Comparative Analysis of Pathfinding Algorithms: JPS, Dijkstra, and A*
Path Searching for Game

Dijkstra, A*, JPS 세 가지 경로 탐색 알고리즘에 대하여 이 시리즈에서 다루었다. 먼저 알고리즘의 원리를 이해하기 위해 능숙하게 사용할 수 있는 파이썬으로 먼저 구현해보고, 다시 C++에서 재구현해보았다.
이제 이 세 가지 알고리즘을 동일한 복잡한 맵에서 구현하고 그 성능을 비교해보고자 한다.
기존에 C++에서 구현한 Dijkstra 알고리즘(링크)과 A* 알고리즘(링크)은 간단하게 표현하기 위해 맵을 인접 리스트로 표현했다. 이걸 JPS에서와 마찬가지로(링크) 2D 그리드 맵으로 바꿔보고자 한다.
2D 그리드 맵으로 변경
Dijkstra 2D Grid Map function
vector<pair<int, int>> dijkstra(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, pair<int, int> start, pair<int, int> goal) {
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid[0].size();
// 각 노드까지의 최단 거리를 저장하는 2D 벡터 (초기값: 무한대)
vector<vector<int>> distances(rows, vector<int>(cols, numeric_limits<int>::max()));
distances[start.first][start.second] = 0;
// 우선순위 큐 초기화
priority_queue<pair<int, pair<int, int>>, vector<pair<int, pair<int, int>>>, greater<>> pq;
pq.push({0, start});
// 이동 가능한 방향
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}};
// 경로 추적용 map
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>, pair_hash> came_from;
while (!pq.empty()) {
int current_distance = pq.top().first;
auto current = pq.top().second;
pq.pop();
if (current == goal) {
break; // 목표에 도달하면 종료
}
// 인접한 노드 탐색
for (const auto& direction : directions) {
int new_row = current.first + direction.first;
int new_col = current.second + direction.second;
// 맵 경계 및 장애물 체크
if (new_row < 0 || new_col < 0 || new_row >= rows || new_col >= cols || grid[new_row][new_col] == 1) {
continue;
}
int new_distance = current_distance + 1; // 가중치는 1로 고정
// 최단 거리 갱신
if (new_distance < distances[new_row][new_col]) {
distances[new_row][new_col] = new_distance;
pq.push({new_distance, {new_row, new_col}});
came_from[{new_row, new_col}] = current; // 경로 추적
}
}
}
// 경로 추적
vector<pair<int, int>> path;
pair<int, int> current = goal;
while (came_from.find(current) != came_from.end()) {
path.push_back(current);
current = came_from[current];
}
path.push_back(start);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
return path;
}그리고 Dijkstra.cpp의 메인 함수는 충돌 방지를 위해 주석처리.
A* 2D Grid Map Function
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
#include <queue>
#include <unordered_map>
#include <cmath>
#include <limits>
#include <utility>
#include <algorithm>
using namespace std;
// 사용자 정의 해시 함수
struct pair_hash {
template <class T1, class T2>
size_t operator()(const pair<T1, T2>& p) const {
auto hash1 = hash<T1>{}(p.first);
auto hash2 = hash<T2>{}(p.second);
return hash1 ^ (hash2 << 1);
}
};
// 두 좌표 사이의 유클리드 거리 (휴리스틱)
double heuristic(pair<int, int> node1, pair<int, int> node2) {
int x1 = node1.first, y1 = node1.second;
int x2 = node2.first, y2 = node2.second;
return sqrt((x1 - x2) * (x1 - x2) + (y1 - y2) * (y1 - y2));
}
// A* 알고리즘 (그리드 기반)
vector<pair<int, int>> astar(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, pair<int, int> start, pair<int, int> goal) {
int rows = grid.size();
int cols = grid[0].size();
// 각 노드의 g-cost 저장
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, double, pair_hash> g_costs;
unordered_map<pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>, pair_hash> came_from;
// 초기화
g_costs[start] = 0;
// 우선순위 큐
priority_queue<pair<double, pair<int, int>>, vector<pair<double, pair<int, int>>>, greater<>> pq;
pq.push({heuristic(start, goal), start});
// 이동 가능한 방향
vector<pair<int, int>> directions = {
{-1, 0}, {1, 0}, {0, -1}, {0, 1}, // 상하좌우
{-1, -1}, {1, 1}, {1, -1}, {-1, 1} // 대각선
};
while (!pq.empty()) {
auto [current_f_cost, current_node] = pq.top();
pq.pop();
if (current_node == goal) {
// 목표 도달 시 경로 추적
vector<pair<int, int>> path;
while (came_from.find(current_node) != came_from.end()) {
path.push_back(current_node);
current_node = came_from[current_node];
}
path.push_back(start);
reverse(path.begin(), path.end());
return path;
}
// 이웃 노드 탐색
for (const auto& direction : directions) {
int new_row = current_node.first + direction.first;
int new_col = current_node.second + direction.second;
// 맵 경계 및 장애물 체크
if (new_row < 0 || new_col < 0 || new_row >= rows || new_col >= cols || grid[new_row][new_col] == 1) {
continue;
}
double new_g_cost = g_costs[current_node] + (abs(direction.first) + abs(direction.second) == 2 ? sqrt(2) : 1);
if (g_costs.find({new_row, new_col}) == g_costs.end() || new_g_cost < g_costs[{new_row, new_col}]) {
g_costs[{new_row, new_col}] = new_g_cost;
double f_cost = new_g_cost + heuristic({new_row, new_col}, goal);
pq.push({f_cost, {new_row, new_col}});
came_from[{new_row, new_col}] = current_node;
}
}
}
return {}; // 경로가 없는 경우
}Dijkstra Header File
#ifndef DIJKSTRA_H
#define DIJKSTRA_H
#include <vector>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int, int>> dijkstra(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, pair<int, int> start, pair<int, int> goal);
#endifA* Header File
#ifndef ASTAR_H
#define ASTAR_H
#include <vector>
#include <utility>
using namespace std;
vector<pair<int, int>> astar(const vector<vector<int>>& grid, pair<int, int> start, pair<int, int> goal);
#endifmain_compare.cpp에 통합
#include "Dijkstra.h"
#include "Astar.h"
#include "JPS.h"
#include <SFML/Graphics.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
using namespace std;
const int CELL_SIZE = 20;
const int GRID_ROWS = 30;
const int GRID_COLS = 30;
const int OBSTACLE_COUNT = 100;
vector<vector<int>> grid;
pair<int, int> start = {0, 0};
pair<int, int> goal = {29, 29};
// 랜덤 맵 생성 함수
vector<vector<int>> generateRandomMap(int rows, int cols, int obstacleCount) {
vector<vector<int>> grid(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0));
srand(time(0));
while (obstacleCount > 0) {
int r = rand() % rows;
int c = rand() % cols;
if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
grid[r][c] = 1;
--obstacleCount;
}
}
grid[start.first][start.second] = 0;
grid[goal.first][goal.second] = 0;
return grid;
}
void drawGrid(sf::RenderWindow& window) {
for (int row = 0; row < GRID_ROWS; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < GRID_COLS; ++col) {
sf::RectangleShape cell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
cell.setPosition(col * CELL_SIZE, row * CELL_SIZE);
if (grid[row][col] == 1) {
cell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Black);
} else {
cell.setFillColor(sf::Color::White);
}
cell.setOutlineThickness(1);
cell.setOutlineColor(sf::Color(200, 200, 200));
window.draw(cell);
}
}
}
void displayAlgorithmName(sf::RenderWindow& window, const string& algorithmName) {
sf::Font font;
if (!font.loadFromFile("Arial Unicode.ttf")) {
cout << "Failed to load font!" << endl;
return;
}
sf::Text text;
text.setFont(font);
text.setString("Algorithm: " + algorithmName);
text.setCharacterSize(20);
text.setFillColor(sf::Color::Black);
text.setPosition(10, GRID_ROWS * CELL_SIZE + 10);
window.clear(sf::Color::White);
drawGrid(window);
window.draw(text);
window.display();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
void animatePath(sf::RenderWindow& window, const vector<pair<int, int>>& path, const sf::Color& color) {
for (auto pos : path) {
int row = pos.first;
int col = pos.second;
window.clear(sf::Color::White);
drawGrid(window);
sf::RectangleShape startCell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
startCell.setPosition(start.second * CELL_SIZE, start.first * CELL_SIZE);
startCell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Blue);
window.draw(startCell);
sf::RectangleShape goalCell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
goalCell.setPosition(goal.second * CELL_SIZE, goal.first * CELL_SIZE);
goalCell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Red);
window.draw(goalCell);
sf::RectangleShape cell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
cell.setPosition(col * CELL_SIZE, row * CELL_SIZE);
cell.setFillColor(color);
cell.setOutlineThickness(1);
cell.setOutlineColor(sf::Color(200, 200, 200));
window.draw(cell);
window.display();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
int main() {
grid = generateRandomMap(GRID_ROWS, GRID_COLS, OBSTACLE_COUNT);
if (grid[start.first][start.second] == 1 || grid[goal.first][goal.second] == 1) {
cout << "Error: Start or Goal position is blocked!" << endl;
return 1;
}
cout << "Generated Map:" << endl;
for (const auto& row : grid) {
for (const auto& cell : row) {
cout << (cell == 1 ? '#' : '.') << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
sf::RenderWindow window(sf::VideoMode(GRID_COLS * CELL_SIZE, GRID_ROWS * CELL_SIZE + 50), "Pathfinding Visualization");
auto startTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
vector<pair<int, int>> jpsPath = jps(grid, start, goal);
auto endTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto jpsDuration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(endTime - startTime).count();
cout << "JPS 경로 길이: " << jpsPath.size() << ", 실행 시간: " << jpsDuration / 1000.0 << " ms" << endl;
startTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
vector<pair<int, int>> dijkstraPath = dijkstra(grid, start, goal);
endTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto dijkstraDuration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(endTime - startTime).count();
cout << "Dijkstra 경로 길이: " << dijkstraPath.size() << ", 실행 시간: " << dijkstraDuration / 1000.0 << " ms" << endl;
startTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
vector<pair<int, int>> aStarPath = astar(grid, start, goal);
endTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto aStarDuration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(endTime - startTime).count();
cout << "A* 경로 길이: " << aStarPath.size() << ", 실행 시간: " << aStarDuration / 1000.0 << " ms" << endl;
while (window.isOpen()) {
sf::Event event;
while (window.pollEvent(event)) {
if (event.type == sf::Event::Closed) {
window.close();
}
}
displayAlgorithmName(window, "Dijkstra");
animatePath(window, dijkstraPath, sf::Color::Yellow);
displayAlgorithmName(window, "A*");
animatePath(window, aStarPath, sf::Color::Cyan);
displayAlgorithmName(window, "JPS");
animatePath(window, jpsPath, sf::Color::Green);
break; // 애니메이션 실행 후 종료
}
return 0;
}코드 실행
실행 명령어
g++ -std=c++17 main_compare.cpp JPS.cpp Dijkstra.cpp Astar.cpp -o Pathfinding_compare -lsfml-graphics -lsfml-window -lsfml-system
./Pathfinding_compare실행 결과

노란색 : Dijkstra, 하늘색 : A*, 초록색 : JPS
JPS 경로 길이: 27, 실행 시간: 1.416 ms
Dijkstra 경로 길이: 59, 실행 시간: 1.022 ms
A* 경로 길이: 31, 실행 시간: 0.545 ms실행 결과를 보면, A* 알고리즘의 경우에는 대각선으로 가로막힌 장애물 사이를 뚫고 지나간다. A* 알고리즘을 처음 구현할 때는, 2D 그리드에서 구현한 것이 아니었기 때문에, 대각선 방향의 목표 지점이 장애물이 아니면 이동이 가능한 것으로 작성했기 때문이다.
2D 맵상에서 NPC가 장애물을 뚫고 지나가는 일이 발생하는 것은 있을 수 없는 일이고, 다른 알고리즘과의 정확한 비교를 위해서는 대각선 로직을 추가하는 것이 좋다고 생각되었다.
A* 알고리즘 로직 수정
기존 A* 알고리즘 코드
for (const auto& direction : directions) {
int new_row = current_node.first + direction.first;
int new_col = current_node.second + direction.second;
// 맵 경계 및 장애물 체크
if (new_row < 0 || new_col < 0 || new_row >= rows || new_col >= cols || grid[new_row][new_col] == 1) {
continue;
}
// g-cost 계산
double new_g_cost = g_costs[current_node] + (abs(direction.first) + abs(direction.second) == 2 ? sqrt(2) : 1);
if (g_costs.find({new_row, new_col}) == g_costs.end() || new_g_cost < g_costs[{new_row, new_col}]) {
g_costs[{new_row, new_col}] = new_g_cost;
double f_cost = new_g_cost + heuristic({new_row, new_col}, goal);
pq.push({f_cost, {new_row, new_col}});
came_from[{new_row, new_col}] = current_node;
}
}수정된 A* 알고리즘
for (const auto& direction : directions) {
int new_row = current_node.first + direction.first;
int new_col = current_node.second + direction.second;
// 맵 경계 및 장애물 체크
if (new_row < 0 || new_col < 0 || new_row >= rows || new_col >= cols || grid[new_row][new_col] == 1) {
continue;
}
// === 대각선 이동 시 중간 장애물 체크 ===
if (abs(direction.first) == 1 && abs(direction.second) == 1) { // 대각선 방향
int intermediate_row = current_node.first + direction.first; // 세로 이동
int intermediate_col = current_node.second; // 가로 이동
int intermediate_col_alt = current_node.second + direction.second; // 대각선 이동의 두 경로
if (grid[intermediate_row][current_node.second] == 1 && grid[current_node.first][intermediate_col_alt] == 1) {
continue; // 중간 장애물이 있으면 대각선 이동 차단
}
}
// g-cost 계산
double new_g_cost = g_costs[current_node] + (abs(direction.first) + abs(direction.second) == 2 ? sqrt(2) : 1);
if (g_costs.find({new_row, new_col}) == g_costs.end() || new_g_cost < g_costs[{new_row, new_col}]) {
g_costs[{new_row, new_col}] = new_g_cost;
double f_cost = new_g_cost + heuristic({new_row, new_col}, goal);
pq.push({f_cost, {new_row, new_col}});
came_from[{new_row, new_col}] = current_node;
}
}수정 후

노란색 : Dijkstra, 하늘색 : A*, 초록색 : JPS
JPS 경로 길이: 30, 실행 시간: 0.771 ms
Dijkstra 경로 길이: 59, 실행 시간: 1.054 ms
A* 경로 길이: 32, 실행 시간: 0.911 ms이제 A* 알고리즘에서도 대각선 방향을 그냥 통과해버리지 않고 비켜간다.
메모리 사용량 비교
각 알고리즘을 애니메이션으로 비교해보았고, 경로 길이와 실행 시간도 비교해보았다.
이번에는 각 알고리즘의 메모리 사용량도 비교해보려고 한다.
main_compare.cpp를 이렇게 수정했다.
-
메모리 사용량 출력 추가 :
printMemoryUsage함수 추가.- 알고리즘 실행 후 메모리 사용량 출력.
-
알고리즘 실행 코드 정리 :
executeAlgorithm함수로 중복 로직 통합.- 실행 시간 측정, 경로 길이 출력, 애니메이션까지 하나의 함수에서 처리.
-
애니메이션 전 알고리즘 이름 출력
- displayAlgorithmName 함수 호출로 화면에 알고리즘 이름 표시.
#include "Dijkstra.h"
#include "Astar.h"
#include "JPS.h"
#include <SFML/Graphics.hpp>
#include <vector>
#include <thread>
#include <chrono>
#include <iostream>
#include <cstdlib>
#include <ctime>
#include <sys/resource.h>
using namespace std;
const int CELL_SIZE = 20;
const int GRID_ROWS = 30;
const int GRID_COLS = 30;
const int OBSTACLE_COUNT = 100;
vector<vector<int>> grid;
pair<int, int> start = {0, 0};
pair<int, int> goal = {29, 29};
void printMemoryUsage(const std::string& algorithmName) {
struct rusage usage;
getrusage(RUSAGE_SELF, &usage);
std::cout << algorithmName << " Memory usage: " << usage.ru_maxrss / 1024.0 << " MB" << std::endl;
}
// 랜덤 맵 생성 함수
vector<vector<int>> generateRandomMap(int rows, int cols, int obstacleCount) {
vector<vector<int>> grid(rows, vector<int>(cols, 0));
srand(time(0));
while (obstacleCount > 0) {
int r = rand() % rows;
int c = rand() % cols;
if (grid[r][c] == 0) {
grid[r][c] = 1;
--obstacleCount;
}
}
grid[start.first][start.second] = 0;
grid[goal.first][goal.second] = 0;
return grid;
}
void drawGrid(sf::RenderWindow& window) {
for (int row = 0; row < GRID_ROWS; ++row) {
for (int col = 0; col < GRID_COLS; ++col) {
sf::RectangleShape cell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
cell.setPosition(col * CELL_SIZE, row * CELL_SIZE);
if (grid[row][col] == 1) {
cell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Black);
} else {
cell.setFillColor(sf::Color::White);
}
cell.setOutlineThickness(1);
cell.setOutlineColor(sf::Color(200, 200, 200));
window.draw(cell);
}
}
}
void displayAlgorithmName(sf::RenderWindow& window, const string& algorithmName) {
sf::Font font;
if (!font.loadFromFile("Arial Unicode.ttf")) {
cout << "Failed to load font!" << endl;
return;
}
sf::Text text;
text.setFont(font);
text.setString("Algorithm: " + algorithmName);
text.setCharacterSize(20);
text.setFillColor(sf::Color::Black);
text.setPosition(10, GRID_ROWS * CELL_SIZE + 10);
window.clear(sf::Color::White);
drawGrid(window);
window.draw(text);
window.display();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::seconds(1));
}
void animatePath(sf::RenderWindow& window, const vector<pair<int, int>>& path, const sf::Color& color) {
for (auto pos : path) {
int row = pos.first;
int col = pos.second;
window.clear(sf::Color::White);
drawGrid(window);
sf::RectangleShape startCell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
startCell.setPosition(start.second * CELL_SIZE, start.first * CELL_SIZE);
startCell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Blue);
window.draw(startCell);
sf::RectangleShape goalCell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
goalCell.setPosition(goal.second * CELL_SIZE, goal.first * CELL_SIZE);
goalCell.setFillColor(sf::Color::Red);
window.draw(goalCell);
sf::RectangleShape cell(sf::Vector2f(CELL_SIZE, CELL_SIZE));
cell.setPosition(col * CELL_SIZE, row * CELL_SIZE);
cell.setFillColor(color);
cell.setOutlineThickness(1);
cell.setOutlineColor(sf::Color(200, 200, 200));
window.draw(cell);
window.display();
this_thread::sleep_for(chrono::milliseconds(100));
}
}
// === 알고리즘 실행 및 결과 출력 함수 ===
vector<pair<int, int>> executeAlgorithm(
const string& algorithmName,
vector<pair<int, int>> (*algorithm)(const vector<vector<int>>&, pair<int, int>, pair<int, int>),
sf::Color pathColor,
sf::RenderWindow& window
) {
// 알고리즘 실행
auto startTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
vector<pair<int, int>> path = algorithm(grid, start, goal);
auto endTime = chrono::high_resolution_clock::now();
auto duration = chrono::duration_cast<chrono::microseconds>(endTime - startTime).count();
// 결과 출력
cout << algorithmName << " 경로 길이: " << path.size()
<< ", 실행 시간: " << duration / 1000.0 << " ms" << endl;
printMemoryUsage(algorithmName);
// 애니메이션 실행
displayAlgorithmName(window, algorithmName);
animatePath(window, path, pathColor);
return path;
}
// === 메인 함수 ===
int main() {
// 랜덤 맵 생성
grid = generateRandomMap(GRID_ROWS, GRID_COLS, OBSTACLE_COUNT);
// 시작점과 목표점 유효성 검사
if (grid[start.first][start.second] == 1 || grid[goal.first][goal.second] == 1) {
cout << "Error: Start or Goal position is blocked!" << endl;
return 1;
}
// 디버깅용: 맵 출력
cout << "Generated Map:" << endl;
for (const auto& row : grid) {
for (const auto& cell : row) {
cout << (cell == 1 ? '#' : '.') << " ";
}
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
// SFML 윈도우 생성
sf::RenderWindow window(sf::VideoMode(GRID_COLS * CELL_SIZE, GRID_ROWS * CELL_SIZE + 50), "Pathfinding Visualization");
while (window.isOpen()) {
sf::Event event;
while (window.pollEvent(event)) {
if (event.type == sf::Event::Closed) {
window.close();
}
}
// 알고리즘 실행 및 시각화
executeAlgorithm("Dijkstra", dijkstra, sf::Color::Yellow, window);
executeAlgorithm("A*", astar, sf::Color::Cyan, window);
executeAlgorithm("JPS", jps, sf::Color::Green, window);
break; // 애니메이션 실행 후 종료
}
return 0;
}실행 결과
결과 로그
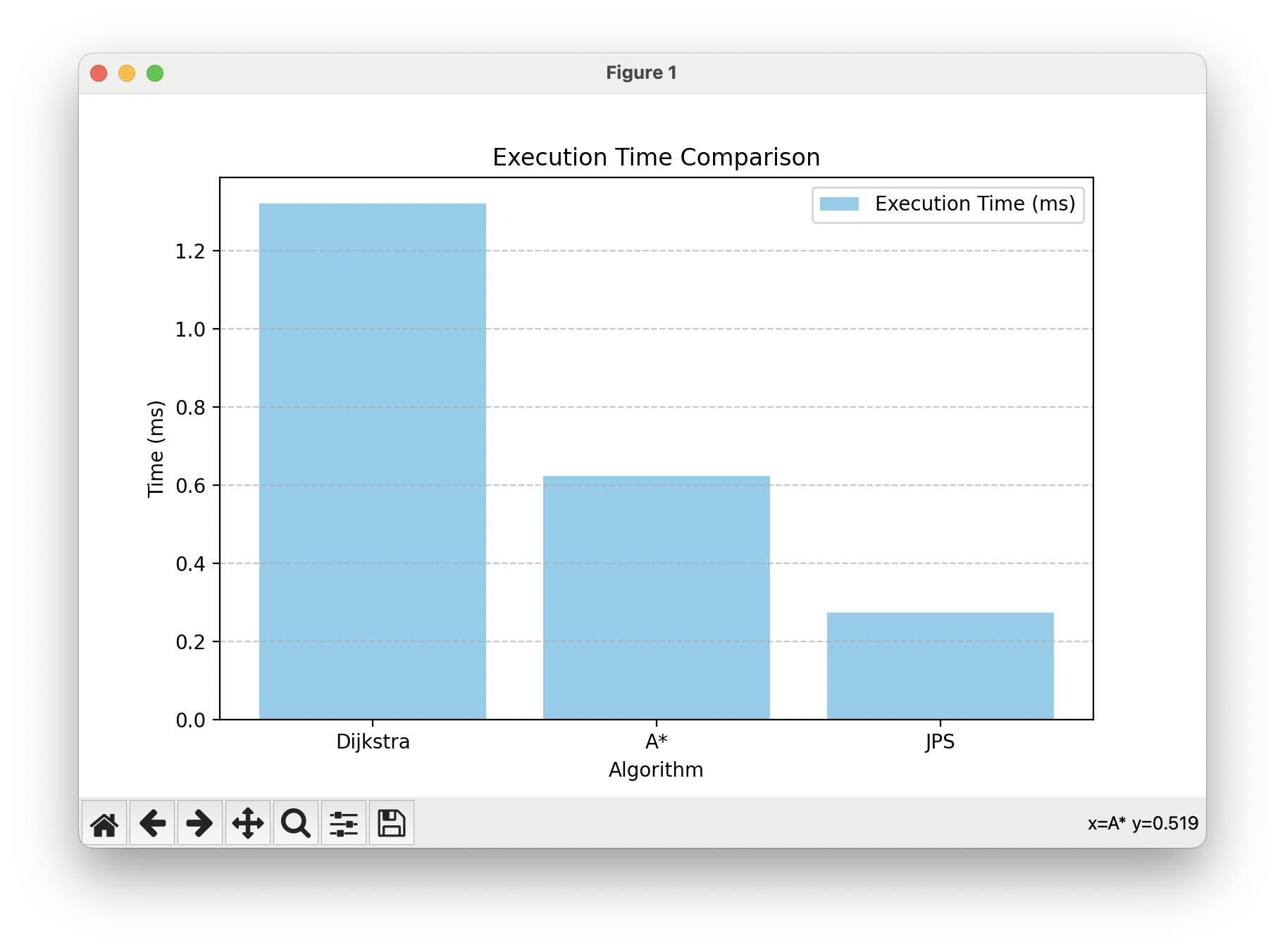
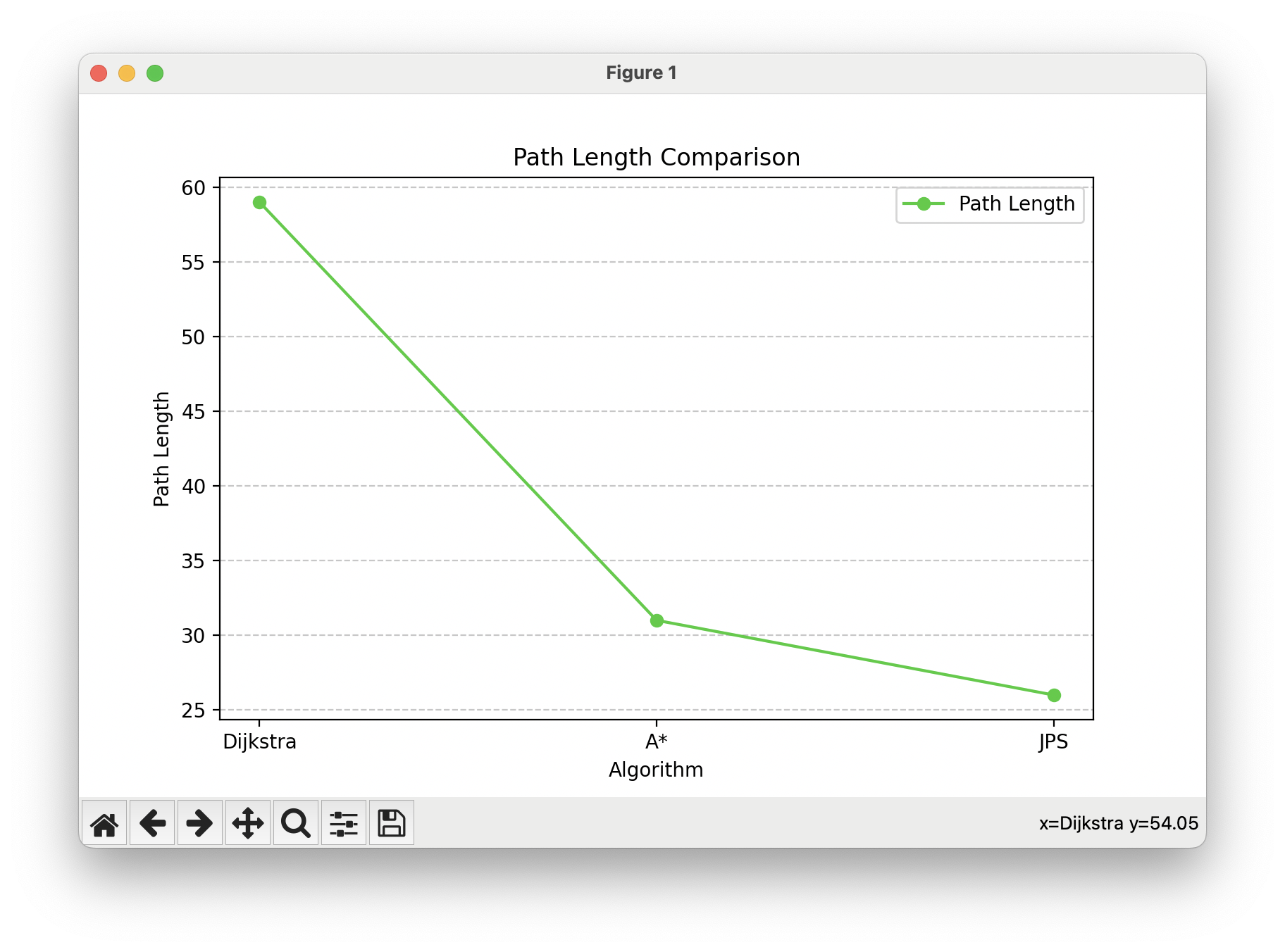
Dijkstra 경로 길이: 59, 실행 시간: 1.321 ms
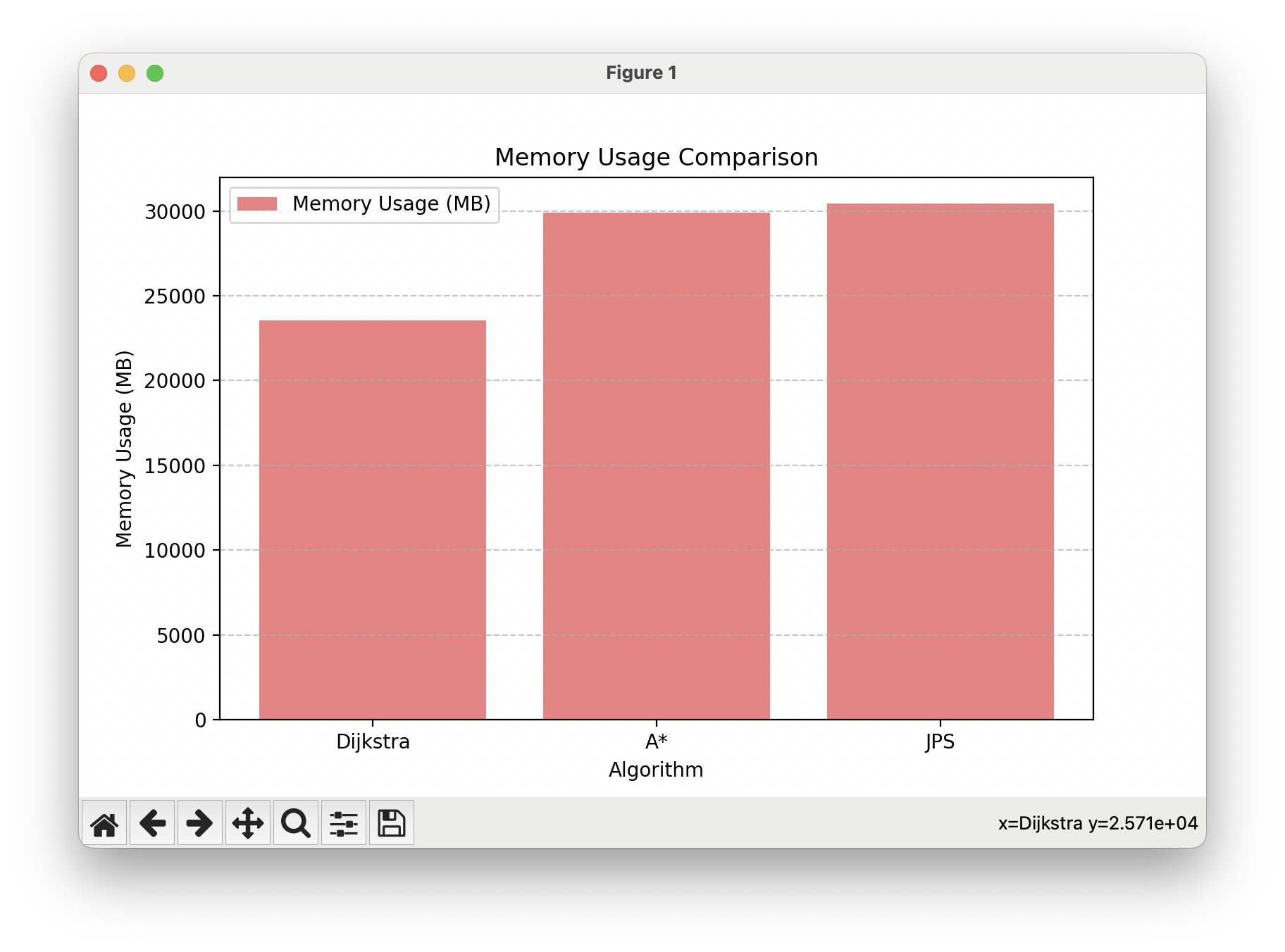
Dijkstra Memory usage: 23532 MB
A* 경로 길이: 31, 실행 시간: 0.624 ms
A* Memory usage: 29888 MB
JPS 경로 길이: 26, 실행 시간: 0.273 ms
JPS Memory usage: 30456 MB표로 정리
| 알고리즘 | 경로 길이 | 실행 시간 (ms) | 메모리 사용량 (MB) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Dijkstra | 59 | 1.321 | 23532 |
| A* | 31 | 0.624 | 29888 |
| JPS | 26 | 0.273 | 30456 |
그래프로 정리
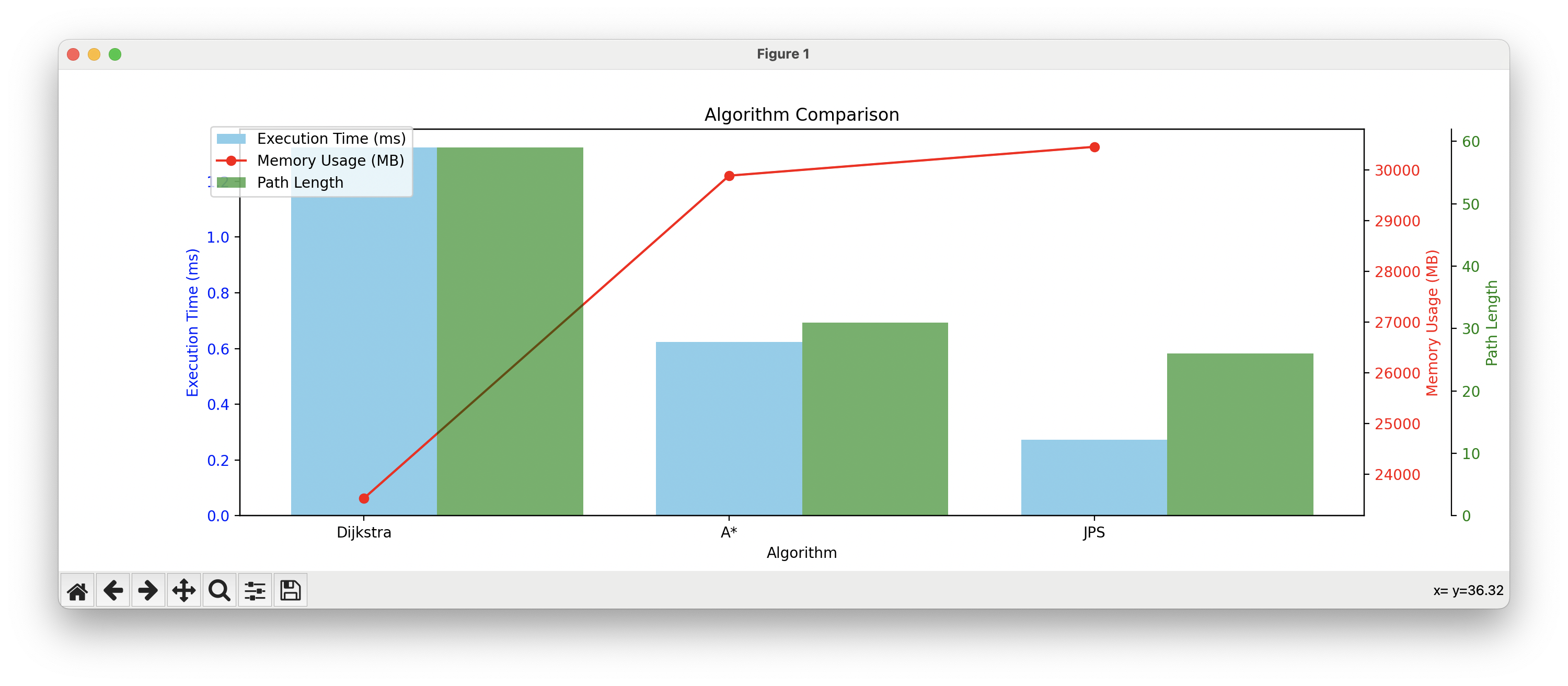
비교 결과
1. 경로 길이
- JPS (26) : 가장 짧은 경로를 찾았음. 이는 JPS가 불필요한 경로 탐색을 생략하며 최적화된 경로를 찾는 데 강점이 있음을 보여준다.
- A* (31) : JPS보다는 길지만 Dijkstra보다는 더 짧은 경로를 발견했다. 이는 A의 휴리스틱 기능이 경로 길이를 줄이는 데 기여했음을 나타낸다.
- Dijkstra (59) : 가장 긴 경로를 찾았다. 이는 Dijkstra가 휴리스틱을 사용하지 않고 모든 경로를 탐색하기 때문에 발생한 결과로 볼 수 있다.
분석
JPS는 최적의 경로를 가장 효과적으로 찾았으며, A*도 충분히 최적화된 경로를 제공했다. 반면 Dijkstra는 정확하지만 덜 효율적이다.
2. 실행 시간
- JPS (0.273 ms) : 가장 빠른 실행 시간을 기록. 이는 JPS가 휴리스틱을 활용하고 대각선으로 빠르게 탐색하며, Jump Point를 이용해 중간 불필요한 노드를 제거했기 때문이다.
- A* (0.624 ms) : 두 번째로 빠르다. A는 대각선 이동을 포함하며 효율적인 탐색을 하지만, JPS에 비해 탐색 경로 최적화가 덜 효과적이다.
- Dijkstra (1.321 ms) : 가장 느림. 이는 Dijkstra가 휴리스틱 없이 모든 경로를 완전 탐색하기 때문이다.
분석
JPS는 실행 시간 면에서 압도적으로 효율적이며, A*도 상당히 빠르다. 반면 Dijkstra는 시간 효율성이 낮다.
3. 메모리 사용량
- Dijkstra (23,532 MB) : 가장 적은 메모리를 사용했다. 이는 Dijkstra가 모든 노드를 탐색하더라도, 추가적인 휴리스틱 정보나 점프 노드를 관리하지 않기 때문이다.
- A* (29,888 MB) : 두 번째로 높은 메모리를 사용했다. 이는 휴리스틱 값을 계산하고 저장하는 데 필요한 메모리 때문이다.
- JPS (30,456 MB) : 가장 높은 메모리를 사용했다. JPS는 점프 노드와 대각선 탐색 관련 추가적인 데이터 구조를 관리하기 때문에 메모리 사용량이 가장 많았다.
분석
메모리 사용량 면에서는 Dijkstra가 가장 효율적이며, A*와 JPS는 메모리 사용량이 상대적으로 높았다. 특히 JPS는 가장 많은 메모리를 사용했다.
종합하면
- JPS는 가장 짧은 경로를 가장 빠르게 탐색하지만, 메모리 사용량은 가장 높다. 메모리 여유가 있는 환경에서 최적의 알고리즘이 될 것이다.
- A*는 균형 잡힌 성능을 보여준다. 실행 시간과 메모리 사용량이 중간 수준이며, 경로 최적화도 잘 수행하는 편이다.
- Dijkstra는 메모리 효율적이지만, 경로 길이가 길고 실행 시간이 느리다. 메모리 제약이 클 때 적합한 선택일 수 있다.
