Matrix Derivatives
Types of Matrix Derivative
| Type | Scalar y | Vector y (m×1) | Matrix Y (m×n) |
|---|
| Scalar x | ∂x∂y | ∂x∂y: (m×1) | ∂x∂Y: (m×n) |
| Vector x (n×1) | ∂x∂y: (1×n) | ∂x∂y: (m×n) | |
| Matrix X (p×q) | ∂X∂y: (p×q) | | |
Dimension을 주의할 것!
Gradient and Hessian
- ∇f(x) = the gradient of f
- The transpose of the first derivatives of f
∇f(x):=⎣⎢⎢⎡∂x1∂f⋮∂xn∂f⎦⎥⎥⎤=(∂x∂f)T∈Rn×1
- ∇2f(x) = the Hessian of f
- The matrix of second partial derivatives of f
- The Hessian is a symmetric matrix
∇2f(x):=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡∂x12∂2f∂x2∂x1∂2f⋮∂xn∂x1∂2f∂x1∂x2∂2f∂x22∂2f⋮∂xn∂x2∂2f……⋱…∂x1∂xn∂2f∂x2∂xn∂2f⋮∂xn2∂2f⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∈Rn×n
Jacobian and Matrix Derivative
- Jacobian when x∈Rn,y∈Rm
J:=∂x∂y=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡∂x1∂y1∂x1∂y2⋮∂x1∂ym∂x2∂y1∂x2∂y2⋮∂x2∂ym……⋱…∂xn∂y1∂xn∂y2⋮∂xn∂ym⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤∈Rm×n
- Matrix derivative when X∈Rp×q,Y∈Rm×n,z∈R
∂X∂z=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡∂x11∂z∂x21∂z⋮∂xp1∂z∂x12∂z∂x22∂z⋮∂xp2∂z……⋱…∂x1q∂z∂x2q∂z⋮∂xpq∂z⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤,∂z∂Y=⎣⎢⎢⎢⎢⎡∂z∂y11∂z∂y21⋮∂z∂ym1∂z∂y12∂z∂y22⋮∂z∂ym2……⋱…∂z∂y1n∂z∂y2n⋮∂z∂ymn⎦⎥⎥⎥⎥⎤,
Useful Matrix Derivative
For A∈Rn×n,
-
∂x∂(bTx)=∂x∂(xTb)=bT
-
∂x∂(xTx)=∂x∂∥x∥2=2xT
-
∂x∂(xTAx)=xT(A+AT)
- 2xTA if A is symmetric.
Chain Rule
Chain Rule
Theorem: Chain Rule
When the vector x in turn depens on another vector t, the chain rule for the univariate function f:Rn→R can be extended as follows:
dtdf(x(t))=∂x∂fdtdx=∇f(x(t))Tdtdx
- If z=f(y) and y=g(x) where x∈Rn,y∈Rm,z∈R, then
dxidz=j∑dyjdzdxidyj=j∑dxidyjdyjdz
(gradients from all possible paths)
dxdz=dydzdxdy
[1×n][1×m][m×n]
Neural Net에서의 BackPropagation 기법의 기초가 된다.
Chain Rule on Level Curve
- level curve : f(x,y)=c를 만족하는 (x,y)의 집합.
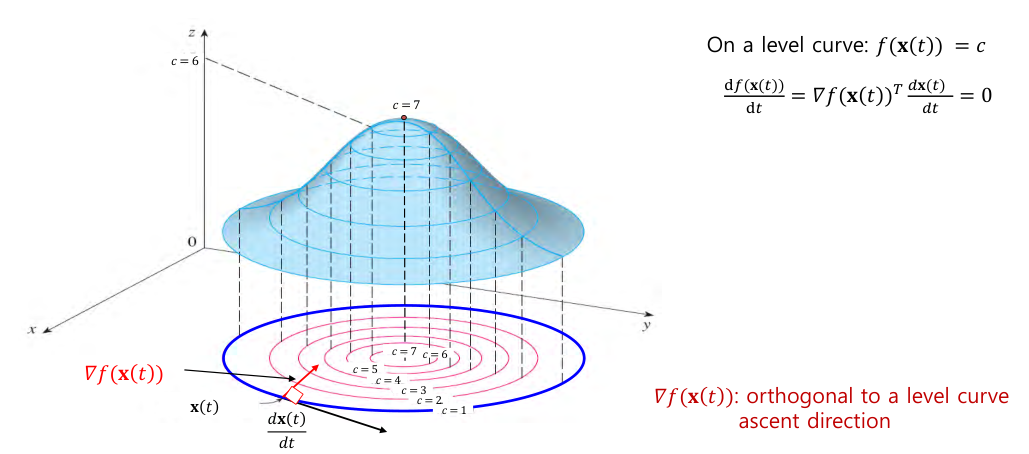
- On level curve f(x(t))=c,
dtdf(x(t))=∇f(x(t))Tdtdx(t)=0
즉, ∇f(x(t))는 level curve에서 수직(orthogonal)이며, f가 증가하는 방향(ascent direction)을 가르킨다.
Directional Derivatives
- f is continuously differentiable and p∈Rn, directional derivative of f in the direction of p is given by
D(f(x);p)=ε→0limεf(x+εp)−f(x)=∇f(x)Tp
Taylor Series Expansion
-
First order
f(x+p)≊f(x)+∇f(x)Tp
-
Second order
f(x+p)≊f(x)+∇f(x)Tp+21pT∇2f(x)p
추후 나올 일반적인 search(또는 learning) algorithm에서는 1st order expansion이면 충분하다.
Taylor Series Expansion을 통해 간단하게 ∇f(x)가 ascent direction임을 보일 수 있다.
f(x+λ∇f(x))≊f(x)+λ∇f(x)T∇f(x)=f(x)+λ∥∇f(x)∥2≥f(x) 
