1. Stanley Method란?
-
2005년 Darpa Grand Challenge에서 우승을 차지한 Standford University 팀이 사용한 사용한 Contoller
-
Pure pursuit과는 다르게 앞바퀴를 reference point로 잡음
-
Cross track Error와 heading error 를 고려하여 제어를 한다.
2. Formulation
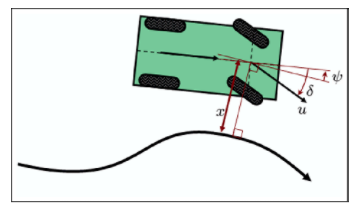
-
는 heading error를 잡아주고, 는 CTR 를 잡아주는 역할
-
속도가 낮을 경우를 보정하기 위해 다음과 같이 를 추가할 수도 있음.
3. 예시
- heading error가 클시
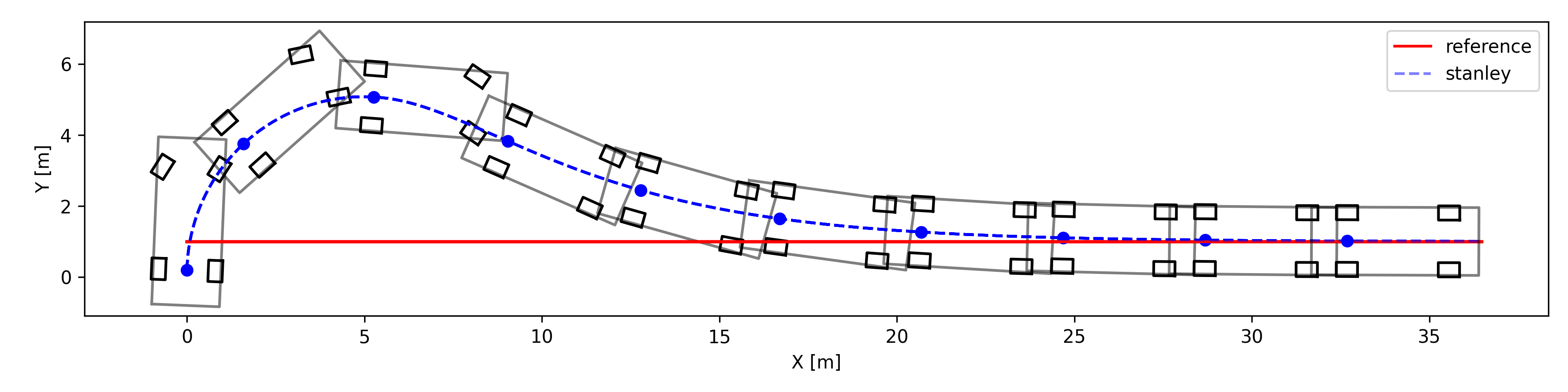
- CTR이 클시
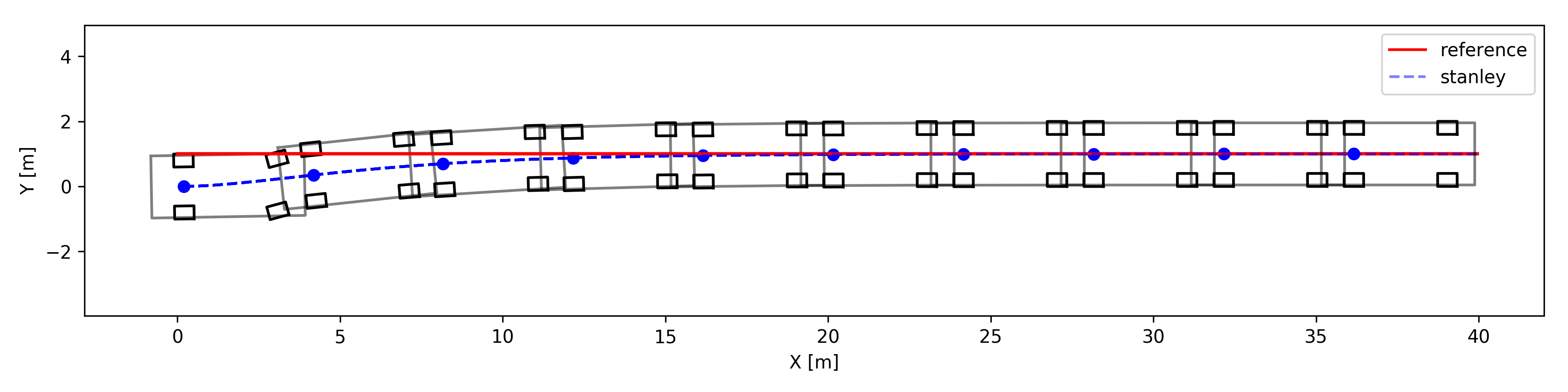
4. 파이썬 구현
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
# paramters
dt = 0.1
k = 0.5 # control gain
# GV70 PARAMETERS
LENGTH = 4.715
WIDTH = 1.910
L = 2.875
BACKTOWHEEL = 1.0
WHEEL_LEN = 0.3 # [m]
WHEEL_WIDTH = 0.2 # [m]
TREAD = 0.8 # [m]
class VehicleModel(object):
def __init__(self, x=0.0, y=0.0, yaw=0.0, v=0.0):
self.x = x
self.y = y
self.yaw = yaw
self.v = v
self.max_steering = np.radians(30)
def update(self, steer, a=0):
steer = np.clip(steer, -self.max_steering, self.max_steering)
self.x += self.v * np.cos(self.yaw) * dt
self.y += self.v * np.sin(self.yaw) * dt
self.yaw += self.v / L * np.tan(steer) * dt
self.yaw = self.yaw % (2.0 * np.pi)
self.v += a * dt
def normalize_angle(angle):
while angle > np.pi:
angle -= 2.0 * np.pi
while angle < -np.pi:
angle += 2.0 * np.pi
return angle
def stanley_control(x, y, yaw, v, map_xs, map_ys, map_yaws):
# find nearest point
min_dist = 1e9
min_index = 0
n_points = len(map_xs)
front_x = x + L * np.cos(yaw)
front_y = y + L * np.sin(yaw)
for i in range(n_points):
dx = front_x - map_xs[i]
dy = front_y - map_ys[i]
dist = np.sqrt(dx * dx + dy * dy)
if dist < min_dist:
min_dist = dist
min_index = i
# compute cte at front axle
map_x = map_xs[min_index]
map_y = map_ys[min_index]
map_yaw = map_yaws[min_index]
dx = map_x - front_x
dy = map_y - front_y
perp_vec = [np.cos(yaw + np.pi/2), np.sin(yaw + np.pi/2)]
cte = np.dot([dx, dy], perp_vec)
# control law
yaw_term = normalize_angle(map_yaw - yaw)
cte_term = np.arctan2(k*cte, v)
# steering
steer = yaw_term + cte_term
return steer
# map
target_y = 1.0
map_xs = np.linspace(0, 500, 500)
map_ys = np.ones_like(map_xs) * target_y
map_yaws = np.ones_like(map_xs) * 0.0
# vehicle
model = VehicleModel(x=0.0, y=0.0, yaw=0.0, v=2.0)
steer = 0
xs = []
ys = []
yaws = []
steers = []
ts = []
for step in range(200):
# plt.clf()
t = step * dt
steer = stanley_control(model.x, model.y, model.yaw, model.v, map_xs, map_ys, map_yaws)
steer = np.clip(steer, -model.max_steering, model.max_steering)
model.update(steer)
xs.append(model.x)
ys.append(model.y)
yaws.append(model.yaw)
ts.append(t)
steers.append(steer)
# plot car
plt.figure(figsize=(12, 3))
plt.plot([0, xs[-1]], [target_y, target_y], 'r-', label="reference")
plt.plot(xs, ys, 'b--', alpha=0.5, label="stanley")
for i in range(len(xs)):
# plt.clf()
if i % 20 == 0:
plt.plot([0, xs[-1]], [target_y, target_y], 'r-')
plt.plot(xs, ys, 'b--', alpha=0.5)
x = xs[i]
y = ys[i]
yaw = yaws[i]
steer = steers[i]
outline = np.array([[-BACKTOWHEEL, (LENGTH - BACKTOWHEEL), (LENGTH - BACKTOWHEEL), -BACKTOWHEEL, -BACKTOWHEEL],
[WIDTH / 2, WIDTH / 2, - WIDTH / 2, -WIDTH / 2, WIDTH / 2]])
fr_wheel = np.array([[WHEEL_LEN, -WHEEL_LEN, -WHEEL_LEN, WHEEL_LEN, WHEEL_LEN],
[-WHEEL_WIDTH, -WHEEL_WIDTH, WHEEL_WIDTH, WHEEL_WIDTH, -WHEEL_WIDTH]])
rr_wheel = np.copy(fr_wheel)
fl_wheel = np.copy(fr_wheel)
rl_wheel = np.copy(rr_wheel)
Rot1 = np.array([[np.cos(yaw), np.sin(yaw)],
[-np.sin(yaw), np.cos(yaw)]])
Rot2 = np.array([[np.cos(steer+yaw), np.sin(steer+yaw)],
[-np.sin(steer+yaw), np.cos(steer+yaw)]])
fr_wheel = (fr_wheel.T.dot(Rot2)).T
fl_wheel = (fl_wheel.T.dot(Rot2)).T
fr_wheel[0, :] += L * np.cos(yaw) - TREAD * np.sin(yaw)
fl_wheel[0, :] += L * np.cos(yaw) + TREAD * np.sin(yaw)
fr_wheel[1, :] += L * np.sin(yaw) + TREAD * np.cos(yaw)
fl_wheel[1, :] += L * np.sin(yaw) - TREAD * np.cos(yaw)
rr_wheel[1, :] += TREAD
rl_wheel[1, :] -= TREAD
outline = (outline.T.dot(Rot1)).T
rr_wheel = (rr_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
rl_wheel = (rl_wheel.T.dot(Rot1)).T
outline[0, :] += x
outline[1, :] += y
fr_wheel[0, :] += x
fr_wheel[1, :] += y
rr_wheel[0, :] += x
rr_wheel[1, :] += y
fl_wheel[0, :] += x
fl_wheel[1, :] += y
rl_wheel[0, :] += x
rl_wheel[1, :] += y
plt.plot(np.array(outline[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(outline[1, :]).flatten(), 'k-', alpha=0.5)
plt.plot(np.array(fr_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(fr_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), 'k-')
plt.plot(np.array(rr_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(rr_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), 'k-')
plt.plot(np.array(fl_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(fl_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), 'k-')
plt.plot(np.array(rl_wheel[0, :]).flatten(),
np.array(rl_wheel[1, :]).flatten(), 'k-')
plt.plot(x, y, "bo")
plt.axis("equal")
# plt.pause(0.1)
plt.xlabel("X [m]")
plt.ylabel("Y [m]")
plt.legend(loc="best")
plt.tight_layout()
plt.savefig("stanley_method.png", dpi=300)
plt.show()