Summary
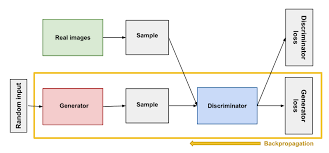
본 논문은 두 모델을 동시에 학습하는 생성모델 GAN을 제안한다. generative model G는 data의 분포를 원본 데이터와 비슷하게 만들고, discriminative model D는 샘플이 G보다 원본 데이터에서 나왔을 확률을 계산한다. 두 모델이 서로 적대적으로 동작하여 backpropagation을 통해 학습된다. markov chain과 같은 별다른 트릭을 요구하지 않아 생성모델의 benchmark model로 자리잡게 되었다.
This paper proposes a generative model GAN that learns two models at the same time. The generative model G makes the distribution of data similar to the original data, and the discriminative model D calculates the probability that the sample comes from the original data rather than G. The two models operate adversary to each other and are learned through backpropagation. It has become a benchmark model of the generated model because it does not require any tricks such as markov chain.
Strength
- markov chain이 사용되지 않는다.
- backprop을 사용해서 효율적으로 모델을 최적화 한다.
- 학습 동안, inference가 필요하지 않다.
- input이 generator의 parameter로 그대로 복사되지 않기 때문에, 통계적인 장점을 가질 수 있다.
- 생성한 이미지가 정교하다.
- The generated image is elaborate.
- Since input is not copied to the parameter of the generator as it is, it may have a statistical advantage.
Weakness
- p_g(x)에 대한 explicit한 representation이 없다.
- G를 학습하면서 D또한 반드시 동기화 되어야 한다. 즉 D 없이 G 혼자서 학습되지 말아야 한다.
- There is no explicit representation for p_g(x).
- D must also be synchronized while learning G. In other words, G should not be learned alone without D.
Questions
- minimax game으로 학습을 진행하는데, 여기서 발생하는 불안정성은 어떻게 해결할 수 있을까요?
- 학습이 완료된 discriminator도 활용할 수 있을까요?
- How can we solve the instability that occurs here when learning is conducted with minimax game?
- Can we also use the discriminator that has been learned?
Comments
NLP에서는 vision domain에 비해 GAN이 활발하게 사용되지 않는 것 같은데, 이는 왜 그런지 궁금하다.
