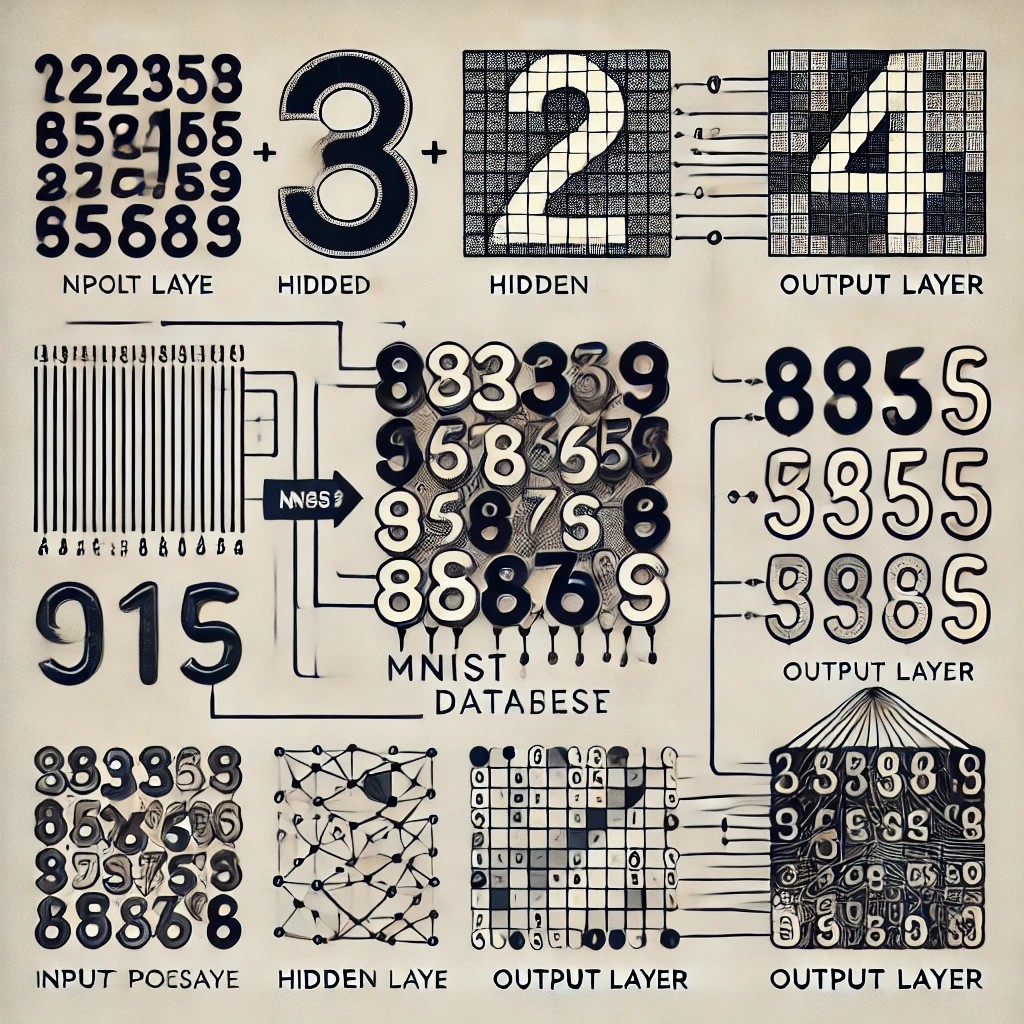
Chapter 4 딥러닝을 이용한 MNIST
MNIST

- 각 픽셀에서 255값이 최댓값이라 0~1사이 값으로 조정
import tensorflow as tf
mnist = tf.keras.datasets.mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = mnist.load_data()
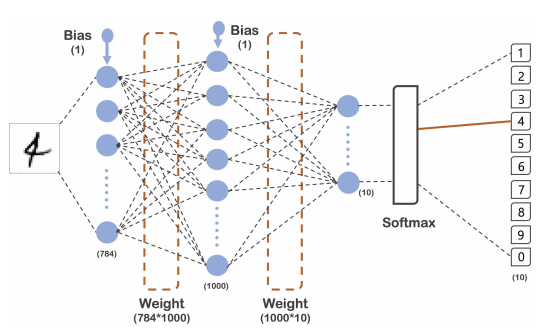
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.0model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1000, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])
model.summary() 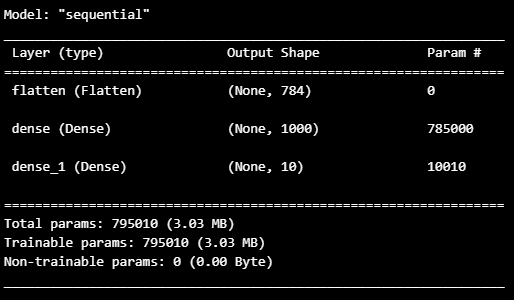
import time
start_time = time.time()
hist = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10,
batch_size=100,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))
print("--- %s seconds ---" % (time.time() - start_time))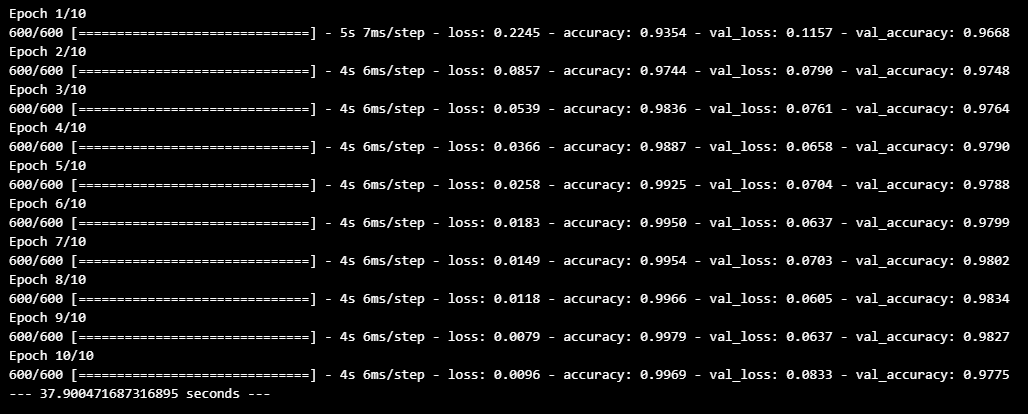
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plot_target = ['loss', 'val_loss', 'accuracy', 'val_accuracy']
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
for each in plot_target:
plt.plot(hist.history[each], label=each)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()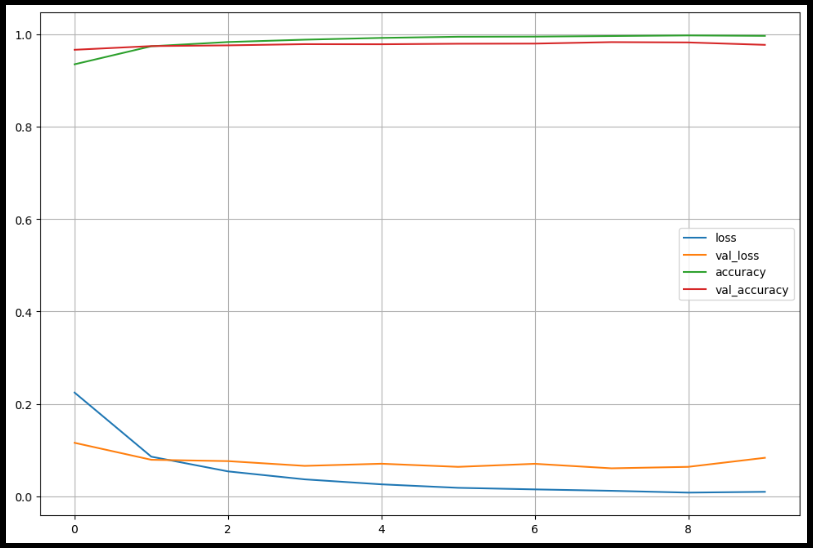
- 틀린 내용 확인
import numpy as np
predicted_result = model.predict(x_test)
predicted_labels = np.argmax(predicted_result, axis=1)
predicted_labels[:10]
wrong_result = []
for n in range(0, len(y_test)):
if predicted_labels[n] != y_test[n]:
wrong_result.append(n)
len(wrong_result)
import random
samples = random.choices(population=wrong_result, k=16)
samples
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
for index, n in enumerate(samples):
plt.subplot(4, 4, index+1)
plt.imshow(x_test[n].reshape(28,28), cmap='Greys')
plt.title('Label : ' + str(y_test[n]) + ', Prediction : ' + str(predicted_labels[n]))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()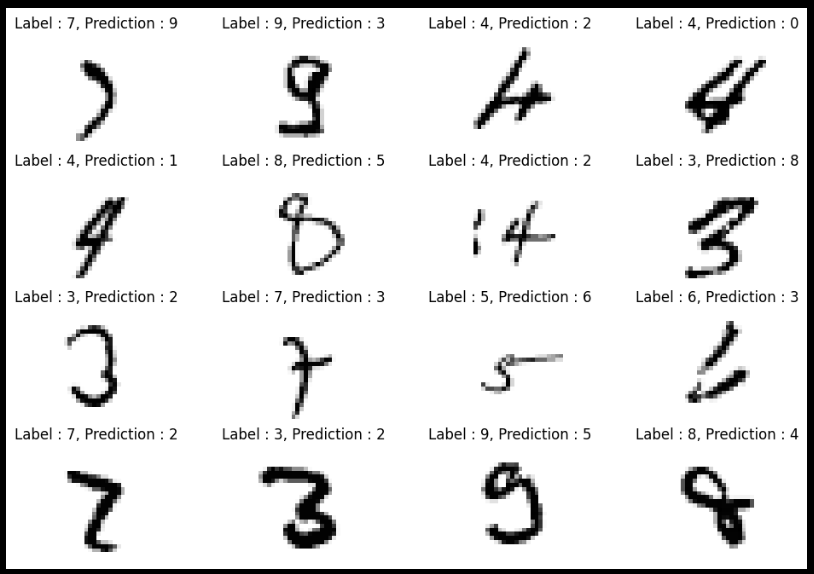
MNIST fashion

import tensorflow as tf
fashion_mnist = tf.keras.datasets.fashion_mnist
(x_train, y_train), (x_test, y_test) = fashion_mnist.load_data()
x_train, x_test = x_train / 255.0, x_test / 255.model = tf.keras.models.Sequential([
tf.keras.layers.Flatten(input_shape=(28, 28)),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(1000, activation='relu'),
tf.keras.layers.Dense(10, activation='softmax')
])
model.compile(optimizer='adam',
loss='sparse_categorical_crossentropy',
metrics=['accuracy'])hist = model.fit(x_train, y_train, epochs=10,
batch_size=100,
validation_data=(x_test, y_test))import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
plot_target = ['loss', 'val_loss', 'accuracy', 'val_accuracy']
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
for each in plot_target:
plt.plot(hist.history[each], label=each)
plt.legend()
plt.grid()
plt.show()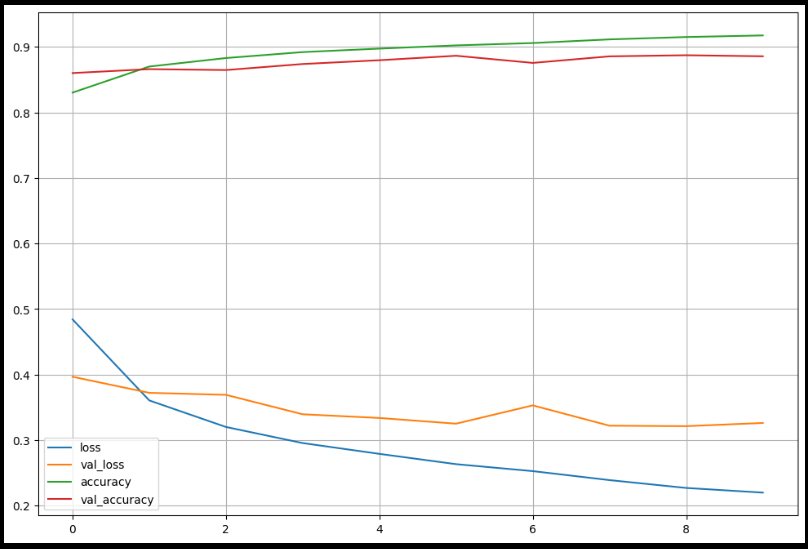
- 틀린 내용 확인
import numpy as np
predicted_result = model.predict(x_test)
predicted_labels = np.argmax(predicted_result, axis=1)
predicted_labels[:10]
wrong_result = []
for n in range(0, len(y_test)):
if predicted_labels[n] != y_test[n]:
wrong_result.append(n)
len(wrong_result)
import random
samples = random.choices(population=wrong_result, k=16)
plt.figure(figsize=(12,8))
for index, n in enumerate(samples):
plt.subplot(4, 4, index+1)
plt.imshow(x_test[n].reshape(28,28), cmap='Greys')
plt.title('Label : ' + str(y_test[n]) + ', Prediction : ' + str(predicted_labels[n]))
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()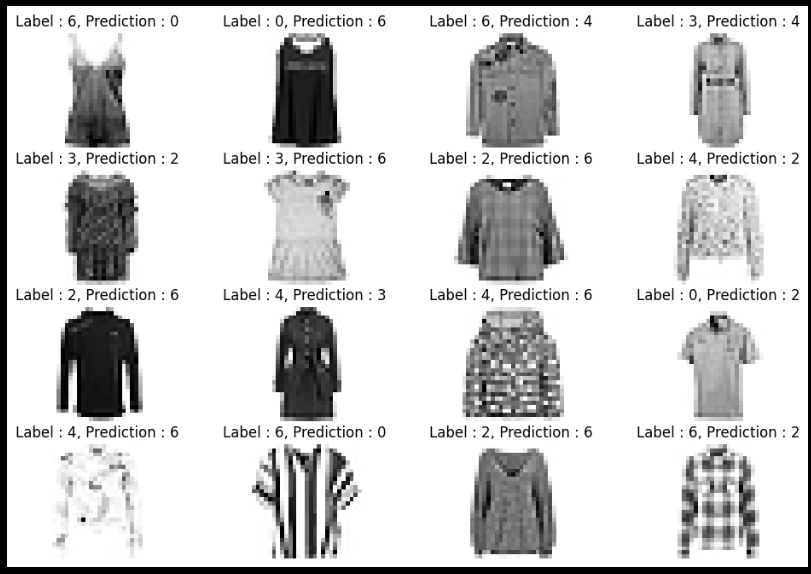
이 글은 제로베이스 데이터 취업 스쿨의 강의 자료 일부를 발췌하여 작성되었습니다