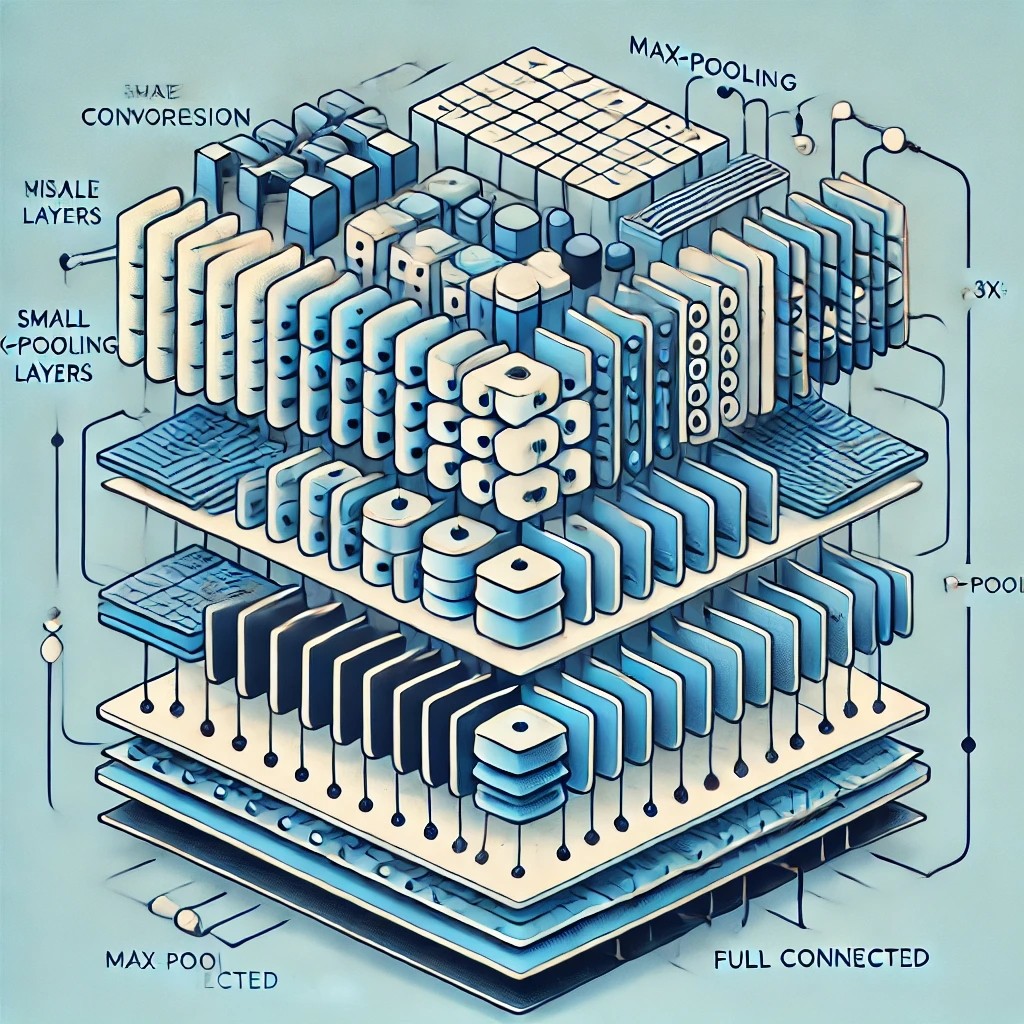
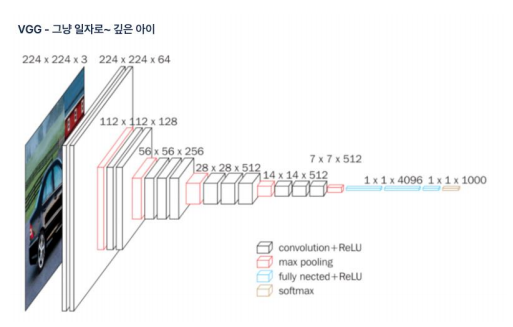
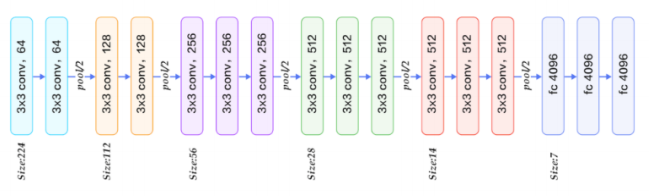
Chapter 8 VGG
import cv2
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import img_to_array
model = VGG16(weights='imagenet')import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
image = cv2.imread('dog.jpg')
plt.imshow(cv2.cvtColor(image, cv2.COLOR_BGR2RGB));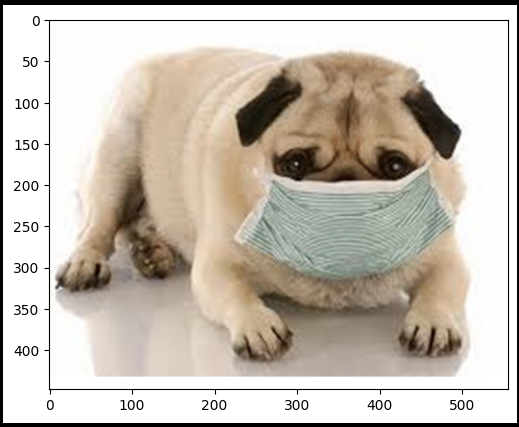
image = cv2.resize(image, (224, 224))
image = img_to_array(image)
image = image.reshape((1, image.shape[0], image.shape[1], image.shape[2]))
image = preprocess_input(image)
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import decode_predictions
yhat = model.predict(image)
label = decode_predictions(yhat)
label = label[0][0]
print(label[1], label[2])decode_predictions(yhat)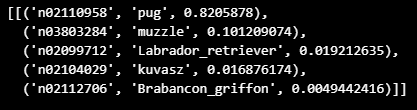
import os
path = './train/'
full_names = os.listdir(path)
labels = [each.split('.')[0] for each in full_names]
file_id = [each.split('.')[1] for each in full_names]
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(224, 224))
image = img_to_array(image)
image = image.reshape((1, image.shape[0], image.shape[1], image.shape[2]))
image = preprocess_input(image)
yhat = model.predict(image)
label = decode_predictions(yhat)
label = label[0][0]
print(label[1], label[2])
def resize_and_preproces_vgg(image):
image = cv2.resize(image, dsize=(224, 224))
image = img_to_array(image)
image = image.reshape((1, image.shape[0], image.shape[1], image.shape[2]))
image = preprocess_input(image)
return image
def predict_vgg(image):
yhat = model.predict(image)
label = decode_predictions(yhat)
return label[0][0][1]
plt.figure(figsize=(14,12))
idx = 1
for each in random.choices(full_names, k=6):
image = mpimg.imread(path+each)
plt.subplot(3, 2, idx)
plt.imshow(image)
idx += 1
image = resize_and_preproces_vgg(image)
print(each)
result = predict_vgg(image)
plt.title(result)
plt.axis('off')
plt.show()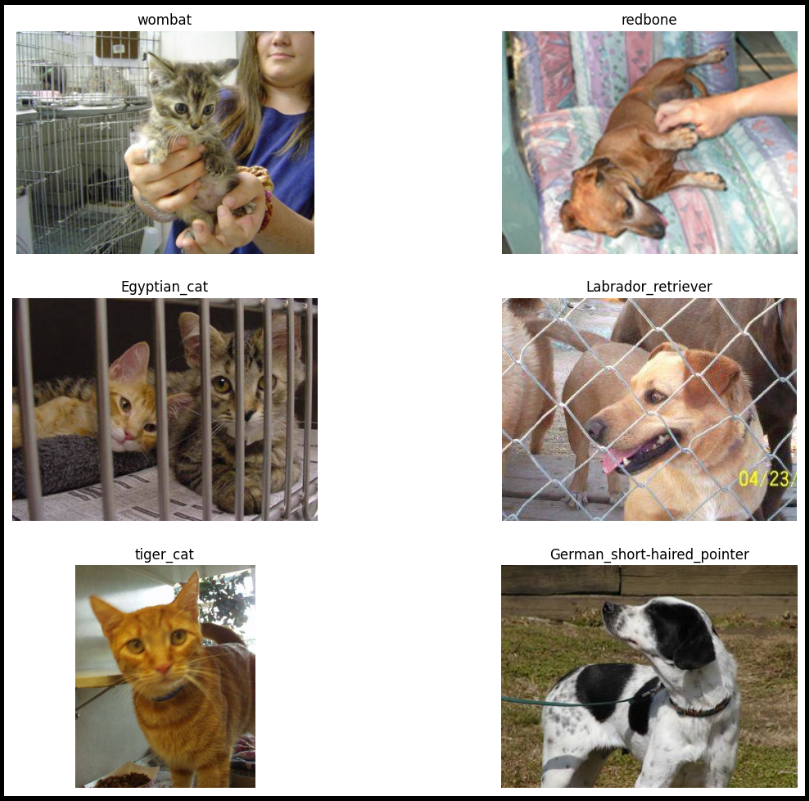 
-
imagenet으로 학습한 VGG net의 라벨은 1000개
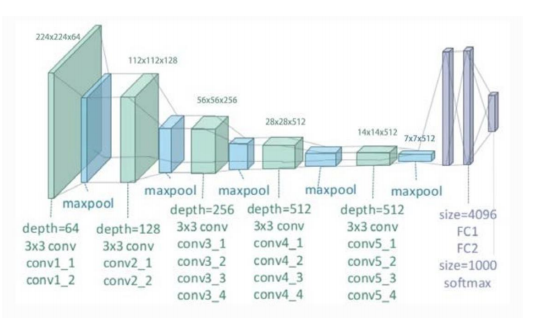
-
출력의 형태를 바꾸기 위해서는 전이학습 활용
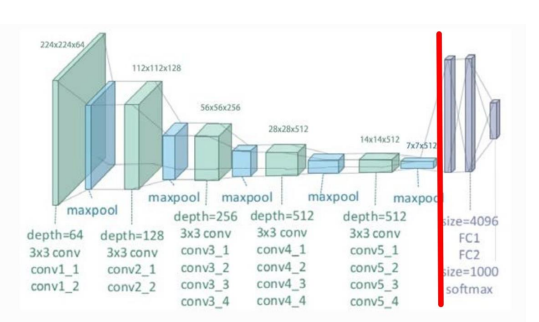
import tensorflow as tf
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
import os
from tensorflow.keras.layers import GlobalAveragePooling2D, Dense, Dropout
from tensorflow.keras.models import Sequential
from tensorflow.keras.applications.vgg16 import VGG16, preprocess_input
from tensorflow.keras.preprocessing.image import ImageDataGenerator
train_df = pd.DataFrame({'file' : os.listdir('./train')})
train_df['label'] = train_df['file'].apply(lambda x: x.split('.')[0])
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
train_data, val_data = train_test_split(train_df, test_size=0.2,
stratify=train_df['label'],
random_state=13)
train_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
rotation_range=15,
horizontal_flip=True,
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input
)
val_datagen = ImageDataGenerator(
preprocessing_function=preprocess_input
)
FILES = './'
batch_size = 16
train_generator = train_datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
dataframe=train_data,
directory=FILES + 'train',
x_col='file',
y_col='label',
class_mode='categorical',
target_size=(224, 224),
batch_size=batch_size,
seed=13,
)
val_generator = val_datagen.flow_from_dataframe(
dataframe=val_data,
directory=FILES + 'train',
x_col='file',
y_col='label',
class_mode='categorical',
target_size=(224, 224),
batch_size=batch_size,
seed=13,
shuffle=False
)base_model = VGG16(
weights='imagenet',
include_top=False,
input_shape=(224, 224, 3)
)
for layers in base_model.layers:
layers.trainable = False
base_model.summary()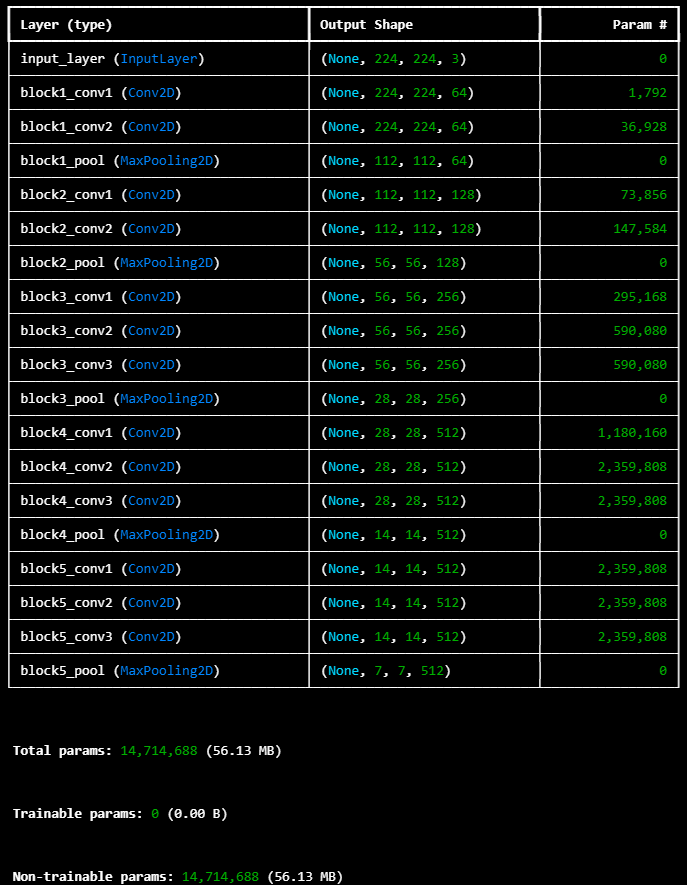
def vgg16_pretrained():
inputs = tf.keras.Input(shape=(224, 224, 3))
x = base_model(inputs)
x = GlobalAveragePooling2D()(x)
x = Dense(100, activation='relu')(x)
x = Dropout(0.5)(x)
x = Dense(64, activation='relu')(x)
outputs = Dense(2, activation='softmax')(x)
model = tf.keras.Model(inputs, outputs)
return model
model = vgg16_pretrained()
model.summary()
model.compile(
loss = 'categorical_crossentropy',
optimizer = 'adam',
metrics = ['accuracy']
)
reduce_lr = tf.keras.callbacks.ReduceLROnPlateau(
monitor='val_loss', factor=0.2,
patience=3, min_lr=0.0001)
early_stop = tf.keras.callbacks.EarlyStopping(
monitor='val_loss', patience=3,
)
check_point = tf.keras.callbacks.ModelCheckpoint(
monitor = 'val_accuracy',
filepath = './vgg16_pretrained.weights.h5',
save_best_only=True,
save_weights_only=True
)
history = model.fit(
train_generator,
validation_data=val_generator,
epochs=5,
callbacks=[reduce_lr, early_stop, check_point]
)import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import seaborn as sns
fig, axes = plt.subplots(1, 2, figsize = (12, 4))
sns.lineplot(x = range(len(history.history["loss"])),
y = history.history["loss"], ax = axes[0],
label = "Training Loss")
sns.lineplot(x = range(len(history.history["loss"])),
y = history.history["val_loss"], ax = axes[0],
label = "Validation Loss")
sns.lineplot(x = range(len(history.history["accuracy"])),
y = history.history["accuracy"], ax = axes[1],
label = "Training Accuracy")
sns.lineplot(x = range(len(history.history["accuracy"])),
y = history.history["val_accuracy"], ax = axes[1],
label = "Validation Accuracy")
axes[0].set_title("Loss"); axes[1].set_title("Accuracy")
sns.despine()
plt.show()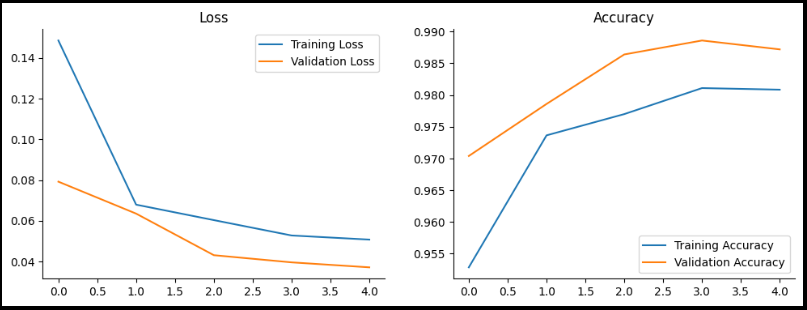
from sklearn.metrics import confusion_matrix
from sklearn.metrics import ConfusionMatrixDisplay
fig, ax = plt.subplots(figsize=(10, 10))
cm = confusion_matrix(val_data['label'], val_data['val_pred'])
#disp = confusion_matrix(val_data['label'], val_data['val_pred'])
disp = ConfusionMatrixDisplay(confusion_matrix=cm, display_labels=labels.values())
disp.plot(cmap=plt.cm.Blues, ax=ax)
plt.show()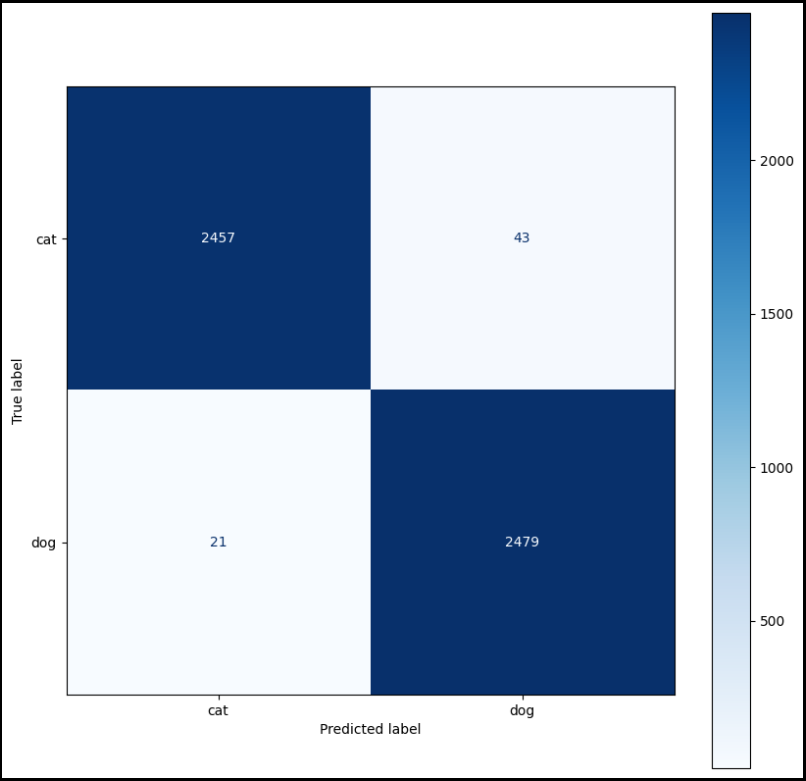
이 글은 제로베이스 데이터 취업 스쿨의 강의 자료 일부를 발췌하여 작성되었습니다