ConTinTin: Continual Learning from Task Instructions
ACL 2022
분야 및 배경지식
Continual Learning, Learning from Task Instructions
- Continual Learning
- 크게 CCL(Class Continual Learning; 레이블이나 범주 등을 연속학습), DCL(Domain; 동일 태스크이나 다른 도메인 학습(=다른 데이터 분포)), TCL(Task; 다른 태스크 학습)로 분류 가능
- 대부분의 연구가 catastrophic forgetting, 즉 연속학습 시 이전에 학습한 지식을 까먹는 현상을 완화하는 데에 주력
- Textual Instructions
- 거대한 규모의 사전학습된 언어 모델에 자연어로 이루어진 instruction을 input으로 주면 원하는 output을 얻을 수 있다는 사실이 밝혀짐
- 최근 가장 주요하게 사용되는 insturction format은 prompt(=a short piece of text describing the core concept of the task)
문제점
- 기존 NLP 연구는 목표하는 태스크가 이미 정해져있고 정적이며(predefined and static), 태스크의 supervision이 주로 labeled data를 통해 온다고 가정
- 태스크마다 다른 annotation(labeled data)은 비용이 많이 들음. 이를 완화하기 위해 사람의 학습 방식에서 영감을 받아 대안적인 supervision, 즉 task instruction을 통해 새로운 태스크들을 연속적으로 학습할 수는 없을까?
해결책
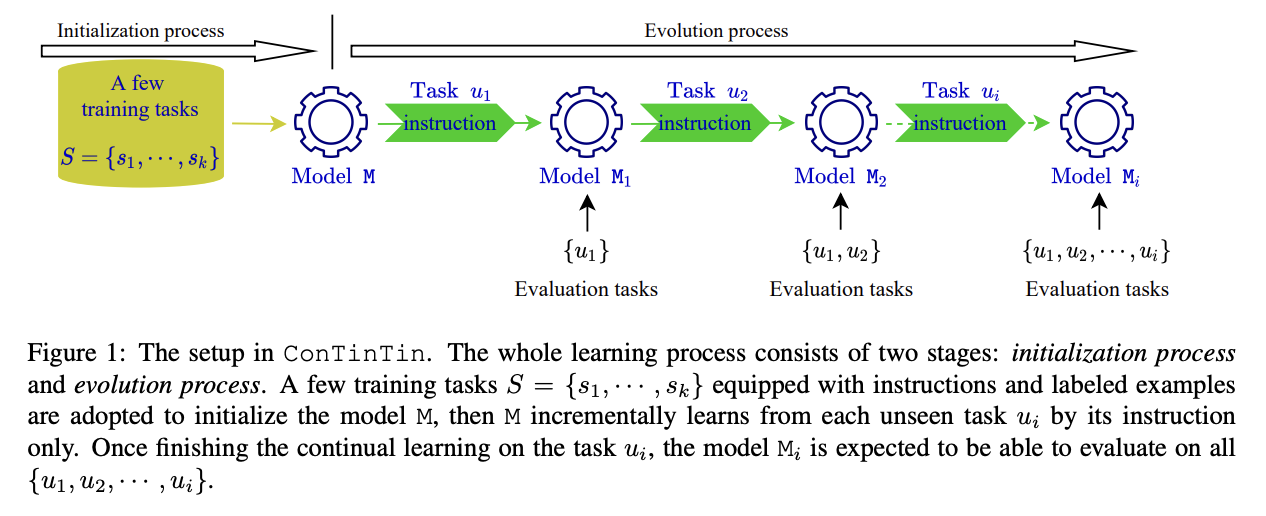
ConTinTin(Continual Learning from Task Instructions)
- New problem formation and System
- 새로운 일련의 태스크들을 textual instructions를 통해 학습하는 시스템
- initialization process: 새로운 태스크를 배우기 전 시작 상태. n개의 labeled examples와 instruction을 활용해 학습
- evolution process: insturction을 구비한 a sequence of unseen tasks 활용해 연속적으로 진화(evolve). unseen tasks의 경우 instructions으로만 학습
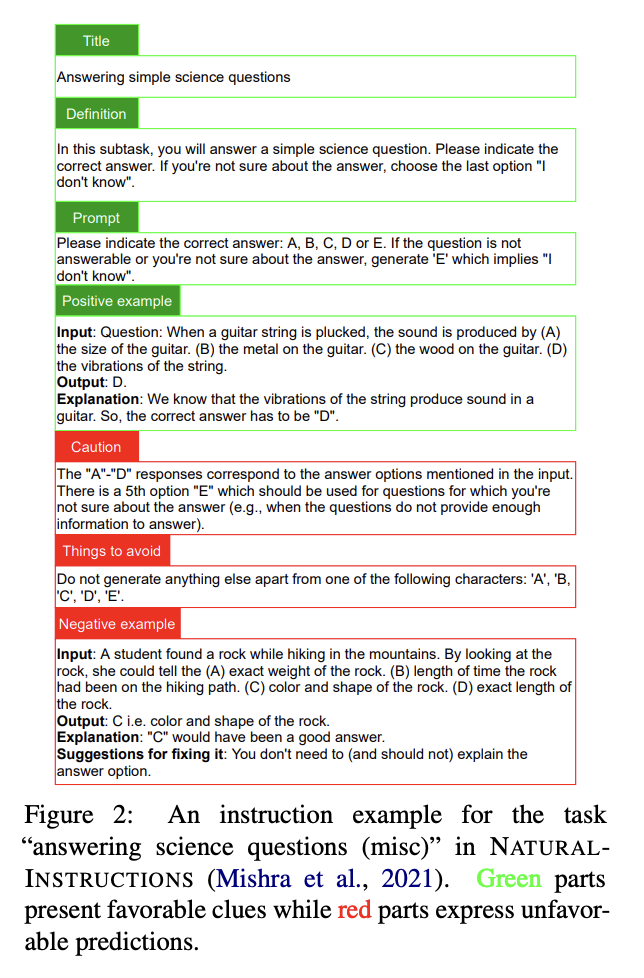

InstructionSpeak (based on BART)
- Negative Training
- 태스크 이해도와 forward-transfer를 증가시키기 위해 unfavorable clues 활용
- negative examples를 마치 positive examples처럼 활용, negative examples에 대해 먼저 pretrain하고 positive examples에 대해 finetune을 진행
- negative example이 여전히 유용한 정보를 포함하고 있음을 활용 (negative output means not equal to ground truth(gold output))
- History Training
- catastrophic forgetting을 경감시키기 위해 이전 태스크들의 instructions를 revisit
- instruction의 경우 길이도 짧고 더 많은 supervision을 담고 있기 때문에 예시를 반복하는 것보다 효율적이라고 주장
평가
- 데이터셋: Natural Instructions 활용 (61개 태스크)
- 태스크: QG (question generation), AG (answer generation), CF (classification), IAG (incorrect answer generation), MM (minimal modification), VF (verification)
- metrics
- forward-tansfer: target task t에 대해서 i 크기만큼의 태스크를 더 학습할 시 얼마만큼의 성능 개선이 일어나는지; target task t는 sequence에서 가장 마지막에 위치
- backward-transfer: target task t에 대해서 t 학습 후 i 크기만큼의 태스크를 더 학습한다면 t의 성능이 얼마나 달라지는지, 만약 음수가 나오면 catastrophic forgetting이 일어나는 것; target task t는 sequence에서 특정한 index에 위치
한계
- unseen task의 경우 instructions으로만 학습한다고 주장하지만, 실제 instruction의 예시를 보면 몇몇 examples도 포함되어 있어 과연 저자들의 주장이 명확한지 의문이 듦
- GPT 베이스인 LAMOL을 BART로 학습시켜 비교했는데, 이게 과연 공정한 비교인지 의문
- pretrained tasks에 대한 성능 평가가 없음
- task instruction 또한 task의 특징을 잘 반영하도록 데이터를 만드는 과정이 복잡하고 어려울 수 있음 (labeled data와 마찬가지로)
의의
- backward transfer의 경우 CL의 upperbound로 여겨지는 multi-task learning보다 뛰어난 성능
- 기존 CL의 replay와 유사하지만, labeled data가 아니라 instructions을 사용해 cost-effective
