Condition Variables
Condition Variables
- Construct for managing control flow
Condition variables are not locks- Each condition variable is associated with a mutex
- Threads that can't run yet wait() for some condition to become satisfied
- When the condition is satisfied, some other thread can signal() to the waiting threads
Producer & Consumer (Bounded Buffer Problem)
Producer
- Place data items in a buffer
Consumer
- Grab data items out of the buffer
Bounded buffer
- A bounded buffer is used when you pipe the output
- Bounded buffer is shared resource -> Synchronized access is required
Put and Get ver. 1

Problem
- No lock
Single Condition variable & associated lock


- In p3, we put mutex as args so that thread can unlock mutex before wait
- printf(IO) can be blocked -> should be conducted out of critical section
Problems
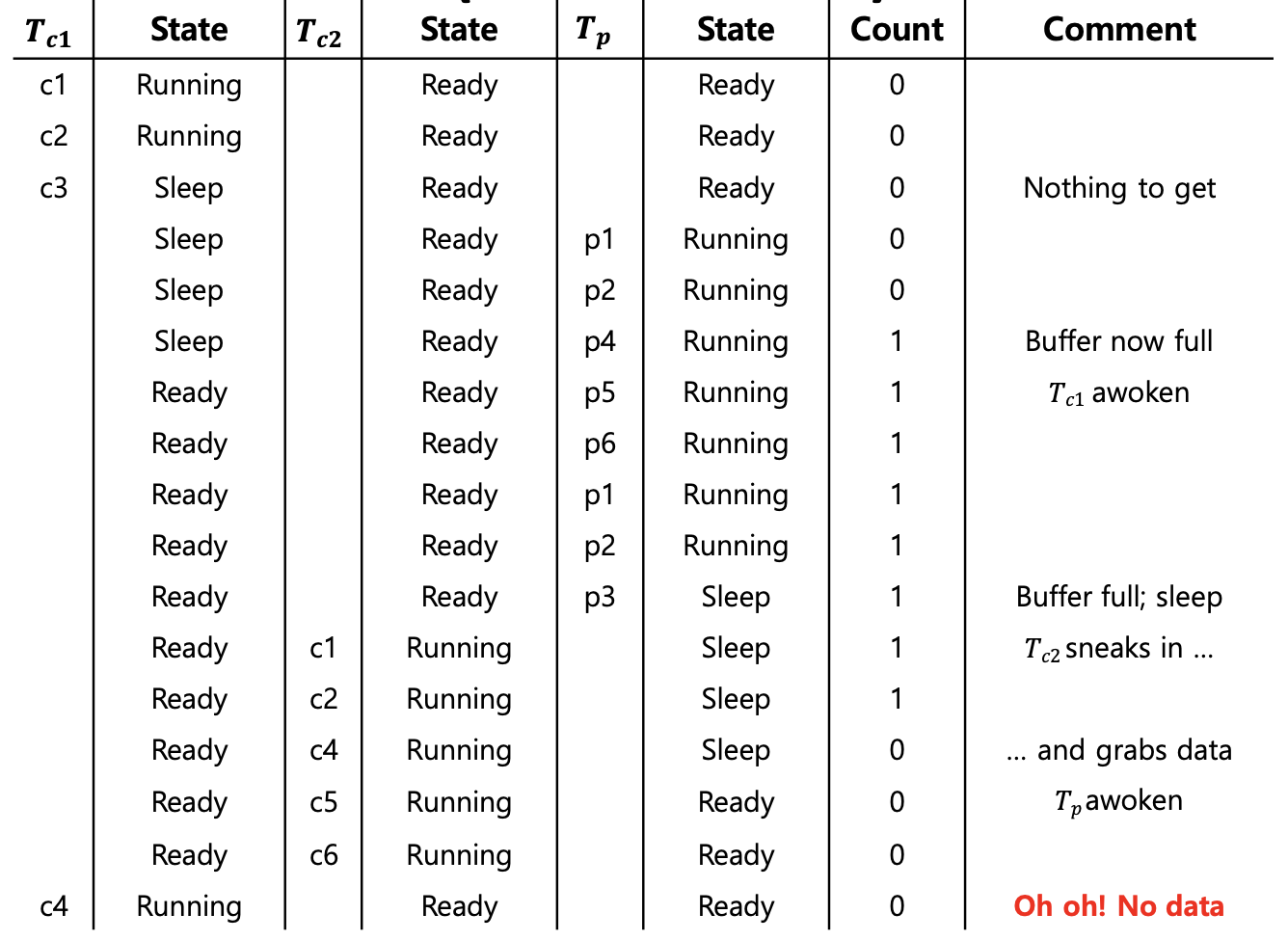
- After the producer woke , expected full state but the state is empty
- There is no guarantee that when the woken thread runs, the state will still be as desired
(Mesa semantics) - Stronger guarantee that the woken thread will run immediately upon being woken
(Hoare semantics)
Single Condition variable & While

- if -> while
- When wakes up, re-checks the state of conditon variable
- When we check Condition variables, always use while loops
Problems
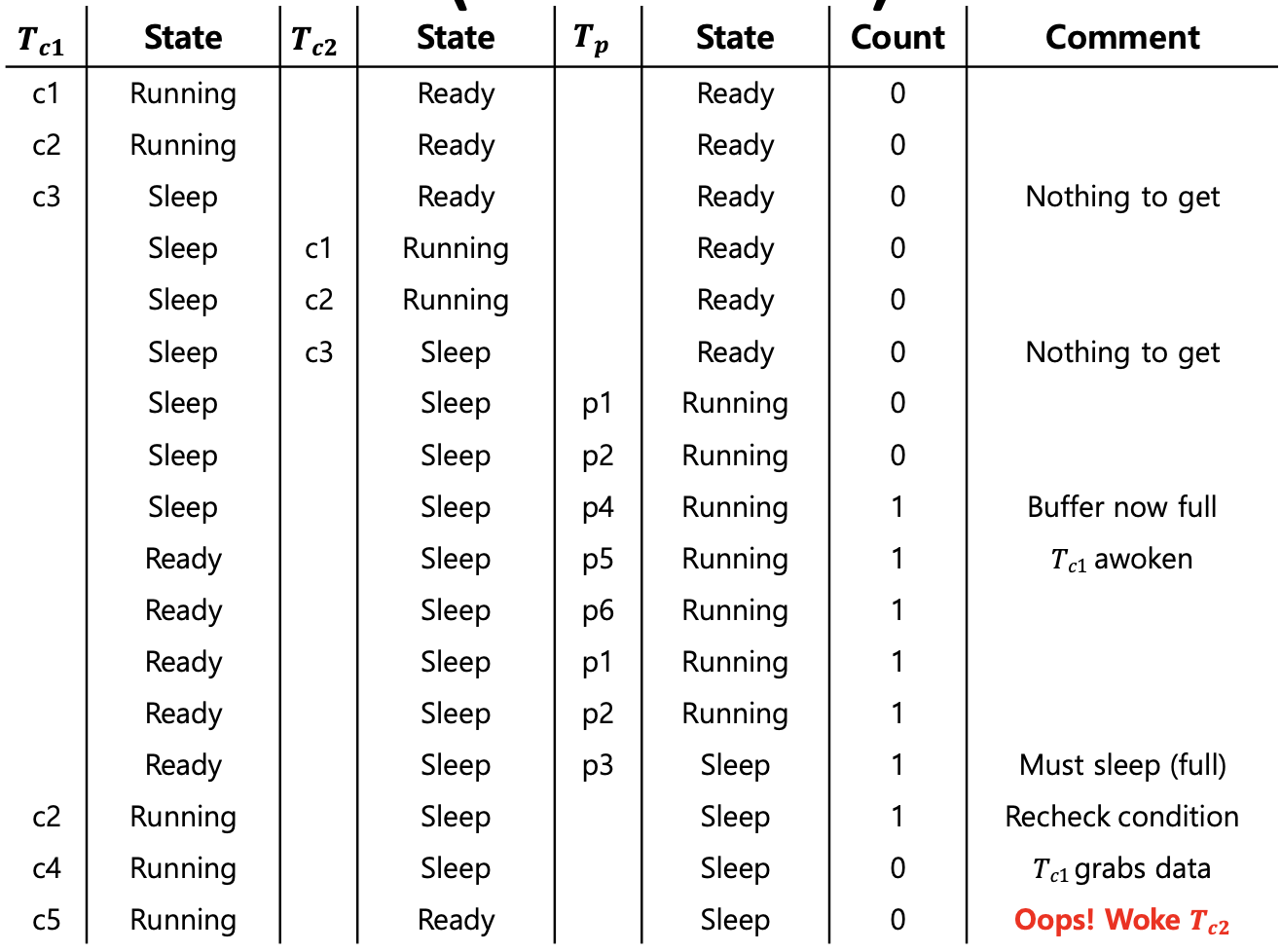
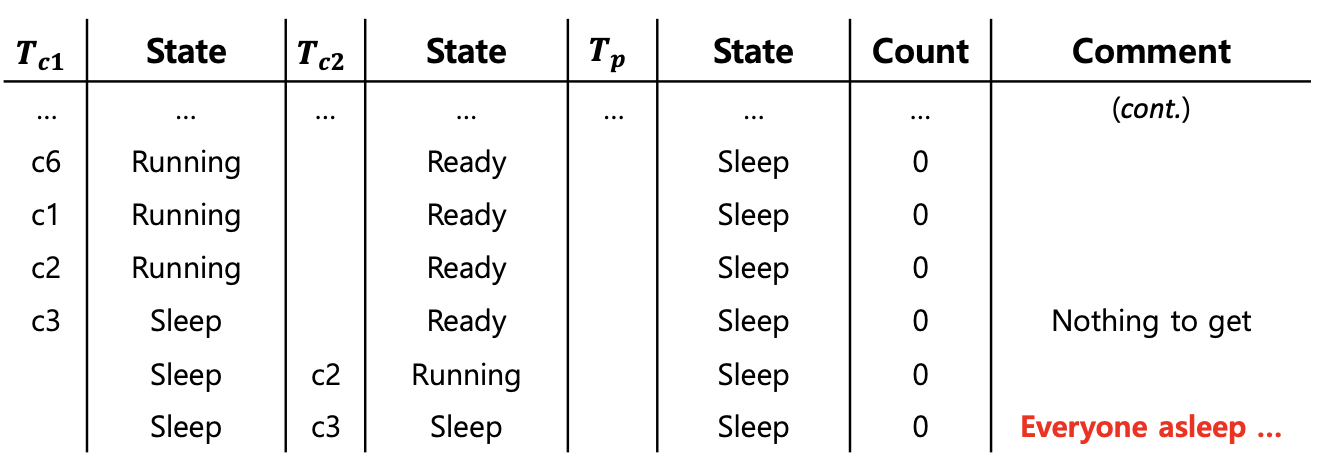
- A consumer should not wake other consumers, only producers
Two Condition variables & While
- Producer wait on empty and signals fill
- Consumer wait on fill and signals empty


Monitors
- Combination of a mutex and a condition variable
Semaphores
Semaphores
-
Generalization of a mutex
- May be locked by up to
-
Methods
- P : wait
- --, if sleep
- V : signal
- ++, if waiting thread > 0, wake one up
- P : wait
-
Initialization

- Initialize to the value 1
- The second argument 0 includes that the semaphore is shared
-
sem_wait()
- Decrement the semaphore value
- If the value of semaphore is one or higher, return right away
- When negative, the value of semaphore is equal to the number of waiting threads
-
sem_post()
- Increment the semaphore value
- If there is a thread waiting to be woken, wakes one
As Lock (Binary Semaphore)

- What should be X?
- The initial value should be 1
- The number of threads that can have lock
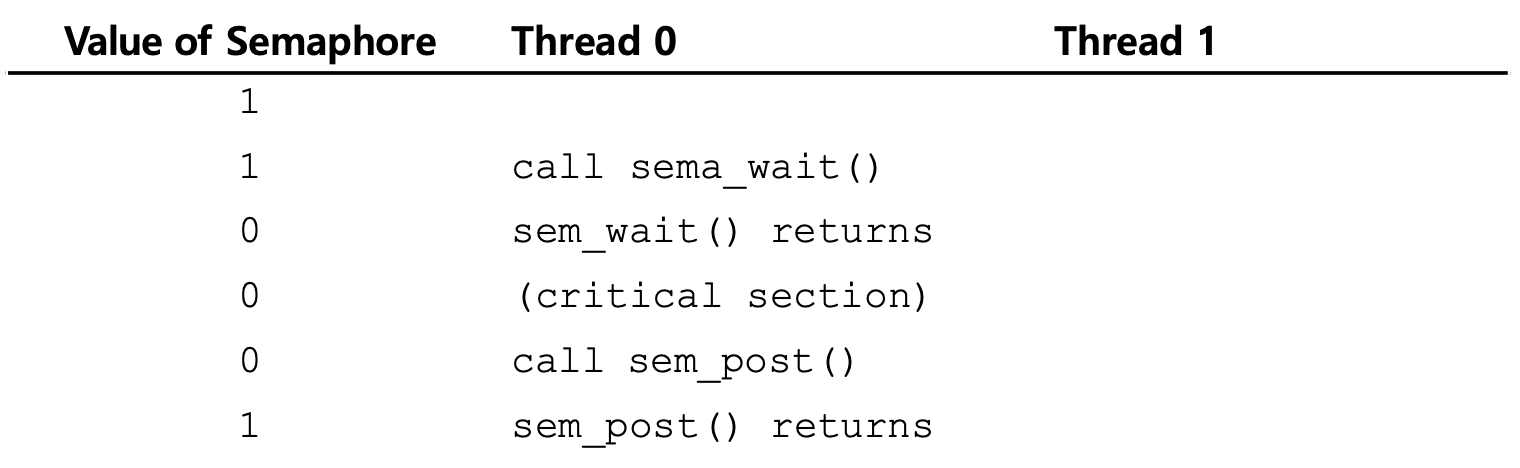
- Of course, semaphore value is a shared resource
-> Need HW support so that can be atmoic instruction
As Condition Variables
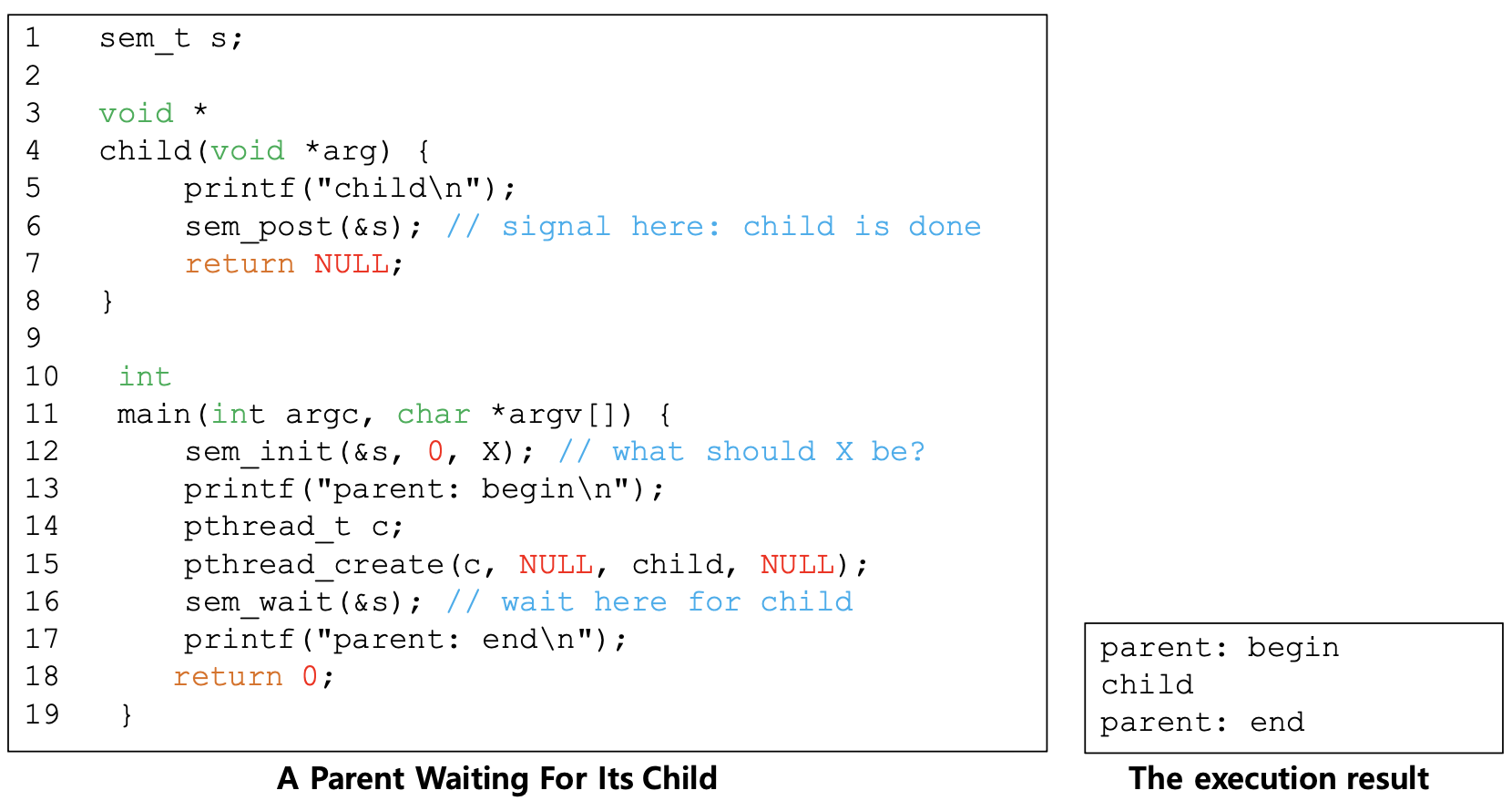
- What should be X?
- When parent call sem_wait(), parent should wait
- The initial value should be 0
- The parent call sem_wait() before the child call sem_post()

- The child run to completion before the parent call sem_wait()
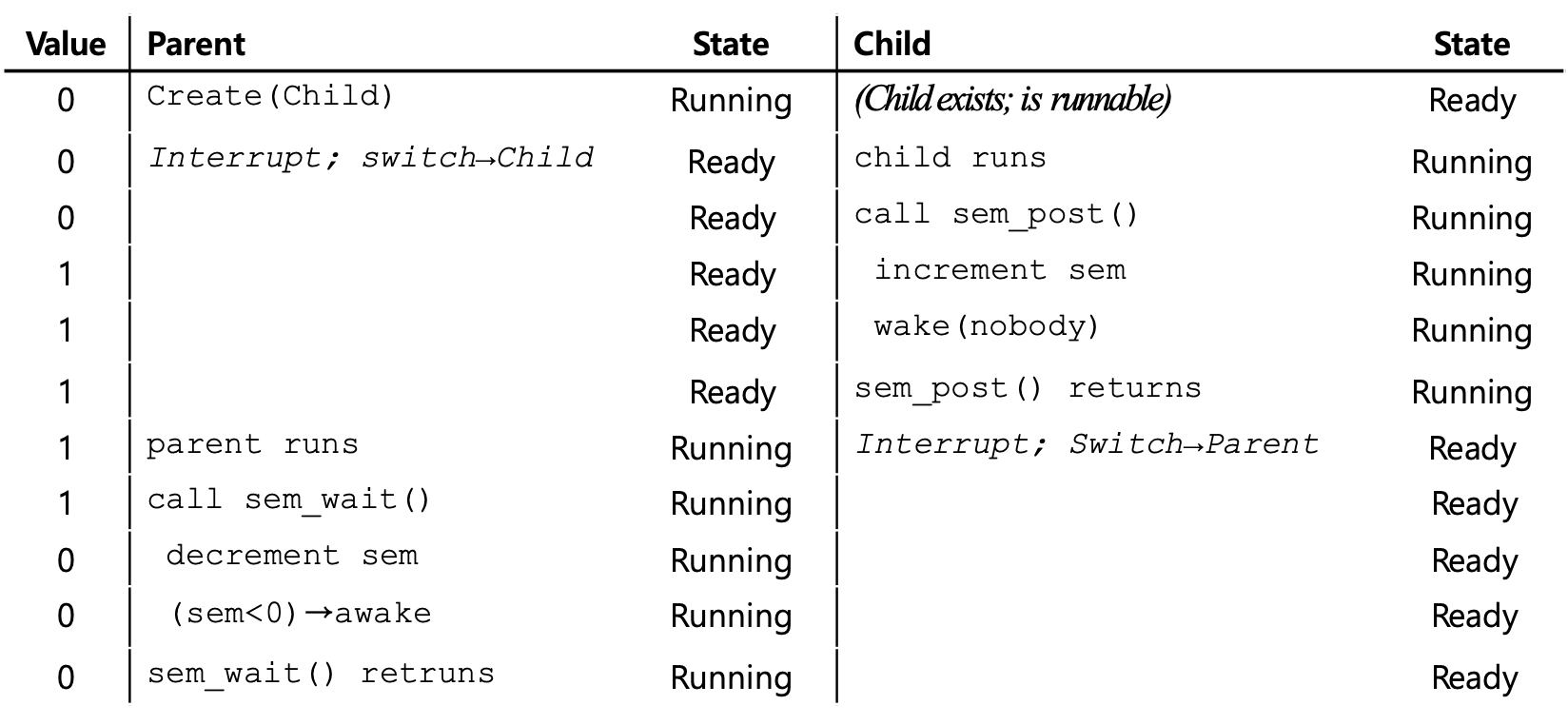
Producer & Consumer (Bounded Buffer Problem)


- Case) MAX is greater than 1
- If multiple producers, race condition can happen in line p2
- We forgot Mutex
- Accessing the buffer should be in critical section
Sol 1. Add Mutex

- Semaphore doesn't unlock the mutex when thread call sem_wait()
Sol 2. Hold Condition variable first

- Acquire the condition variable first and then acquire the lock
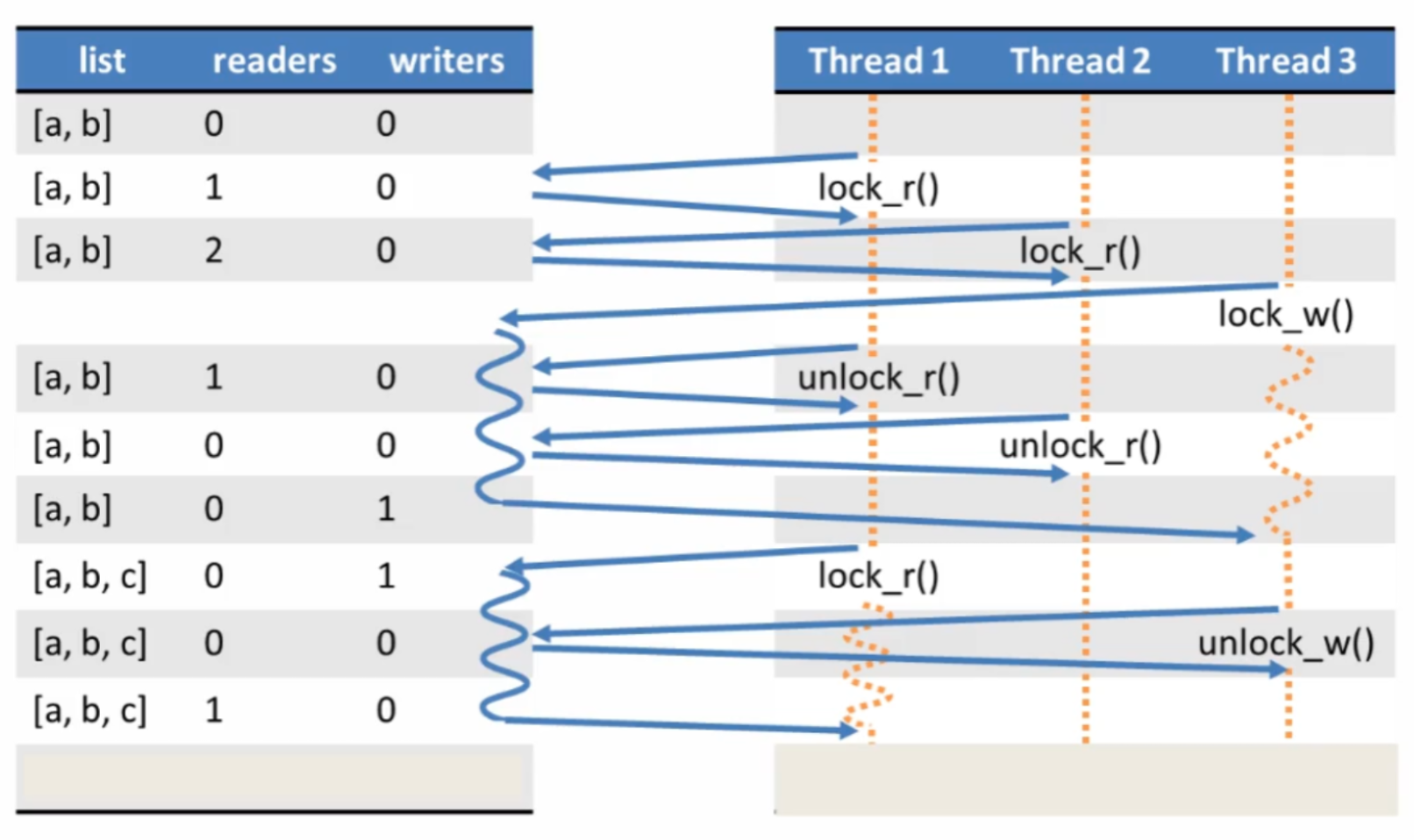
Read/Write Lock
- Many threads hold the read lock in parallel
- Only one thread hold the write lock at a time
- Write lock cannot be acquired until all read locks are released
- New read lock cannot be acquired if a writer is waiting
Dining philosophers
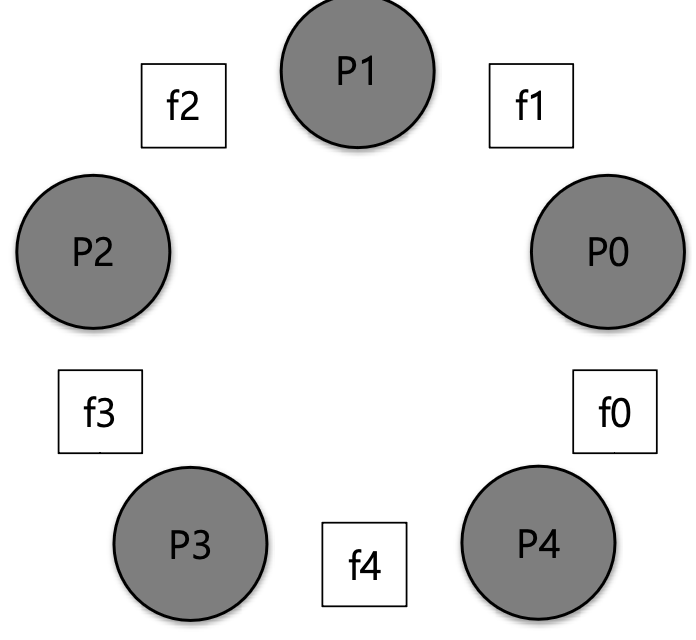
- In order to eat, need two forks
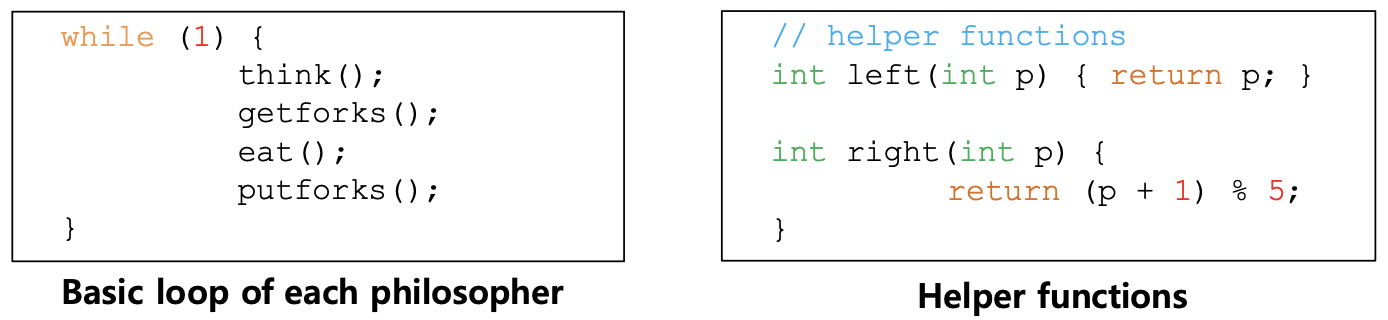
- If each philosophers grab the left fork, Each will be stuck holding one fork
Solution

- The cycle is broken