Machine Learning by professor Andrew Ng in Coursera
1) Principal Component Analysis Problem Formulation
PCA problem formulation
인 data
이 데이터를 로 바꾸려고 한다.
이때 각 데이터들을 할 직선이 필요하다.
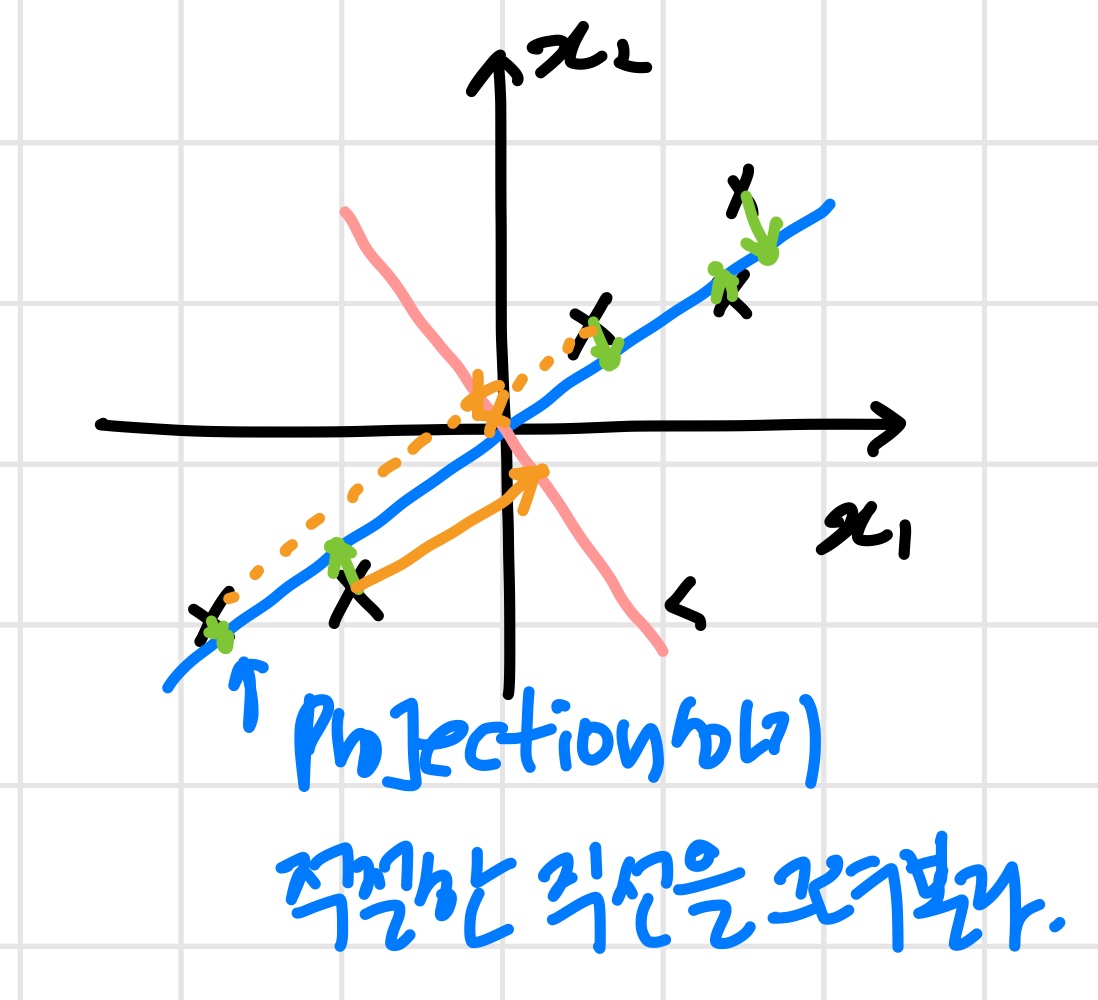
위의 그림과 같이 직선, 직선을 그렸다.
이때 PCA가 하는 일 :
원래 데이터와 projection 된 점들의 거리제곱을 최소화하는 직선
()을 찾는다.
minimize projection error
직선에 projection하면 projection error가 직선과 비교했을 때 값이 매우 커진다.
따라서 직선이 더 적절하다.
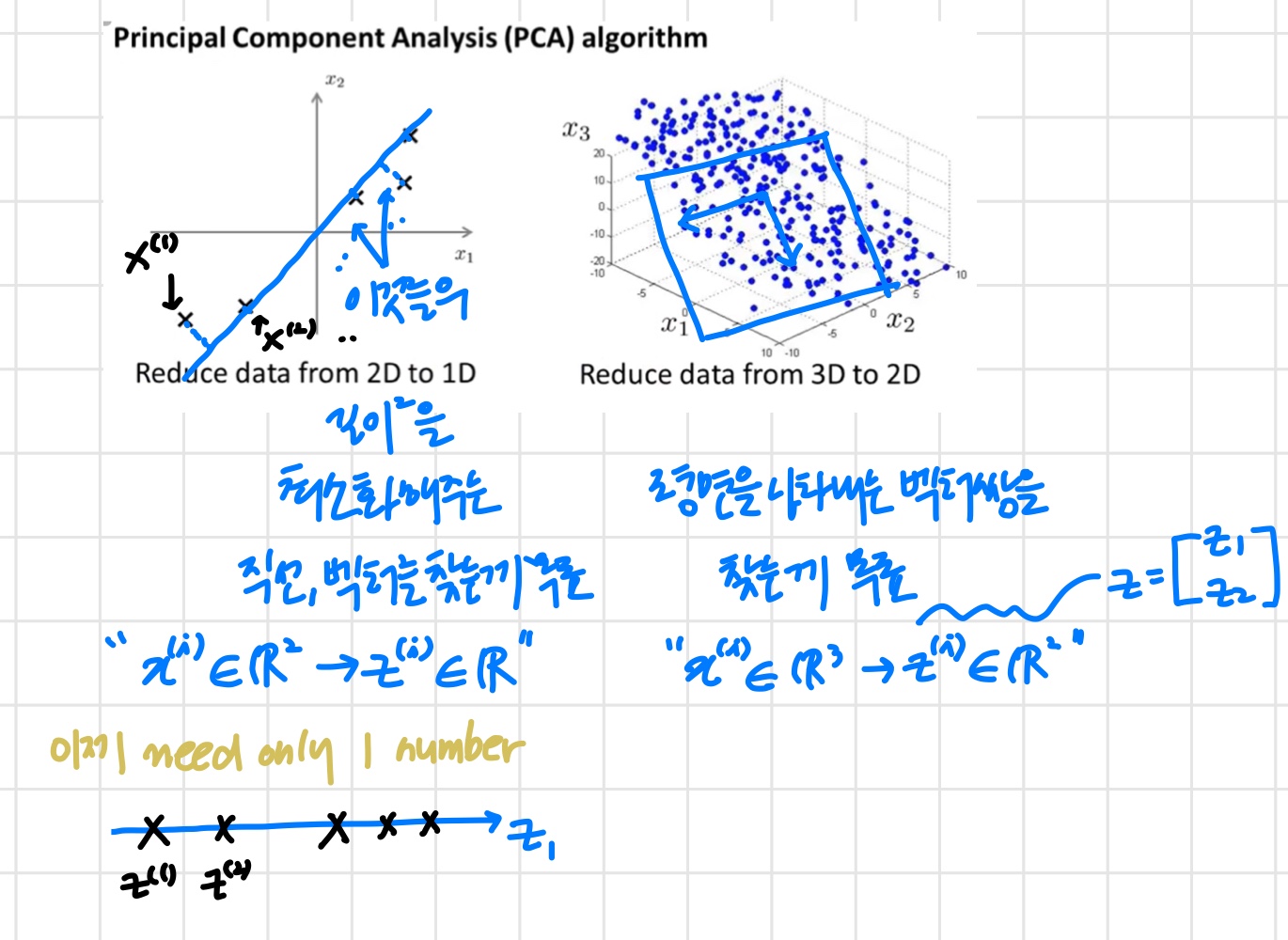
데이터를 데이터로 바꾸려고 한다면?
우선 벡터 한 쌍을 찾는다. ( '평면 만들기위해' )
두 벡터로 이루어진 평면에 데이터들을 projection한다.
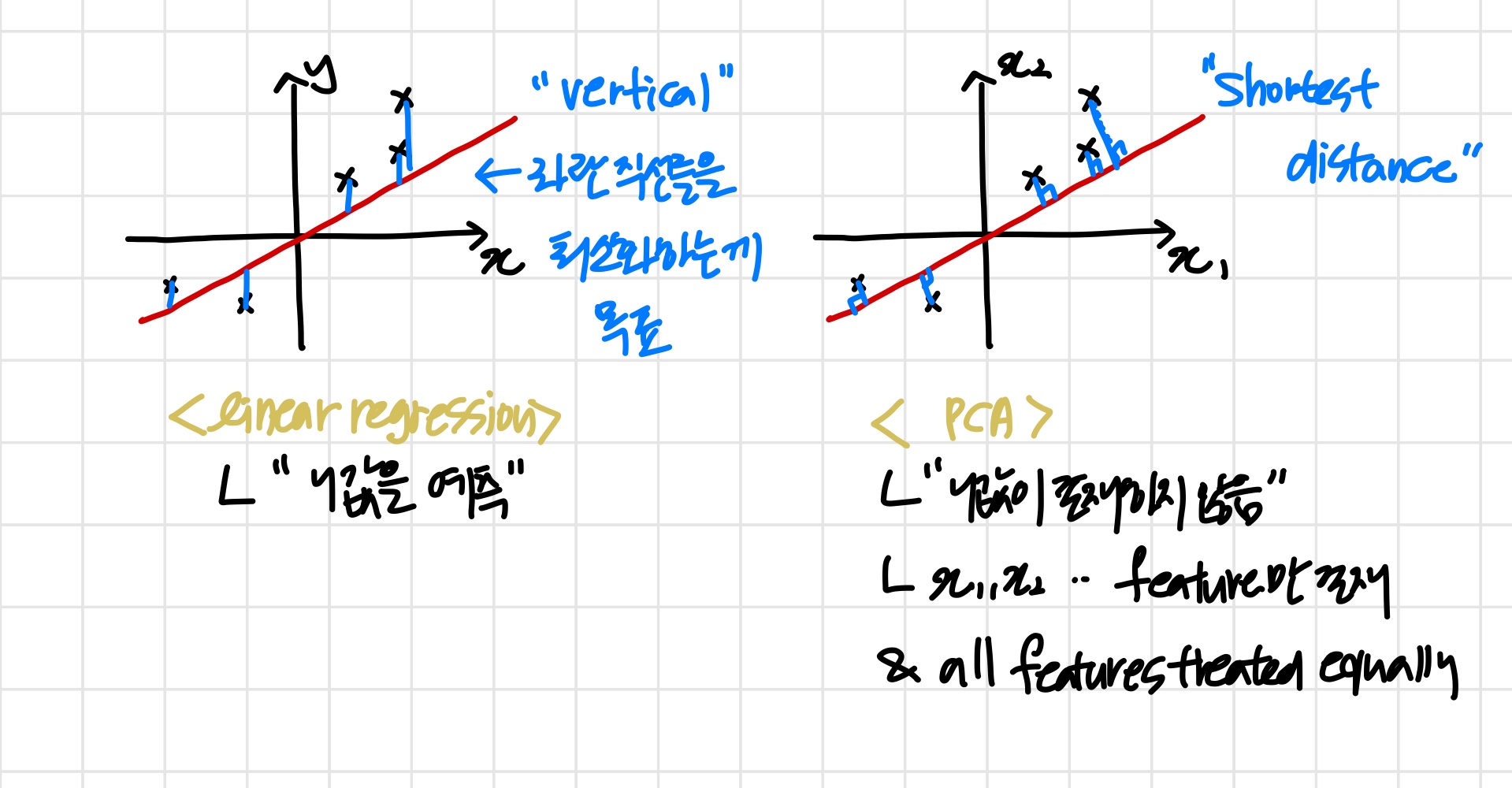
이때 pca의 과정이 linear regression과 비슷해 보일 수 있다.
하지만 둘은 전혀 다르다 .
PCA is not linear regression
2) Principal Component Analysis Algorithm
Data preprocessing
PCA를 하기 전 아래의 data pre-processing 단계를 반드시 거쳐야 한다.
Training set :
' unlabeled example'
Preprocessing (feature scaling/mean normalization):
'mean normalization 중요 ! + 데이터에 따라 feature scaling도 하거나 안 하거나'
Replace each with
'를 통해 feature들의 평균은 0이 된다.'
If different features on different scales(e.g., = size of house, = number of bedrooms), scale features to have comparable range of values.
PCA algorithm
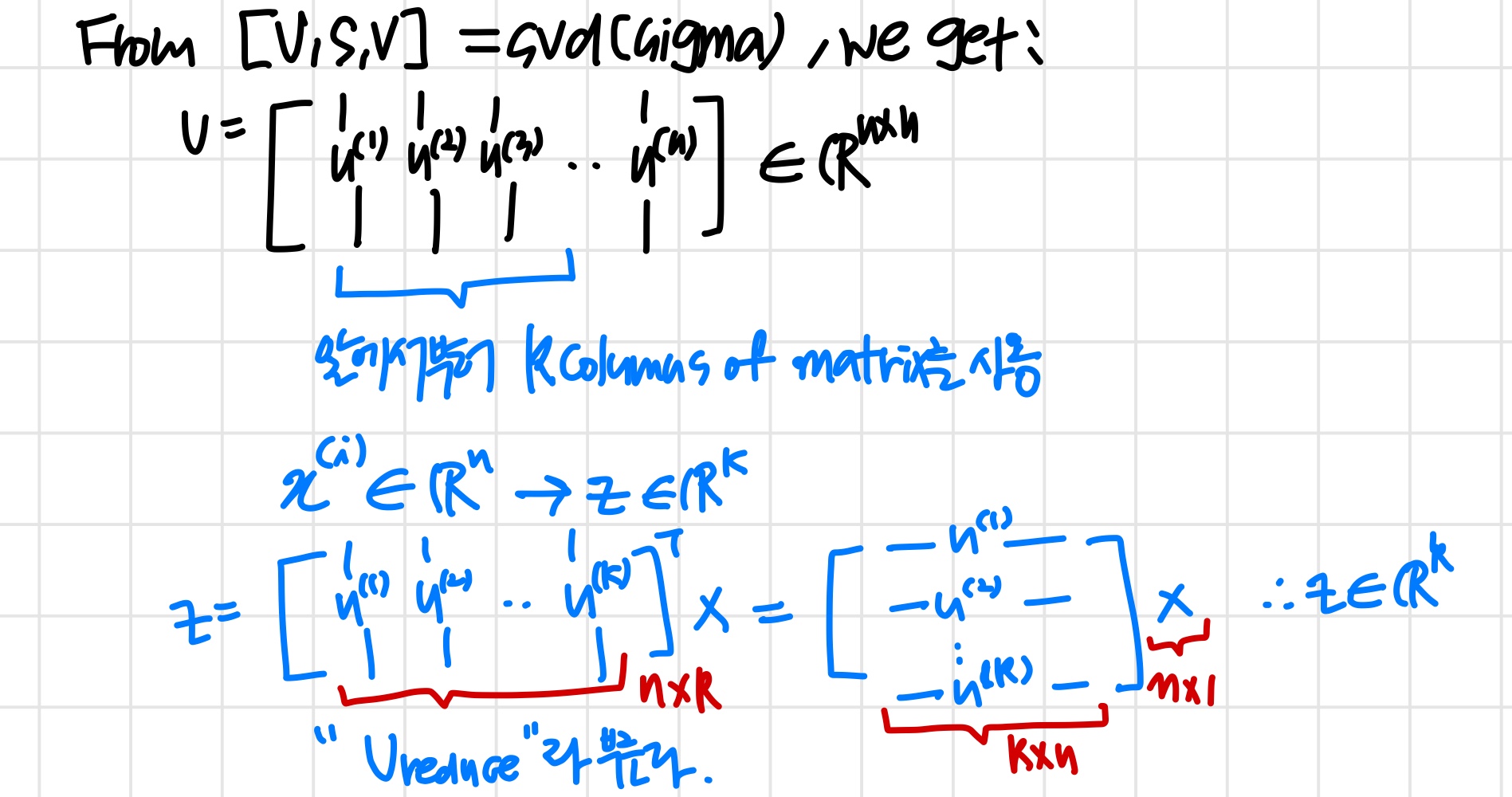
Reduce data from n-dimensional to k-dimensional
우선 "covariance matrix" 계산 :
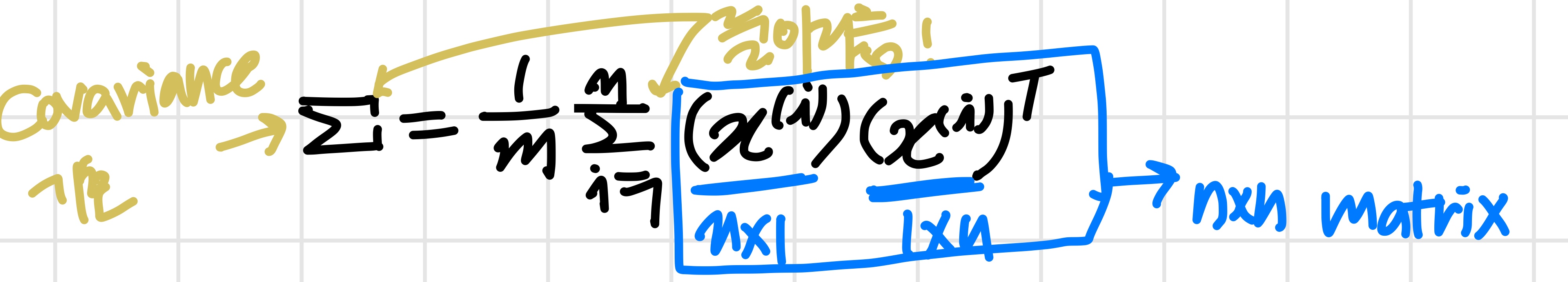
"eigenvectors" of covariance matrix 계산 :
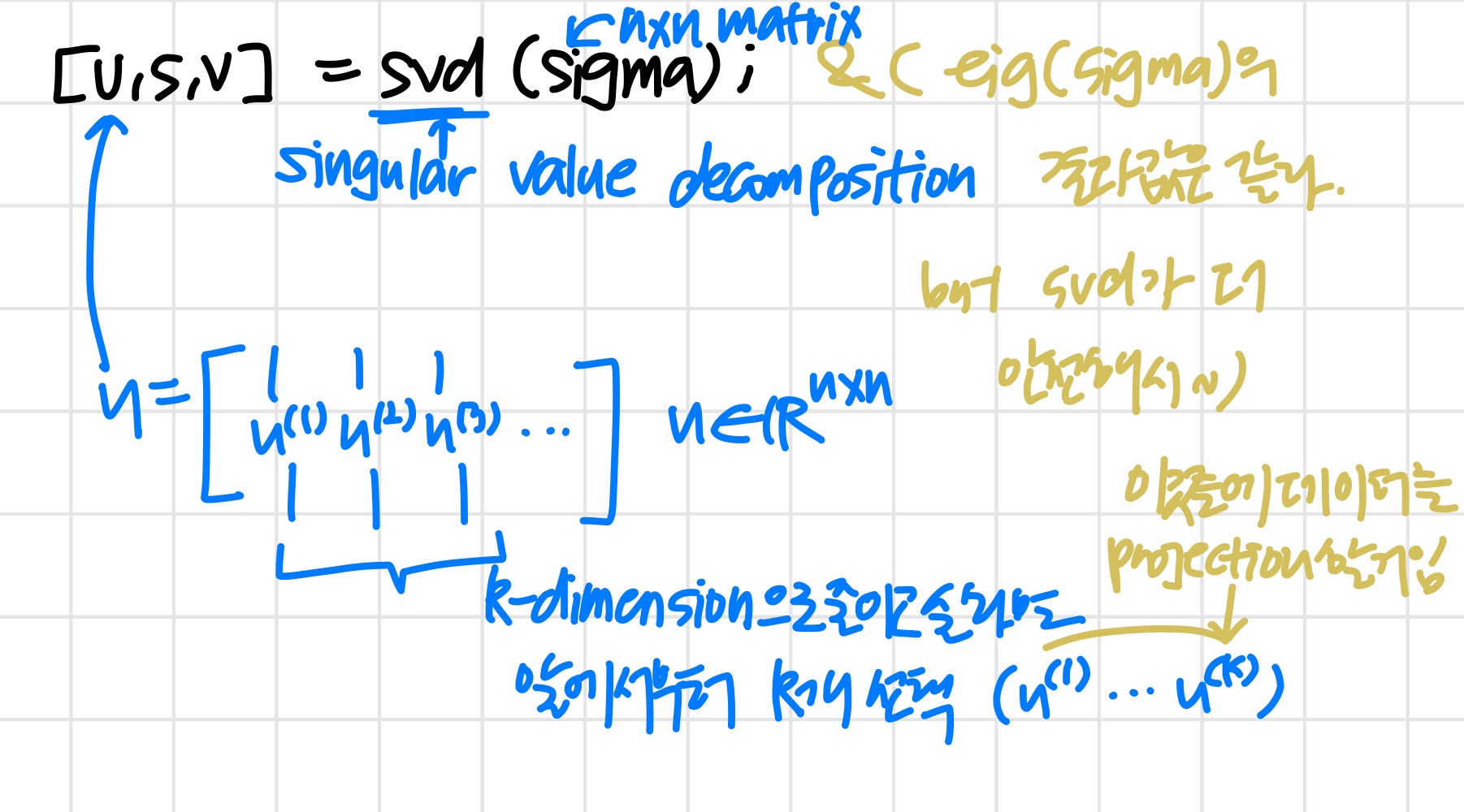
'svd & eig는 서로 다른 함수다. 그런데 covariance matrix에 적용하면 같은 결과를 얻게 된다.'
PCA algorithm summary
After mean normalization(ensure every feature has zero mean) and optionally feature scaling:
Sigma =
[U, S, V] = svd(Sigma)
=
z = ' * x (이때 )
