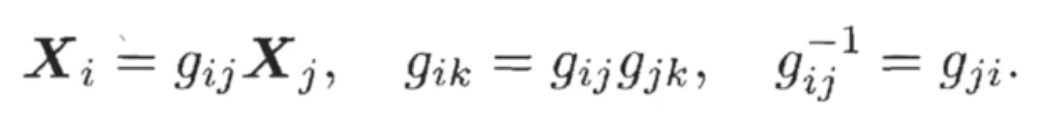3-Dimensional Euclidean Space
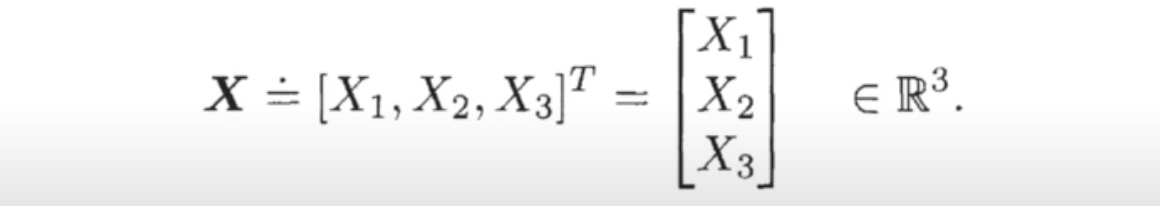
- Euclidean space 내의 모든 point 는 three cartesian coordinates를 가지는 내의 point와 동일하다.
- Euclidean space에서 vector 는 두 개의 point 에 의해 결정되며 방향성을 가진다. 에서 를 향할 경우 로 나타낸다.
- 의 좌표가 , 의 좌표가 일 때 는 이다. 이와 같이 base point가 명시되는 vector를 bound vector라 한다.
- Free vector는 base point에 의존하지 않는 벡터로 로 동일한 free vector이다. 이 둘은 에서 평행하다.
- 우리는 cartesian frame의 origin이 base point라고 가정하며 free vector의 조합은 linear vector space를 형성한다.
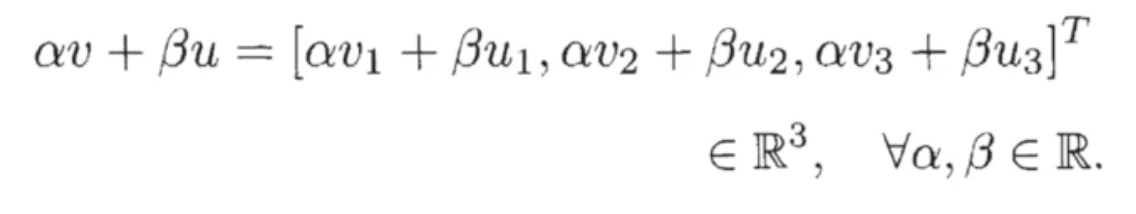
Inner and Outer Products in
-
두 벡터 의 inner product는 다음과 같다.

-
Inner product는 거리나 사이각을 measure 하는데 활용할 수 있다.

-
두 벡터의 cross(outer) product는 다음과 같으며 그 결과는 두 벡터에 orthogonal한 벡터가 된다. 두 벡터의 순서를 바꾸면 부호가 바뀐다.
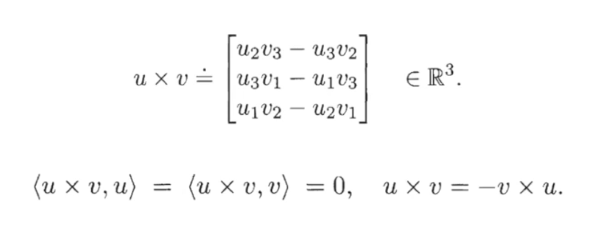
-
Cross product는 to 의 linear mapping으로 skw-symmetric matrix(로 표현할 수 있다.
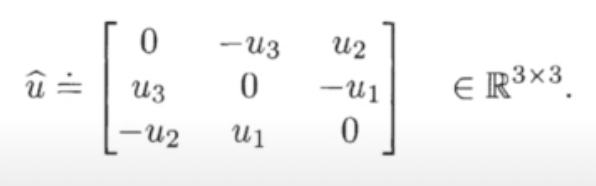
-
Standard cartesian frame에서 X축과 Y축의 cross product는 Z축이 된다.(Right-hand rule)

Coordinate Frames
- Rigid object는 right-handed orthonormal frame과 연관되기 때문에 object coordinate frame 혹은 body coordinate frame이라 칭한다.
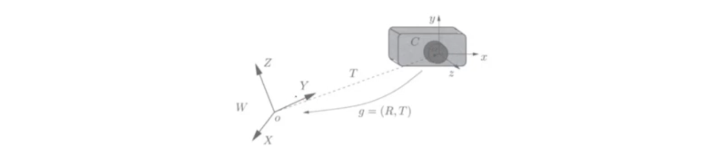
- 또한, rigid-body motion은 어떠한 reference frame에서의 motion에 의해 명시되는데 이를 world frame이라 한다.
- Camera frame 과 world reference frame 를 예로 들면 camera의 configuration은 와 의 원점 사이의 관계인 translation vector 와 좌표축 간의 relative orientation 로 결정된다.
Rigid-body Motion
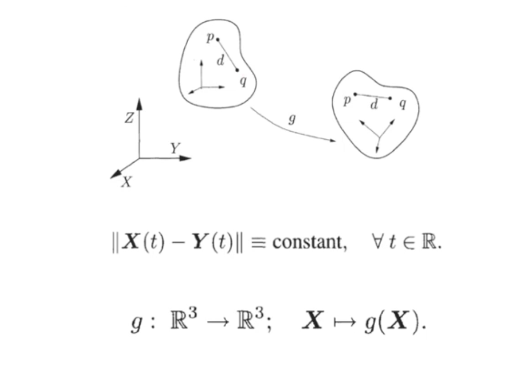
- Rigid-body motion(transformation)은 point들 간의 거리를 유지한다는 제약 조건을 가진 mapping function을 의미한다.
- 일 때 mapping 후 vector는 다른 방향을 가지지만 거리는 유지한다.

Euclidean Transformation
-
거리를 유지하는 mapping을 euclidean transformation이라 하며 으로 표현한다.
-
하지만, 두 점의 거리를 유지한다는 것은 rigid object moving을 충분히 표현하지 못한다.(거리는 유지하지만 phisically realizable한 경우->아래 예시는 rule of thumb을 위반한다.)
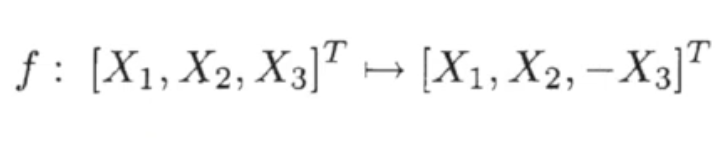
-
따라서, rigid-body motion은 거리와 orientation을 모두 유지해야 한다.
-
이는 norm of vector(distance)와 cross product(orientation)을 유지한다고 할 수 있다.
-
Rigid-body motion에 의한 transformation을 special euclidean transformation이라 한다.()
-
Inner product 는 polarization identity에 의해 norm 으로 표현할 수 있다.
-
따라서, 이기 때문에 rigid-body motion 에 대해 가 된다. 이는 두 벡터의 사이각이 변환 이후에도 유지됨을 의미한다.
-
위 특성들에 의해 rigid-body motion은 triple product(volume) 또한 유지한다.
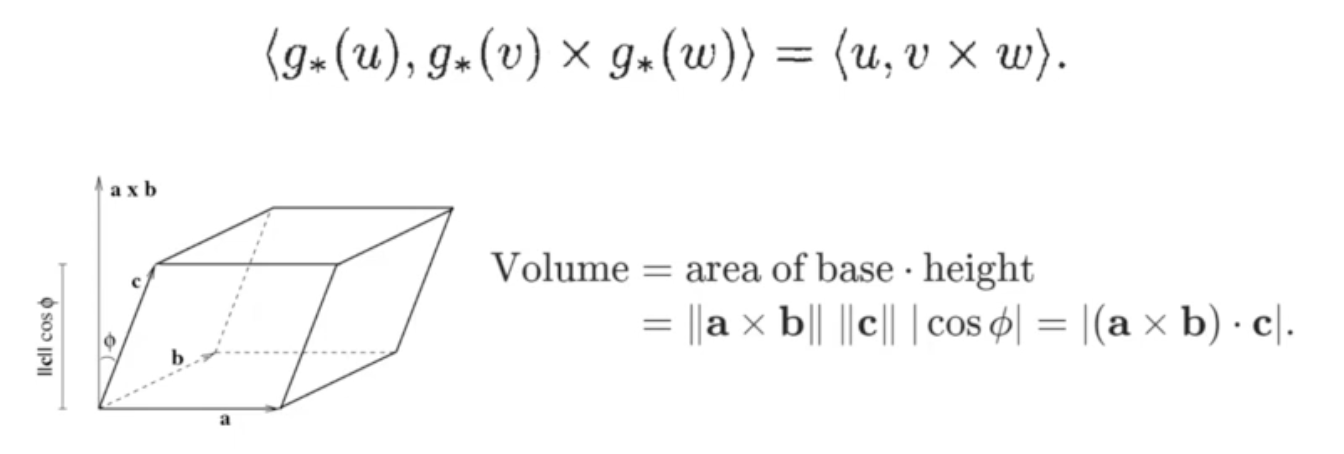
Orthogonal Matrix Representation of Rotations
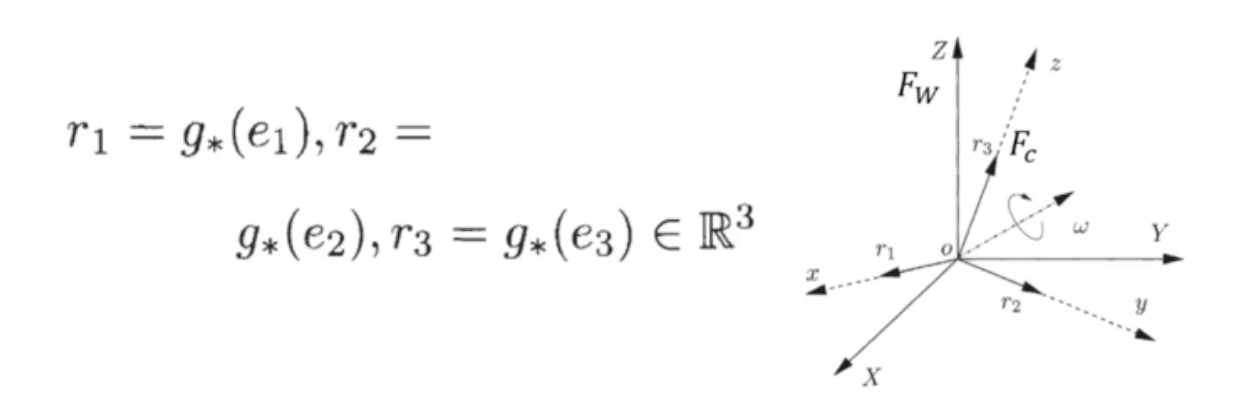
- Fixed point 에 대한 rigid object rotating이 있을 때 의 에 대한 configuration(orientation)은 세 개의 orthonormal vectors에 의해 결정된다.
- 는 unit vector로 frame에서의 주축 를 의미한다.
- Rotation은 세 벡터로 구성된 3x3 matrix로 나타낼 수 있다.
- 는 orthonormal frame을 형성하기 때문에 가 되고 따라서 rotation matrix는 orthogonal matrix이다.
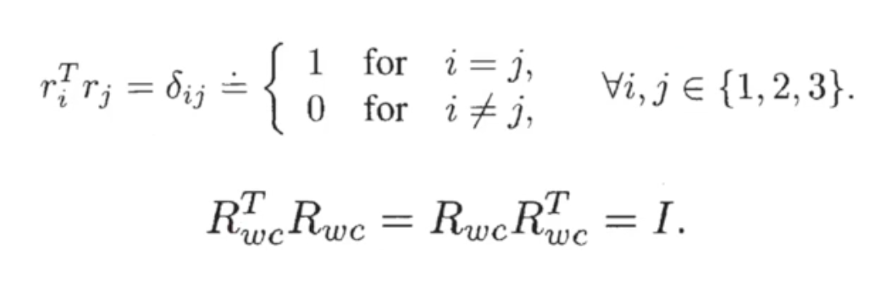
- 이며 가 right-handed frame이기 때문에 det()=1이다.
- Special orthogonal matrices의 space는 다음과 같이 로 나타낼 수 있으며 rotation matrices라 부른다.
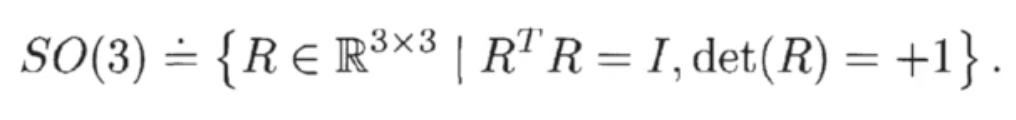
Euler Angles to Rotation Matrix
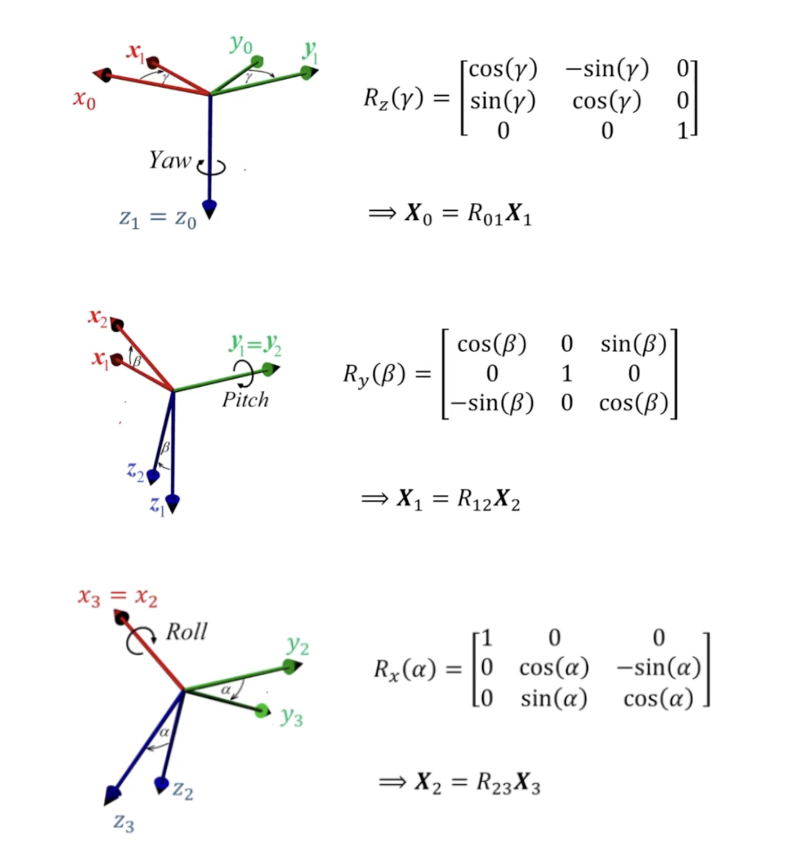
- Yaw angle 는 z축, pitch angle 는 y축, roll angle 는 x축 방향으로의 회전을 의미한다.
- 각 축에 대해 회전할 때 나머지 2개의 축이 바뀌는 것을 볼 수 있으며 따라서 기준 축 column은 그대로 두고 나머지 축 column이 바뀌는 matrix를 가진다.
- Tait-Bryan angles는 z-y'-x'' 순서의 rotation을 의미한다.
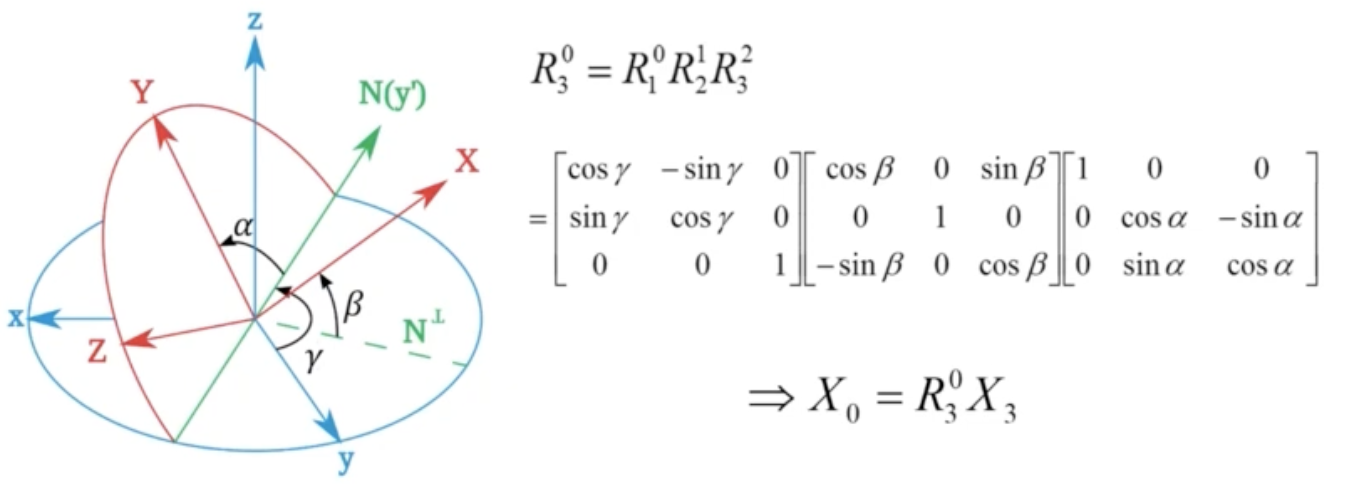
Rigid-body motion and its Representations
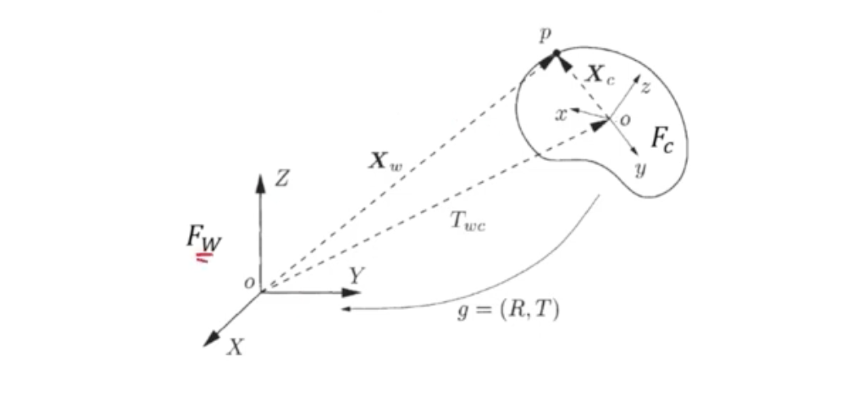
- Object 상의 point 는 에서 vector 로 나타낼 수 있다.
- 는 로의 translation 과 에서의 의 합이 된다.
- 는 에서의 point 이기 때문에 에서는 로 나타낼 수 있다.
Homogeneous Representation
- 는 linear form으로 다음과 같이 쓸 수 있다.
- 따라서 는 homogeneous representation으로 표현된다.
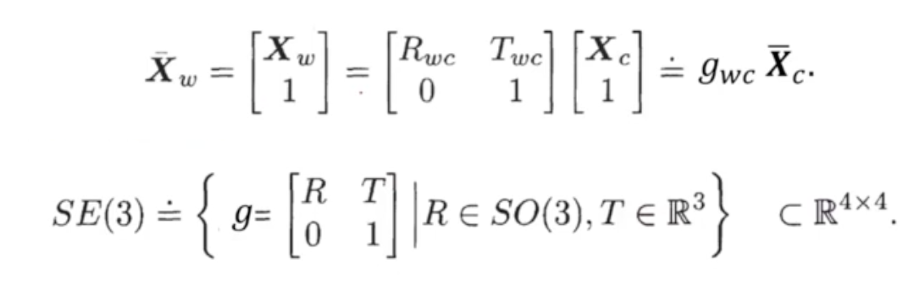
- 모든 에 대해 은 닫혀있다.
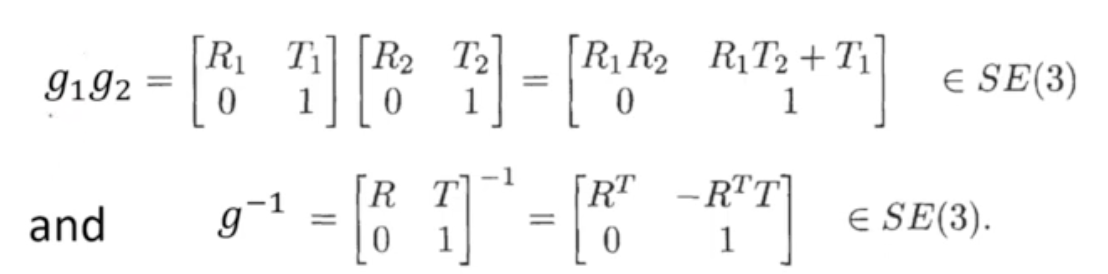
Composition of Rigid-body Motions
-
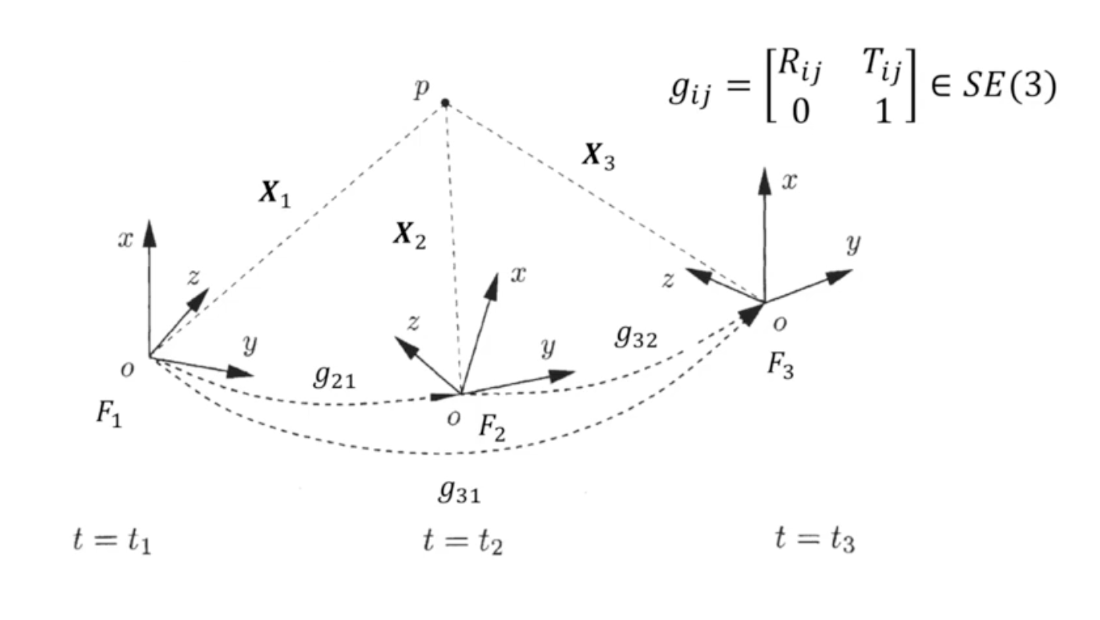
3개의 camera frame에 대해서 각각의 가 존재한다고 할 때 이며 composition rule에 의해 가 된다.
-
또한, 이므로 inverse rule 도 정의된다.
-
General하게 표현하면 아래와 같다.