해당 글은 FastCampus - '[skill-up] 처음부터 시작하는 딥러닝 유치원 강의를 듣고,
추가 학습한 내용을 덧붙여 작성하였습니다.
1. Gradient Descent vs Stochastic Gradient Descent
1.1 Gradient Descent (GD)
- 전체 데이터셋의 Loss를 기반으로 파라미터 1회 업데이트
- 정확한 gradient 방향이지만 계산량이 매우 큼
- 실제로 N의 크기가 매우 크면 OOM 에러 날 것
1.2 Stochastic Gradient Descent (SGD)
- 무작위로 선택된 K개의 샘플(mini-batch)에 대한 Loss로 파라미터를 여러번 업데이트
- 계산량이 작고 빠르지만, gradient는 noisy할 수 있음
- Stochastic(확률론적) ↔ Deterministic(결정론적)
1.3 SGD의 특성
- 각 미니배치 gradient는 전체 gradient와 다를 수 있으나, 기대값은 같음
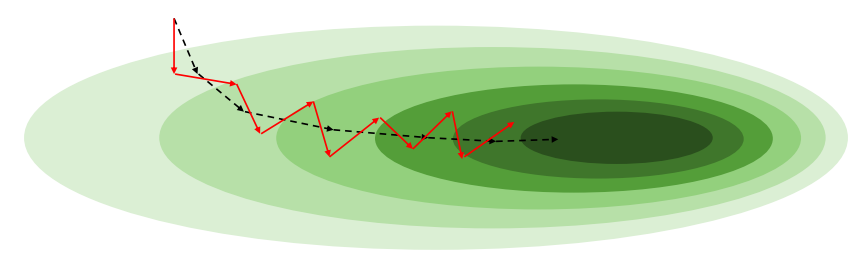
- 미니배치가 작을수록 gradient의 분산이 커짐
- 이로 인해 local minima에서 탈출 가능성이 생기기도 함
- 반면 batch size가 크면 빠른 수렴 가능
- Pytorch에서 optim.SGD는 전체 데이터를 넣으면 GD처럼 작동하고, 미니배치를 넣으면 SGD 또는 Mini-batch GD처럼 작동
2. Epoch과 Iteration
2.1 Epoch
- 전체 데이터셋이 한 번 학습된 횟수 (미니배치를 비복원추출 시 모든 데이터를 학습한 경우)
- 모든 데이터셋의 샘플들이 forward & backward 된 횟수
- Epoch의 시작에 데이터셋을 random shuffling 해준 후, 미니 배치로 나눔
2.2 Iteration
- 한 미니배치가 학습된 횟수
2.3 총 업데이트 횟수
- 파라미터 전체 업데이트 횟수 =
- 이중 for loop이 만들어짐
for epoch_idx in n_epochs:
for iteration_idx in n_iterations:
~~3. Batch Size에 따른 특성
3.1 Full Batch (= 전체 데이터셋 크기)
- 전체 데이터의 분포를 잘 반영한 gradient
- 매우 정확하지만 계산량이 많고 업데이트 횟수가 적음
3.2 Small Batch
- 편향된 gradient를 가질 수 있음
- 오히려 local minima 탈출을 도울 수 있음
- 너무 작으면 gradient가 noisy하여 수렴이 어려워질 수 있음
3.3 적당한 Batch size는?
- 크기의 적절한 batchsize를 사용한다
e.g. 64, 128, 256 - 근데 요즘은 GPU 하드웨어(메모리)의 성능이 뒷받쳐주기 때문에 큰 batch_size를 가져가기도 한다
e.g. 2048, 4096 ,...
4. Pytorch 실습 코드
import pandas as pd
import seaborn as sns
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
from sklearn.preprocessing import StandardScaler
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
import torch.optim as optim
from sklearn.datasets import fetch_california_housing
california = fetch_california_housing()
df = pd.DataFrame(california.data, columns=california.feature_names)
df["Target"] = california.target
# df.tail()
# sns.pairplot(df.sample(1000))
# plt.show()
scaler = StandardScaler()
scaler.fit(df.values[:, :-1])
df.values[:, :-1] = scaler.transform(df.values[:, :-1])
# sns.pairplot(df.sample(1000))
# plt.show()
data = torch.from_numpy(df.values).float()
print(data.shape)
x = data[:, :-1]
y = data[:, -1:]
print(x.shape, y.shape)
n_epochs = 4000
batch_size = 128
print_interval = 200
learning_rate = 1e-5
model = nn.Sequential(
nn.Linear(x.size(-1), 10),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(10, 9),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(9, 8),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(8, 7),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(7, 6),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(6, 5),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(5, 4),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(4, 3),
nn.LeakyReLU(),
nn.Linear(3, y.size(-1)),
)
print(model)
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
# |x| = (total_size, input_dim)
# |y| = (total_size, output_dim)
for i in range(n_epochs):
# the index to feed-forward.
indices = torch.randperm(x.size(0)) # Shuffle
x_ = torch.index_select(x, dim=0, index=indices) # x와 y indices 동일하게 써야 함
y_ = torch.index_select(y, dim=0, index=indices)
x_ = x_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
y_ = y_.split(batch_size, dim=0)
# |x_[i]| = (batch_size, input_dim)
# |y_[i]| = (batch_size, output_dim)
y_hat = []
total_loss = 0
for x_i, y_i in zip(x_, y_):
# |x_i| = |x_[i]|
# |y_i| = |y_[i]|
y_hat_i = model(x_i)
loss = F.mse_loss(y_hat_i, y_i)
optimizer.zero_grad()
loss.backward()
optimizer.step()
total_loss += float(loss) # Gradient graph 끊어짐 → float로 변환해서 memory leak 방지
y_hat += [y_hat_i]
total_loss = total_loss / len(x_)
if (i + 1) % print_interval == 0:
print('Epoch %d: loss=%.4e' % (i + 1, total_loss))
y_hat = torch.cat(y_hat, dim=0)
y = torch.cat(y_, dim=0)
# |y_hat| = (total_size, output_dim)
# |y| = (total_size, output_dim)
df = pd.DataFrame(torch.cat([y, y_hat], dim=1).detach().numpy(),
columns=["y", "y_hat"])
sns.pairplot(df, height=5)
plt.show()