CNN(Convolution Neural Network)
- Convolution layer(합성곱 계층)
- Pooling layer(풀링 계층)
지금까지 본 신경망은 인접하는 계층의 모든 뉴런과 결합되어 있었다. 이를 완전 연결(fully-connected)이라고 하며, 완전히 연결된 계층을 Affine계층이라는 이름으로 하였다.
ex) 5개층 완전연결 신경망
{[Affine][Relu]} {[Affine][Relu]} {[Affine][Relu]} {[Affine][Relu]} {[Affine][Softmax]}
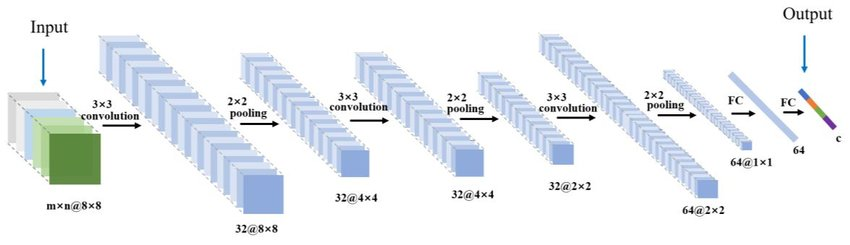
CNN의 구조
{[Conv][Relu][Pooling]} {[Conv][Relu][Pooling]} {[Conv][Relu]} {[Affine][Relu]} {[Affine][Softmax]}
- CNN의 계층은 'Conv-ReLU-(Pooling)'흐름으로 연결된다.
Fully connected layer의 문제점
- 완전연결 계층의 가장 큰 문제점은 데이터의 형상이 무시된다는 사실이다.
- 이때까지, MNIST 데이터 셋의 경우 (1, 28, 28)을 1줄로 세운 784개의 데이터를 첫 Affine 계층에 입력하였다.
- 이미지는 3차원 형상이며, 이 형상에는 중요한 공간적 정보가 담겨져 있다. 즉 공각적으로 가까운 픽셀은 값이 비슷하거나 , RGB의 각 채널은 서로 밀접하게 관련되어 있거나, 거리가 먼 픽셀끼리는 별 연관이 없는 등, 3차원 속에서 의미를 갖는 본질적인 패턴이 숨어있다.
- 완전연결 계층은 형상을 무시하고 모든 입력 데이터를 동등한 뉴런(같은 차원의 뉴런)으로 취급하여 형상에 담긴 정보를 살릴 수 없다.
Convolution layer의 가장 큰 장점은 형상을 유지한다는 점이다.
Convolution
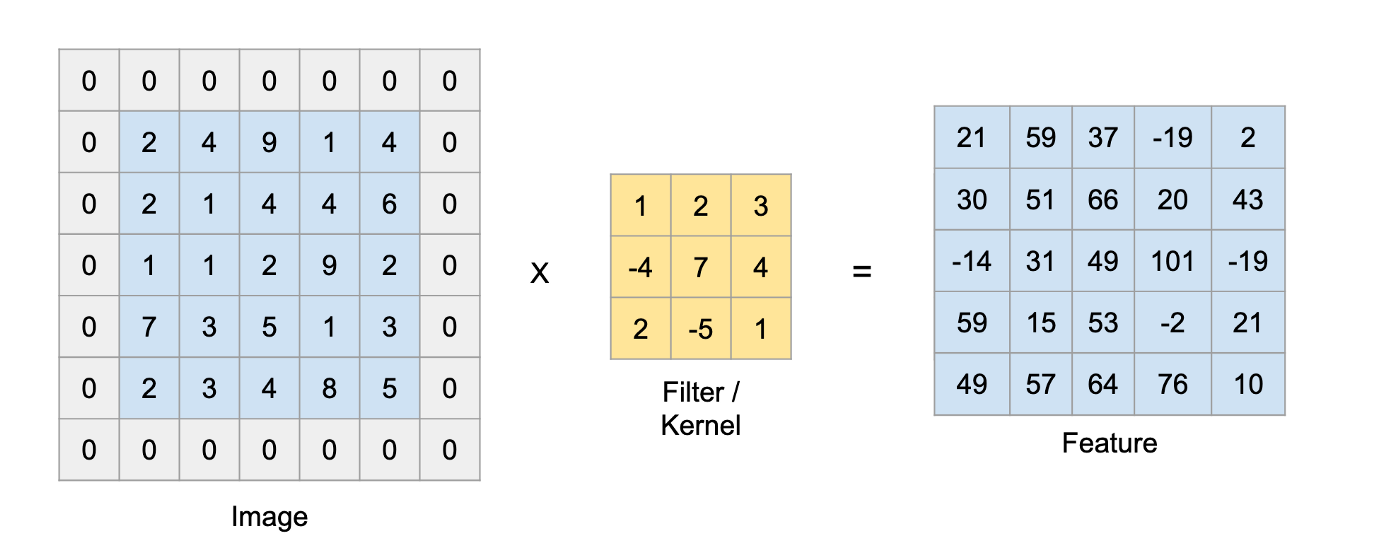
- 일정크기의 필터 또는 커널을 일정 간격으로 이동해가며 곱셈 연산을 이에 대한 결과를 모두 총합하여 해당 픽셀 위치의 대표값으로 정한다.
- 예를 들어 4 4 입력데이터와 3 3 커널을 convolution연산하면 2 * 2의 출력 데이터가 계산된다.
Padding
- 합성곱 연산을 수행하기 전에 입력 데이터 주변을 특정값(주로 0)으로 채우는 것
- 폭이 1짜리 패딩: 입력 데이터 사방 1픽셀만큼 특정 값으로 채우는 것
- 4 4의 입력데이터에 패딩1을 적용 후 3 3 커널 연산을 실행하면 출력 데이터의 크기는 4 * 4로 유지된다.
Stride
- 필터를 적용하는 위치의 간격을 스트라이드라고 칭한다.
- 예를 들어 스트라이드를 2로 하면 필터를 적용하는 윈도우가 두 칸씩 이동한다.
입력크기: (H, W)
필터크기: (FH, FW)
출력크기: (OH, OW)
패딩: P
스트라이드: S 단 위 식이 무조건 정수로 나눠 떨어져야하는 값이다. 딥러닝 프레임워크 중에는 값이 integer가 아닐 경우 반올림등의 기법을 쓰고 있음
3차원 데이터의 합성곱 연산
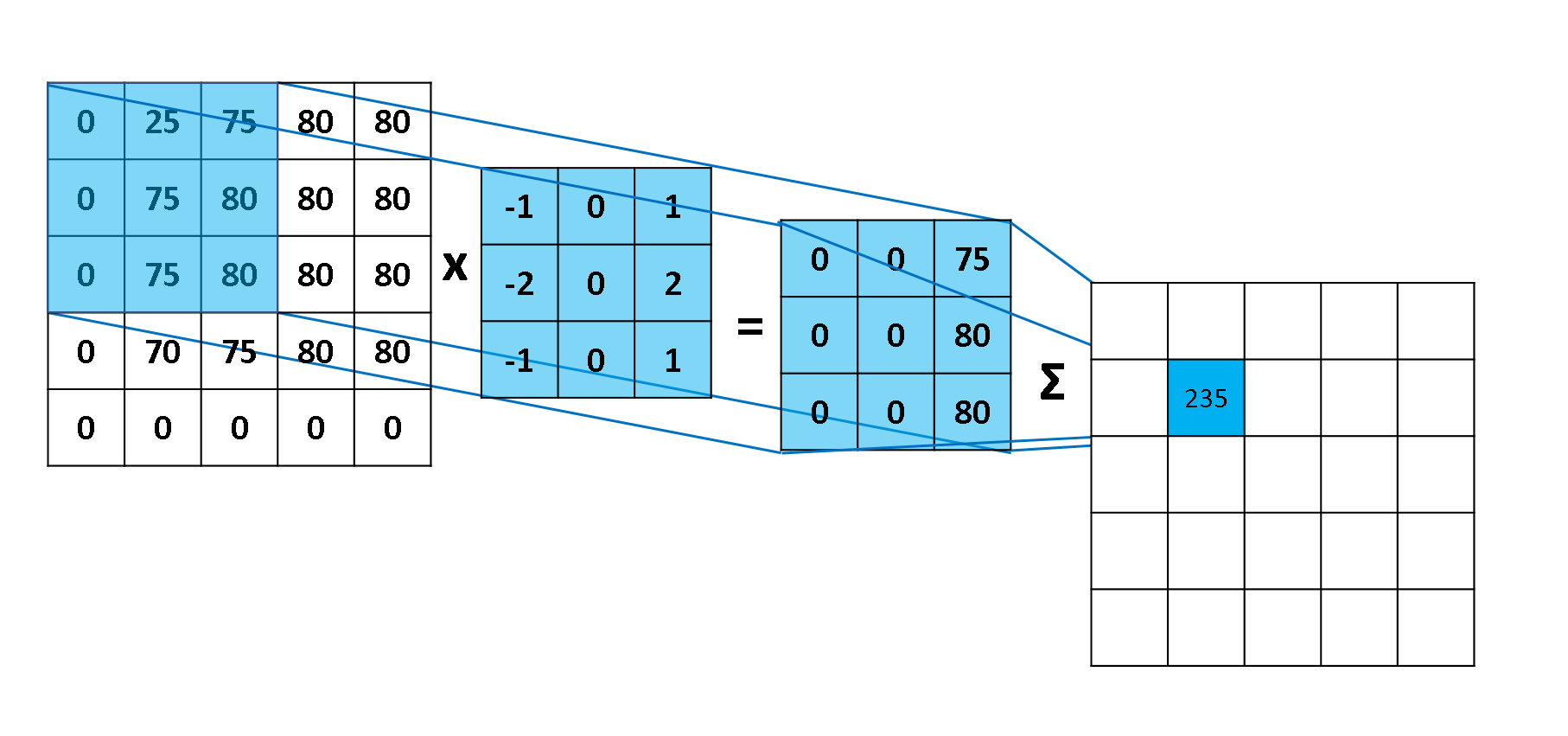
- 각 입력 채널(R, G, B)마다 필터의 합성곱 연산을 수행하고, 그 결과를 더해서 하나의 채널(1, m, n)을 얻는다.
- 3차원 합성곱 연산에서 주의할 점은 입력 데이터의 채널 수와 필터의 채널 수가 같아야 한다는 것이다.(또한, 모든 채널의 필터가 같은 크기여야 한다.)
- 만약 3채널을 합성곱 연산 후 3채널로 출력하기 위해서는 여러개의 3차원 필터를 사용하는 것이다.
Pooling layer
- 풀링은 세로*가로 방향의 공간을 줄이는 연산이다.
- 풀링의 종류에는 최대값을 대표값으로 하는 max pooling
- 평균을 이용하는 average pooling이 있다.
max pooling은 대상 영역에서 최댓값을 취하는 연산인 반면, average pooling은 대상 영역의 평균을 계산한다. 이미지 인식 분야에서는 주로 최대 풀링을 사용한다.
가장 큰 특징은 다음과 같다.
- 학습해야 할 매개변수가 없다.(풀링은 대상 영역에서 최댓값이나 평균을 취하는 산술적인 연산이기 때문)
- 채널 수가 변하지 않는다.(풀링 연산은 입력 데이터의 채널 수 그대로 출력데이터를 내보낸다. 채널마다 독립적으로 계산하기 때문(다만, 각 채널의 크기 자체는 줄어듦)
- 입력 변화에 영향을 적게 받는다.
Pytorch Example
class CNN(torch.nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super(CNN, self).__init__()
self.keep_prob = 0.5
# L1 ImgIn shape=(?, 28, 28, 1)
# Conv -> (?, 28, 28, 32)
# Pool -> (?, 14, 14, 32)
self.layer1 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(1, 32, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
# L2 ImgIn shape=(?, 14, 14, 32)
# Conv ->(?, 14, 14, 64)
# Pool ->(?, 7, 7, 64)
self.layer2 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(32, 64, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2))
# L3 ImgIn shape=(?, 7, 7, 64)
# Conv ->(?, 7, 7, 128)
# Pool ->(?, 4, 4, 128)
self.layer3 = torch.nn.Sequential(
torch.nn.Conv2d(64, 128, kernel_size=3, stride=1, padding=1),
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=2, stride=2, padding=1))
# L4 FC 4x4x128 inputs -> 625 outputs
self.fc1 = torch.nn.Linear(4 * 4 * 128, 625, bias=True)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc1.weight)
self.layer4 = torch.nn.Sequential(
self.fc1,
torch.nn.ReLU(),
torch.nn.Dropout(p=1 - self.keep_prob))
# L5 Final FC 625 inputs -> 10 outputs
self.fc2 = torch.nn.Linear(625, 10, bias=True)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(self.fc2.weight)
def forward(self, x):
out = self.layer1(x)
out = self.layer2(out)
out = self.layer3(out)
out = out.view(out.size(0), -1) # Flatten them for FC
out = self.layer4(out)
out = self.fc2(out)
return out