🍀 가장 먼 노드
이 문제에서 가장 멀리 떨어진 노드를 최단 거리로 이동했을 때를 기준으로 한다. 따라서 dfs보다는 bfs 알고리즘을 이용하는 것이 적절해 보여 bfs를 이용하여 문제를 풀었다. 이 문제를 풀기 이전에 푼 문제인 단어 변환에서 python으로 푼 풀이가 굉장히 도움이 되었다. sibling node들의 level을 구한다는 점에서 같은 로직이며 이 문제는 leaf node일 때 가장 먼 노드가 되며 이 때의 거리와 같은 거리를 갖는 node들이 정답이 된다.
1️⃣ Python
문제를 푼 로직은 아래와 같다.
💡 로직
- while queue
- for 현재 노드들 방문
- 방문하지 않았으면서 다음으로 탐색가능한 노드들을 queue에 넣는다.(이 때, sibling node들은 하나의 배열에 넣음)
- 다음 탐색 가능한 노드들을 방문처리한다.
- if not queue => sibling node의 길이가 문제의 해답이다.
구현
먼저 노드들과의 간선정보를 그래프로 표현해야 하는데 간선의 개수가 노드 수 보다 많다는 조건에서는 인접 행렬을 쓰는 것이 좋아보였지만 간선 정보를 파악하는 문제가 아니므로 시간 단축을 위해 인접 리스트를 이용하여 그래프를 만드는 전략을 선택하였다.
먼저 간선 정보를 graph로 변환해보자. 이 때, 조심해야 할 점은 양방향 그래프 이므로 시작 노드와 도착 노드에 간선 정보를 모두 담아 주어야 한다. defaultdict의 초기값을 주어 key가 없을 경우처리를 간편하게 하였다.
from collections import defaultdict
def create_graph(edge):
d = defaultdict(list)
for start, end in edge:
d[start].append(end)
d[end].append(start)
return dgraph를 만들었으니 위의 로직대로 코드를 구현하면 된다.
from collections import deque
def filter_key(next_node, visited):
before_visit = visited[next_node]
visited[next_node] = True
return not before_visit
def solution(n, edge):
answer = 0
q = deque([[1]])
graph = create_graph(edge)
visited = [True, True] + [False] * (n - 1)
while q:
current_nodes = q.popleft()
next_nodes = []
for current_node in current_nodes:
next_nodes += list(filter(lambda next_node: filter_key(next_node, visited), graph[current_node]))
if not next_nodes: # ⭐️
answer += len(current_nodes)
break
q.append(next_nodes)
return answer이 코드에서 방문처리를 filterKey함수 내에서 했는데 지금 짜고 보니까 단일 원칙에 조금 어긋나지 않나 싶기도 한 것 같다... 디버깅을 할 때 방문처리에서 오류가 날 시 추적하기 어려워 보인다... 흠...🤣
주석에 ⭐️ 표시가 중요한데, 다음 탐색할 노드가 없다는 것은 현재 노드가 leaf node임을 뜻한다. bfs의 특징상 처음 노드를 방문할 때 최단거리로 방문하므로 leaf node를 방문했을 때 거리가 최단거리가 된다. 따라서 leaf node방문 시 leaf node의 sibling nodes를 count하면 된다.
2️⃣ Javascript
python으로 풀이한 방법말고 다른 풀이 방법이 떠올라 javascript로 구현할 때는 최단거리를 기록하는 방식으로 풀었다. distances라는 배열의 index를 노드 번호와 매칭시키고 배열의 요소를 노드를 탐색했을 때 최단거리를 기록하는 방식이다. 자신만만하게 코드를 짜고 제출을 했는데 시간 초과가 발생했다....🥺🥺🥺
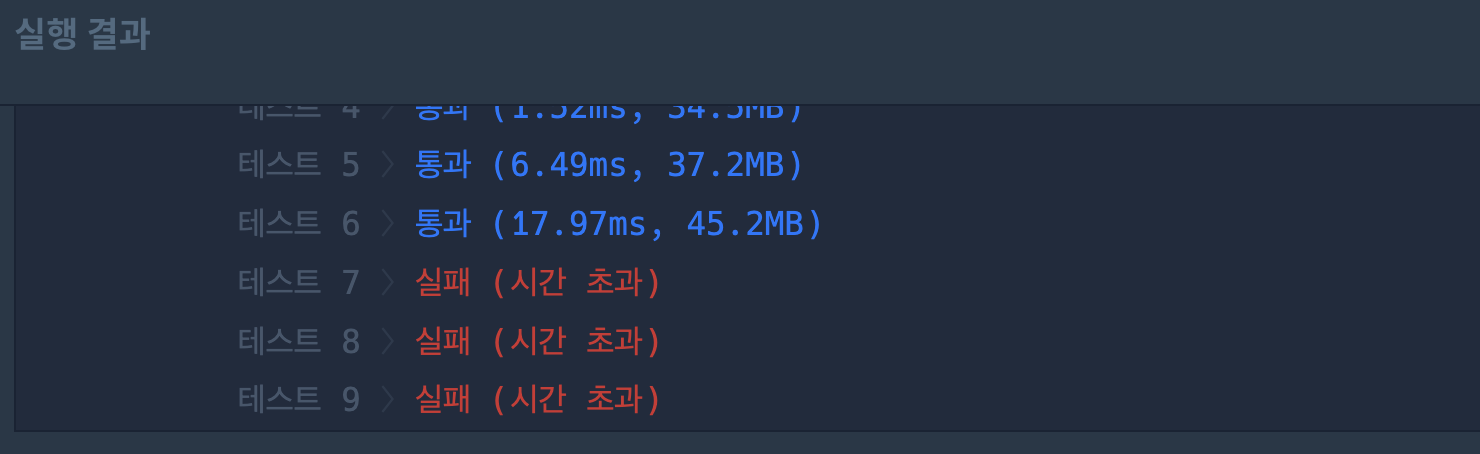
구현
시간초과가 발생하여 queue를 Linked List기반으로 구현 후 다시 도전했다.
// implement Queue
class Node {
constructor(value){
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor(){
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(value){
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.first){
this.first = this.last = newNode;
}else{
this.last.next = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
}
this.size++;
return value;
}
dequeue(){
if (this.first === null) return null;
if (this.first === this.last) this.last = null;
const value = this.first.value;
this.first = this.first.next;
this.size--;
return value;
}
}// createGraph function
const createGraph = (edge) => edge.reduce((acc, [startNode, endNode]) => ({
...acc,
[startNode]: [...(acc[startNode] ?? []), endNode],
[endNode]: [...(acc[endNode] ?? []), startNode]
}), {})하지만, 다시 시간 초과가 났다. 코드를 다시 꼼꼼히 살펴보니 createGraph에서 spread를 통해 복사하는 부분이 최악의 경우 O(N^2) 시간 복잡도를 갖는다는 사실을 발견하였다.
따라서 createGraph를 아래와 같이 다시 구현하여 O(N)을 갖게 변경하였다.
// createGraph function
function createGraph(edge) {
const graph = {};
for (const [start, end] of edge){
graph[start] ?? (graph[start] = []);
graph[end] ?? (graph[end] = []);
graph[start].push(end);
graph[end].push(start);
}
return graph;
}전체 코드
class Node {
constructor(value){
this.value = value;
this.next = null;
}
}
class Queue {
constructor(){
this.first = null;
this.last = null;
this.size = 0;
}
enqueue(value){
const newNode = new Node(value);
if (!this.first){
this.first = this.last = newNode;
}else{
this.last.next = newNode;
this.last = newNode;
}
this.size++;
return value;
}
dequeue(){
if (this.first === null) return null;
if (this.first === this.last) this.last = null;
const value = this.first.value;
this.first = this.first.next;
this.size--;
return value;
}
}
function createGraph(edge) {
const graph = {};
for (const [start, end] of edge){
graph[start] ?? (graph[start] = []);
graph[end] ?? (graph[end] = []);
graph[start].push(end);
graph[end].push(start);
}
return graph;
}
function solution(n, edge) {
const startNode = 1;
let maxDistance = 0;
const queue = new Queue()
queue.enqueue(startNode)
const graph = createGraph(edge);
const distances = Array(n + 1).fill(0);
while (queue.size > 0) {
const currentNode = queue.dequeue();
const nextDistance = distances[currentNode] + 1;
for (const nextNode of graph[currentNode]) {
if (!distances[nextNode] && nextNode !== startNode){
distances[nextNode] = nextDistance;
queue.enqueue(nextNode)
}
}
if (queue.size <= 0) maxDistance = nextDistance - 1;
}
return distances.filter(distance => distance === maxDistance).length;
}위의 코드에서 보면 방문처리 하는 것이 안 보일 수 있는데 거리가 기록되지 않았다면 방문하지 않았음을 유추할 수 있다. 따라서 따로 visited라는 변수를 사용하지 않고 !distance[nextNode]를 통해 방문처리를 해결하였다. 그리고 nextNode !== startNode라는 조건이 있는데 startNode = 1인 최단거리는 0이므로 방문 했음에도 방문처리가 되지 않아 조건을 추가한 것이다.
이제 결과를 살펴보면

통과했다!!!🎉🎉🎉
🔥 마치며
단어 변환에서 고민한 문제가 이 문제를 푸는데 엄청 도움이 되었다. 특히, 블로그를 쓰기 위해 정리하고 자료를 만드는 과정에서 머릿속에서 한 번 더 깔끔하게 정리가 됐다. 블로그를 몇 개 쓰지 않았지만, 블로그를 써저 얻는 이점을 생각해보자면, 같은 문제에 대해 물어볼 시 링크만 주어 시간 단축효과가 있는 것 같고 스스로 다시 정리하여 머릿속에서 정돈되는 효과와 같은 문제에 대한 해결을 빠르게 처리하는 효과가 있는 것 같다. 단어 변환을 푸는데 1시간 이상 걸린 거 같았는데 이 문제를 풀 때 40분으로 단축되었다. 노력에 대한 결실을 맺는 느낌이라 기분이 매우 좋았다. 하지만, 문제를 풀면서 bfs에 대한 구현은 아직 부족하다고 생각이 든다...ㅜㅜ
