Convexity
Convex Sets
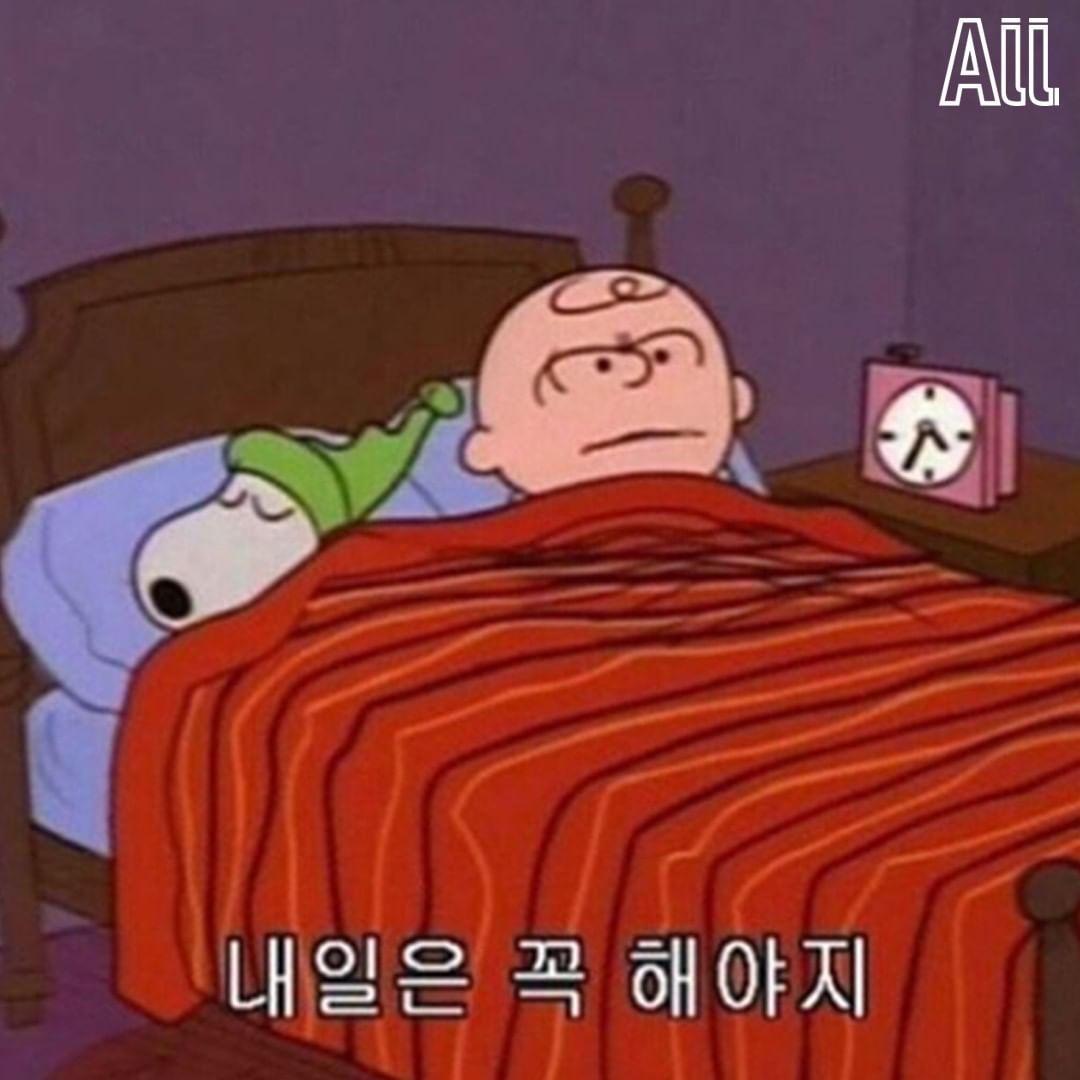
- 두 points의 convex combination 은 line segment between them.
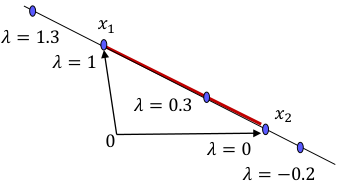
- A set 에 대해, 안의 임의의 두 점 의 convex combination이 항상 에 포함되면 이를 convex 하다고 한다.
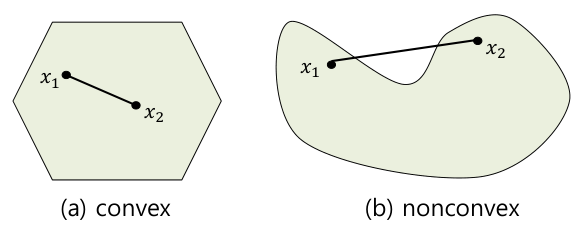
기하학적으로는 오목하게 들어간 부분이나 내부에 구멍이 없는 집합이다.
- A set 내 점들의 모든 convex combination을 의 convex hull () 이라고 한다.
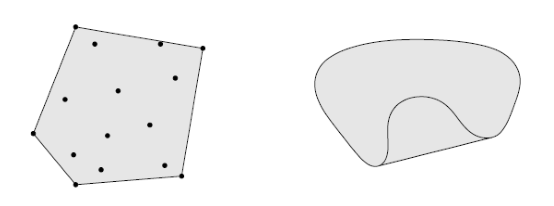
conv(C)는 집합 C를 포함하는 가장 작은 convex set이다.
Convex Functions
- Let , where is a nonempty convex set in .
The function is said to be convex on if with- concave : if is convex on .
- strictly convex or strictly concave if the equality doesn't hold.
Convex function 는 domain 위의 임의의 두 점을 이은 선분이 항상 위에 있다.
Theorem: Jensen's inequality
For a convex function and ,
를 확률(합이 1)에서의 기댓값으로도 볼 수 있다: .
Theorem: First-order conditions
Let be a nonempty open convex set in , and let be differentiable on .
Then is convex if and only if for any , we have,
Convex function은 항상 특정 point (x,f(x))의 접선보다 크거나 같다.
Convexity and Optima
Critical Points
여기서 말하는 제약이 없는 최적화 문제 (unconstrained problem)는 최소화 문제(minimizing problem)을 말한다.
minimizing over 에 대해,
-
If for all , then is called a global minimum.
-
If for all , then is called a local minimum.
-
If is differentiable and , then is called a critical point of .
-
If is a critical point, but neither a maximum nor a minimun, then is called a saddle point.
단, critical point가 아니더라도, local maximum (또는 minimum)이 나타날 수 있다.
Convex Optimization Problem
- Convex set 에 대해, 함수 가 상에서 convex function이면, 를 Convex optimization problem (CO)라고 말한다.
CO에서는 local optima가 곧 global optima라는 좋은 성질이 있다.
Theorem: Convex optimization problem
is a local minimum for (CO), if and only if, is a global minimum for (CO).
주어진 optimization 문제가 CO인지 확인하기 위해서는 우선 domain이 convex set인지 확인해야 하며, 이후 해당 set 위에서의 에 대한 Hessian matrix가 SPD인지 확인해야 한다.
Theorem: Second-order conditions
Let be a nonempty open convex set in , and let be twice differentiable on .
Then is convex if and only if its Hessian is positive semidefinite for all .
또한, 의 Hessian matrix에 대한 postive definiteness 검증을 통해 가 strictly convex function임을 보일 수 있다.
Lemma:
If the Hessian matrix is positive definite, then is strictly convex.
If is strictly convex and quadratic then its Hessian matrix is positive definite at each point of .
참고로, 2x2 matrix , 의 경우 , 를 만족하면 postive definite이다.
