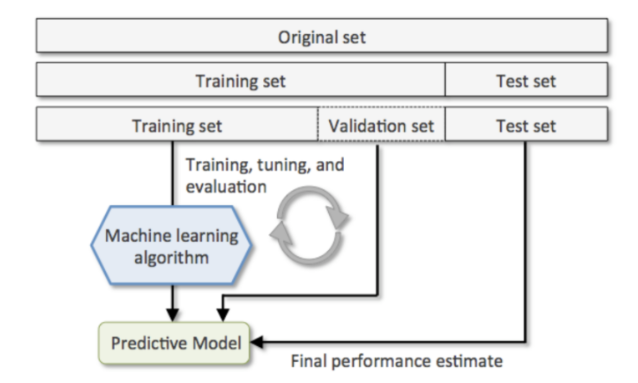
모델 성능 평가를 위한 데이터셋 분리
- 데이터셋(Dataset)
- Train 데이터셋(훈련/학습 데이터셋)
- 모델을 학습시킬 때 사용할 데이터 셋
- Validation 데이터셋 (검증 데이터셋)
- 모델의 성능 중간 검증을 위한 데이터셋
- Test 데이터셋 (평가 데이터셋)
- 모델의 성능을 최종적으로 측정하기 위한 데이터셋
- Test 데이터셋은 마지막에 모델의 성늘을 측정하는 용도로 한번만 사용되야 한다.
- Train 데이터셋(훈련/학습 데이터셋)
- Hold Out - Data분리 방식
- 데이터셋을 Train,Validation,Test set으로 나눈다.
- sklearn.model_selection.train_test_split() 함수 사용 => 하나의 데이터셋을 2분할 하는 함수
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
import numpy as np
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
X.shape, y.shape
# 결과 ((150, 4), (150,))- Train/Test set 분리
X_tmp, X_test, y_tmp, y_test = train_test_split(X,
y,
test_size=0.2,
stratify=y,
random_state=0
)
X_tmp.shape, X_test.shape, y_tmp.shape, y_test.shape
# 결과 ((120, 4), (30, 4), (120,), (30,))- Train/Validation/Test set 분리
- tmp를 train/validation으로 분리
X_train, X_val, y_train, y_val = train_test_split(X_tmp, y_tmp, test_size=0.2,
stratify=y_tmp, random_state=0)
X_train.shape, X_val.shape, X_test.shape
# 결과 ((96, 4), (24, 4), (30, 4))- 모델 학습->검증->튜닝
# max_depth = 1
max_depth = 2
# max_depth = 3
# max_depth = 5
tree = DecisionTreeClassifier(max_depth=max_depth, random_state=0) # 모델생성
tree.fit(X_train, y_train) # 데이터 학습
pred_train = tree.predict(X_train) # 예측
pred_val = tree.predict(X_val)
train_acc = accuracy_score(y_train, pred_train) # 정확도
val_acc = accuracy_score(y_val, pred_val)
print(f"max_depth: {max_depth}")
print("train set 정확도:", train_acc)
print("val set 정확도:", val_acc)
# 결과
max_depth: 2
train set 정확도: 0.9583333333333334
val set 정확도: 1.0- Testset으로 최종검증
pred_test = tree.predict(X_test) #예측
test_acc = accuracy_score(y_test, pred_test) # 정확도
print('test set 정확도:', test_acc)
# 결과
test set 정확도: 0.9333333333333333- Hold out 방식의 단점
- train/validation/test 셋이 어떻게 나눠 지냐에 따라 결과가 달라진다.
- 데이터가 충분해야한다.
- 이상치에 대한 영향을 많이 받는다.
- 데이터가 충분하지 않을 경우 다양한 패턴을 찾을 수가 없기 때문에 새로운 데이터에 대한 예측 성능이 떨어지게 된다.
그러므로 Hold out 방식은 (다양한 패턴을 가진) 데이터의 양이 많을 경우에 사용하는 것이 좋다.
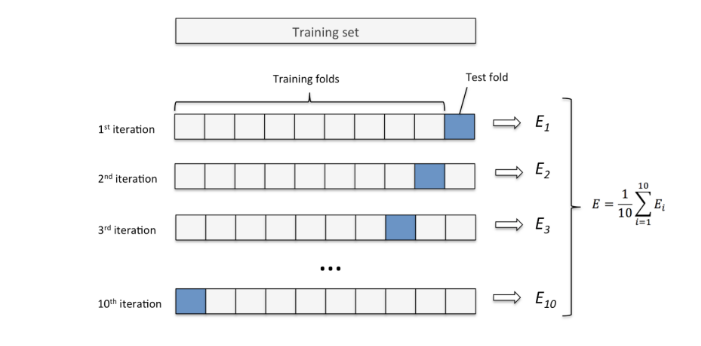
K-겹 교차검증 (K-Fold Cross Validation) - Data분리 방식
- 데이터셋을 설정한 K개로 나눈다.
- K개 중 하나를 검증세트로 나머지는 훈련세트로 하여 모델을 학습시키고 평가
- K개 모두가 한번씩 검증세트가 되도록 K번 반복하여 모델을 학습시킨 뒤 나온 평가지표들을 평균내서 모델의 성능을 평가
해당 방식은 데이터양이 충분하지 않을 때 사용한다. - K개로 나누는 방법(종류)
- KFold
회귀문제의 Dataset을 분리할 때 사용 - StratifiedKFold
분류문제의 Dataset을 분리할 때 사용
- KFold
Boston Housing DataSet
-
보스톤의 지역별 집값 데이터셋
CRIM : 지역별 범죄 발생률
ZN : 25,000 평방피트를 초과하는 거주지역의 비율
INDUS: 비상업지역 토지의 비율
CHAS : 찰스강에 대한 더미변수(강의 경계에 위치한 경우는 1, 아니면 0)
NOX : 일산화질소 농도
RM : 주택 1가구당 평균 방의 개수
AGE : 1940년 이전에 건축된 소유주택의 비율
DIS : 5개의 보스턴 고용센터까지의 접근성 지수
RAD : 고속도로까지의 접근성 지수
TAX : 10,000 달러 당 재산세율
PTRATIO : 지역별 교사 한명당 학생 비율
B : 지역의 흑인 거주 비율
LSTAT: 하위계층의 비율(%)
MEDV : Target 지역의 주택가격 중앙값 (단위: $1,000)
import pandas as pd
boston = pd.read_csv('data/boston_hosing.csv')
boston.shape # 결과 (506, 14)
X = boston.drop(columns='MEDV').values # target data를 위해 MEDV 삭제 후 y값으로 저장
y = boston['MEDV'].values- KFold
- 지정한 개수(K)만큼 분할
이때, Raw dataset의 순서를 유지하면서 지정한 개수로 분할 - 회귀 문제일때 사용
- KFold(n_splits=K)
몇개의 Fold로 나눌지 지정 - KFold객체.split(데이터셋)
데이터셋을 지정한 K개 나눴을때 train/test set에 포 함될 데이터의 index들을 반환하는 generator 생성- Generator란
연속된 값을 제공(생성)하는 객체.
연속된 값을 한번에 메모리에 저장하지 않고 필요시 마다 순서대로 하나씩 제공한다.
함수형식으로 구현하며 return대신 yield를 사용한다.
- Generator란
- 지정한 개수(K)만큼 분할
KFold를 이용해 Boston housing dataset 교차검증
##################### KFold를 이용해 Boston housing dataset 교차검증
from sklearn.model_selection import KFold
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeRegressor
from sklearn.metrics import mean_squared_error
# K개 모두가 한번씩 검증세트가 되도록 K번 반복하여 모델을 학습시킨 뒤 나온 평가지표들을 평균내서 모델의 성능을 평가하기위해
import numpy as np
mse_list = []
#1. KFold 객체 생성 - 폴드개수 (K) 를 설정
kfold = KFold(n_splits=5)
#2. split을 이용해서 generator 생성
index_gen = kfold.split(X)
#3. 반복문 -> 각 folder별 iteration을 처리.
tree = DecisionTreeRegressor(random_state=0)
for train_index, val_index in index_gen:
# train/val dataset을 생성
X_train, y_train = X[train_index], y[train_index]
X_val, y_val = X[val_index], y[val_index]
# 모델 학습
tree.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 검증
## 추론
pred_val = tree.predict(X_val)
## 검증 - mse
mse = mean_squared_error(y_val, pred_val)
mse_list.append(mse)
mse_list
# 결과
[11.887843137254906,
34.88990099009901,
28.17247524752476,
54.44178217821782,
52.59029702970297]
np.mean(mse_list), np.sqrt(np.mean(mse_list)) # sqrt=> 제곱근
# 결과
(36.39645971655989, 6.032947846331832)StratifiedKFold
- 분류문제일 때 사용
- 전체 데이터셋의 class별 개수 비율과 동일한 비율로 fold들이 나뉘도록 한다.
- StratifiedKFold(n_splits=K)
몇개의 Fold로 나눌지 지정 - StratifiedKFold객체.split(X, y)
데이터셋을 지정한 K개 나눴을때 train/test set에 포함될 데이터의 index들을 반환하는 generator 생성
input(X)와 output(y) dataset을 전달한다.
from sklearn.datasets import load_iris
from sklearn.model_selection import StratifiedKFold
from sklearn.tree import DecisionTreeClassifier
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
X, y = load_iris(return_X_y=True)
skf = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=3)
s_gen = skf.split(X, y)
print(type(s_gen))
# 결과 <class 'generator'>
############# iris dataset 교차 검증
acc_list = []
#1. KFold 객체 생성 - 폴드개수 (K) 를 설정
s_kfold = StratifiedKFold(n_splits=4)
#2. split을 이용해서 generator 생성
index_gen_iris = s_kfold.split(X, y)
#3. 반복문 -> 각 folder별 iteration을 처리.
tree_clf = DecisionTreeClassifier(random_state=0)
for train_idx, val_idx in index_gen_iris:
# train/val dataset을 생성
X_train, y_train = X[train_idx], y[train_idx]
X_val, y_val = X[val_idx], y[val_idx]
# 모델학습
tree_clf.fit(X_train, y_train)
# 검증
## 추론
pred = tree_clf.predict(X_val)
acc = accuracy_score(y_val, pred)
## 검증
acc_list.append(acc)
acc_list
# 결과
[0.9736842105263158, 0.9473684210526315, 0.9459459459459459, 1.0]
np.mean(acc_list)
# 결과 0.9667496443812233