Priority Schedulers
Simple Priority Scheduler
SJF, STCF are both priority schedulers
- Priority is CPU burst time
Also, FCFS and RR are priority schedulers
- FCFS's priority is arrival time
- RR's priority is dynamical
Problem with priority scheduling
- Starvation
- High priority tasks can dominate the CPU
low priority tasks will be starved
- High priority tasks can dominate the CPU
Possible solution
- Dynamically vary priorities based on proces behavior
Simple Priority Scheduler
- Schedule high priority tasks first
- No preemption
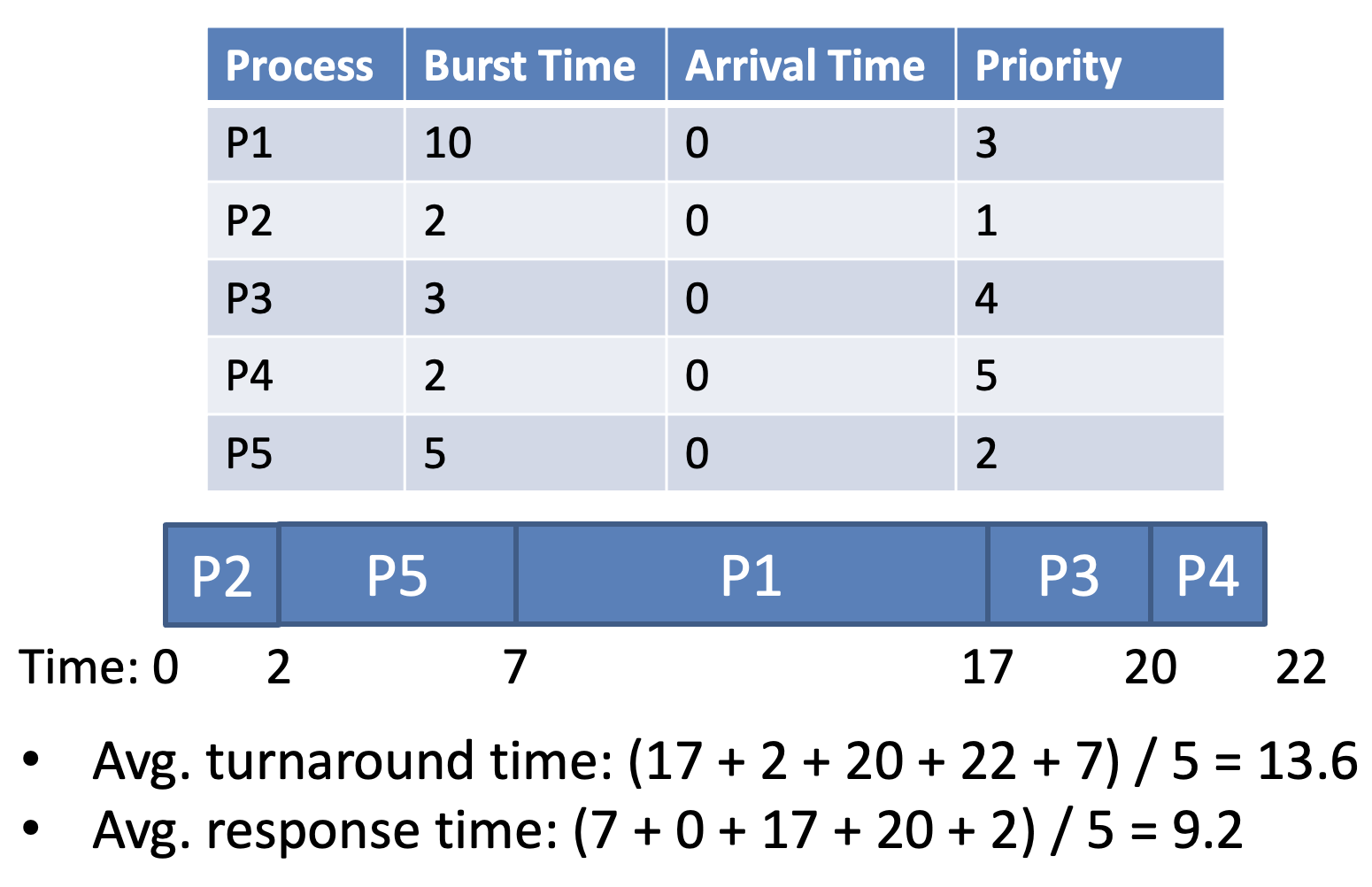
- Cannot automatically balance response and turnaround time
EDF: Earilest Deadline First
Each process has a deadline it must finish
- Tighter deadlines are given higher priority
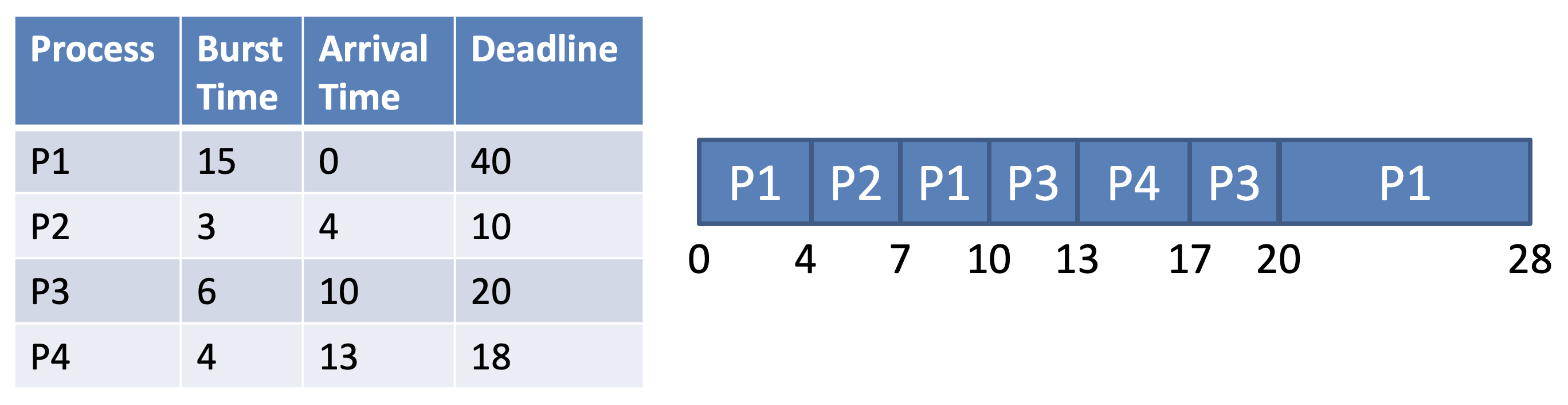
- EDF is optimal (assuming preemption)
- But only useful if processes have known deadlines (e.g. Real-Time OS)
MLQ: Multilevel Queue
Key idea: Divide the ready queue in two
- High priority queue for interactive processes
- RR scheduling
- Low priority queue for CPU bound processes
- FCFS scheduling
Each process is assigned a priority on startup
Each queue is given a fixed amount of CPU time
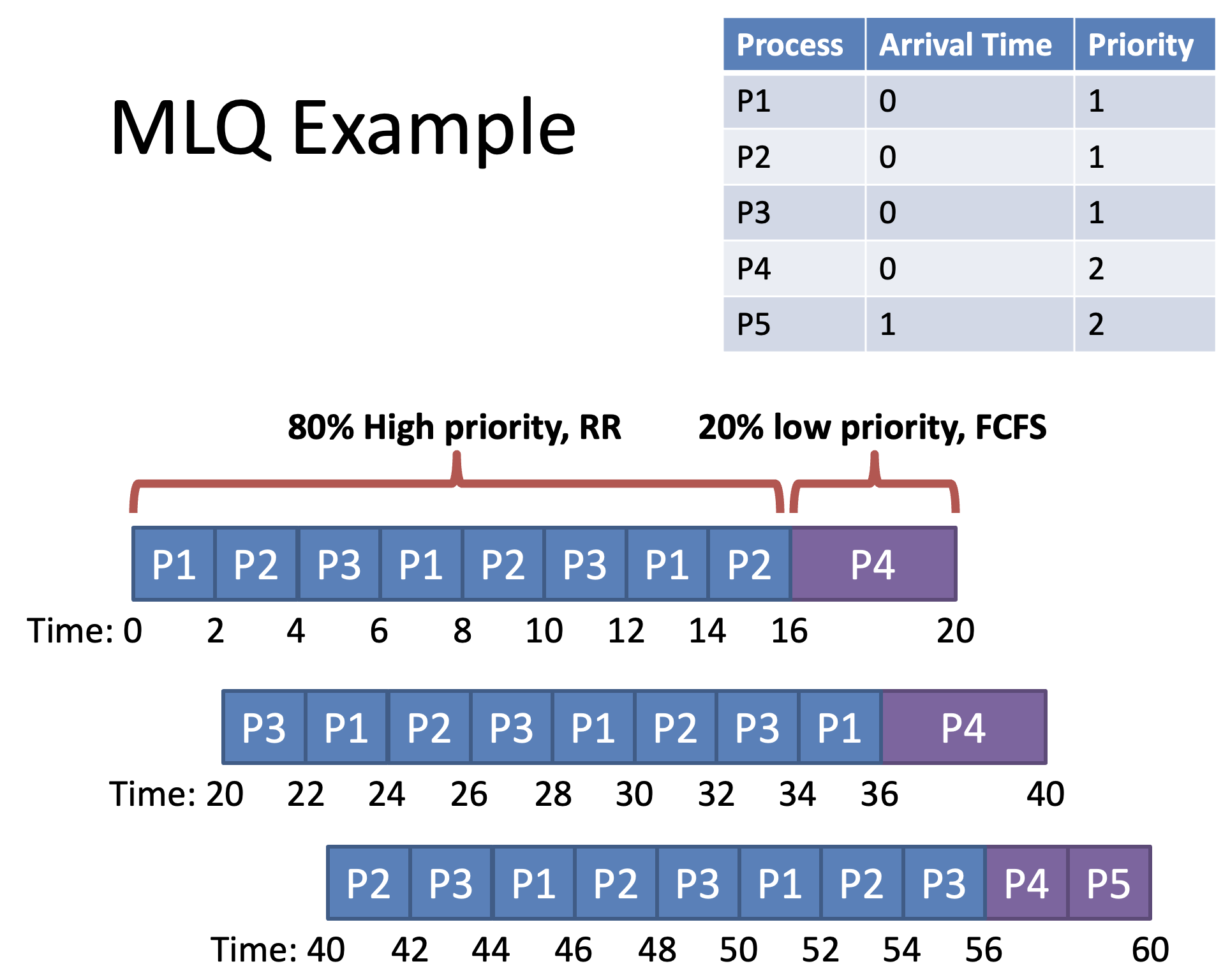
Problems with MLQ
- Assume you can classify processes into high and low priority
- How actually do this at run time
- What if process's behavior changes over time
- High biased use of CPU time
- How can we set the percentage
- Convoy problems for low priority tasks
MLFQ: Multilevel Feedback Queue
Goals
- Minimize resopnse and turnaround time
- Dynamically adjust process priorities over time
= Move processes between queue based on observed behavior- No prior knowledge about burst times or process behavior
First 4 Rules of MLFQ
-
If Priority(A) > Priority(B), A runs
-
If Priority(A) = Priority(B), A & B run in RR
-
Processes start at the highest priority
= Assume initial process is interactive -
Priority change rule
4a) If a process uses an entire time slice, priority is reduced
Each level queue has different time slice4b) If a process gives up the CPU before its time slice is up, priority level remains
e.g.) Process performs I/O operations so that context switching occurs
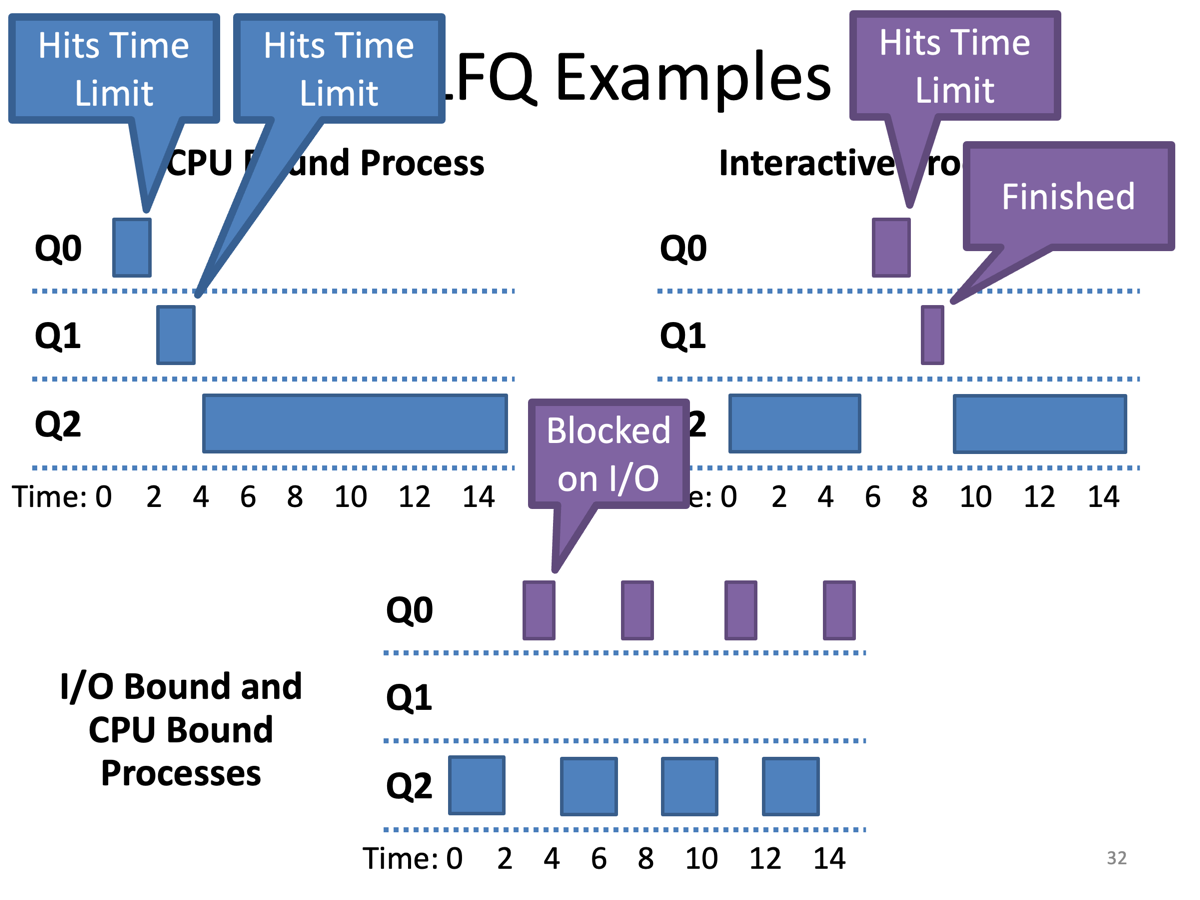
1, 2. Process has time limit priority is reduced
2. MLFQ STCF
3. Blocked on I/O priority level remains
Problems with MLFQ
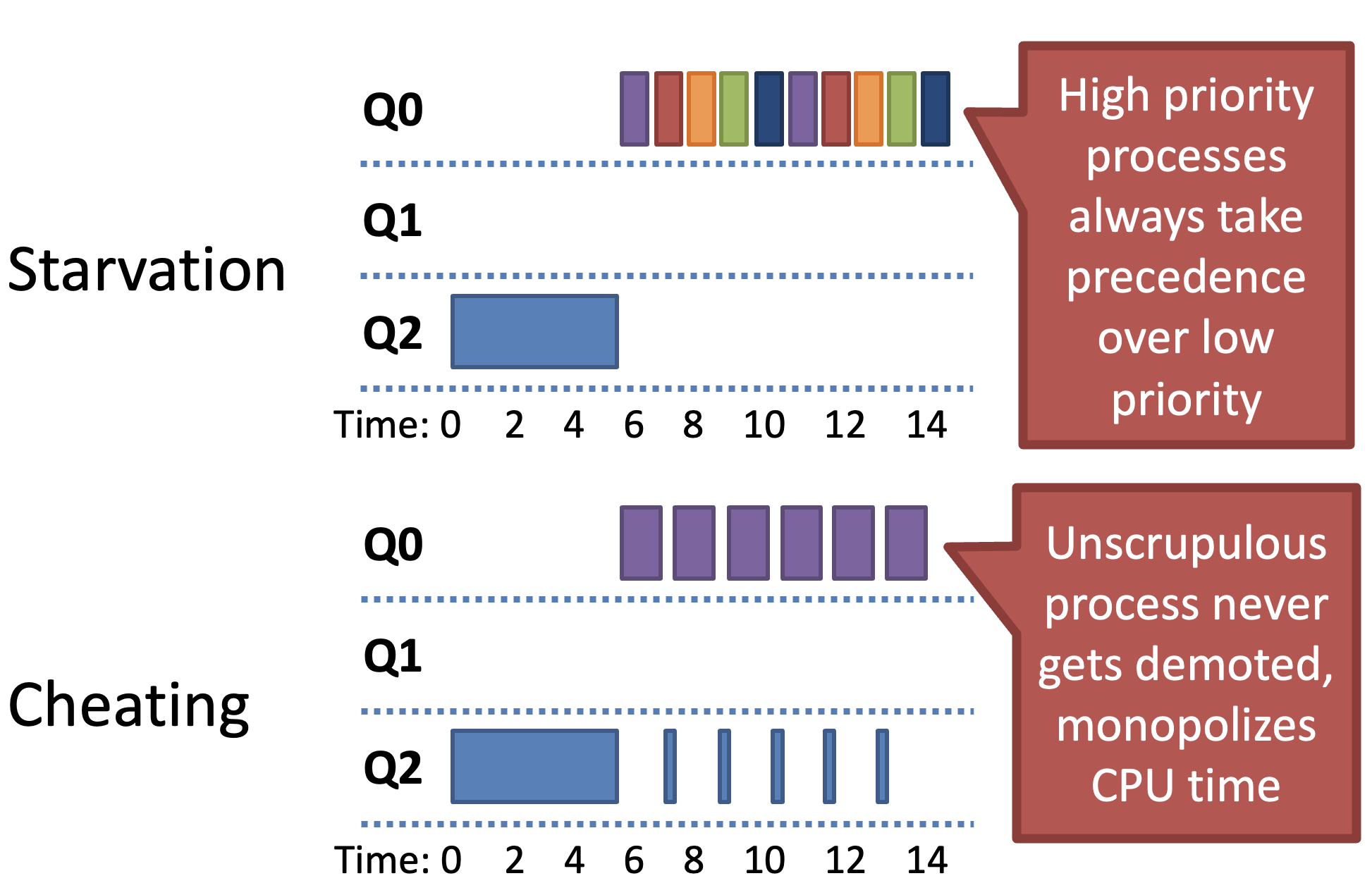
- By Rule 4b) Cheating can occur
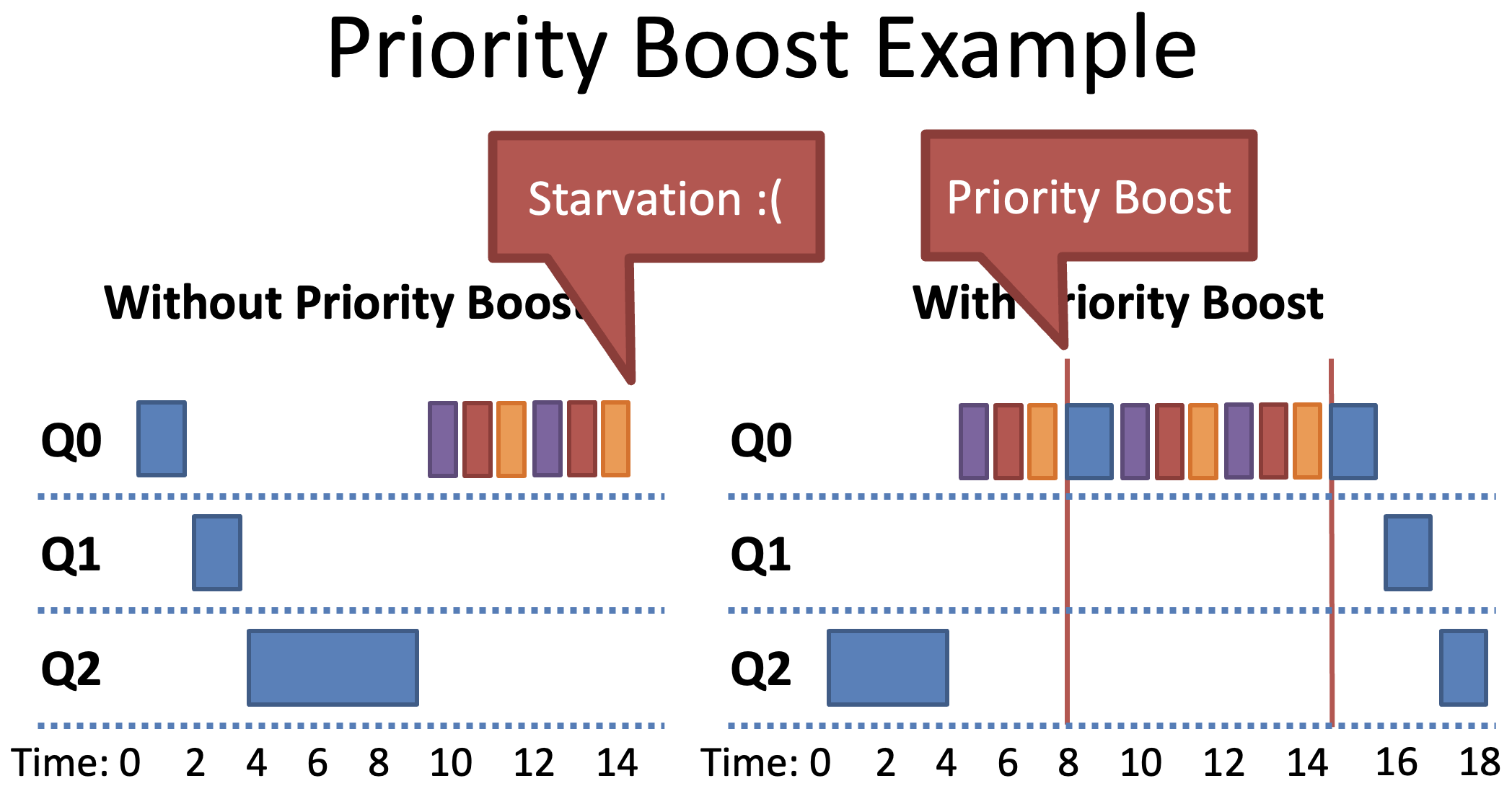
MLFQ Rule 5: Priority Boost
- After period , move all processes to the highest priority queue (=initialize)
- Solves two problems
- Starvation
- Low priority processes will eventually become high priority
- Dynamic behavior
- CPU bound process that has become interactive will be high priority
- Starvation
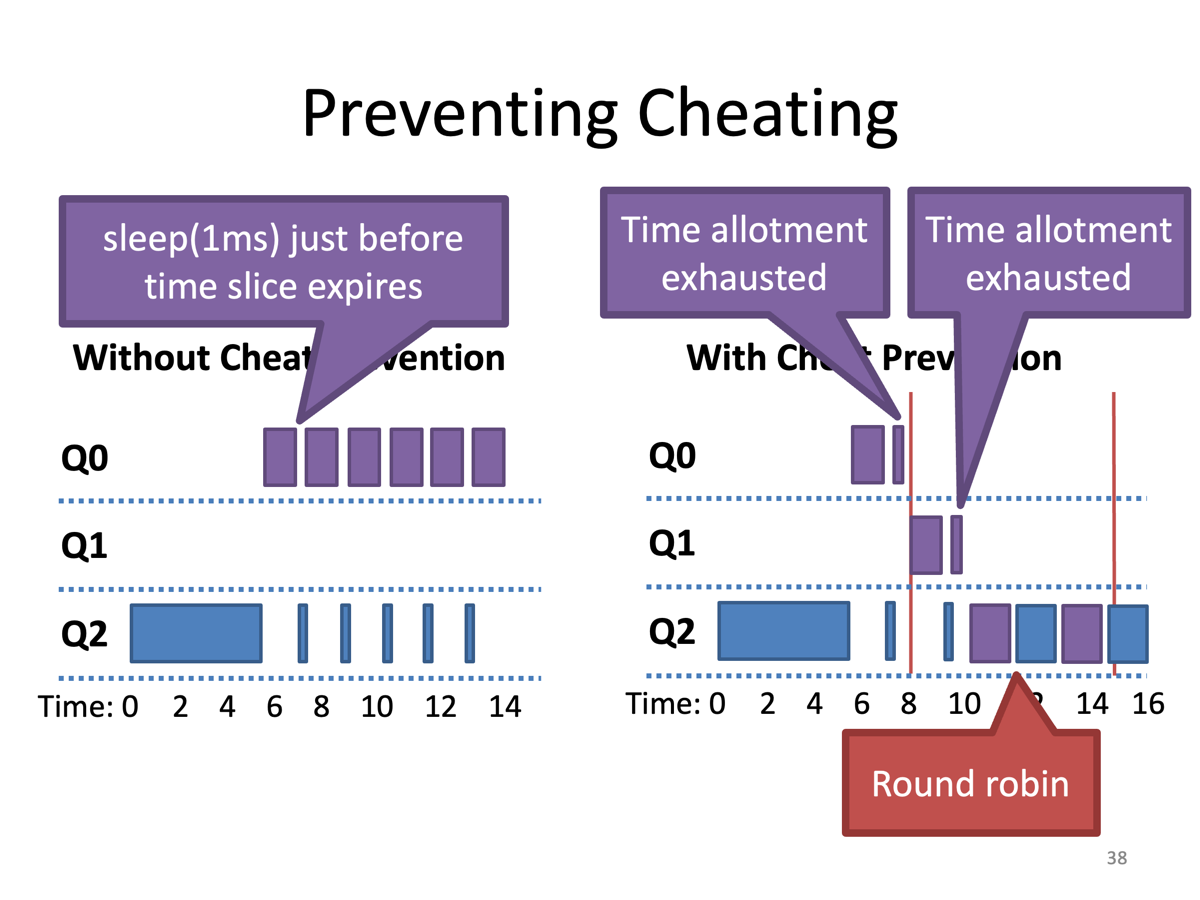
Revised Rule 4 (Cheat prevention)
Problem :
- Cheating (Repeatedly yield just before the time limit expires)
Solution :
- Once a process uses up its time allotment at a given priority, demote its priority
- Keep track of total CPU time during each time interval
- Instead of looking at continuous CPU time
MLFQ Rule Review
- If Priority(A) > Priority(B), A runs
- If Priority(A) = Priority(B), A & B run in RR
- Processes start at the highest priority
= Assume initial process is interactive - Once a process uses up its time allotment at given priority, demote it
- After some time period , move all processes to the highest prioirty queue
Note
- Achieve goals
- MLFQ balances response time and turnaround time
- MLFQ does not require prior knowledge about processes
- Parameters to tune
- Number of queue
- Distribution of CPU time
- For each queue
- Which scheduling regime
- Time slice
- In practice
- High priority queues - short time slices
- Low priority queues - long time slices
- Low priority - CPU bound - Longer time slice
- Priority 0 sometimes reserved for OS processes
- Giving advice
- Some OS allow users/processes to give the scheduler hints about priority
- nice command on Linux
- Run the command with adjusted priority
- Values -20 ~ 19 is added to process priority