Total_url: https://github.com/tianyi-lab/Reflection_Tuning
[Paper 1]
- Title: “Reflection-Tuning: Recycling Data for Better Instruction-Tuning”
- url: https://openreview.net/forum?id=xaqoZZqkPU
[Paper 2]
- Title: “Selective Reflection-Tuning: Student-Selected Data Recycling for LLM Instruction-Tuning”
- url: https://arxiv.org/abs/2402.10110
배경
Paper 1
- 저품질의 데이터가 instruction tuning에 부정적 영향을 끼침 (instruction tuning은 학습 데이터의 퀄리티에 취약)
- 저품질의 학습 데이터가 조금만 있어도 LLM 성능이 저하된다는 연구도 있었음
- 전체 데이터에서 선별된 고품질 데이터만 활용했을 때, LLM 성능 향상을 확인한 연구도 있었음
Paper 2
- Instruction tuning에서 data의 퀄리티 개선에 중점을 두고 있지만, 데이터와 student model 간의 호환성을 간과하는 경우가 많음
- 즉, teacher model이 data quality improvement를 진행했다고 해도, 학생 모델이 이에 어떻게 반응하는지를 확인해야 한다
- 의문1: Is the teacher-refined data compatible to the needs of the student model? 이러한 접근 방식은 일반적으로 생성 모델의 출력과 관련된 고유한 무작위성과 잠재적 저하를 고려하지 않으므로 학생 모델이 이러한 "개선된" 데이터 샘플에 어떻게 반응하는지에 대한 감독이 필요
- 무작위성: decoding strategy를 보면, diverse를 주기 위해 top p, top-k 방법을 쓰는 등 랜덤성을 준다. 이 과정에서 instruction data가 적합한 데이터로 만들어지지 않을 수 있다(몇몇개)
- 잠재적 저하: teacher LLM이 개선한다고 했지만, 너무 복잡하거나 너무 이상하게 instruction과 response를 바꿔 데이터의 퀄리티 저하를 일으킬 수 있음. 또한 너무 복잡한 instruction은 student model에게 적합하지 않을 수 있음
- 의문2: How does the student model decide which enhanced data are needed and critical to its training? (Student model이 어떤 데이터가 필요하고 학습에 중요한지 어떻게 고르나요?)
- 기존: 정교한 모델 사용(e.g., GPT-4) or secondary judge model 사용 → 단점: 학습되는 모델과 다르다. (데이터의 퀄리티를 평가하는 모델과 실제 해당 데이터로 학습되는 모델이 다르다; 달라서 왜 안좋냐? gpt-4에게 안좋은 데이터, 좋은 데이터일 수 있지만 학습 모델에게는 그렇지 않을 수 있다.)
- 즉, judge model의 선호가 실제 student가 필요한 부분(requirements)이 아닐 수 있다.
- 해결 방안: Statistical Method 선택(Instruction-Following Difficulty 활용) → 여기서 나오는 score는 raw student model로 구함
의의
Paper 1
- LLM을 활용해 자동으로 데이터셋 품질 개선
- 추가적인 모델 학습 X → Reflection에 사용되는 Oracle LLM을 별도로 학습시키지 않음(reflection 성능 향상을 위한 학습 진행 X; 논문에서는 Oracle LLM으로 ChatGPT 사용하고, Pre-trained model은 LLaMA2를 사용한다)
- 다양한 instruction-response 구조에 적용할 수 있음
Paper 2
- Selective Reflection-Tuning: Teacher LLM의 reflection & introspection(data quality 개선) + student LLM의 data selection 능력 시너지 → 기존 instruction-tuning data를 자동으로 refine
- Teacher-Student collaboration pipeline → 높은 퀄리티 & student model과 호환이 되는 instruction-response pair를 생성(sample 효율적인 instruction tuning & 우수한 성능의 LLM 초래)
- 새로운 데이터를 수집하지 않고 LLM finetuning과 self-improvement를 개선한 “Data augmentation & synthesis” (방법론을 Alpaca와 WizardLM 데이터셋에 적용해 봄)
- 자동으로 생성된 작은 양(few thousand)의 데이터셋을 사용해 instruction tuning을 진행했음에도 좋은 성적을 냄 → 데이터의 퀄리티가 매우 좋다는 것을 의미
Related Works
Paper 2
- IFD
- 의미
- 주어진 instruction-response 쌍을 가지고, instruction의 difficulty를 측정하는데 사용하는 score
- 모델 가 주어졌을 때, 주어진 instruction 가 해당 response 를 생성하는데 얼마나 영향을 주는지를 나타냄 → Instruction-following data pair를 평가할 수 있는 효과적인 metric
- 참고 논문: “From Quantity to Quality: Boosting LLM Performance with Self-Guided Data Selection for Instruction Tuning”
- 식:
- : context로써 instruction 가 주어졌을 때, response 에 대한 모델 의 perplexity
- : context없이 response 에 대한 모델 의 perplexity
- 의미
방법론
Paper 1
- LLM의 self-improvement & 판단 능력을 통해 안좋은 퀄리티 데이터 문제 해결 → Oracle LLM을 이용, instructions와 response를 다시 보며 quality 향상시킴 (Oracle LLM이라는 것은 학습시킬 LLM과 다른 LLM을 말한다)
- LLM을 judge로 사용했을 때의 단점: 다양한 결과를 얻을 수 없음 → 이를 해결하기 위해 Chain-of-Thought & Tree-of-Thought에 영감을 받은 방법 사용
- 본 논문의 방법론은 크게 2가지 단계가 있음:

- Instruction-reflection

-
Critial Response 생성을 위한 부분
- Instruction을 주어진 기준에 맞춰 분석(Complexity of the Topic, Level of Detail Required, etc.)
- Answer를 주어진 기준에 맞춰 분석(Helpfullness, Relevance, etc.)
- 최종적으로 왜 안좋은 instruction이 안좋은 답변을 만들어 냈는지에 대한 분석
“이 모든 과정이 Criteria에 대한 critical response를 생성하고 있는 것”
-
Original instruction, Original response, Criteria, Critical Response를 이용해서, 새로운 instruction 생성 →
-
새로운 instruction에 대한 answer 생성 →
-
- response-reflection 이 과정이 있는 이유: 바뀐 instruction에 대한 답변이 optimal하지 않을 수 있다. 그래서 answer에 대한 reflection을 한 번 더 진행

- Answer에 대한 Critical Response 생성(Helpfulness, Relevance, Accuracy, etc. 기준에 맞춰)
- New answer 생성(더 나은 답변 생성) →
- 정리
- 최종적으로 갖게되는 new instruction - response pair:
- Instruction-reflection을 이용해서 새로운 instruction-response pair 생성
- 여기서 생성된 새로운 response가 optimal 하지 않을 수 있어서, response-reflection을 통해 response를 다시 생성
- 최종적으로 instruction-reflection에서 생성된 instruction과 response-reflection에서 생성된 response를 하나의 쌍으로 생성
- Instruction-reflection
Paper 2
- 주어진 특정 기준을 가지고 instruction 또는 response를 update → Update가 유익한지 student model이 평가(IFD or r-IFD 기반) → 여기서 선택된 몇몇 samples이 최종 instruction tuning에 사용될 수 있음
- 본 논문은 2단계로 구성: selective instruction reflection 단계, selective response reflection 단계
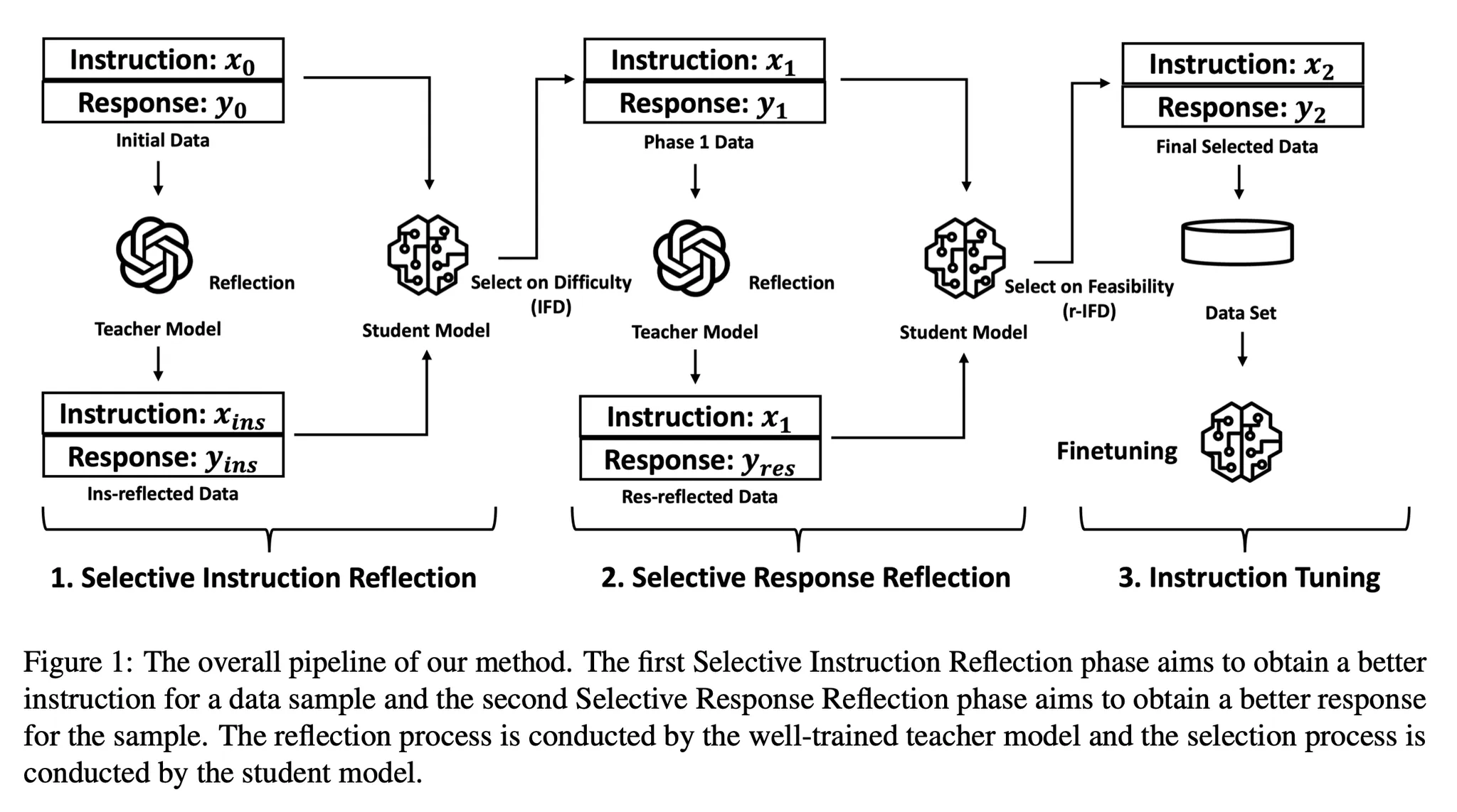
- Selective Instruction Reflection
- Reflection on Instruction
- paper1과 동일하게, teacher model이 특정 기준을 가지고 sample의 instruction을 reflection 하고, 해당 reflection에 따라 더 나은 sample을 생성
- Selection on Instruction
- 목적: “Teacher model이 update한 버전이 student model에게 더 좋은지 평가”
- base student model을 기반으로 updated instruction-response pair에 대한 IFD score 계산 (모델에게 instruction이 response를 생성하는데 얼마나 도움이 되는지를 측정)
- base student model을 기반으로 Original instruction-response pair에 대한 IFD score 계산 (모델에게 instruction이 response를 생성하는데 얼마나 도움이 되는지를 측정)
- Original pair와 updated pair 중 더 높은 IFD score를 가진 pair를 다음 단계로 넘겨 줌 (둘 중 더 높은 score를 가진 instruction-response pair를 다음과 같이 notation: )
- Reflection on Instruction
- Selective Response Reflection
- Reflection on Response
- 이전 과정을 통해 instruction 은 보장이 되었지만, response는 그렇지 않음
- 그렇기에 paper 1의 reflection on response와 같이 updated response를 생성
- 최종적으로 생성되는 pair:
- Selection on Response
- r-IFD
- 의의: response를 보고, 원래의 instruction을 유추하는 것이 얼마나 쉬운가를 측정(low score → instruction을 더 쉽게 예측할 수 있음.
- 관련 논문(Self-alignment with instruction backtranslation)에 확장하여 다음과 같은 가설을 세움: LLM이 response를 가지고 그에 해당하는 instruction을 유추하기 쉬우면, 그 response는 학습에서 더 informative
- 식:
- 순서
- 에 대한 r-IFD score 계산
- 에 대한 r-IFD score 계산
- 둘 중에 더 낮은 r-IFD score를 가진 pair를 로 표현하고 최종적으로 사용
- r-IFD
- Reflection on Response
- 정리
- Original instruction-response pair:
- Selective Instruction Reflection을 통해 생성
- Selective Response Reflection을 통해 생성
- 최종적으로 selective reflection을 통해
- Selective Instruction Reflection
실험 결과
Paper 1
- Pair-wise comparison
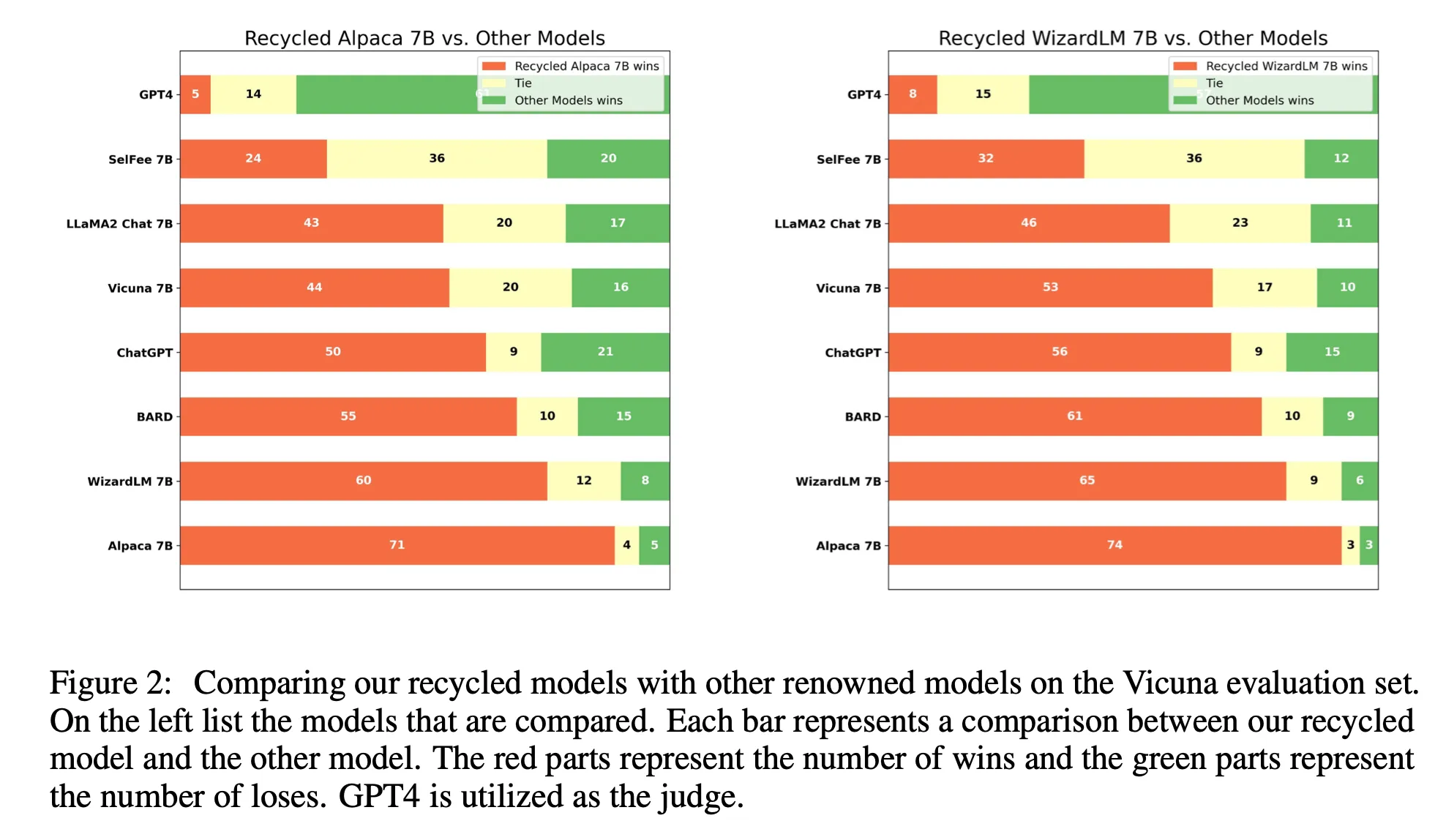 Judge로는 GPT4 or ChatGPT 사용(이유: 사람이 평가하면 너무 비쌈 & 사람마다 편향이 있을 수 있기에) 순서도 결과에 영향을 줄 수 있으므로, 평가할 두 개의 모델 출력을 순서를 다르게 하여 두 번 평가한다.
Judge로는 GPT4 or ChatGPT 사용(이유: 사람이 평가하면 너무 비쌈 & 사람마다 편향이 있을 수 있기에) 순서도 결과에 영향을 줄 수 있으므로, 평가할 두 개의 모델 출력을 순서를 다르게 하여 두 번 평가한다.- 승: “두 순서 모두에서 승리” or “하나의 순서에서 승리 & 하나의 순서에서는 동점”
- 무: “두 순서에서 모두 동점” or “하나의 순서에서 승리 & 하나의 순서에서 패배”
- 패: “두 순서에서 모두 패배” or “하나의 순서에서 패배 & 하나의 순서에서 동점”
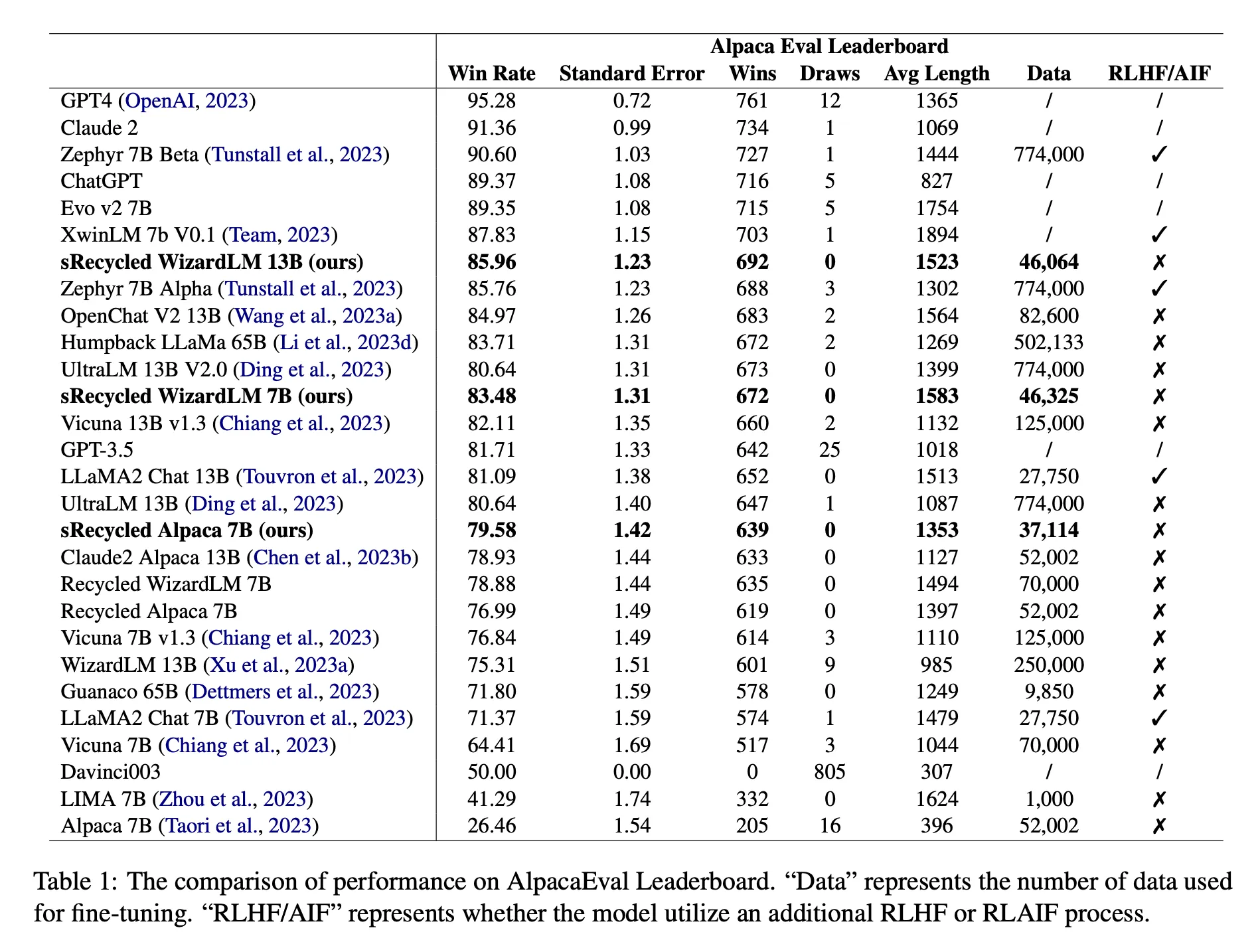
- Alpaca-Eval LeaderBoard
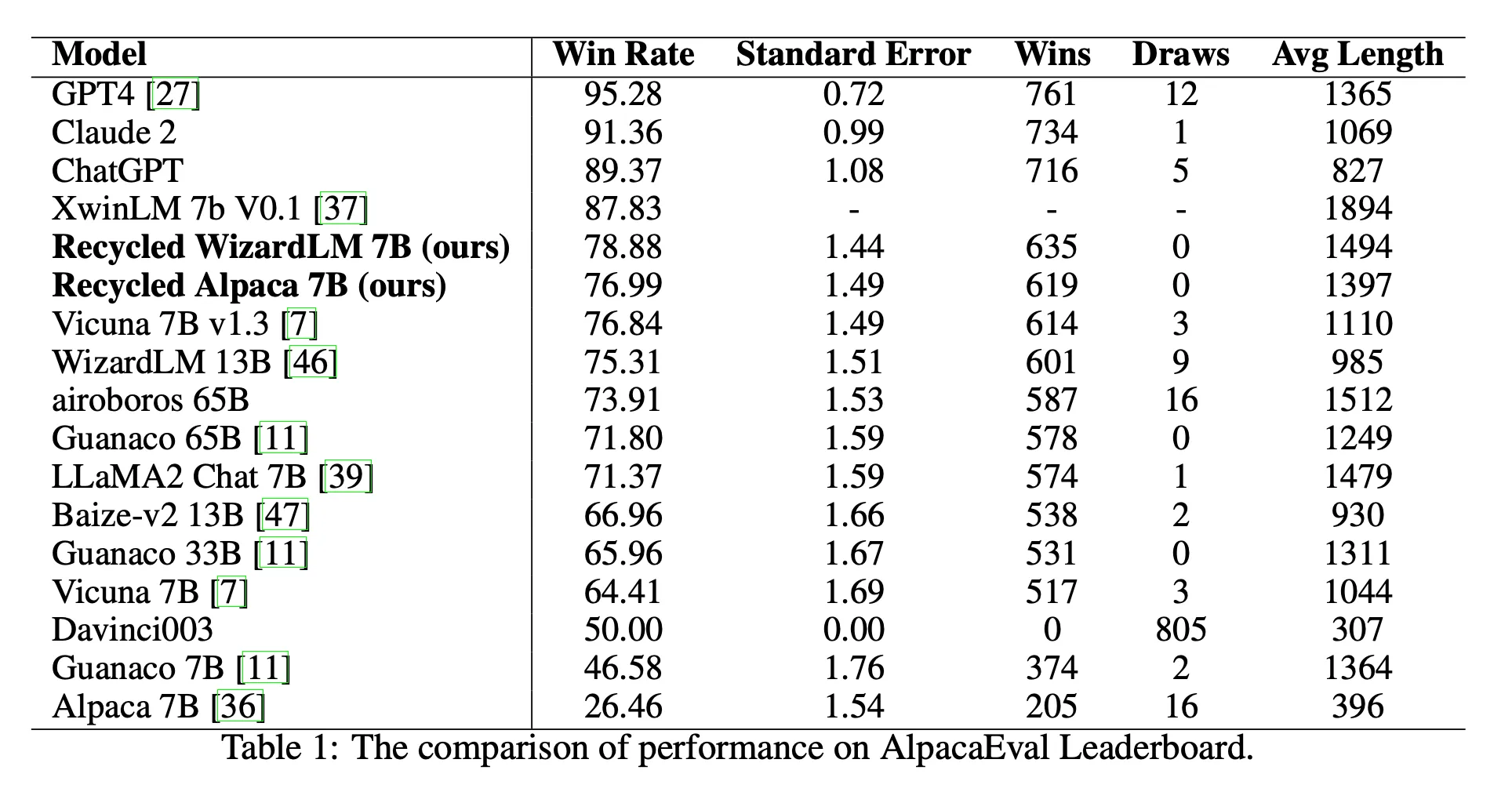
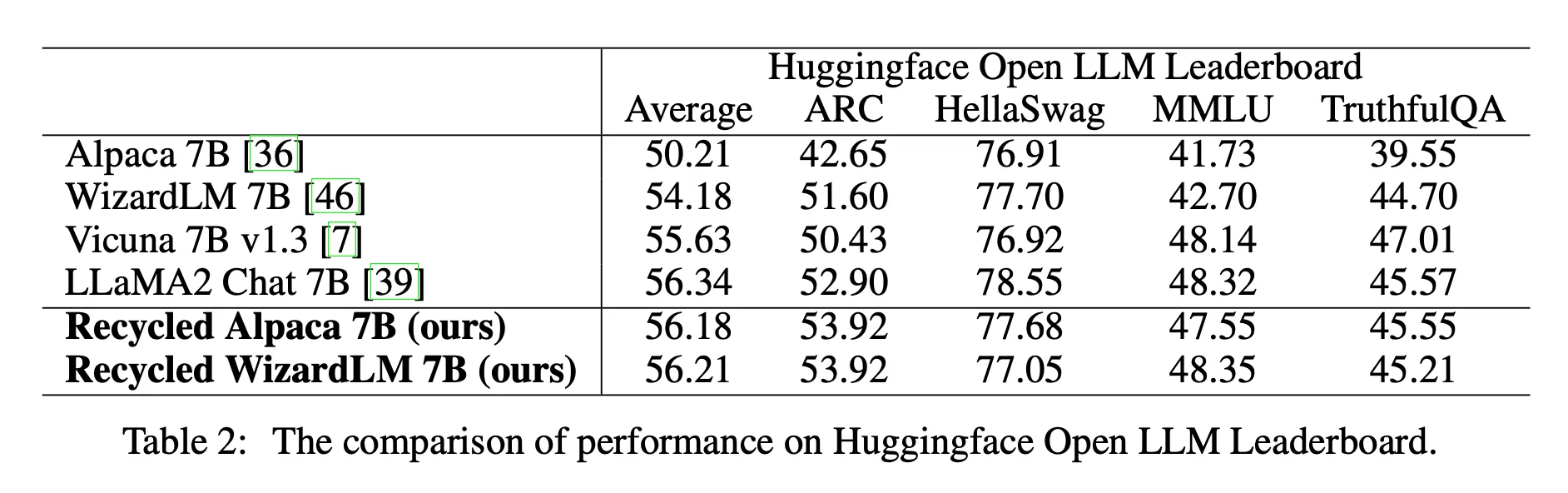
- HuggingFace Open LLM LeaderBoard
Paper 2
- Alpaca-Eval LeaderBoard
- HuggingFace Open LLM LeaderBoard