Conics and Dual Conics
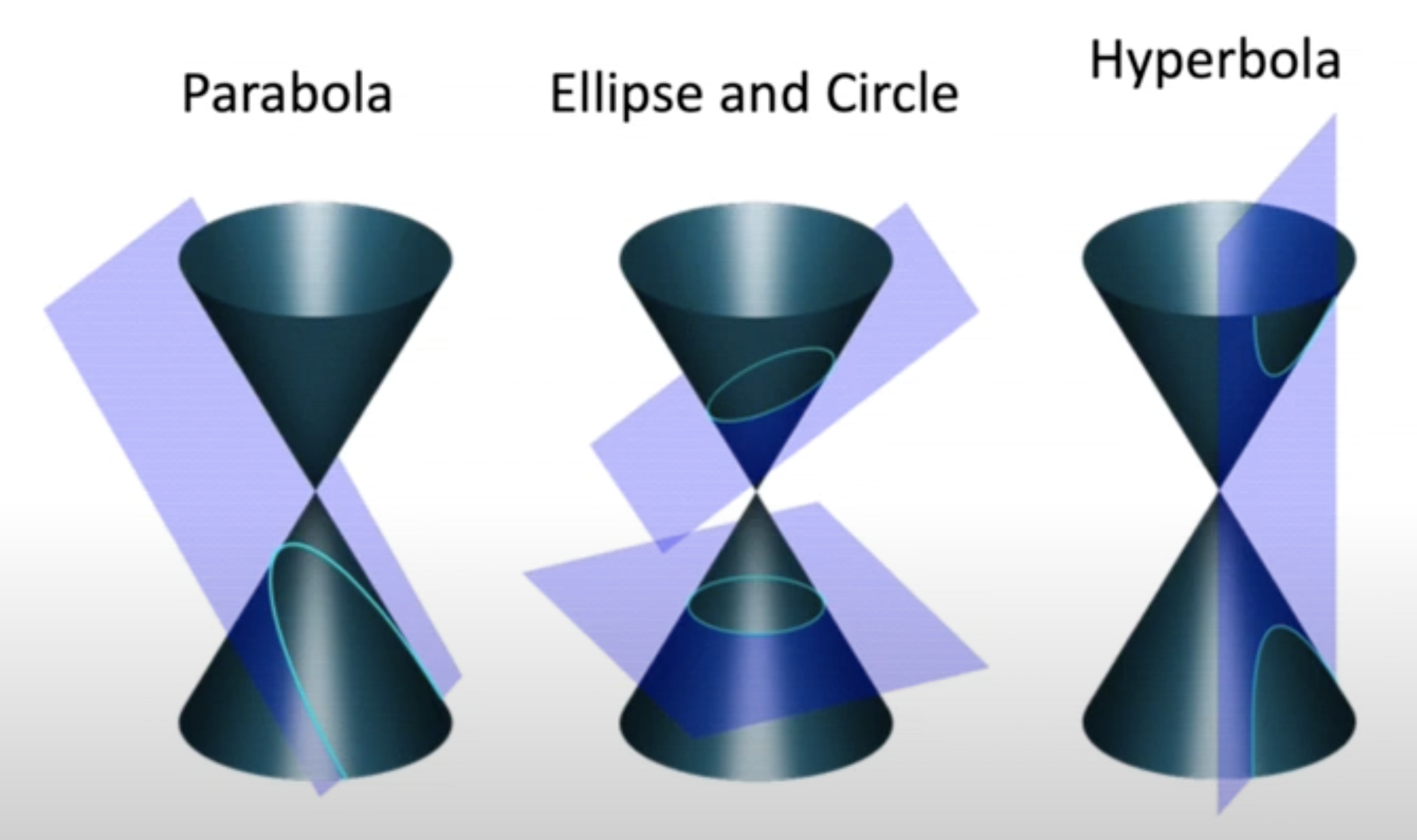
- Conic(원뿔)은 plane에서 2차 방정식으로 나타낼 수 있는 curve를 의미하며 그 유형으로 hyperbola(쌍곡선), ellipse(타원), parabola(포물선)이 존재한다.
- 이 유형들은 다른 orientation을 가지는 plane에 의해 만들어진다.
- 원뿔의 사선에 접하는 plane은 parabola를 만든다.
- 원뿔의 base에 접하는 plane은 circle을 만들고 회전시키면 ellipse를 만든다.
- 수직 방향은 plane은 hyperbola를 만든다.
- Conic의 방정식은 inhomogeneous coordinate에서 다음과 같다.
- 를 통해 homogeneous coordinate으로 바꾸면 다음과 같다.
- 행렬로 나타내면 이 되며 는 symmetric하며 conic의 homogeneous representation이라 할 수 있다.
- Scale은 무시되며 6개의 변수의 비만 생각하면 되므로 5DoF이다.
Five Points Define a Conic
- 각 point 는 conic coefficient에 하나의 constraint를 준다.
, - 5개의 point가 주어진다면 conic은 5x6 행렬의 null vector가 된다.
Conics and Dual Conics
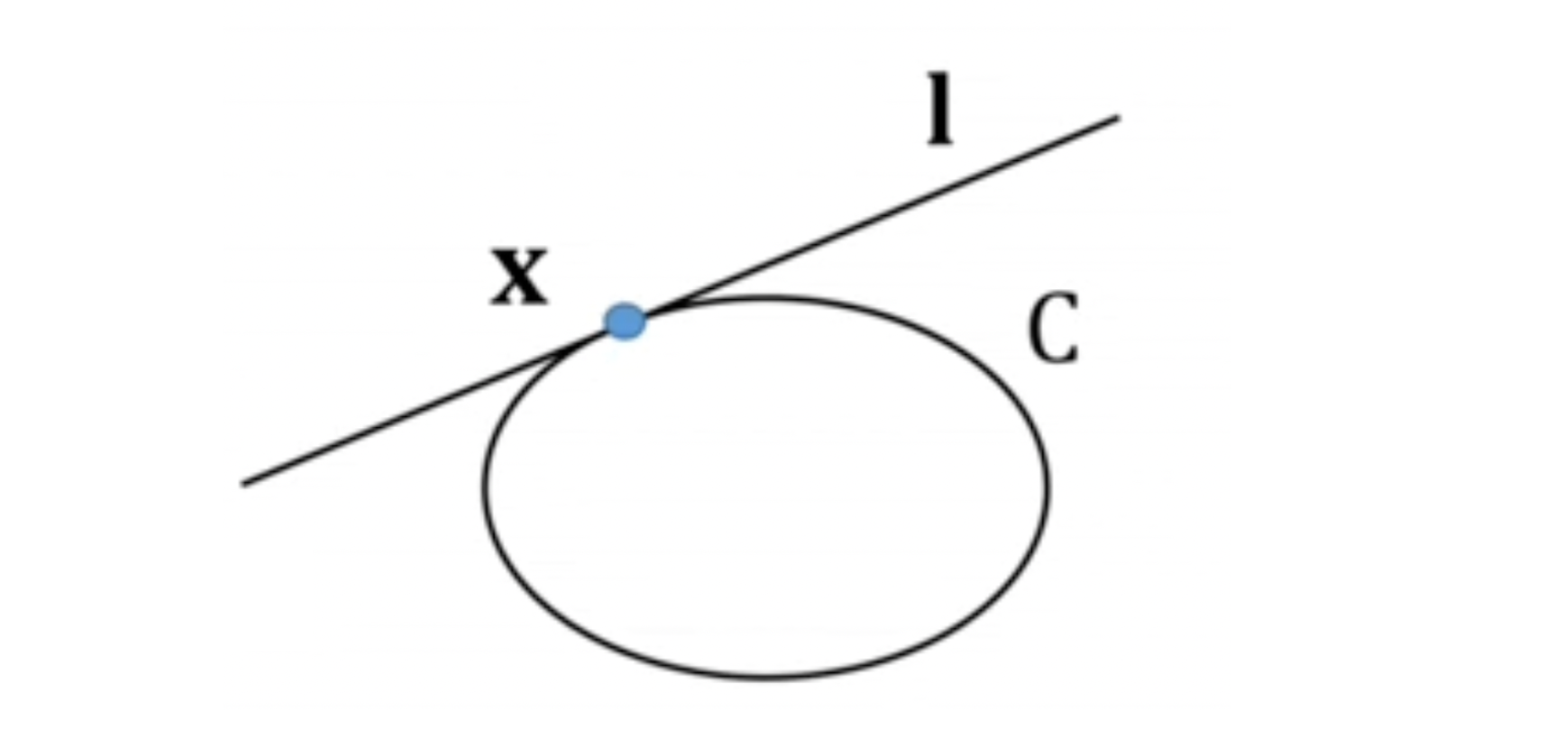
-
Conic 상의 point 에서의 접선 은 이다.
(증명) 이므로 이고 따라서 이다. -
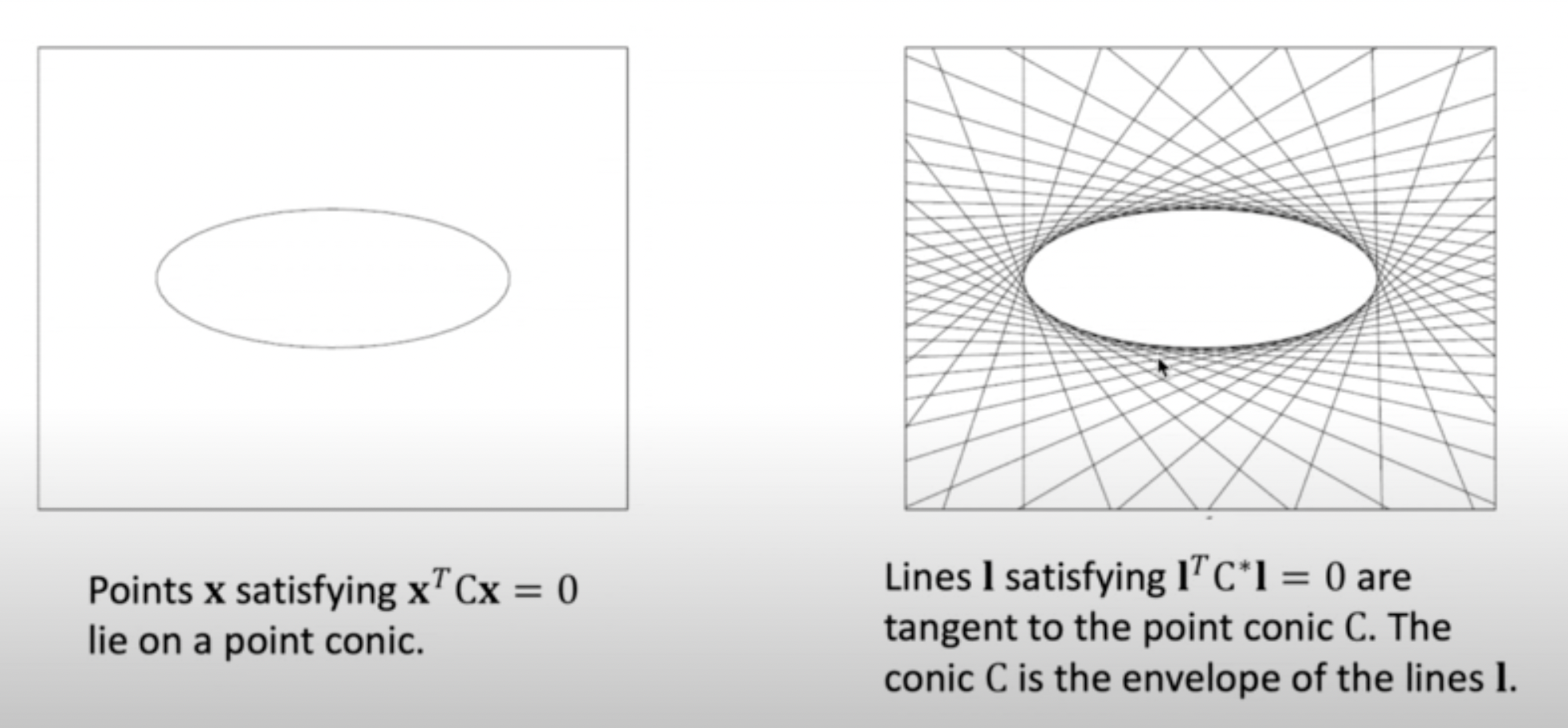
위 설명들은 엄밀히 말하면 점들에 대한 방정식으로 정의한 point conic이라 할 수 있으며 선에 대한 방정식으로 정의한 dual(line) conic도 존재한다.
3x3 행렬 로 표기한다. -
Conic 의 접선 은 을 만족하며 5개의 line을 알면 계산할 수 있다.(5DoF)
-
Non-singular symmetric 행렬 을 만족한다.
(증명) 이므로 로 변형 가능하고 따라서 가 된다. -
또한, 이므로 로부터 을 도출할 수 있다.
-
Dual conics는 conic envelopes라 부르기도 한다.
Degenerate Conics
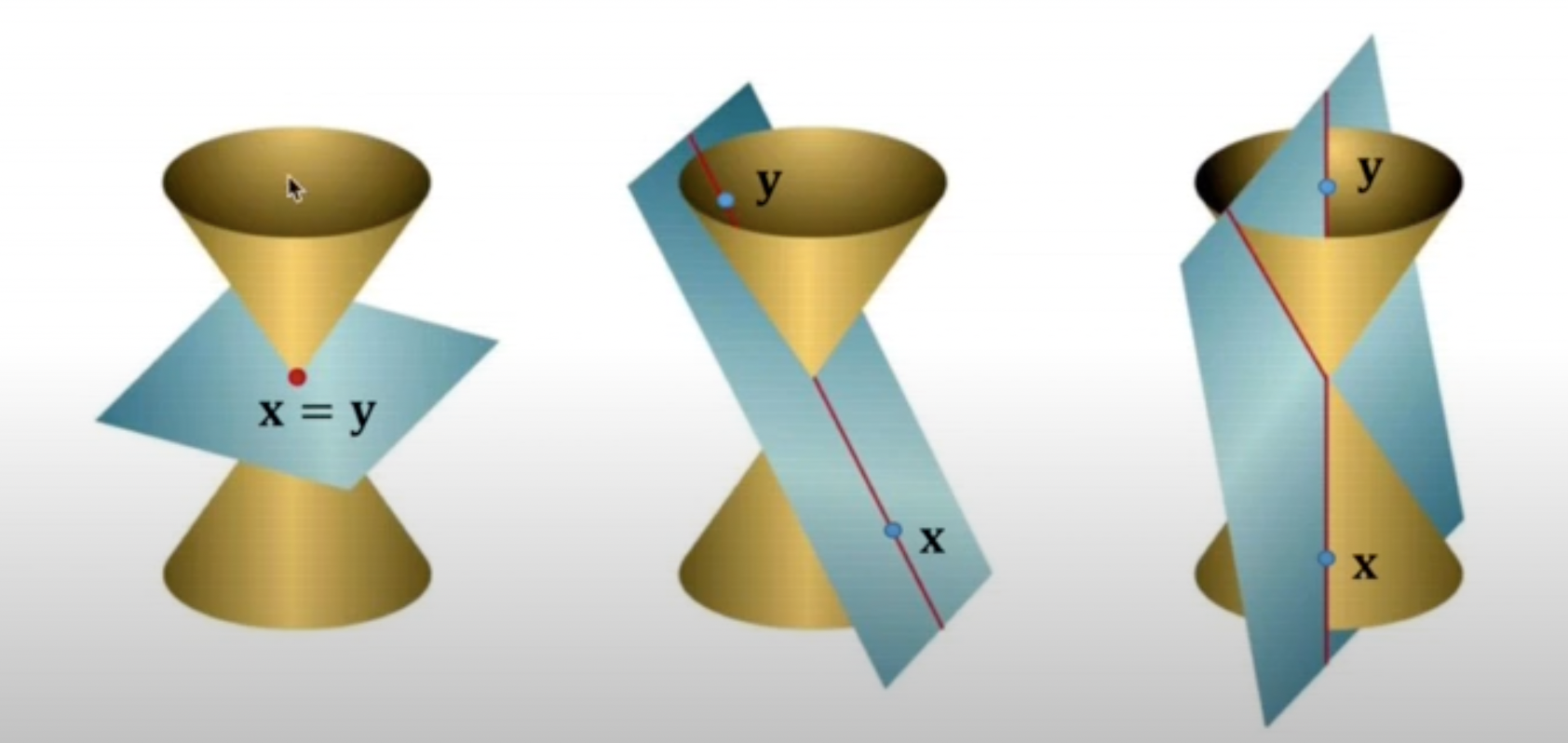
-
이 다른 point 에서 conic을 만난다고 가정하면 이 된다.
-
이 때 모든 에 대해 을 만족한다.
-
이는 를 지나는 모든 line이 conic 상에 존재한다는 의미가 되므로 세 유형에 전부 속하지 않는 degenerate conics가 된다.
-
Degenerate conics의 rank는 full rank가 아니어서 2개의 line과 반복되는 line을 포함한다.
Planar Projective Transformations
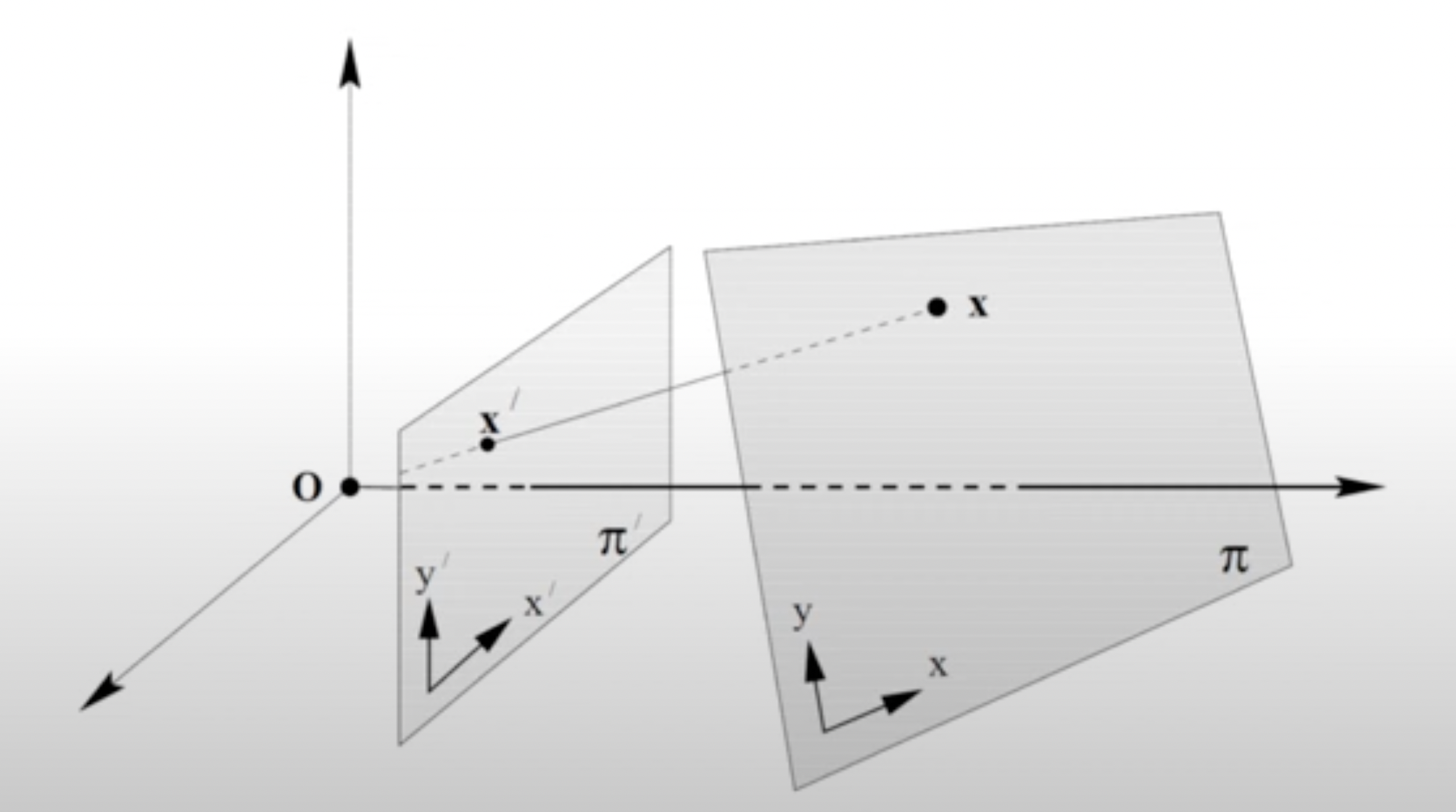
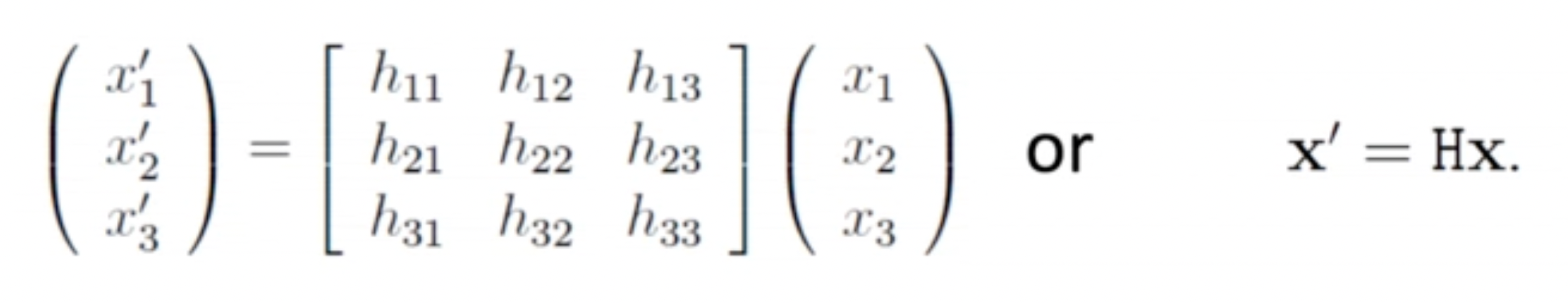
- Projectivity는 인 Invertible mapping으로 homography라고도 부른다.
- 상의 동일한 line 위에 있는 세 점 에 대해 맵핑한 도 동일한 line 위에 위치하게 된다.(collinearity)
- Non-singular 3x3 matrix 로 나타낼 수 있다.
- 행렬 요소들의 ratio만이 중요하기 때문에 homogeneous matrix이며 8DoF이다.
- Transformed plane에 투영한다고 볼 수 있다.
Transformations of Lines and Conics
- Line 상의 point들에 projective transformation을 적용했을 때 여전히 하나의 line 위에 존재하므로 로 표현할 수 있다.
- Conic 의 transform은 로 dual conic 의 transform은 로 표현할 수 있다.
Hierarchy of Transformations:Isometries
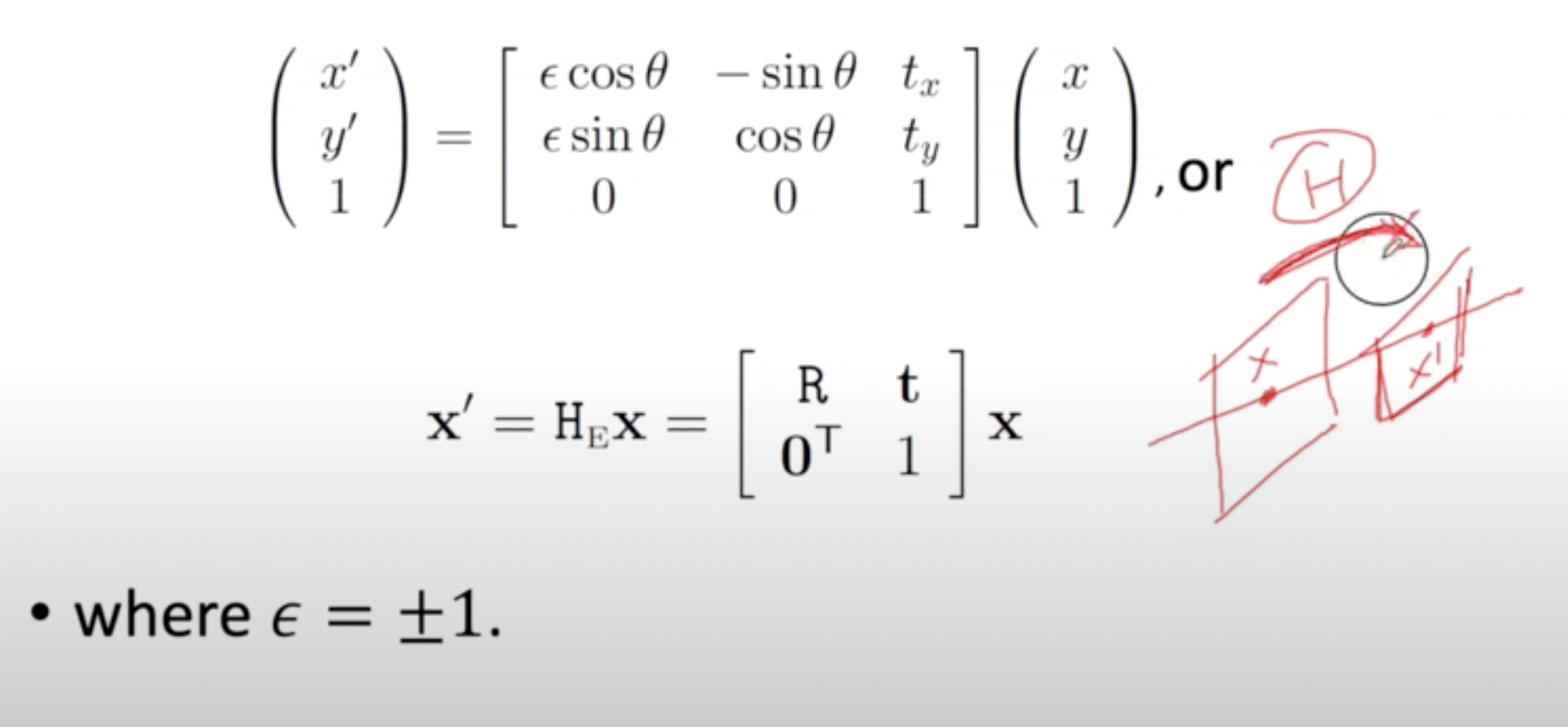
- Isometries란 euclidean distance를 유지하는 상에서의 transformation으로 2개의 plane이 평행하다.
- Length, angle, area에 대해 invariant 하다.
- 3DoF(
Hierarchy of Transformations:Similarity
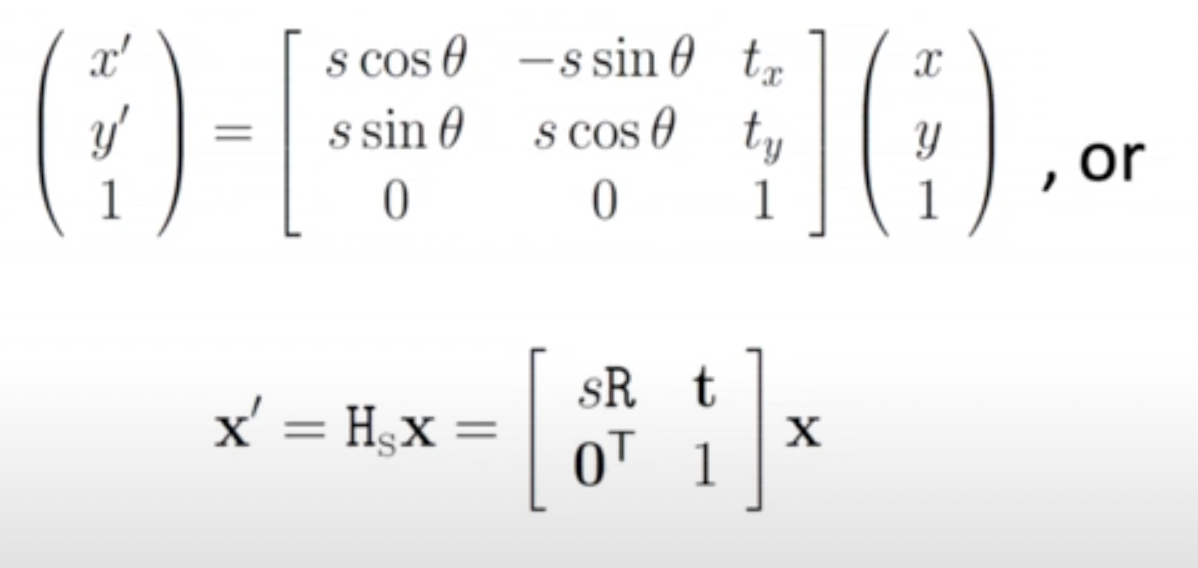
- 에 동일하게 scaling을 적용하는 isotropic scaling이 들어간 isometry라고 볼 수 있다.
- Angles, ratio of two lengths, ratio of areas에 invariant하다.
- 4DoF(
Hierarchy of Transformations:Affinity
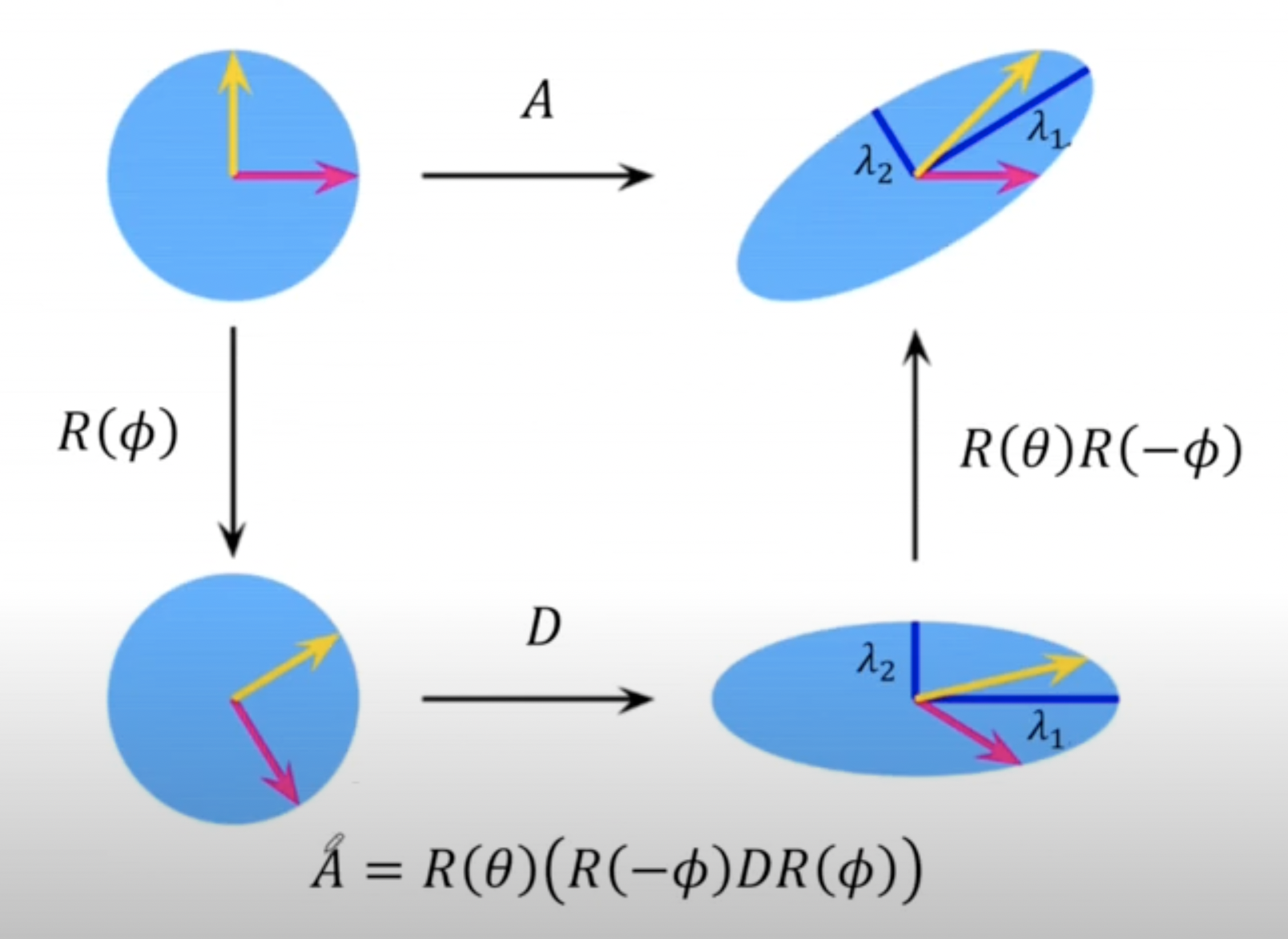
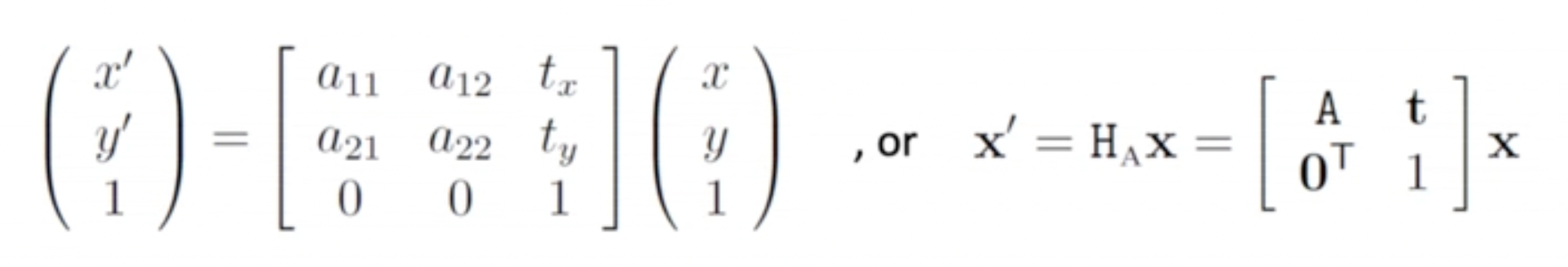
- Translation에 non-singular linear transformation 적용
- Parallel lines, ratio of lengths of parallel line segments, ratio of areas에 invariant하다.
- 6DoF
- Affine matrix 는 SVD에 의해 항상 아래와 같이 분해된다. 은 rotation, D는 diagonal matrix를 의미하며 는 orthogonal matix다.
Hierarchy of Transformations:Projective
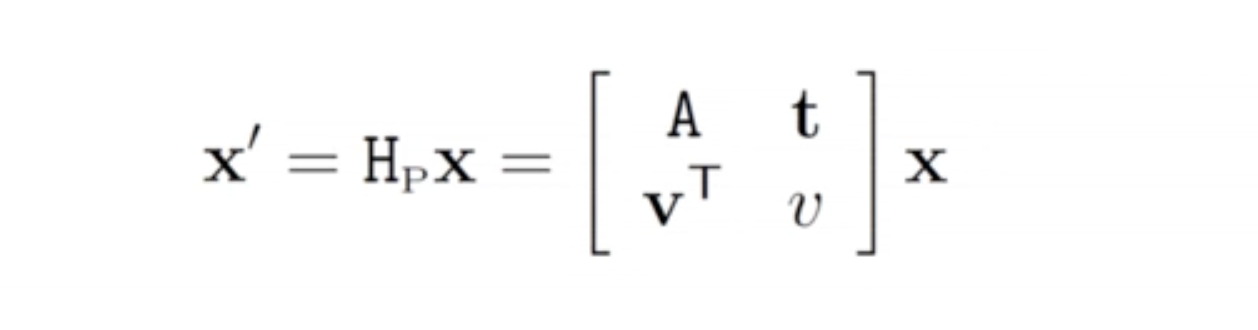
- Non-singular linear transformation
- 가 0일 수 있기 때문에 항상 scale이 가능하지는 않다.
- 두 plane의 4개의 point correspondence로부터 행렬식을 구할 수 있다.
- Order of contact, tangency, cross ratio에 invariant하다.
- 8DoF
Decomposition of a Projective Transformation
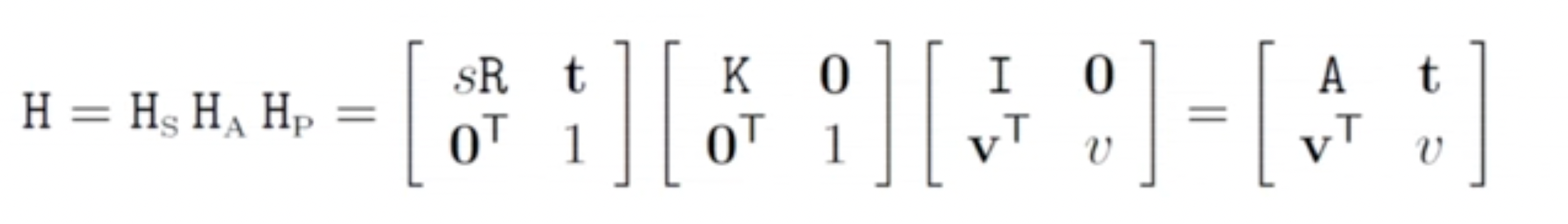
- Projective transformation은 similarity, affine, projective로 분해될 수 있다.
