본 포스팅은 네이버 부스트캠프 3기에서 공부한 내용을 기반으로 작성된 글입니다.
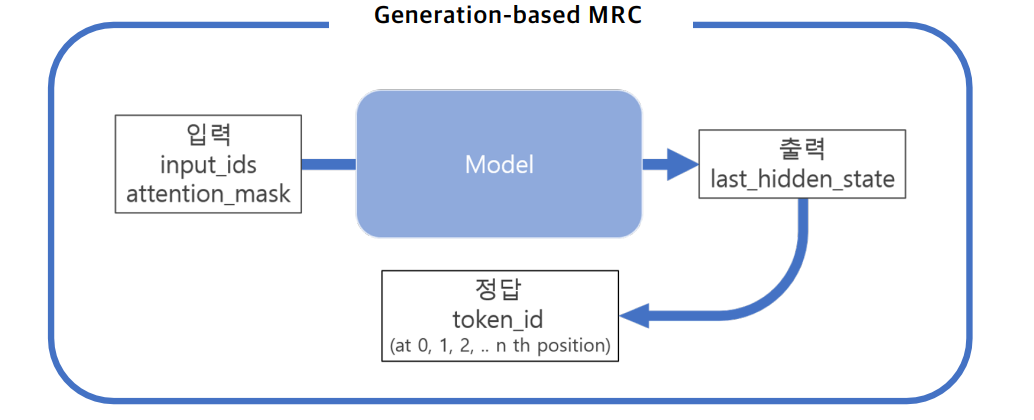
Generation-based MRC?
MRC : 지문(context)을 이해하고 질의(question)의 답변을 추론하는 문제
Generation-based MRC : 주어진 질의를 보고 답변을 생성하는 문제
필요한 라이브러리 설치
!pip install tqdm==4.48.0 -q
!pip install datasets==1.4.1 -q
!pip install transformers==4.5.0 -q
!pip install sentencepiece==0.1.95 -q
!pip install nltk -q데이터셋, 평가지표 불러오기
Huggingface를 이용하여 편리하게 데이터셋을 이용할 수 있습니다.
from datasets import load_dataset
from datasets import load_metric
# KorQuAD 1.0 dataset load
datasets = load_dataset("squad_kor_v1")
metric = load_metric("squad")Pre-trained model 불러오기
Huggingface를 이용하여 필요한 모델을 불러올 수 있습니다.
-
.from_config() : pre-training을 하지 않은 모델을 불러오는 method
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM model_name = "google/mt5-small" # Download configuration from huggingface.co and cache. config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(model_name) model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_config(config) -
.from_pretrained() : pre-trained model을 불러오는 method이고, 스스로 학습한 모델을 불러오려면 model_name 부분에 model이 저장된 directory를 입력해야 함
from transformers import AutoConfig, AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM model_name = "google/mt5-small" # Download model and configuration from huggingface.co and cache. model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
Model type
-
AutoModel : hidden state가 출력되는 기본 모델
model_name = "google/mt5-small" model= AutoModel.from_pretrained(model_name) -
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM : downstream task 모델
model_name = "google/mt5-small" model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(model_name)
Google T5
Raffel, Colin, et al. "Exploring the limits of transfer learning with a unified text-to-text transformer." arXiv preprint arXiv:1910.10683 (2019).
-
text-based 언어 문제들을 text-to-text 형식으로 변환하는 통합된 프레임워크를 도입하여 NLP 분야의 transfer learning 적용을 연구
-
연구를 통해 얻은 insights와 새로운 데이터셋 "Colossal Clean Crawled Corpus"를 결합
-
summarization, question answering, text classification 등 다양한 task에서 SOTA 달성
Google mT5
Xue, Linting, et al. "mT5: A massively multilingual pre-trained text-to-text transformer." arXiv preprint arXiv:2010.11934 (2020)
-
101개 언어 데이터 세트에 대해 사전 학습된 Google T5 모델의 다국어 변형인 모델
-
3억 ~ 130억 개의 매개 변수 (예측에 사용되는 모델 내 변수)를 포함하며 100개 이상의 언어를 학습할 수 있는 모델
QA를 위한 mT5 모델 불러오기
from transformers import (
AutoConfig,
AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM,
AutoTokenizer
)
model_name = "google/mt5-small"
# T5는 seq2seq 모델이므로 model을 불러올 때 AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM을 사용해야 함
config = AutoConfig.from_pretrained(
model_name,
cache_dir=None,
)
tokenizer = AutoTokenizer.from_pretrained(
model_name,
cache_dir=None,
use_fast=True,
)
model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained(
model_name,
config=config,
cache_dir=None,
)
필요한 변수 설정하기
# 데이터 전처리를 위한 파라미터
max_source_length = 1024
max_target_length = 128 # 최대 넘어가지 않도록 막아줌
padding = False
# 학습을 위한 파라미터
preprocessing_num_workers=12
num_beams = 2
max_train_samples = 16
max_val_samples = 16
batch_size = 4
num_train_epochs = 30Preprocessing
데이터셋을 입력형식 맞추어 전처리를 진행합니다.
def preprocess_function(examples):
inputs = [f"question: {q} context: {c} </s>" for q, c in zip(examples["question"], examples["context"])]
targets = [f'{a["text"][0]} </s>' for a in examples['answers']]
model_inputs = tokenizer(
inputs,
max_length=max_source_length,
padding=padding,
truncation=True
)
# targets(label)을 위해 tokenizer 설정
with tokenizer.as_target_tokenizer():
labels = tokenizer(
targets,
max_length=max_target_length,
padding=padding,
truncation=True
)
model_inputs["labels"] = labels["input_ids"]
model_inputs["example_id"] = []
for i in range(len(model_inputs["labels"])):
model_inputs["example_id"].append(examples["id"][i])
return model_inputstrain_dataset = datasets["train"]
column_names = datasets["train"].column_names
train_dataset = train_dataset.map(
preprocess_function,
batched=True,
num_proc=preprocessing_num_workers,
remove_columns=column_names,
load_from_cache_file=False,
)Post processing
원하는 형태로 예측값 추출하기 위해 후처리를 진행합니다.
import nltk
from transformers import (
DataCollatorForSeq2Seq, # 다른 시퀀스 length을 가진 input들을 합쳐줘서 gpu에서 pair computing이 쉽게 만들어 준다.
Seq2SeqTrainer,
Seq2SeqTrainingArguments
)
nltk.download('punkt')
label_pad_token_id = tokenizer.pad_token_id
data_collator = DataCollatorForSeq2Seq(
tokenizer,
model=model,
label_pad_token_id=label_pad_token_id,
pad_to_multiple_of=None,
)
def postprocess_text(preds, labels):
"""
postprocess는 nltk를 이용합니다.
Huggingface의 TemplateProcessing을 사용하여
정규표현식 기반으로 postprocess를 진행할 수 있지만
해당 미션에서는 nltk를 이용하여 간단한 후처리를 진행합니다
"""
preds = [pred.strip() for pred in preds]
labels = [label.strip() for label in labels]
preds = ["\n".join(nltk.sent_tokenize(pred)) for pred in preds]
labels = ["\n".join(nltk.sent_tokenize(label)) for label in labels]
return preds, labels
def compute_metrics(eval_preds):
preds, labels = eval_preds
if isinstance(preds, tuple):
preds = preds[0]
decoded_preds = tokenizer.batch_decode(preds, skip_special_tokens=True)
# decoded_labels은 rouge metric을 위한 것이며, f1/em을 구할 때 사용되지 않음
decoded_labels = tokenizer.batch_decode(labels, skip_special_tokens=True)
# 간단한 post-processing
decoded_preds, decoded_labels = postprocess_text(decoded_preds, decoded_labels)
formatted_predictions = [{"id": ex["id"], "prediction_text": decoded_preds[i]} for i, ex in enumerate(datasets["validation"].select(range(max_val_samples)))]
references = [{"id": ex["id"], "answers": ex["answers"]} for ex in datasets["validation"].select(range(max_val_samples))]
result = metric.compute(predictions=formatted_predictions, references=references)
return resultTrain model
Arguments를 정의하고 학습을 진행합니다.
args = Seq2SeqTrainingArguments(
output_dir='outputs',
do_train=True,
do_eval=True,
predict_with_generate=True,
per_device_train_batch_size=batch_size,
per_device_eval_batch_size=batch_size,
num_train_epochs=num_train_epochs,
save_strategy='epoch',
save_total_limit=2 # 모델 checkpoint를 최대 몇개 저장할지 설정
)trainer = Seq2SeqTrainer(
model=model,
args=args,
train_dataset=train_dataset,
eval_dataset=eval_dataset,
tokenizer=tokenizer,
data_collator=data_collator,
compute_metrics=compute_metrics,
)
train_result = trainer.train(resume_from_checkpoint=None)학습시킨 모델 불러오기
finetuned_model = AutoModelForSeq2SeqLM.from_pretrained('모델저장경로')