Physical Memory and Virtual Memory
Limitation of physical memory
Protection and Isolation
- Evil process can ruin other process or access kernel memory
Pointers in programs
- Compiled programs include fixed pointer addresses
- Ex) two copies of the same program
- Program may not be placed at the correct location
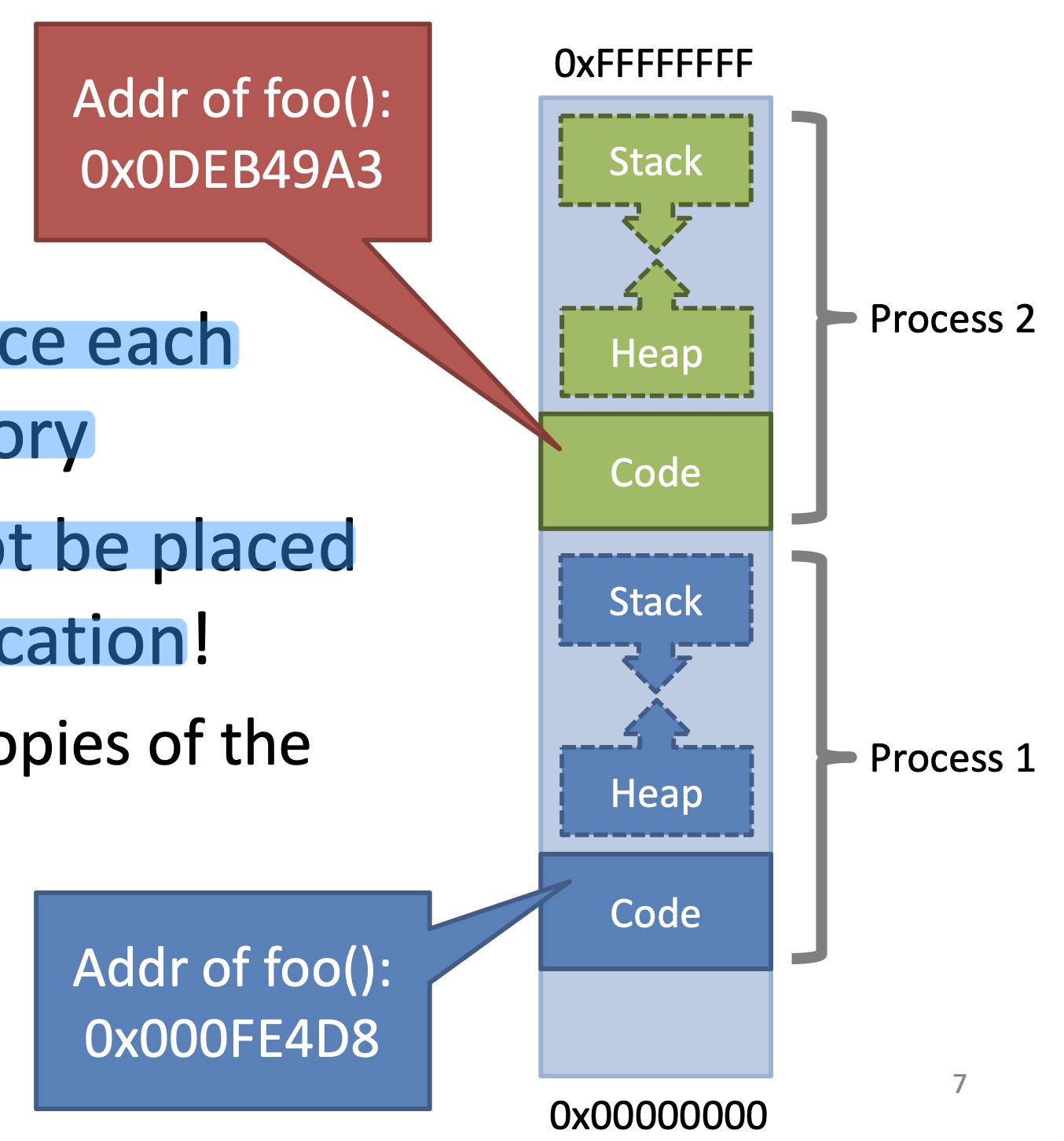
Address spaces for multiple processes
- A process may not always be loaded into the same memory location
1. Fixed address compilation
Multiple copies of each program
- Compile each program multiple times (for each possible starting address)
- Load the appropriate program when the user starts the program
- Multiple copies of the same program
- Should compile multiple times / Should save multiple version of compiled program
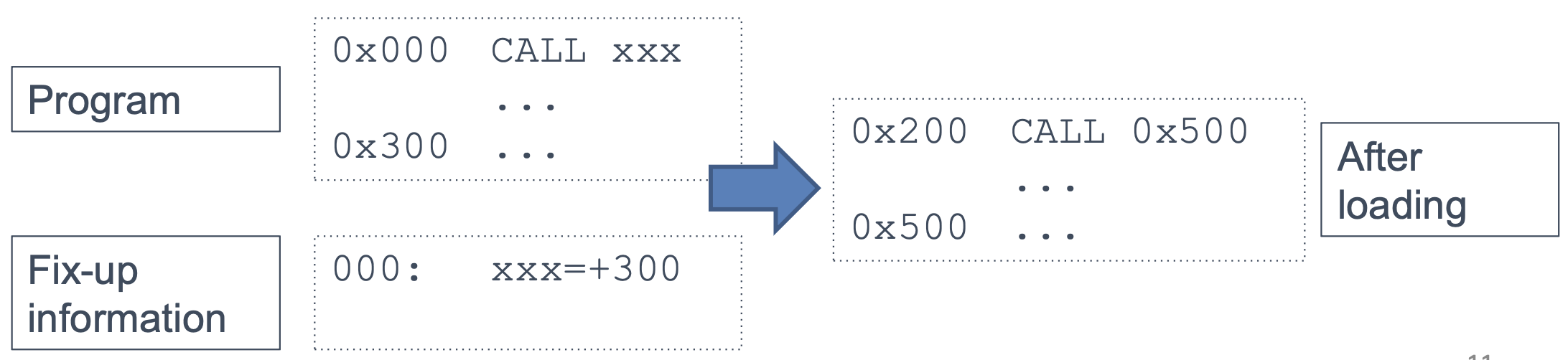
2. Load-time fixup
Calculate addresses at load-time
- Program contains a list of locations that must be modified at startup
- All relative to starting address
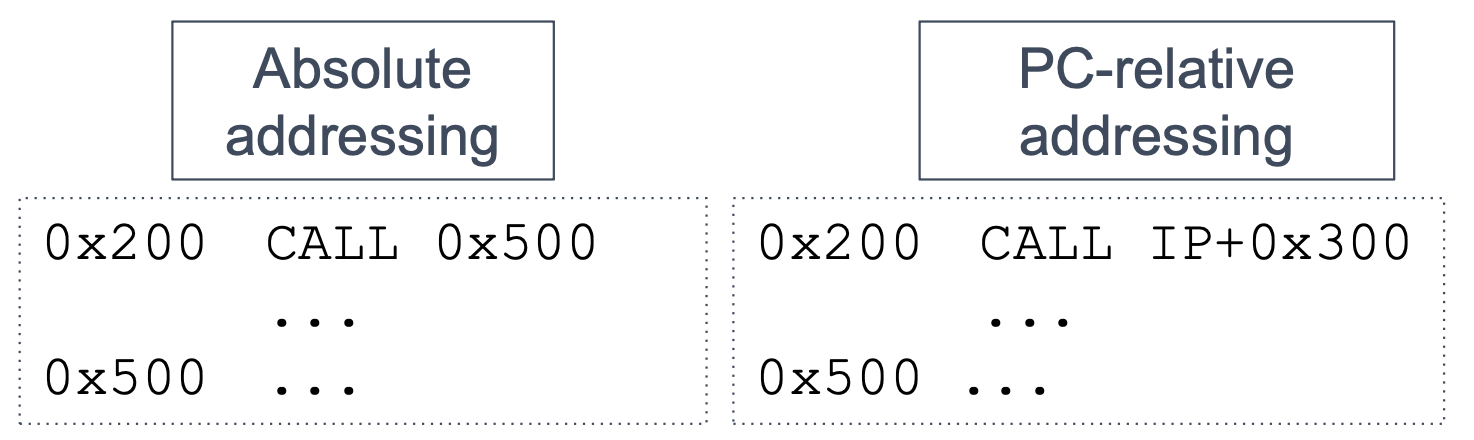
3. Position independent code
Compile programs in a way that is independent of their starting address
- Slightly less efficient than absolute address
- Commonly used today for security reasons
4. Hardware support (Virtual memory)
Program is compiled at a fixed location in virtual memory
OS uses the MMU to map these locations to physical memory
MMU and Virtual Memory
- Memory Management Unit translates between virtual addresses and physical addresses
- Process uses virtual address
- MMU translates virtual addresses to physical addresses
- Physical addresses are the true locations of code and data in RAM


