⏱️ Clock
A faster clock allows CPU to complete instruction cycles more quickly. However, higher speeds generate more heat, which can lead to thermal issues.
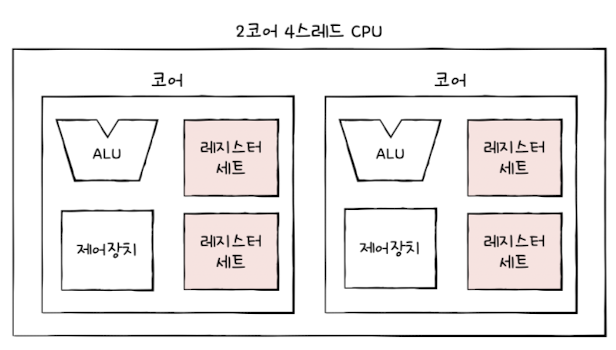
🧠 Multi-Core and Multi-Threaded Processors
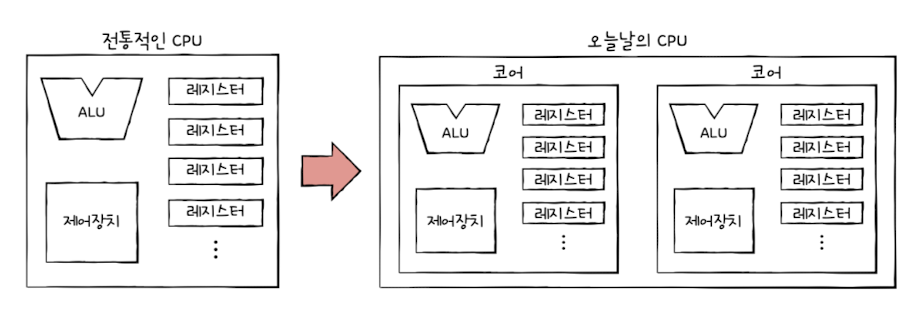
🧩 Traditional vs Modern CPU Definitions
Traditional CPU: A unit that executes one instruction at a time
Modern CPU: A chip that contains multiple cores, each capable of executing instructions
✅ Core = an independent execution unit (includes its own ALU, registers, etc.)
🧵 Multicore Processors = Multicore CPUs
- Multiple cores allow a computer to execute multiple instructions in parallel
- Great for performance, but software must distribute tasks efficiently across cores
🧶 Thread vs Multithreading
There are two types of threads:
👉 ⚠️ “At the same time” means the CPU rapidly switches between threads. This creates the illusion of parallelism, allowing smooth multitasking even on limited hardware.
1️⃣ Hardware Thread
Also known as hyper-threading or logical processor
🧠 One core has multiple register sets and scheduling logic,
allowing it to handle more than one instruction "at the same time"
Q. why logical processor?
A. From the process perspective, it feels like multiple CPUs
2️⃣ Software Thread
A program is divided into multiple software threads - lieghtweight sequences of execution(= series of instructions)
Multithreading is a technique that separates a process into multiple independent tasks (called threads), which can run concurrently — allowing for more efficient and parallel-like execution
Even single-core CPU, you can run many software threads concurrently
➡️ But this is not true parallelism
🚀 Instruction-Level Parallelism (ILP): Reducing CPU Idle Time
In-order:Instructions are executed in order.
1️⃣ Pipelining: it allows multiple instructions to be in progress simultaneously, each at a different stage (fetch, decode, execute, etc.)
2️⃣ Superscalar: Enables multiple pipelines, so two or more independent instructions can be executed in the same clock cycle, as long as they use different functional units (e.g., ALU vs memory access)
🧠 ISA (Instruction Set Architecture)
: ISA defines how a CPU is designed and how it executes machine-level instructions.
Different instruction sets also define how control unit decode instructions, the number of registers, Memory access and management behavior.
🔀 Types of ISA
1️⃣ CISC(Complex Instruction Set Computer)
- Instructions have variable lengths and can perform complex tasks.
- Resulting binaries are compact, reducing program size.
However, each instruction may take a different number of cycles, making pipelining harder to implement.
2️⃣ RISC(Reduced Instruction Set Computer)
- Designed for pipelining efficiency.
- Instructions have fixed length and uniform execution time.
- Frequently used operations are kept simple and fast.