조건 제어문
PL/SQL
IF 조건문 THEN
창일때 수행하는 로직
END IF;IF 조건문 TEHN
참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSE
거짓일때 수행하는 로직
END IF;IF 조건문1 THEN
조건문1이 참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSIF 조건문2 THEN
조건문2이 참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSIF 조건문3 THEN
조건문3이 참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSE
거짓일때 수행하는 로직
END IF;PYTHON 조건문
- IF 조건절
IF 조건문:
참일때 수행하는 로직- IF ELSE 조건절
IF 조건문:
참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSE:
거짓일때 수행하는 로직- IF ELIF ELSE 조건절
IF 조건문 1:
조건문1이 참일때 수행하는 로직
ELIF 조건문2:
조건문2이 참일때 수행하는 로직
ELSE:
거짓일때 수행하는 로직예)
if {}:
print('참')
else:
print('거짓')
x = 8
if x>10 or x%2 == 0:
print('참')
else:
print('거짓')
num = 95
if 90 <= num <= 100:
grade = 'A'
elif 80 <= num < 90:
grade = 'B'
elif 70 <= num < 80:
grade = 'C'
else:
grade = 'F'
print('점수 : {0} 학점 : {1}'.format(num,grade))
print('점수 : %s 학점 : %s'%(num,grade))
print(f'점수 : {num} 학점 : {grade}')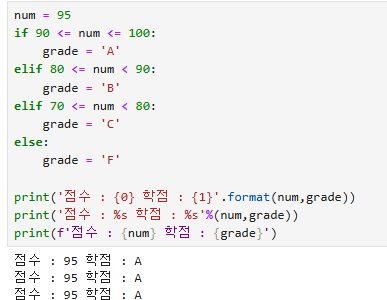
sal = 1000
comm = None #null
sal * 12 + comm
-- 이렇게 하면 오류가 발생한다.
if comm == None:
annnual_salary = sal * 12
else:
annnual_salary = sal * 12 + comm
print(annual_salary)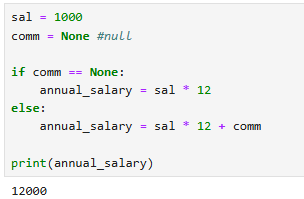
한줄 if 조건문
참값 if 조건문 else 거짓
sal = 1000
comm = None
annual_salary = sal * 12 if comm is None else sal * 12 + comm
print(annual_salary)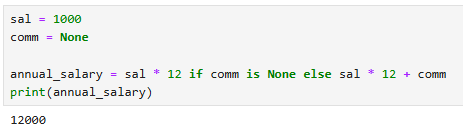
반복문
while 문
- 조건이 True인 동안에 반복을 수행한다.
while 조건문:
반복 수행할 문장i = 1
while i <= 10:
print(i)
i += 1 # i = i + 1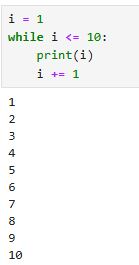
break
- 반복분을 중단하는 문
i = 0
hap = 0
while i <= 100:
i += 3
if i >= 100:
break # 반복분을 중단하는 문
else:
print(i)
hap += i
print(hap)continue
- 다음 반복문을 수행하는 문
i = 1
while i <= 10:
if == 4 or i ==8
i += 1
continue
else:
print(i)
i += 1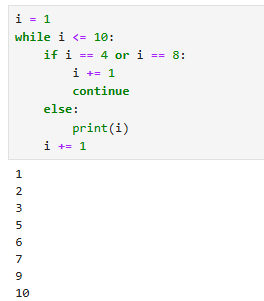
구구단
dan = 2
while dan <= 9:
i = 1
while i <= 9:
print(f'{dan} * {i} = {dan * i}')
i += 1
dan += 1for문
- 리스트, 튜플, 집합, 딕셔너리, 문자열의 첫번째 값부터 마지막 값까지 순서대로 변수에 입력해서 반복 수행한다.
for 변수 in (리스트,튜플,집합,딕셔너리,문자열):
반복수행할 문장- 리스트
x = ['oracle','ibm','ms']
for i in x:
print(i.upper())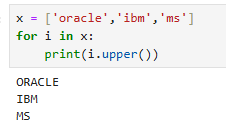
- 튜플
x = [(1,2),(3,4),(5,6)]
for i in x:
print(i)
for i,j in x:
print(i)
print(j)
range
- 연속된 정수 시퀀스를 생성하여 반복문 등에서 순회(iteration)할 수 있도록 해주는 함수
- range(시작,끝(미만),증가분)
for i in range(1,101):
print(i)for i in range(1,11):
if i == 4 or i == 8:
continue
else:
print(i) 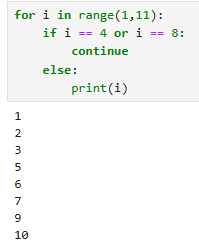
- for문을 이용한 구구단
for dan in range(2,10):
for i in range(1,10):
print(f'{dan} * {i} = {dan*i}')pandas
- 데이터 분석 기능을 제공하는 라이브러리
- 1차원 배열 : Series
- 2차원 배열 : DataFrame
from pandas import Series,DataFrameimport pandas as pd
Series
- 1차원 배열
- 인덱스(색인) 배열의 데이터에 연관된 이름을 가지고 있다.
- 단일 데이터 타입만 가능하다.
lst = [1,2,3,4,5]
type(lst)
lst + 100
-- 오류발생한다.--해결방법
new_lst = []
for i in lst:
new_lst.append(i+100)- list 내장 객체
new_lst = [i + 100 for i in lst]- Series 활용
import pandas
from pandas import Series,DataFrame
x = Series([1,2,3,4,5])
print(x)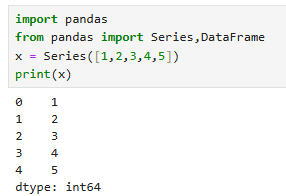
x + 100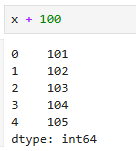
- Series 자료형 확인
x.astype 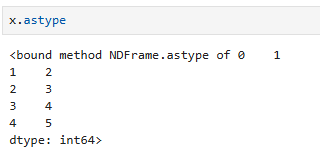
- 시리즈는 문자와 숫자가 같이 있으면 문자형으로 나온다.
dtype : object = 문자타입
x1 = Series(['1',2,3,4,5])
print(x1)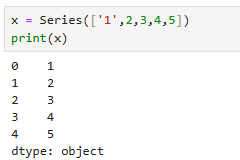
x1 + 100 # 문자타입은 연산작업할 수 없다. 오류발생Series 타입 변경
astype('변경타입')
x1 = x1.astype('int64')
print(x1)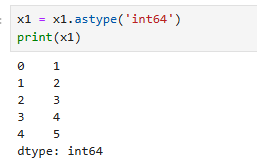
x1 + 100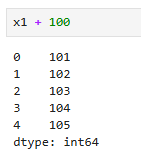
index 정보
x1.index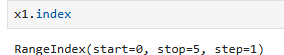
values 정보
x1.values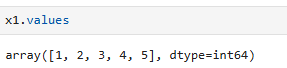
Seires indexing
print(x1[0])
print(x1[1])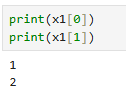
Series slicing
x1[0:3] #[시작인덱스 : 끝인덱스 -1]
- 조건
x1 >= 3
x1[x1 >= 3]
-
Series 값 수정
x1[0] = 100
x1 -
Series 값 추가
x1[5] = 500 -
Series 값 삭제
del x1[5]
x1
DataFrame
- 2차원배열(행과 열로 구성)
- 표형식(테이블)의 자료구조
- 각 컬럼의 서로 다른 종류 데이터 타입을 사용할 수 있다.(문자,숫자,블리언,날짜)
df = DataFrame([[1,2,3],
[4,5,6],
[7,8,9]])
df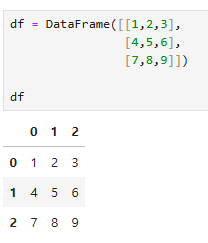
type(df)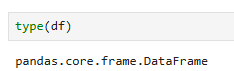
data = {'도시' : ['서울','부산','강원','인천'],
'인구수' : [500,400,200,300]}
data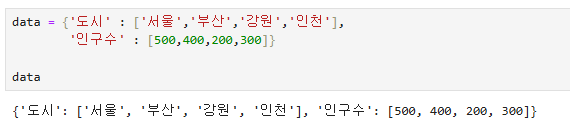
df = DataFrame(data)
df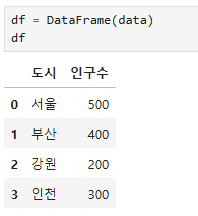
DataFrame 정보
.info()
df.info()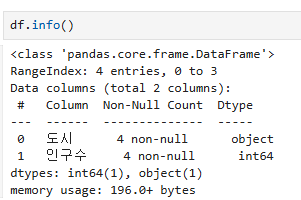
.columns : 컬럼 정보
.index : 인덱스 정보
.values : 값정보
csv파일로 DataFrame 생성
employees = pd.read_csv('C:/Temp/employees.csv')
departments = pd.read_csv('C:/Temp/departments.csv')
DataFrame 행,컬럼 설정
-
출려 행 보기
employees.shape #(행수, 열수)
employees.head() # 상위 5행 출력
employees.head(10) # 상위 10행 출력
employees.tail() # 하위 5행 출력
employees.tail(10) # 하위 10행 출력 -
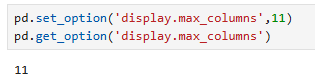
출력할 수 있는 컬럼의 수 확인
pd.options.display.max_columns
pd.get_option('display.max_columns') -
출력할 수 있는 컬럼의 수 설정
pd.set_option('display.max_columns',11)
-
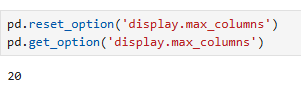
출력할 수 있는 컬럼의 수를 기본값으로 설정
pd.reset_option('display.max_columns')
-
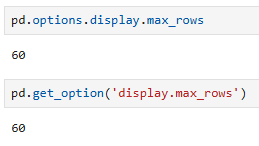
출력할 수 있는 행의 수 확인
pd.options.display.max_rows
pd.get_option('display.max_rows')
-
출력할 수 있는 행의 수 설정
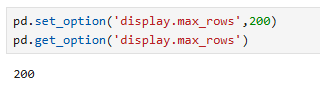
pd.set_option('display.max_rows',200)
-
출력할 수 있는 컬럼의 수를 기본값으로 설정
pd.reset_option('display.max_rows')
DataFrame indexing
-
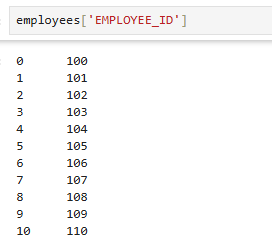
특정 컬럼값만 확인
employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']
-
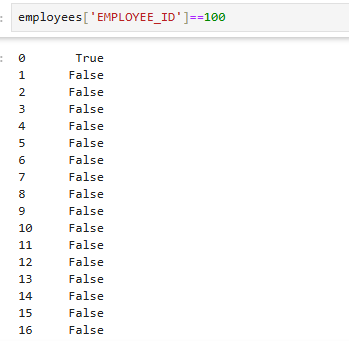
True or False인 값 확인
employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100
-
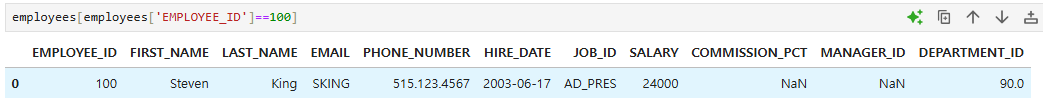
조건이 True인 row만 확인
employees[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100]
-
조건이 True인 row의 특정 컬럼만 조회
employees[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100][['LAST_NAME','SALARY']]
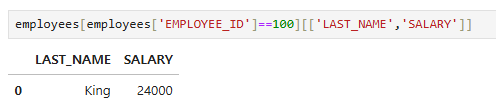
-
employee_id가 100인 row의 last_name, salary 컬럼만 출력
employees[['LAST_NAME','SALARY']][employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100]
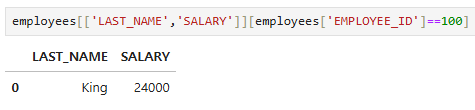
-
salary값이 10000 이상인 row 출력
employees[employees['SALARY'] >= 10000]
loc
employees.loc[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100,]
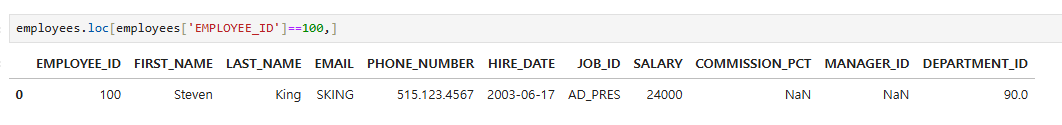
employees.loc[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100,'LAST_NAME']
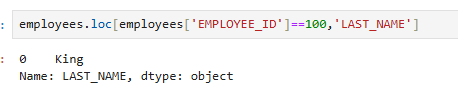
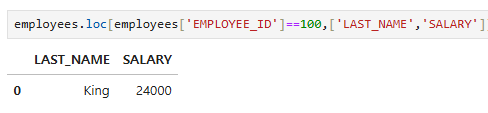
employees.loc[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==100,['LAST_NAME','SALARY']]
pandas 정렬
- 오름차순
x = employees[employees['SALARY'] >= 10000][['LAST_NAME','SALARY','DEPARTMENT_ID']]
x.sort_values(by='DEPARTMENT_ID') # 기본값은 오름차순
x.sort_values(by='DEPARTMENT_ID',ascending=True)- 내림차순
x = employees[employees['SALARY'] >= 10000][['LAST_NAME','SALARY','DEPARTMENT_ID']]
x.sort_values(by='DEPARTMENT_ID',ascending=False)- 각 컬렴별 정렬 지정
x = employees[employees['SALARY'] >= 10000][['LAST_NAME','SALARY','DEPARTMENT_ID']]
result = x.sort_values(by=['DEPARTMENT_ID','SALARY'], ascending=[False,True])
result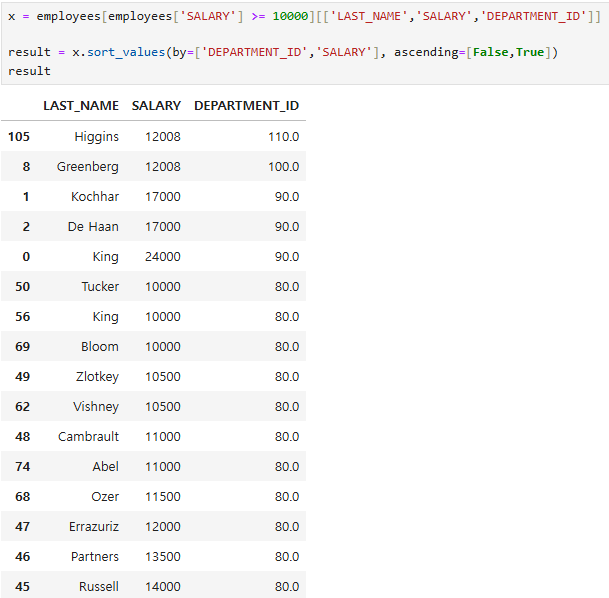
index 재설정
- .reset_index()
-- 변수에 결과값 입력
result = x.sort_values(by='DEPARTMENT_ID',ascending=False)
result.reset_index()# 미리보기, 기존인덱스가 컬럼으로 추가되었다.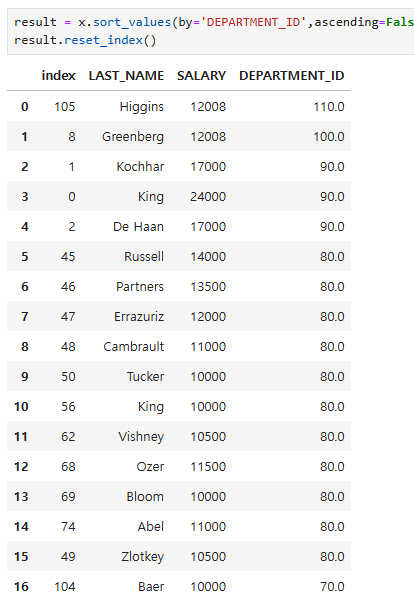
- drop 옵션, 기존 인덱스가 컬럼으로 추가되는걸 삭제
result = result.reset_index(drop=True)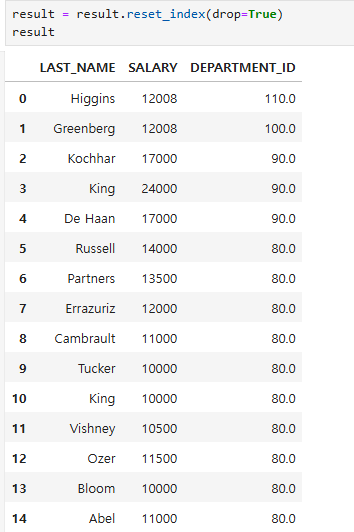
함수
- 여러 조건을 or로 묶을때는 | 연산자를 이용한 방법
employees[(employees['EMPLOYEE_ID'] == 100) | (employees['EMPLOYEE_ID']==101)]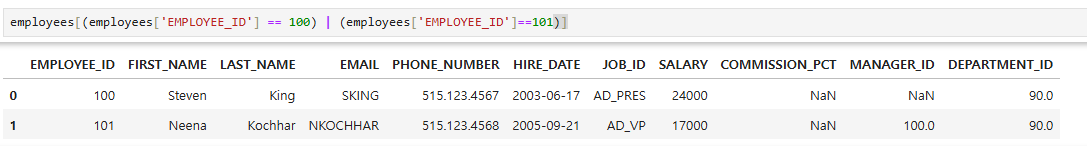
- isin() 함수 사용
employees[employees['EMPLOYEE_ID'].isin([100,101])]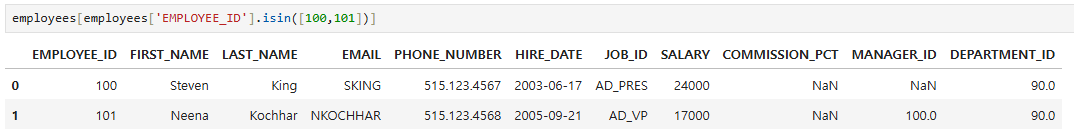
- pandas에서는 not in은 없기 때문에 ~로 표현
employees[~employees['EMPLOYEE_ID'].isin([100,101])]- pandas에서 is null은 isnull()함수 사용
employees[employees['COMMISSION_PCT'].isnull()]- pandas에서 is not null은 ~ isnull()로 표현하면 된다.
employees[~employees['COMMISSION_PCT'].isnull()]- 여러조건들을 and로 묶을때는 & 기호를 사용
employees[employees['COMMISSION_PCT'].isnull()&((employees['SALARY']>=5000)&(employees['SALARY']<=10000))]str 함수
- 각 row의 단어 길이
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.len()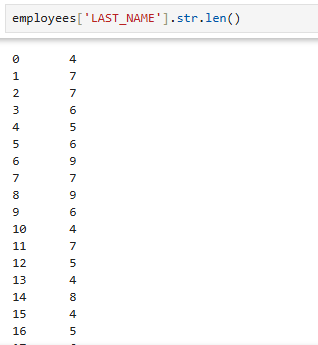
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.len() #문자열의 길이를 반환합니다.
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.upper() #문자열을 대문자로 변환합니다.
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.lower() #문자열을 소문자로 변환합니다.
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.capitalize() #문자열의 첫 글자만 대문자로 변환합니다
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.title() #각 단어의 첫 글자를 대문자로 변환합니다
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.swapcase() #대문자는 소문자로, 소문자는 대문자로 변환합니다
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.findall('a') #문자열에서 특정 패턴('a')을 찾아 리스트로 반환합니다- 문자를 찾아 위치를 반환하는 함수
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.find('a')- 문자가 포함되어 있는지를 체크하는 함수
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.contains('a')
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.contains('a',case=True) # 대소문자구분(기본값)
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.contains('a',case=False) # 대소문자구분하지 않고 찾는다.- 문자의 위치를 기준으로 추출하는 함수
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.get(0)
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.get(1)- 3번째 위치의 문자가 a or e 인지에 따라 True, Flase 반환
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.get(2).isin(['a','e'])- 문자의 위치 범위를 기준으로 추출하는 함수
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.slice(start=0,stop=2) 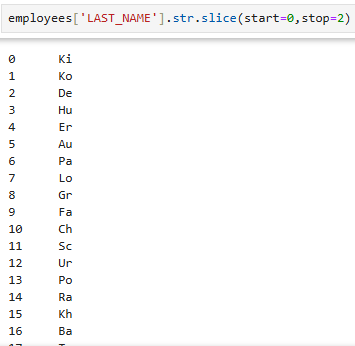
- 문자의 자리수를 고정한 후 왼쪽, 오른쪽 기준으로 출력
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.pad(width=20,side='left')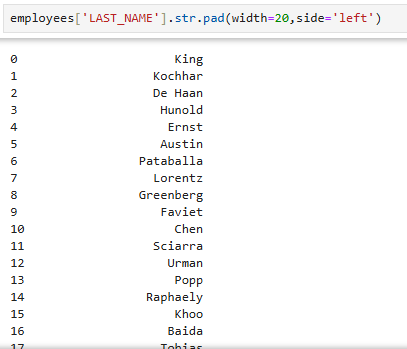
- 공백을 채우는 옵션까지 추가
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.pad(width=20,side='left',fillchar='_')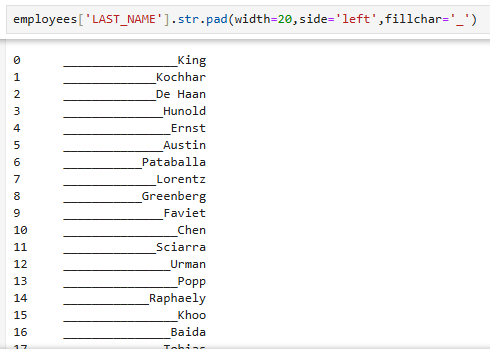
- 문자열을 자리수를 고정시킨후 중앙에 배치
employees['LAST_NAME'].str.center(width=20,fillchar='_')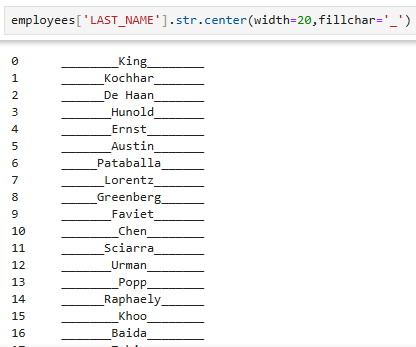
그룹함수
- sum()
obj = Series([2,3,4,5,6,None])
obj
obj.sum()
obj.sum(skipna=True) # NaN(null)제거 기본값
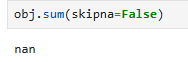
obj.sum(skipna=False) 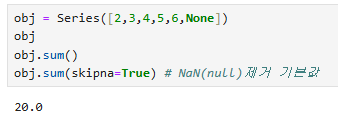
- mean()
obj.mean() #평균
obj.median() #중앙값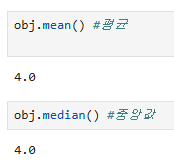
- 이외
obj.var() #분산
obj.std() #표준편차
obj.max() #최대값
obj.min() #최소값
obj.idxmax() #최대값의 인덱스
obj.argmax()
obj.idxmin() #최소값의 인덱스
obj.argmin()
obj.cumsum() #누적합
obj.cumprod() #누적곱