machine learning
Feature을 정해주는지(manually), 스스로 찾아주는지(automatically)에 따라 구분됨.
Why deep learning suddenly become popular?
- Availability of cheap and massive computational power.
→ Law of Moore (GPU computing & cloud computing)
- Availability of large data sets
- social media applications
- sensor networks (Internet of Things)
- next-generation sequencing (NGS)
- single-cell analysis
New techniques
-
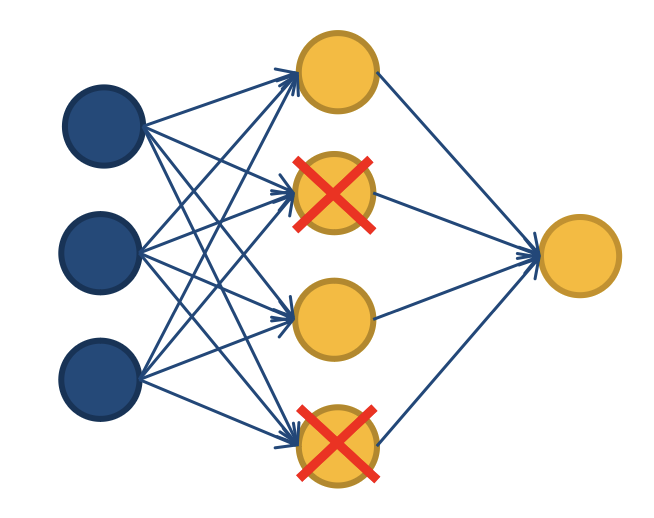
Dropout
overfitting을 완화하기 위해 쓰임
Neurons are randomly disabled during training, preventing the learning of features that are too complicated.
-
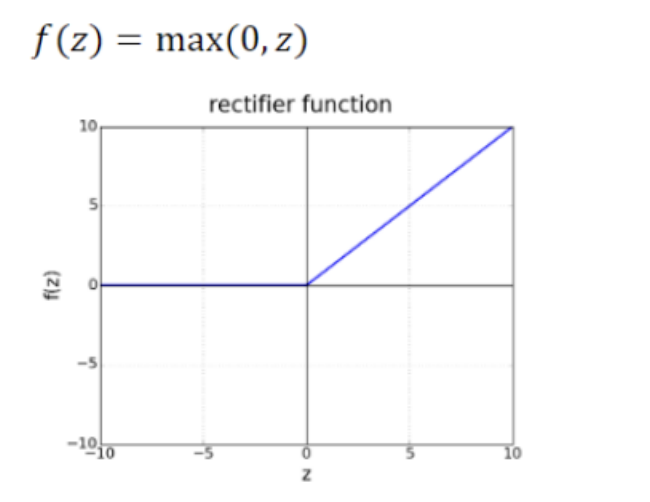
Rectified linear unit(ReLUs)
-
Exponential linear units(ELUs)
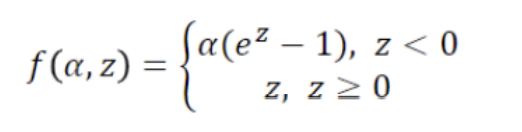
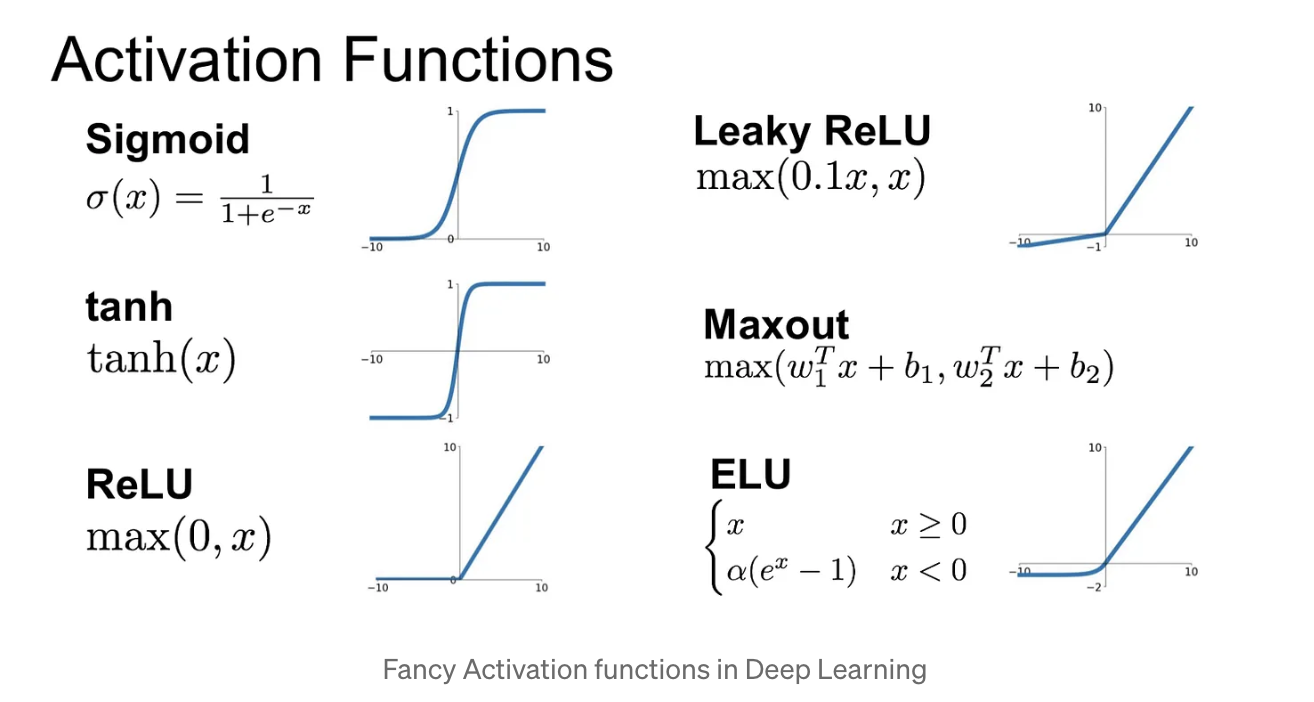
Conclustion and critical remarks
-
Deep learning is well suited for predictive analysis
- state-of-the-art(최첨단) prediction performance.
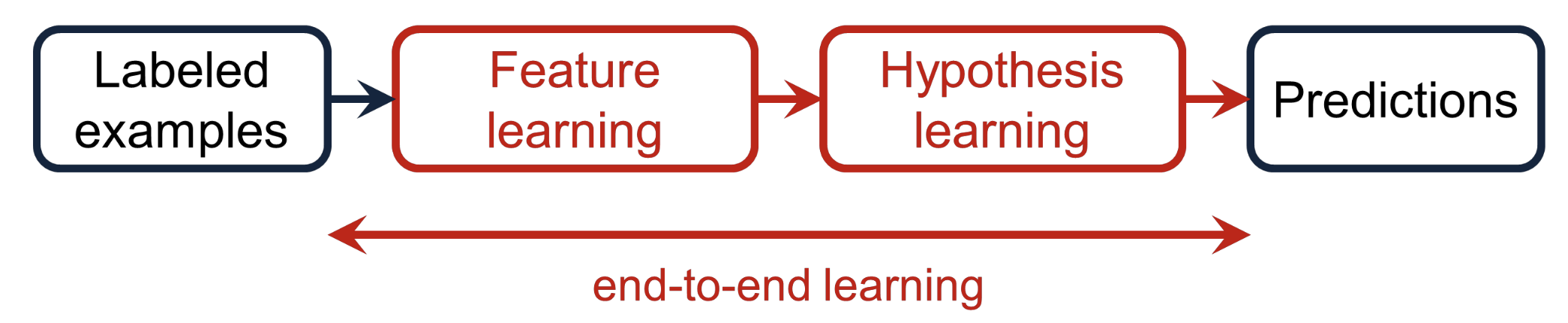
- end-to-end learning → feature extraction & hypothesis learning
-
Data intensive
- rule of thumb: 8,000 to 10,000 labeled exmples per class
-
Design is an art
- NO hard and fast ruls available on how to create and train effective neural networks.
-
Adversial examples
- Malicious inputs can force networks to make wrong predictions.
-
Black-box predictive models
-
limited knowledge available about internal workings
-
makes debugging neural networks very challenging
→ difficult to understand why neural network can come to certain decisions
-