데이터 설명
- 28 * 28 픽셀의 0~9 사이의 숫자 이미지와 레이블로 구성된 세트
- 60000개의 훈련용 세트와 10000개의 실험용 세트로 구성
- kaggle 데이터 활용: https://www.kaggle.com/oddrationale/mnist-in-csv
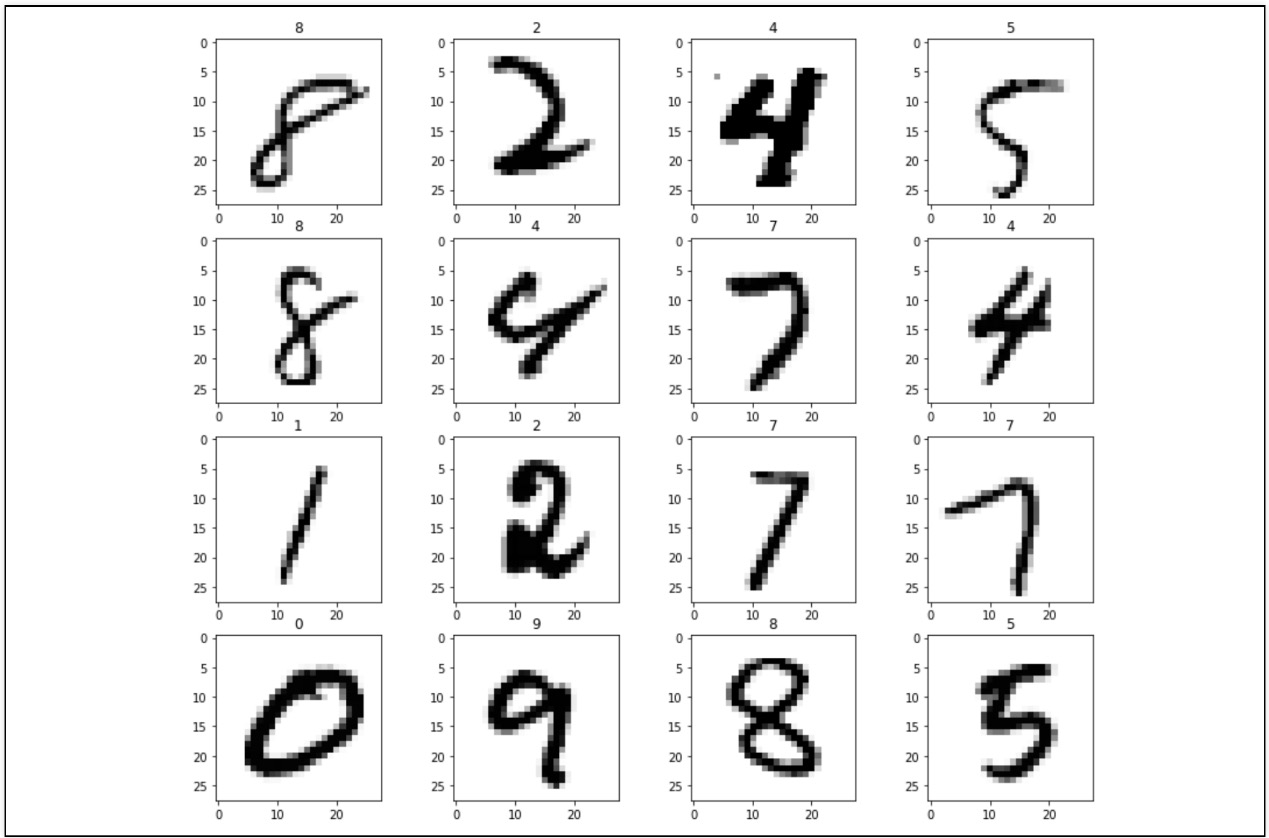
1. 데이터 확인
import pandas as pd
df_train = pd.read_csv('./data/mnist_train.csv')
df_test = pd.read_csv('./data/mnist_test.csv')
df_test
2. 데이터 정리
import numpy as np
X_train = np.array(df_train.iloc[:, 1:])
y_train = np.array(df_train['label'])
X_test = np.array(df_test.iloc[:, 1:])
y_test = np.array(df_test['label'])
X_train.shape, y_train.shape, X_test.shape, y_test.shape # ((60000, 784), (60000,), (10000, 784), (10000,))3. KNeighborsClassifier fit
- 거리를 구하는 KNeighborsClassifier의 경우, 데이터가 많으면 많이 걸린다
from sklearn.neighbors import KNeighborsClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
clf = KNeighborsClassifier(n_neighbors=5)
clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
pred = clf.predict(X_test)
print(accuracy_score(y_test, pred)) # 0.96884. PCA로 차원을 줄이기
- 데이터가 너무 많아 시간이 오래 걸렸다고 가정하고 차원 줄이기
from sklearn.pipeline import Pipeline
from sklearn.decomposition import PCA
from sklearn.model_selection import GridSearchCV, StratifiedKFold
pipe = Pipeline([
('pca', PCA()),
('clf', KNeighborsClassifier())
])
parameters = {
'pca__n_components' : [2, 5, 10],
'clf__n_neighbors' : [5, 10, 15]
}
kf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=5, shuffle=True, random_state=13)
grid = GridSearchCV(pipe, parameters, cv=kf, n_jobs=-1, verbose=1)
grid.fit(X_train, y_train)
print('Best score: %0.3f' % grid.best_score_)
print('Best parameter set: ')
best_parameters = grid.best_estimator_.get_params()
for param_name in sorted(parameters.keys()):
print("\t%s: %r" % (param_name, best_parameters[param_name]))
print(accuracy_score(y_test, grid.best_estimator_.predict(X_test)))
'''
Fitting 5 folds for each of 9 candidates, totalling 45 fits
Best score: 0.931
Best parameter set:
clf__n_neighbors: 10
pca__n_components: 10
0.929
'''5. precision, recall, f1-score, support 출력 함수
- 대체적으로 비슷한 결과이지만 떨어져 보이는 것이 있긴 하다.
def results(y_pred, y_test):
from sklearn.metrics import classification_report, confusion_matrix
print(classification_report(y_test, y_pred))
results(grid.predict(X_train), y_train)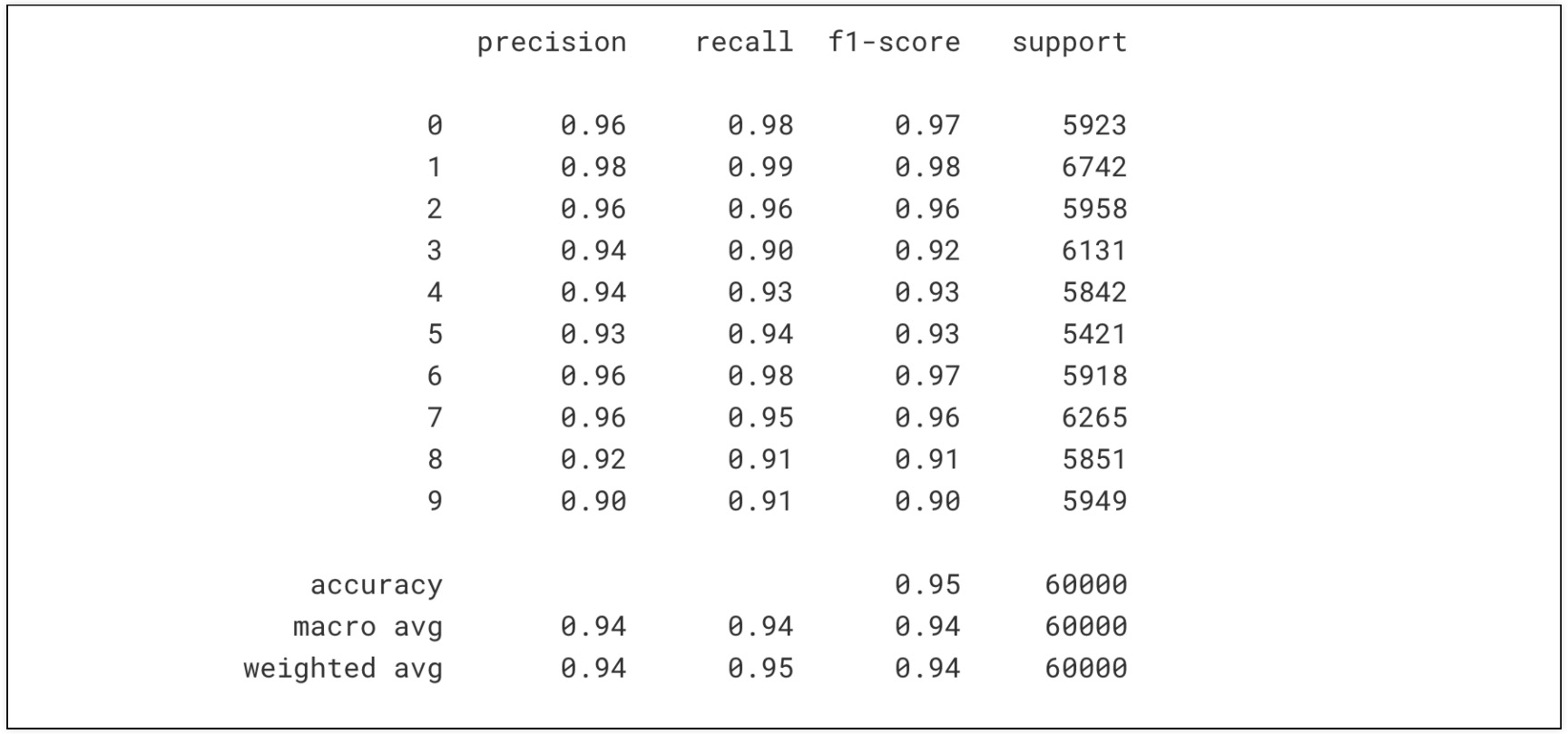
6. 틀린 데이터 확인
preds = grid.best_estimator_.predict(X_test)
worng_results = X_test[y_test != preds]
samples = random.sample(range(0, worng_results.shape[0]), k=16)
plt.figure(figsize=(14, 12))
for idx, n in enumerate(samples):
plt.subplot(4, 4, idx+1)
plt.imshow(worng_results[n].reshape(28,28), cmap='Greys', interpolation='nearest')
plt.title(grid.best_estimator_.predict(worng_results[n].reshape(1, 784))[0])
plt.show()
Reference
1) 제로베이스 데이터스쿨 강의자료
