예제 1
데이터프레임 생성을 통해 베이즈 정리를 구현해보자
import pandas as pd
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['Spam', 'Ham'])
## LINK
table['prior'] = 0.5
table['likelihood'] = 0.6, 0.2
table['joint'] = table['prior'] * table['likelihood']
norm_const = table['joint'].sum()
table['posterior'] = table['joint'] / norm_const
print(table)
## WORD
table['prior'] = table['posterior']
table['likelihood'] = 0.4, 0.05 #특정 단어 W가 있는 상황을 가정
table['joint'] = table['prior'] * table['likelihood']
norm_const = table2['joint'].sum()
table['posterior'] = table['joint'] / norm_const
print(table)예제2
함수를 선언해 출력값을 불러오자.
def bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood):
if 'posterior' in table.columns: table['prior'] = table['posterior']
else: table['prior'] = prior
table['likelihood'] = likelihood
table['joint'] = table['prior'] * table['likelihood']
norm_const = table['joint'].sum()
table['posterior'] = table['joint'] / norm_const
return table
Bayes’ Theorem 예제
[문제설정]
- 눈 앞에 단지가 하나 있는데, 단지 X 혹은 Y라는 사실은 알고 있지만, 겉으로 봐서는 어느 쪽인지 알 수 없다.
- 단지 X에는 흰 공 아홉 개, 검은 공 한 개
- 단지 Y에는 흰 공 두 개, 검은 공 여덟 개가 들어있다는 정보를 갖고 있다
- 공을 꺼내 색깔을 확인하고, 나오는 색깔을 통해 눈앞의 단지가 X인지 Y인지 추측한다
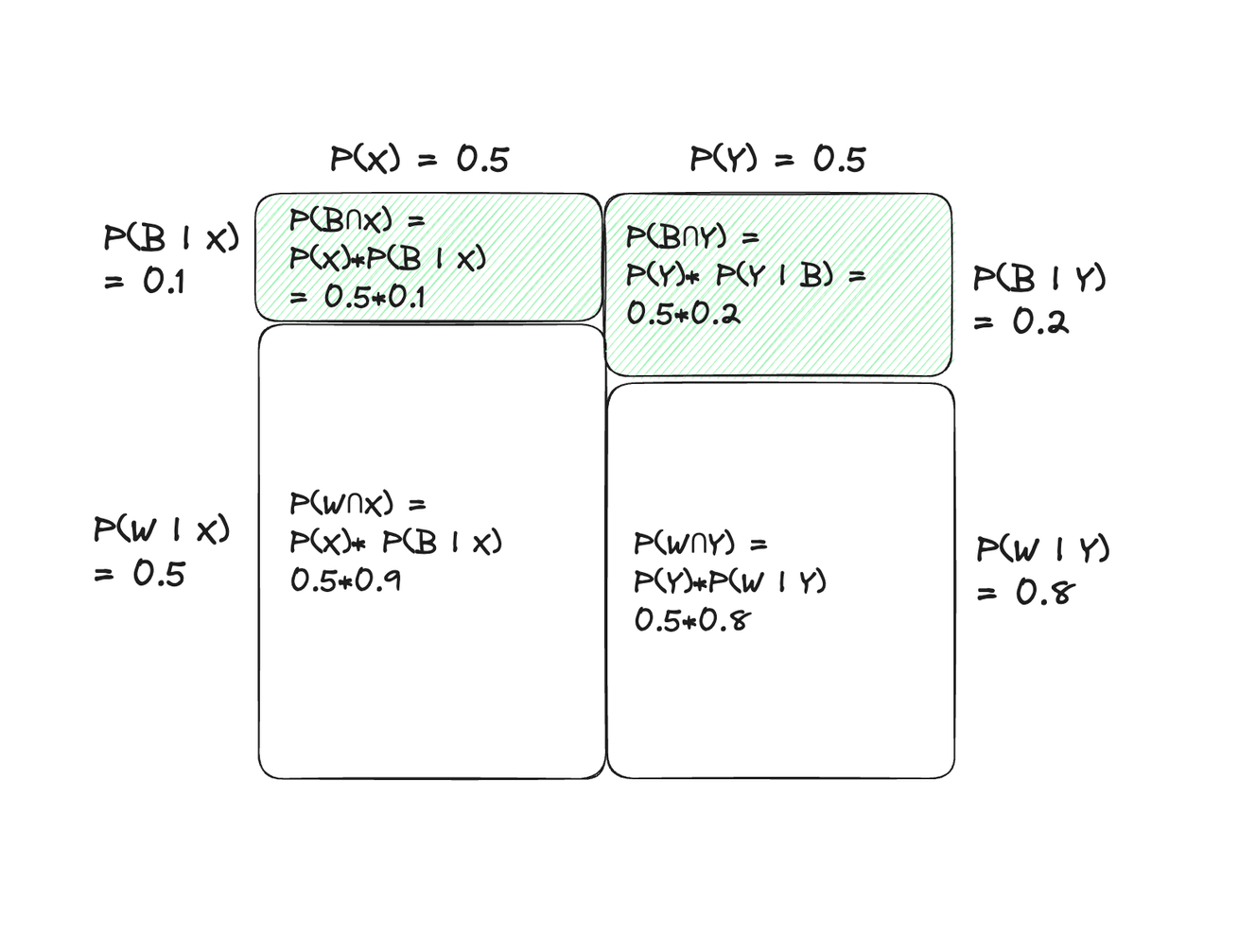
[ex1. 공을 하나 꺼냈을 때, 검은색]
- prior probability
- P(X) = 0.5, P(Y) = 0.5
- likelihood
- P(B | X) = 0.1
- P(W | X) = 0.9
- P(B | Y) = 0.8
- P(W | Y) = 0.2
- 눈 앞의 단지가 X 타입일 posterior
- P(X | B) = [P(B | X)*P(X)]/P(B) = (0.50.1) / ((0.50.1)+(0.5*0.8)) = 0.11
- 눈 앞의 단지가 Y 타입일 posterior
- P(Y | B) = [P(B | Y)*P(Y)]/P(B) = (0.50.8) / ((0.50.1)+(0.5*0.8)) = 0.89
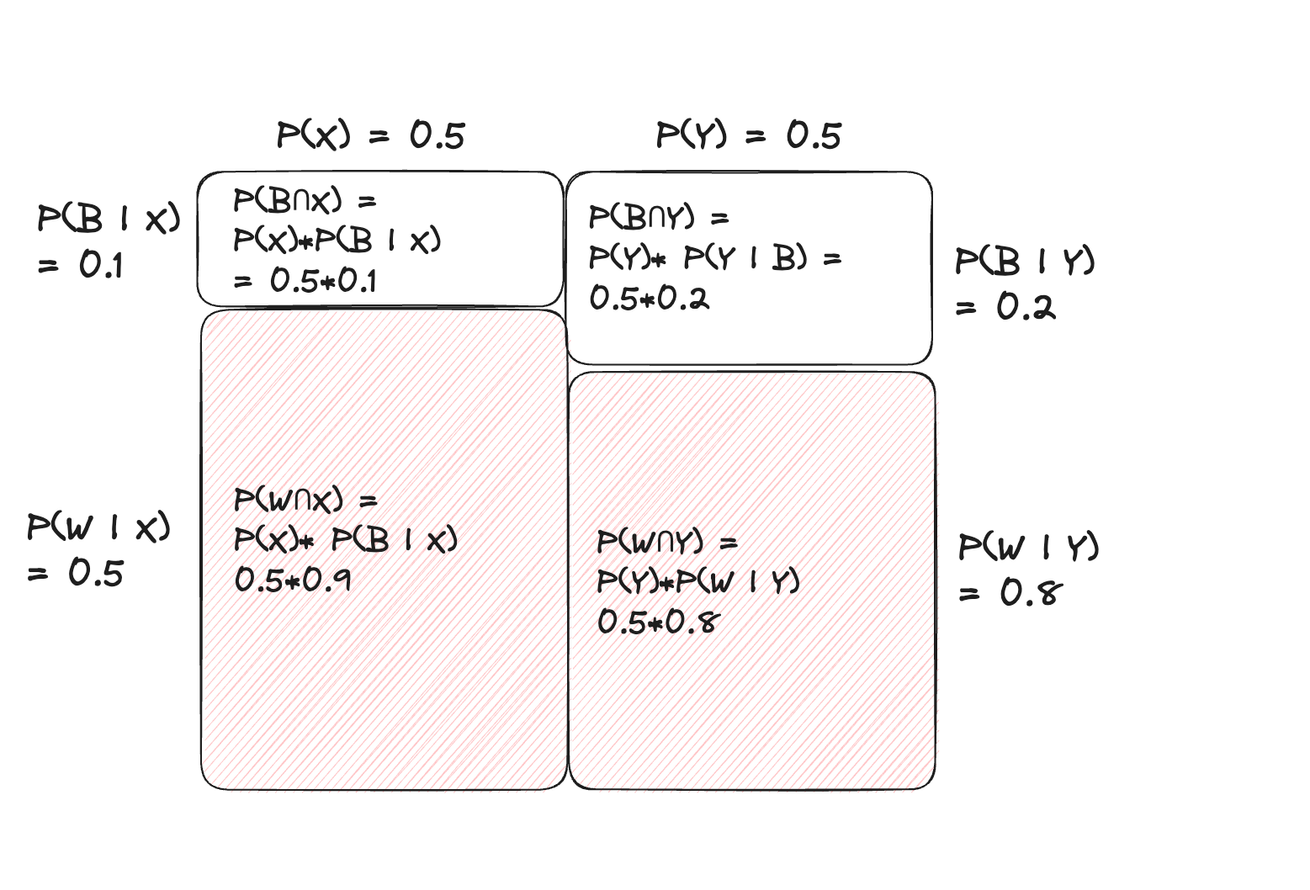
[ex2. 공을 하나 꺼냈을 때, 흰색]
- prior probability P(X) = 0.5, P(Y) = 0.5
- P(X) = 0.5, P(Y) = 0.5
- likelihood
- P(B | X) = 0.1
- P(W | X) = 0.9
- P(B | Y) = 0.8
- P(W | Y) = 0.2
- 눈 앞의 단지가 X 타입일 posterior
- P(X | W) = [P(W | X)*P(X)]/P(W) = (0.50.9) / ((0.50.9)+(0.5*0.2)) = 0.82
- 눈 앞의 단지가 Y 타입일 posterior
- P(Y | W) = [P(W | Y)*P(Y)]/P(W) = (0.50.2) / ((0.50.9)+(0.5*0.2)) = 0.18
pandas를 통해 Posterior를 구하면 결과는 아래와 같다
import pandas as pd
def bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood):
table['prior'] = prior
table['likelihood'] = likelihood
table['joint'] = table['prior'] * table['likelihood']
norm_const = table['joint'].sum()
table['posterior'] = table['joint'] / norm_const
return tabletable = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
prior = 0.5
w_likelihood = [0.9, 0.2]
b_likelihood = [0.1, 0.8]
print("========================Black========================")
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
b_table = bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood=b_likelihood)
print(table, '\n')
print("========================White========================")
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
w_table = bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood=w_likelihood)
print(w_table, '\n')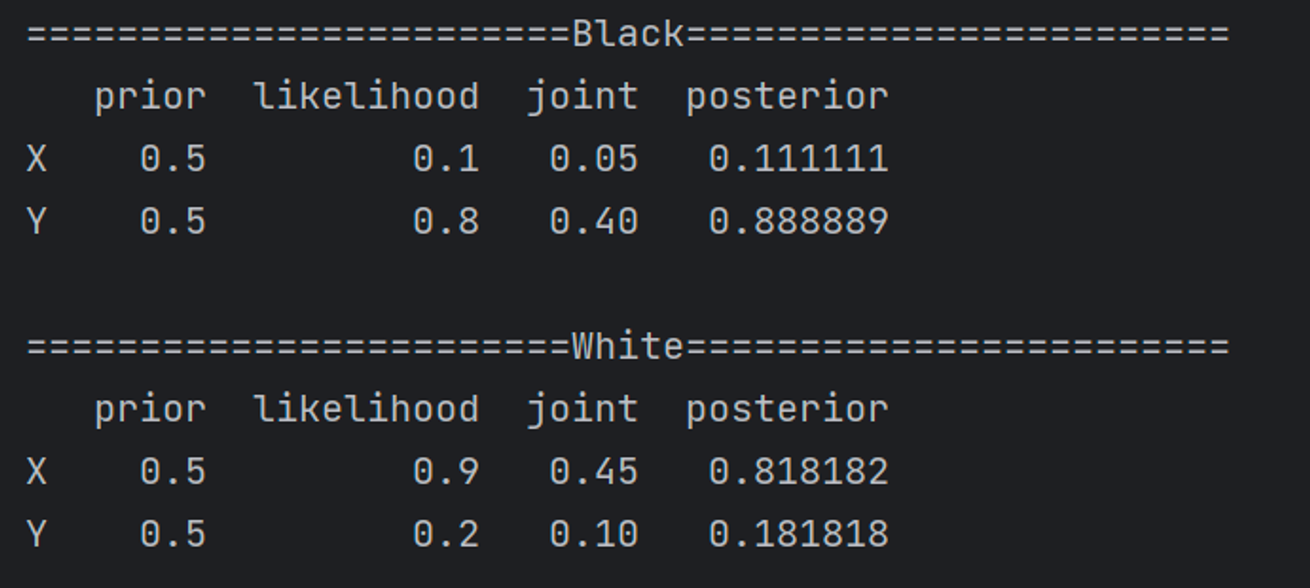
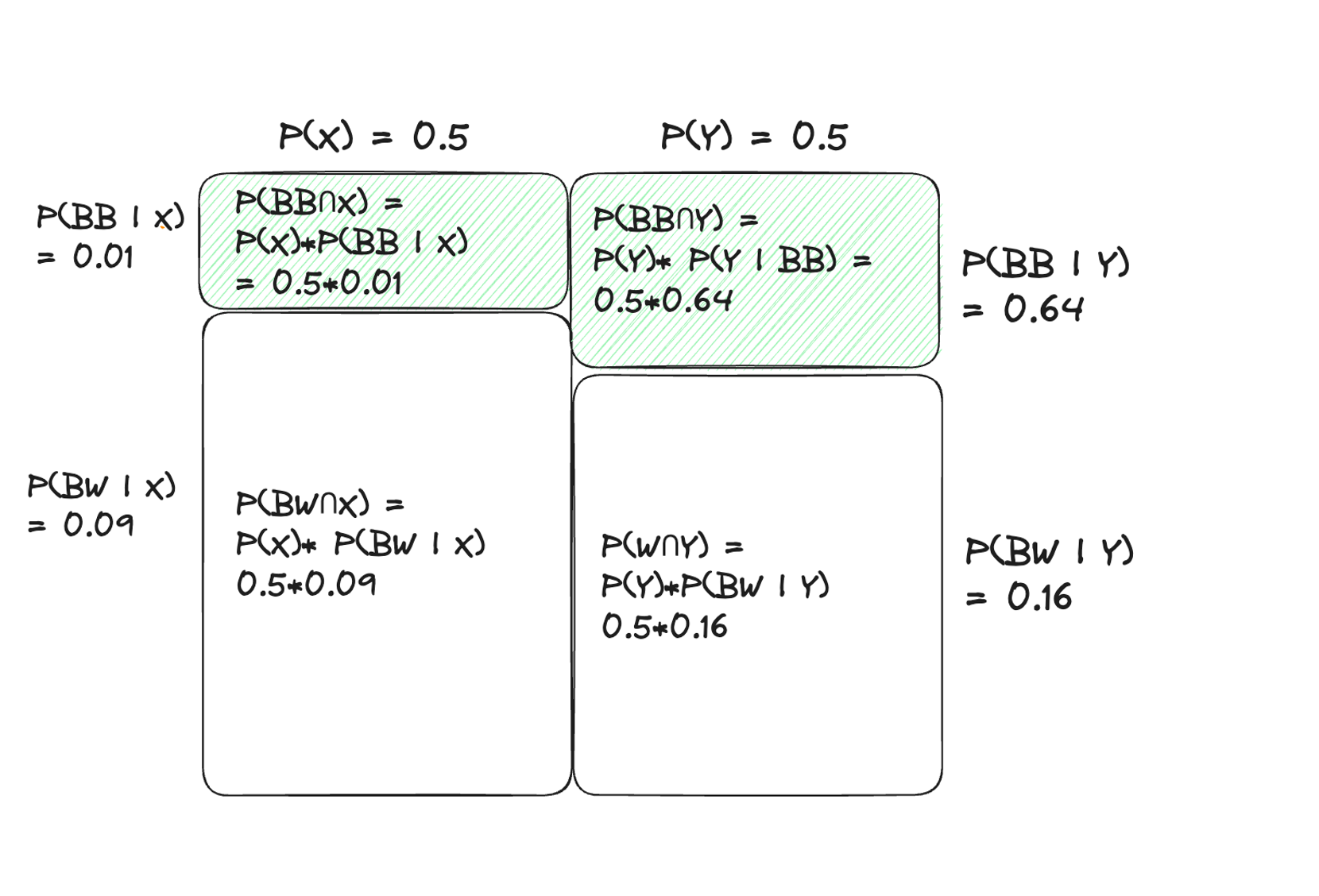
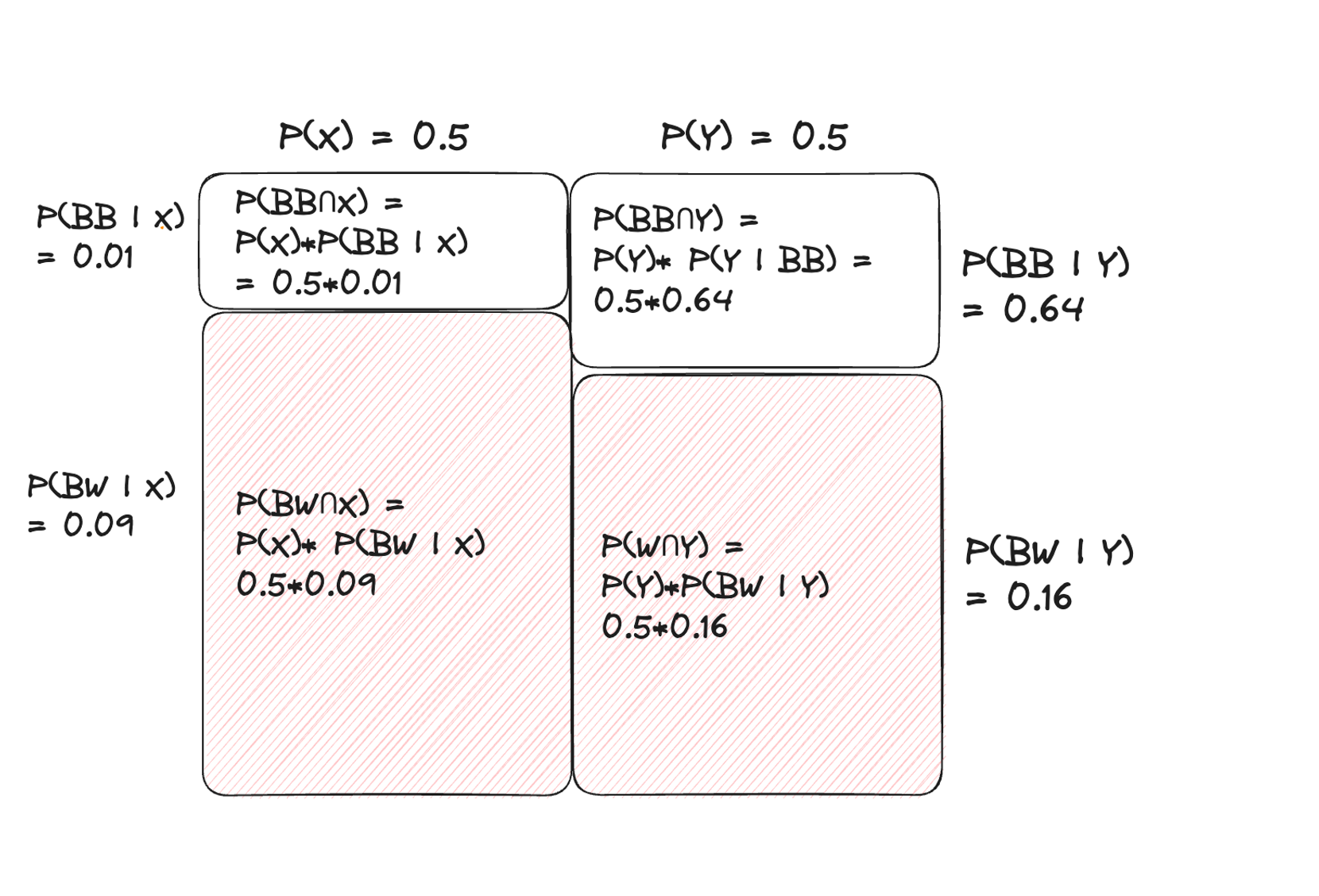
[ex3. 공을 두 번 뽑았을 때, 검은색&검은색]
-
prior probability : P(X) = 0.5, P(Y) = 0.5
-
likelihood = P(BB | X) = 0.01
- P(BW | X) = 0.09
- P(BB | Y) = 0.64
- P(BW | Y) = 0.16
-
눈 앞의 단지가 X 타입일 posterior
- P(X | BB) = [P(BB | X)*P(X)]/P(BB) = (0.50.01) / ((0.50.01)+(0.5*0.64)) = 0.015
-
눈 앞의 단지가 Y 타입일 posterior
- P(Y | BB) = [P(BB | Y)*P(Y)]/P(BB) = (0.50.64) / ((0.50.01)+(0.5*0.64)) = 0.985
[ex4. 공을 두 번 뽑았을 때, 검은색&흰색]
- prior probability : P(X) = 0.5, P(Y) = 0.5
- likelihood
- P(BB | X) = 0.01
- P(BW | X) = 0.09
- P(BB | Y) = 0.64
- P(BW | Y) = 0.16
- 눈 앞의 단지가 X 타입일 posterior = P(X | BW) = [P(BW | X)*P(X)]/P(BW) = (0.50.09) / ((0.50.09)+(0.5*0.16)) = 0.36
- 눈 앞의 단지가 Y 타입일 posterior = P(Y | BW) = [P(BW | Y)*P(Y)]/P(BW) = (0.50.16) / ((0.50.09)+(0.5*0.16)) = 0.64
import pandas as pd
def bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood):
table['prior'] = prior
table['likelihood'] = likelihood
table['joint'] = table['prior'] * table['likelihood']
norm_const = table['joint'].sum()
table['posterior'] = table['joint'] / norm_const
return table
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
prior = 0.5
w_likelihood = [0.9, 0.2]
b_likelihood = [0.1, 0.8]
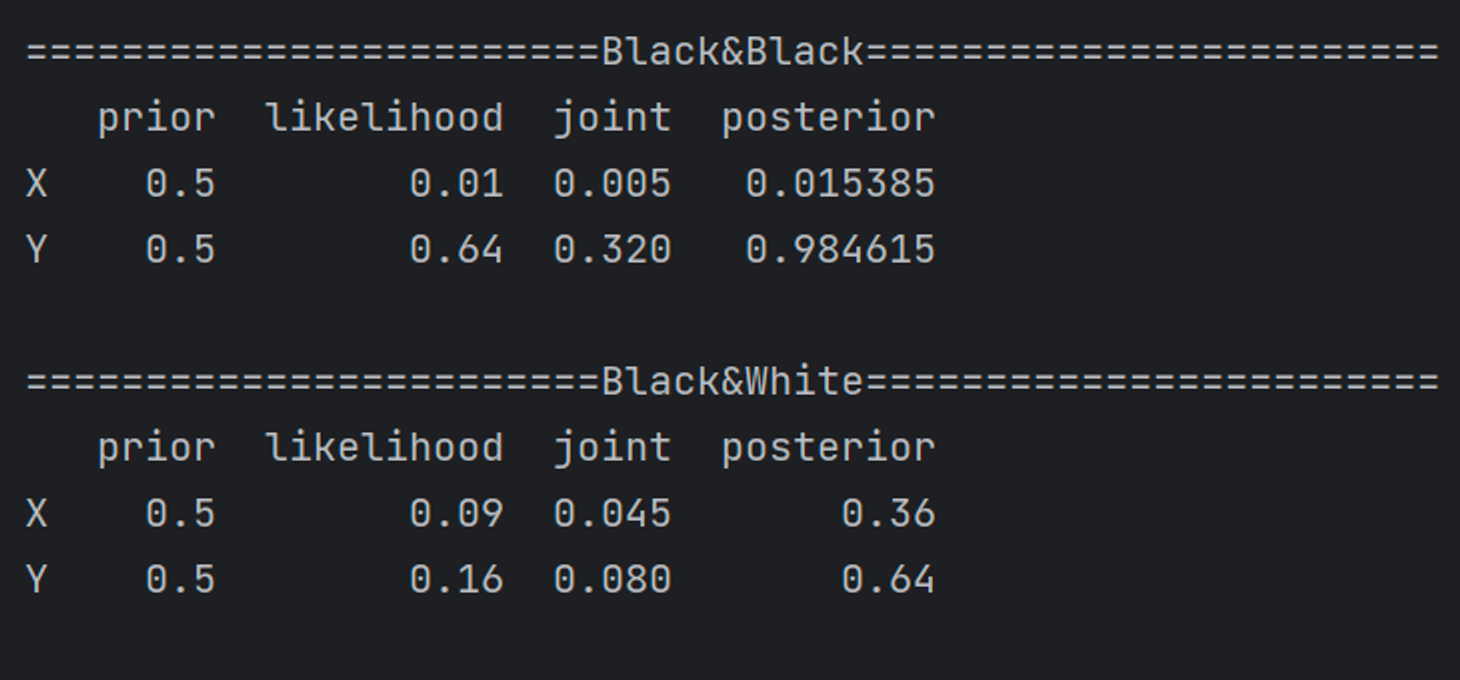
print("========================Black&Black========================")
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
bb_table = bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood=[likelihood**2 for likelihood in b_likelihood])
print(table, '\n')
print("========================Black&White========================")
table = pd.DataFrame(index=['X', 'Y'])
bw_table = bayesian_table(table, prior, likelihood=[likelihood*(1-likelihood) for likelihood in b_likelihood])
print(table, '\n')
학습 후 느낀점
- Likelihood를 잘못 넣어서 오랜 시간이 소요되었다. 머리로만 생각하고 그리질 않으니 벌어진 문제라고 생각한다.
- 막막함을 느끼는 건 당연하다. 아무것도 하지 않고 질문만하는 행위가 문제가 될 뿐이다. 질문을 하고 해결을 하려는 노력을 해보아야 한다.
