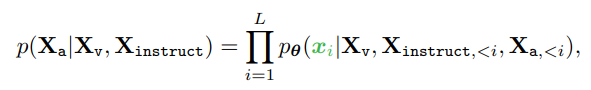Visual Instruction Tuning (NeurIPS 2023)

Introduction
- Multi-modal vision language model을 만드는 것은 core inspiration
- Language는 image content를 describe 함
- 이는 image가 visual signal을 language semantic으로 전환할 수 있음을 뜻함
- 이는 보통의 인간의 소통과 유사
- LLM은 wider role을 가짐
- 우리는 visual instruction-tuning을 제시
- Multimodal instruction-following data: GPT4를 통해 image-text pair의 적절한 intruction following data를 수집
- Lage multimodal models: visual encoder CLIP과 language decoder Vicuna를 결합한 multimodal model 개발
- Multimodal instruction following benchmark: LLaVA-Bench라는 두 benchmark set 개발
- Open-source: 이는 모두 오픈 소스로 공개됨
GPT-assisted Visual Instruction Data Generation

- 기존 Instruction following data는 (CC, LAION)은 양이 총체적으로 부족
- Time consuming / less well-defined
- GPT의 text annotation tasks를 통해, 우리는 GPT4를 multimodal instruction-following data collector로 활용
- image Xv, caption Xc, question Xq
- 이러한 pair는 construct하기 쉬우나, diversity와 in-depth reasoning에서 한계가 존재
- 이를 해결하기 위해, GPT-4와 ChatGPT를 활용
- image를 text-only GPT의 input으로 활용하기 위해 symbolic representation을 활용
- Caption과 bounding box
- 이를 통해 LLM-recognizable sequence로 encoding
- 우리는 COCO image를 통해 three type의 instruction-following data를 제작

- In-context에는 manually design한 few example이 포함됨
- Type은 총 3가지
- Conversation
- assistant와 person이 photo에 관해 QA
- Detailed description
- list of question을 통해 detail한 description을 생성
- Complex reasoning
- 상위 두 타입을 통해 visual content를 이해한 뒤, in-depth reasoning question을 통해 step-by-step reasoning을 가능케 함
Visual Instruction Tuning
Architecture
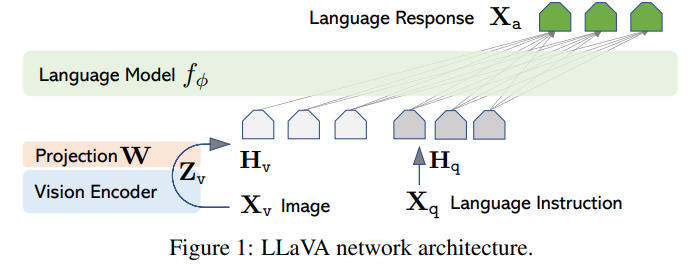
- 목표는 효과적으로 pre-trained LLM과 Visual Model을 leverage하는 것
- image를 Visual Encoder로 인코딩 한 뒤, projection (trainable)하여 이 visual token 획득
Training

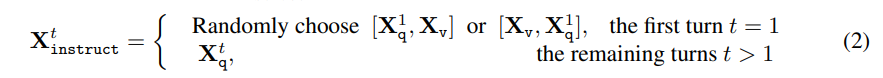
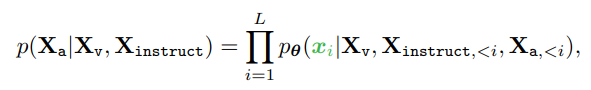
- image에 대하여, 우리는 multi-turn conversation을 generate
- 우리는 sequence로 조직화하여 모든 답을 assistant의 answer로 여기게 함
- auto-regressive하게 학습
Stage 1: Pre-training for Feature Alignment
- Filtering을 통해 naive한 single-turn instruction-following data 생성
- Visual Encoder와 Text Decoder가 freeze된 상태로, projection matrix를 학습
- frozen LLM이 visual token을 잘 이해하도록 하는 것
Stage 2: Fine-tuning End-to-End
- Visual Encoder는 항상 freeze인 상태로, projection layer와 LLM을 학습
- 두 개의 scenario를 가정하고 학습
- Multimodal Chatbot
- conversation을 multi-turn으로, 나머지 type을 single-turn으로 학습
- Science QA
- Science QA benchmark를 활용하여 task solving
Experiments
Multimodal Chatbot
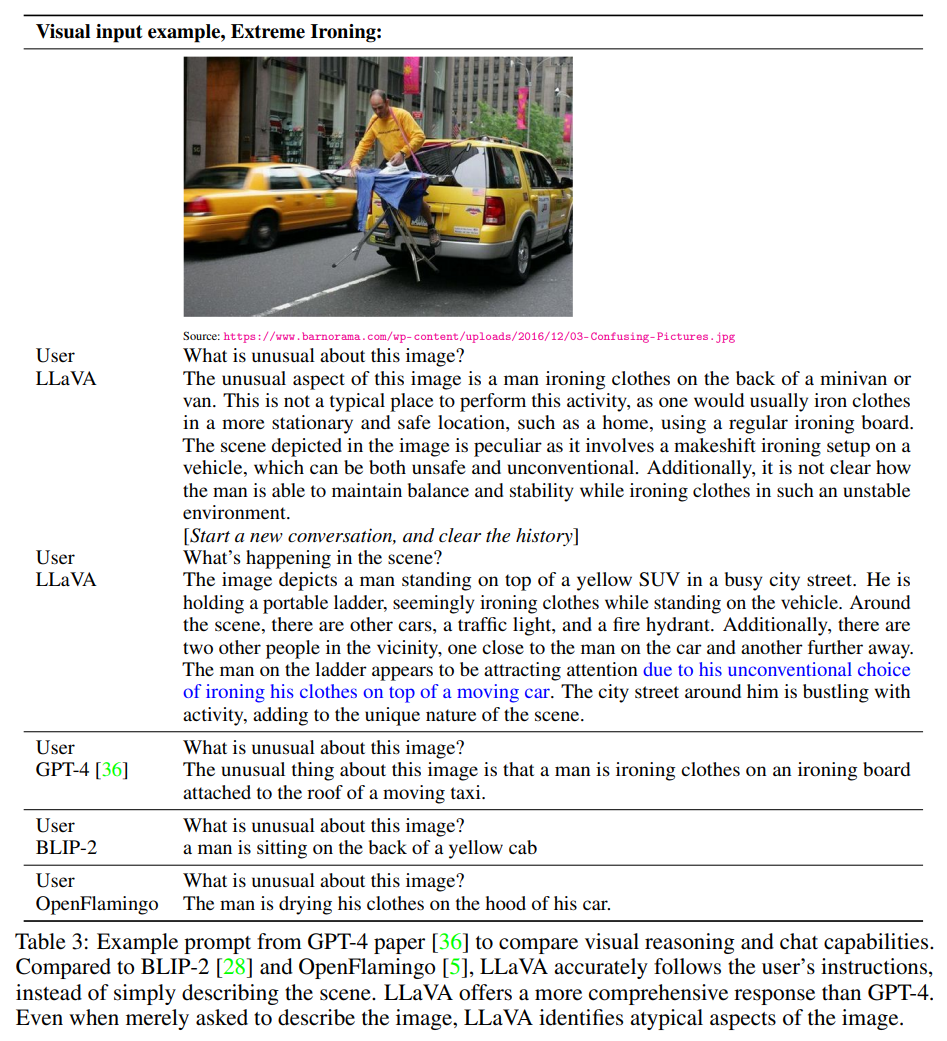
- original GPT-4 paper의 example
- 적은 데이터 셋 숫자임에도 불구하고 GPT-4에 견주는 성능
- 또한 이는 out-domain의 image임에도 resonable한 답변
- BLIP-2와 OpenFlamingo는 image를 describe하는 데 집중하였지만, user의 instruction을 따르지는 않았음
Limitation

- 학습 데이터 부족으로 multilingual에서는 약점을 보임
- LLaVA는 image를 단순히 'bag-of-patches'로 인식하여 complex reasoning에서 약점을 보임