📌 다항회귀분석(Polynomial regression analysis)
- 단순회귀분석처럼 한 개의 연속형 독립변수를 이용하여 한 개의 연속형 종속변수를 예측한다.
- 단순회귀분석과 달리 선형관계는 독립변수의 n차 다항식으로 모델링한다.
- y = B_0 + B_1 x + B_2 x^2
- 산점도에 관측값을 통과하는 추세선을 그렸을 때 n-1개의 굴절이 관찰되면 일반적으로 이를 n차 다항식으로 모델링
> library(car)
> str(Prestige)
'data.frame': 102 obs. of 6 variables:
$ education: num 13.1 12.3 12.8 11.4 14.6 ...
$ income : int 12351 25879 9271 8865 8403 11030 8258 14163 11377 11023 ...
$ women : num 11.16 4.02 15.7 9.11 11.68 ...
$ prestige : num 68.8 69.1 63.4 56.8 73.5 77.6 72.6 78.1 73.1 68.8 ...
$ census : int 1113 1130 1171 1175 2111 2113 2133 2141 2143 2153 ...
$ type : Factor w/ 3 levels "bc","prof","wc": 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 2 ...📌 교육기관과 소득 간의 관계 분석
단순회귀분석
> Prestige.lm <- lm(income ~ education, data=Prestige)
> summary(Prestige.lm)
Call:
lm(formula = income ~ education, data = Prestige)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-5493.2 -2433.8 -41.9 1491.5 17713.1
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -2853.6 1407.0 -2.028 0.0452 *
education 898.8 127.0 7.075 2.08e-10 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3483 on 100 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.3336, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3269
F-statistic: 50.06 on 1 and 100 DF, p-value: 2.079e-10회귀식 : income = -2853.6 + 898.8 * education
교육기간이 1년 증가할 때 마다 소득은 898.8 달러씩 증가한다.
> windows(width=12, height=8)
> plot(Prestige$income ~ Prestige$education,
+ col="cornflowerblue", pch=19,
+ xlab="Education (years)", ylab="Income (dollars)",
+ main="Education and Income")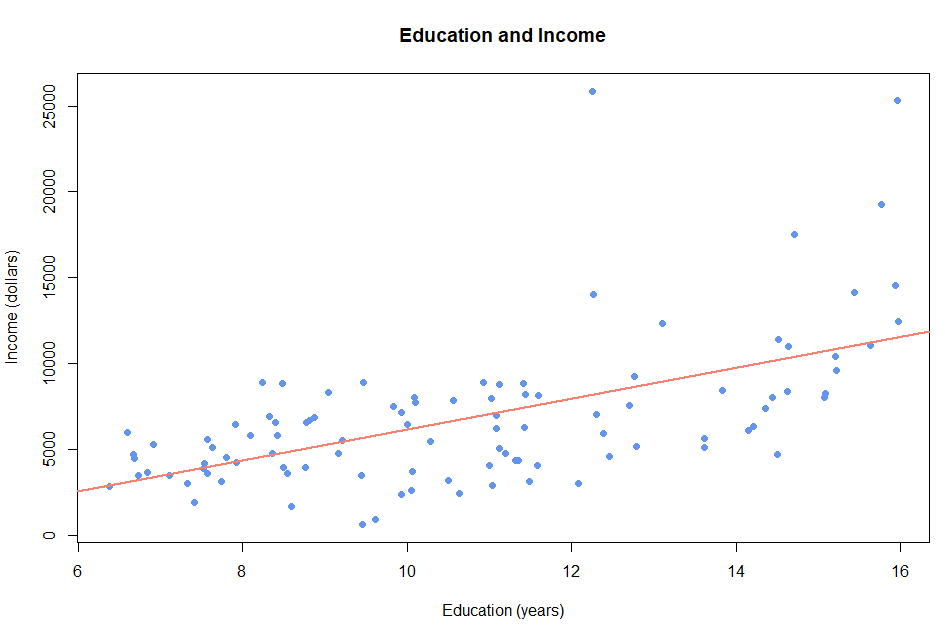
산점도 관측값들을 보면 교육기관이 짧을 때와 길 때 소득에 미치는 영향이 다르다. 교육기관이 길 때는 짧을 때에 비해 한 단위 증가에 따른 소득의 증가폭이 더 크다. 직선이 교육기관과 소득 간의 관계를 잘 표현하는지는 더 생각해볼 필요가 있다.
📌 교육기관이 짧은 집단과 긴 집단으로 나누어 회귀분석
> lm(income ~ education, data=Prestige,
+ subset=(education > mean(Prestige$education))) # 긴 집단
Call:
lm(formula = income ~ education, data = Prestige, subset = (education >
mean(Prestige$education)))
Coefficients:
(Intercept) education
-10299 1455
> lm(income ~ education, data=Prestige,
+ subset=(education <= mean(Prestige$education))) # 짧은 집단
Call:
lm(formula = income ~ education, data = Prestige, subset = (education <=
mean(Prestige$education)))
Coefficients:
(Intercept) education
2546.6 281.8 긴 집단 : 독립변수 회귀계수 1455
짧은 집단 : 독립변수 회귀계수 281.8
두 집단에 있어서 회귀선의 기울이가 다르다는 것은 단일 직선의 회귀선 보다는 굴절을 갖는 곡선에 의해서 더 잘 설명될지도 모른다.
> scatterplot(income ~ education, data=Prestige,
+ pch=19, col="orangered", cex=1.2,
+ regLine=list(method=lm, lty=2, lwd=3, col="royalblue"),
+ smooth=list(soother=loessLine, spread=FALSE,
+ lty.smooth=1, lwd.smooth=3, col.smooth="green3"),
+ xlab="Education (years)", ylab="Income (dollars)",
+ main="Education and Income")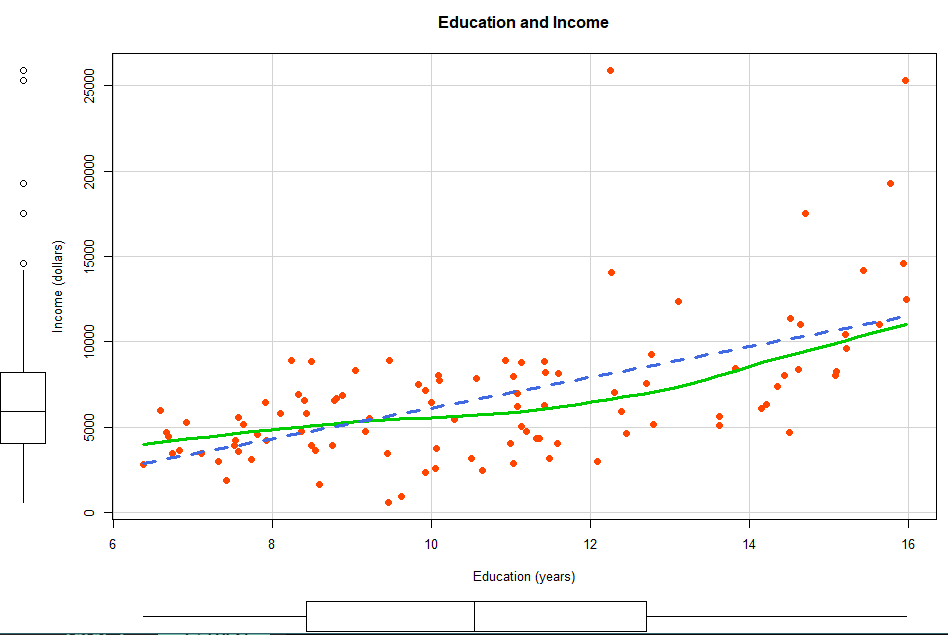
- regLine : 직선
- method=lm : 선형 회귀선
- smooth : 곡선 추세선
- soother=loessLine : 현제 데이터의 구간별 가장 적합한 추세선
곡선 loess 추세선이 개별 데이터를 더 잘 나타낸다. 따라서 2차항 회귀모델이 더 적합하다.
다항회귀분석
📝 포뮬러 심볼
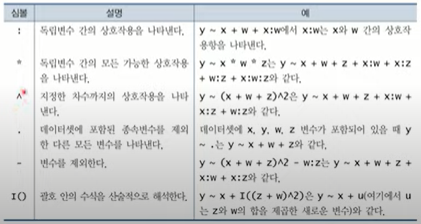
> summary(prestige.poly)
Call:
lm(formula = income ~ education + I(education^2), data = Prestige)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-5951.4 -2091.1 -358.2 1762.4 18574.2
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 12918.23 5762.27 2.242 0.02720 *
education -2102.90 1072.73 -1.960 0.05277 .
I(education^2) 134.18 47.64 2.817 0.00586 **
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3369 on 99 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.383, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3706
F-statistic: 30.73 on 2 and 99 DF, p-value: 4.146e-11
- p-value = 4.146e-11이므로 다항회귀 모델의 회귀식은 통계적으로 유의하다.
- RSE = 3369
- R-squared = 0.383
📌 단순회귀 결과와 비교
> Prestige.lm <- lm(income ~ education, data=Prestige)
> summary(Prestige.lm)
Call:
lm(formula = income ~ education, data = Prestige)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-5493.2 -2433.8 -41.9 1491.5 17713.1
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -2853.6 1407.0 -2.028 0.0452 *
education 898.8 127.0 7.075 2.08e-10 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 3483 on 100 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.3336, Adjusted R-squared: 0.3269
F-statistic: 50.06 on 1 and 100 DF, p-value: 2.079e-10
- p-value = 2.079e-10이므로 단순회귀 모델의 회귀식은 통계적으로 유의하다.
- RSE = 3483
- R-squared = 0.3336
RSE 값은 작을수록 좋고, R-squared 값은 클수록 좋다.
따라서 다항회귀 모델이 단순회귀 모델에 비해서 더 우수하다.
⭐ 다중공선성 ⭐
- I(education^2)의 p-value = 0.00586 통계적으로 유의하다.
- education의 p-value = 0.05277 통계적으로 유의하지 않다.
두 독립변수 간의 통계적 유의성이 다르게 나타난 이유는 ❓
두 독립변수 간의 강한 상관관계가 이유일 수도 있다. => ⭐다중공선성⭐
다항회귀분석은 다중공선성이 나타날 확률이 크다.
왜 ❓
2차항은 원래의 독립변수를 바탕으로 계산되기 때문에 상관관계가 크다. 다만 회귀식은 통계적으로 유의하기 때문에 예측이 주 목적이라면, 문제가 되지 않는다.
📌 faithful 데이터 셋으로 다항 회귀 분석
> str(faithful)
'data.frame': 272 obs. of 2 variables:
$ eruptions: num 3.6 1.8 3.33 2.28 4.53 ...
$ waiting : num 79 54 74 62 85 55 88 85 51 85 ...
> # 분출 대기시간과 분출 지속시간 간의 관계
> scatterplot(eruptions ~ waiting, data=faithful,
+ pch=19, col="deepskyblue", cex=1.2,
+ regLine=list(method=lm, lty=2, lwd=3, col="blueviolet"),
+ smooth=list(soother=loessLine, spread=FALSE,
+ lty.smooth=1, lwd.smooth=3, col.smooth="coral"),
+ xlab="waiting (minutes)", ylab="Eruptions (minutes)",
+ main="Waiting Time Between Eruptions and the Duration of the Eruptions")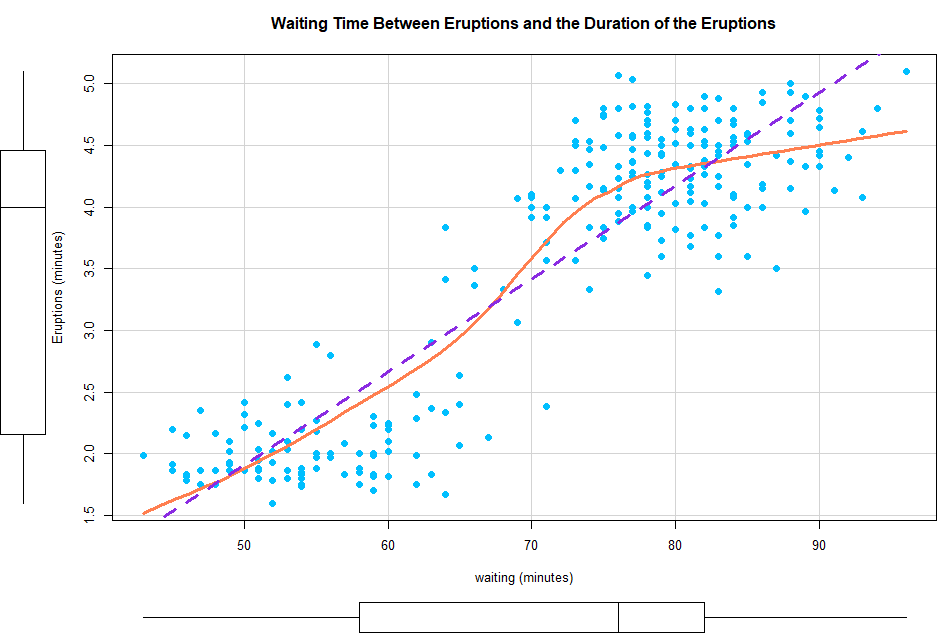
2개의 굴절이 나타나기 때문에 3차 다항식 회귀 모델을 해야 한다.
> faithful.ploy <- lm(eruptions ~ waiting + I(waiting^2) + I(waiting^3), data=faithful)
> summary(faithful.ploy)
Call:
lm(formula = eruptions ~ waiting + I(waiting^2) + I(waiting^3),
data = faithful)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.20224 -0.21761 -0.02508 0.27463 1.28682
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) 3.063e+01 3.722e+00 8.229 8.27e-15 ***
waiting -1.438e+00 1.672e-01 -8.601 6.74e-16 ***
I(waiting^2) 2.290e-02 2.450e-03 9.346 < 2e-16 ***
I(waiting^3) -1.128e-04 1.176e-05 -9.593 < 2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.4238 on 268 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8637, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8622
F-statistic: 566 on 3 and 268 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
- p-value = < 2.2e-16 이므로 다항 회귀모델의 회귀식은 통계적으로 유의하다.
- RSE = 0.4238
- R-squared = 0.8637
📌 단순회귀분석과 비교
faithful.lm <- lm(eruptions ~ waiting, data=faithful)
> summary(faithful.lm)
Call:
lm(formula = eruptions ~ waiting, data = faithful)
Residuals:
Min 1Q Median 3Q Max
-1.29917 -0.37689 0.03508 0.34909 1.19329
Coefficients:
Estimate Std. Error t value Pr(>|t|)
(Intercept) -1.874016 0.160143 -11.70 <2e-16 ***
waiting 0.075628 0.002219 34.09 <2e-16 ***
---
Signif. codes: 0 ‘***’ 0.001 ‘**’ 0.01 ‘*’ 0.05 ‘.’ 0.1 ‘ ’ 1
Residual standard error: 0.4965 on 270 degrees of freedom
Multiple R-squared: 0.8115, Adjusted R-squared: 0.8108
F-statistic: 1162 on 1 and 270 DF, p-value: < 2.2e-16
- p-value = < 2.2e-16
- RSE = 0.4965
- R-squared = 0.8115
따라서 다항 회귀 모델의 성능이 조금 더 뛰어나다.
