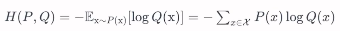
소프트맥스 회귀
3개 이상의 선택지 중에서 1개를 고르는 다중 클래스 분류 문제
이산적인 확률분포이며, 모든 확률을 다 더하면 1이 됨
어쨌거나 확률이 가장 큰 값을 뽑아 낼 수가 있음
z = torch.FloatTensor([1, 2, 3])
hypothesis = F.softmax(z, dim=0)
# hypothesis.sum()을 print하면 1이 나옴크로스 엔트로피
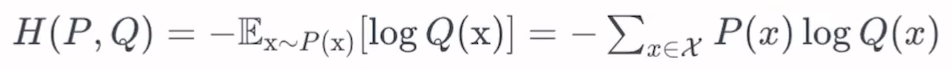
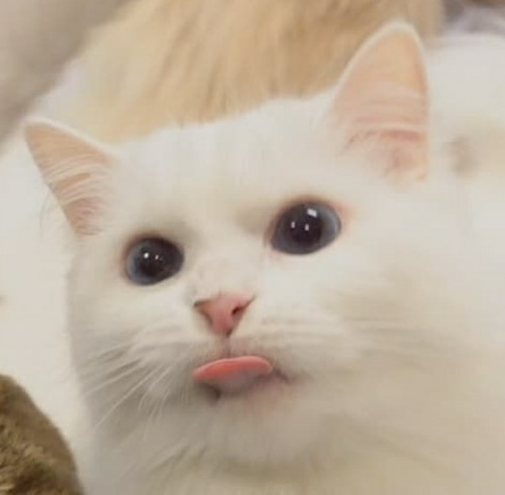
실제 분포 P에 대해 알지 못하는 상태에서, 모델링을 통해 예측한 Q를 통하여 P를 예측
실제값과 예측값이 맞는 경우 0으로 수렴하고, 틀릴 경우 값이 커지기 때문에
실제 값과 예측 값의 차이를 줄이기 위한 엔트로피
구현 (1)
z = torch.rand(3, 5, requires_grad=True)
hypothesis = F.softmax(z, dim=1) # dimension=1에 대하여 softmax>>>
tensor([[0.2645, 0.1639, 0.1855, 0.2585, 0.1277],
[0.2430, 0.1624, 0.2322, 0.1930, 0.1694],
[0.2226, 0.1986, 0.2326, 0.1594, 0.1868]], grad_fn=<SoftmaxBackward0>)지금은 dimension = 1에 대하여 softmax를 실행해서 각 행들의 합이 1이 되었지만
만약 dimension = 0에 대하여 softmax를 실행하면 각 열들의 합이 1이 된다
y = torch.randint(5, (3,)).long()
# 각 sample(행)에 대하여 임의로 정답 index를 설정해 봄tensor([0, 2, 1])
# 0.2645, 0.2322, 0.1986원-핫 (One-Hot) 인코딩
학습할 때 데이터를 벡터로 나타내어, 쉽게 중복 없이 표현할 때 사용하는 형식
Discrete representation의 일종이며, 단점으로는
- 아이템이 많아질 때 size가 급격하게 늘어남
- 단어의 속성이 벡터에 반영되지 않음
원-핫 인코딩의 과정
- 각 데이터에 고유한 인덱스를 부여하며,
- 표현하고 싶은 단어의 인덱스 위치에 1을 부여하고
- 다른 단어의 인덱스 위치에는 0을 부여함
보통 자연어 처리에 많이 쓰이는 것 같다
그러나 여기에서는 정답 인덱스를 원-핫 인코딩으로 나타냄
구현 (2)
y_one_hot = torch.zeros_like(hypothesis)
y_one_hot.scatter_(1, y.unsqueeze(1), 1)
# dimension=1의 index=y.unsqueeze(1)에 1을 뿌려라참고로 y의 dimension=(3,)이므로
y.unsqueeze(1)을 하면 y의 dimension=(3,1)
한번 scatter 함수에 y를 넣어 봤는데...
Index tensor must have the same number of dimensions as self tensor
인덱스 텐서는 자체 텐서와 동일한 수의 차원을 가져야 합니다
라고 오류 뜸
hypothesis 크기가 (3, 5)이니까 그런 듯
y의 실제값과 예측값에 대한 크로스 엔트로피는
아래 수식을 이용함
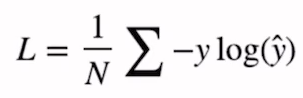
cost = (y_one_hot * -torch.log(hypothesis)).sum(dim=1).mean()
# 각 행에 대하여 sum 수행
print(cost)tensor(1.4689, grad_fn=<MeanBackward0>)torch.nn.functional 이용
결론적으로 z에 대한 softmax와 cost를 간단히 나타내면
torch.log(F.softmax(z, dim=1))
cost = (y_one_hot * -torch.log(F.softmax(z, dim=1))).sum(dim=1).mean()그러나... log_softmax, 함수가 모두 torch.nn.functional 에 존재함
F.log_softmax(z, dim=1)
cost = F.nll_loss(F.log_softmax(z, dim=1), y)NLL = Negative Log Likelihood
... 근데 F.log_softmax()와 F.nll_loss()를 또 결합할 수 있다고 함
F = cross_entropy(z, y)nn.Module, F.cross_entropy 를 이용한 최종 구현
class SoftmaxClassifierModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Linear(4, 3)
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
model = SoftmaxClassifierModel()
x_train = [[1, 2, 1, 1],
[2, 1, 3, 2],
[3, 1, 3, 4],
[4, 1, 5, 5],
[1, 7, 5, 5],
[1, 2, 5, 6],
[1, 6, 6, 6],
[1, 7, 7, 7]]
y_train = [2, 2, 2, 1, 1, 1, 0, 0]
x_train = torch.FloatTensor(x_train)
y_train = torch.LongTensor(y_train)
# 모델 초기화
W = torch.zeros((4, 3), requires_grad=True)
b = torch.zeros(1, requires_grad=True)
# optimizer 설정
optimizer = optim.SGD(model.parameters(), lr=0.1)
nb_epochs = 1000
for epoch in range(nb_epochs + 1):
# H(x) 계산
prediction = model(x_train)
# cost 계산
cost = F.cross_entropy(prediction, y_train)
# 100번마다 로그 출력
if epoch % 100 == 0:
print('Epoch {:4d}/{} Cost: {:.6f}'.format(
epoch, nb_epochs, cost.item()
))SoftmaxClassifierModel은 4개의 input을 받아서 3개 class에 대하여 확률값을 output으로 내며
x의 dimension은 (m, 4) (m은 데이터 개수)가 되고, prediction의 dimension은 (m, 3)이 됨
y_train은 one-hot 벡터로 만들지 않았기 때문에 (m, 1)
- 이전 강의처럼, 예측값이 두 가지(0/1, 예/아니요)라면
BCE(Binary Cross Entropy)와 Sigmoid 함수를 사용하고
예측값이 여러 가지라면, 지금처럼 CE(Cross Entropy)와 Softmax 사용!
