참고 사이트
요구 및 제약사항
- Window size : 480X360
- 텍스트 size : 120X360 (Text, TextEdit, TextInput 중 선택해서 적용)
- Grid Layout 활용
- 절대좌표가 아닌 상대좌표로 구현
ex) x: 0 y: 0 -> anchors.top: parent.top- 추가적으로 C++ 계산기 소스코드에서의 요구 및 제약사항도 준수
- 필요한 추가 예외처리 : num1 혹은 num2 미입력 시, Text에 "0" 출력
활용 자료
1. 클래스 파일 생성
이전 게시물에서 만들어 둔 계산기 GUI 파일에서
제일 상위 폴더를 마우스 오른쪽 클릭 > [Add New...] 클릭 > [C++ Class] 클릭 > [Choose] 클릭
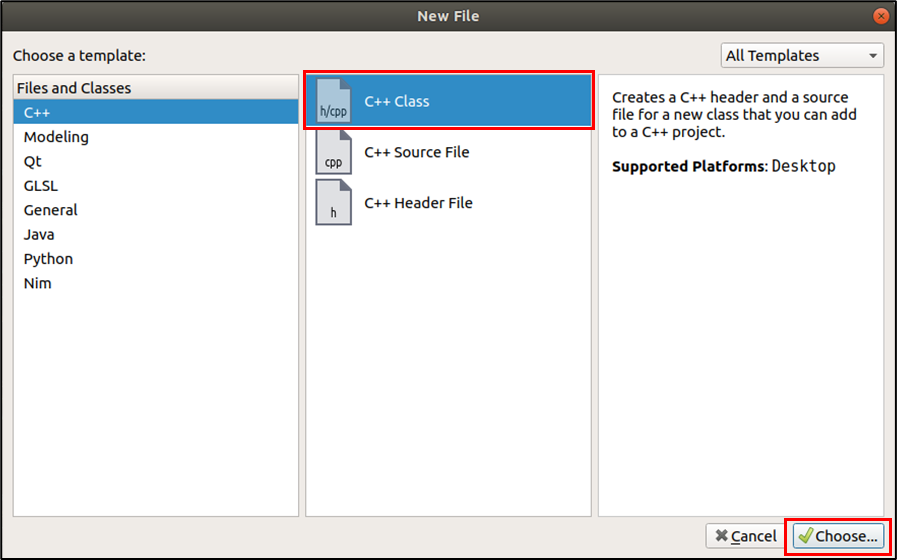
클래스명을 입력하면, 헤더 파일과 소스 파일은 자동으로 설정됨
베이스 클래스는 QObject 로 선택 > [Next] 클릭
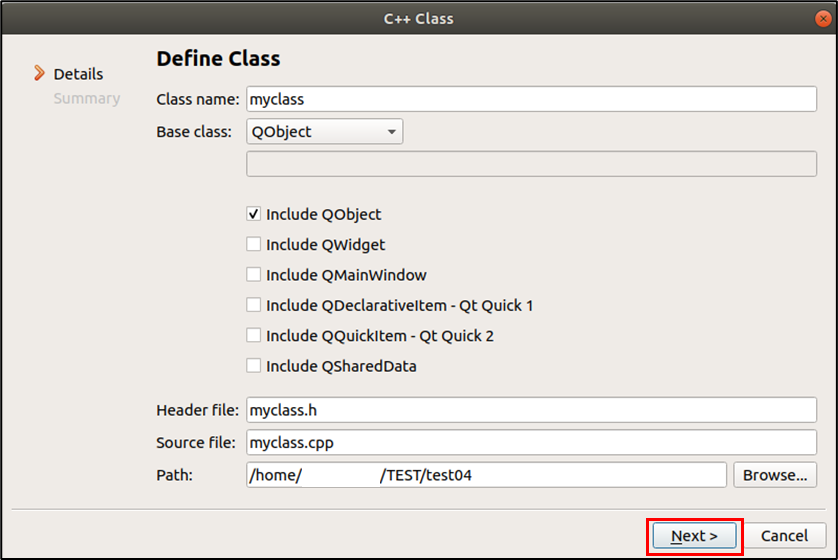
[Finish] 클릭
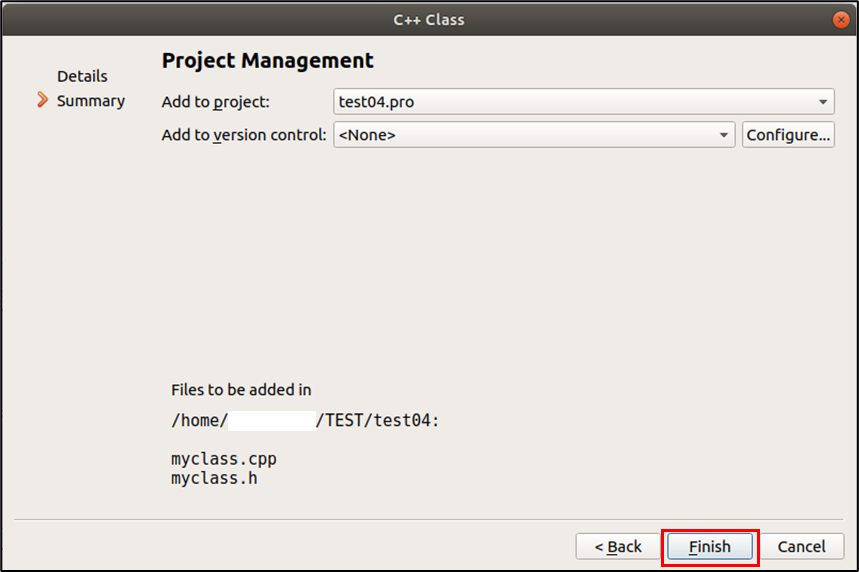
생성된 것을 확인 가능
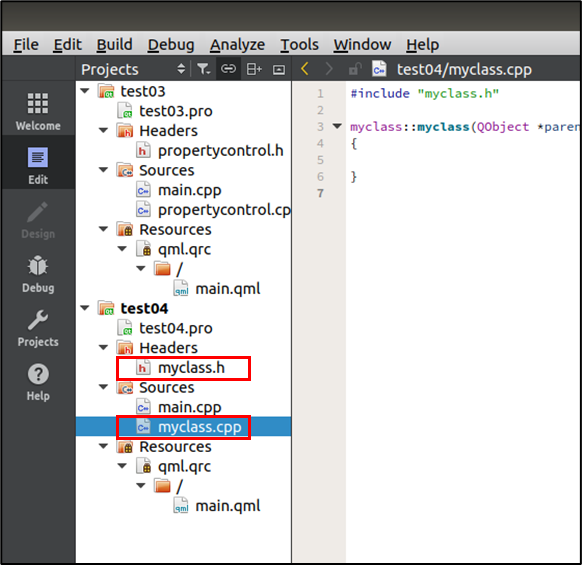
2. main.cpp
- QQmlApplicationEngine 객체를 생성하고, main.qml 로드
- QQmlApplicationEngine 클래스 : QQmlEngine을 서브클래싱
- QQmlEngine 클래스 : QML 엔진의 root context를 얻을 수 있도록 rootContext() 함수를 제공
- rootContext() : QQmlContext 포인터를 반환하고 QQmlContext의 setContextProperty() 함수를 통해 C++ 인스턴스를 등록할 수 있도록 함
Calculator 객체를 생성하고, QML 엔진 context에 "Calculator" 이라는 이름으로 등록
그러면, 이제 QML에서 "Calculator" 이라는 이름으로 C++ 객체의 함수 호출 가능
[main.cpp]
#include <QGuiApplication>
#include <QQmlApplicationEngine>
#include <QQmlContext>
#include <calculator.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
Calculator *ca = new Calculator();
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("Calculator", ca);
return app.exec();
}3. 프로퍼티를 사용한 C++과 QML간 데이터 전달
1) Q_PROPERTY
Q_PROPERTY
Q_PROPERTY(type name READ name WRITE setname NOTIFY nameChanged)
- QML에서 property에 값을 넣을 때는 WRITE의 set 함수가 호출되고, property의 값을 읽을 때는 READ의 get 함수를 호출
- QML로 바인딩하는 경우 값이 변경되었음을 알리는 SIGNAL도 선언 필요
[Calculator.h]
// result 데이터를 QML에 전달하기 위한 것
Q_PROPERTY(double result READ getResult WRITE setResult NOTIFY resultChanged)
// QML 안의 text 데이터를 C++에 전달하기 위한 것
Q_PROPERTY(QVariant input_string READ getInput_string WRITE setInput_string NOTIFY input_stringChanged)
...
private:
double result;
QVariant input_string;
protected:
// signal은 emit을 통해 발생시킴
void setResult(double result) { this->result = result; emit resultChanged(); }
public:
double getResult() { return result; }
//Q_INVOKABLE double getResult() { calculate(); return result; }
void setInput_string(QVariant input_string) { this->input_string = input_string; emit input_stringChanged(); }
QVariant getInput_string() { return input_string; }
signals:
void input_stringChanged();
void resultChanged();[main.qml]
Text {
id: calculator_text
...
}
...
Button {
id: button_equal
text: qsTr("=")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
// 1. C++에서 선언한 Q_PROPERTY를 통해 C++의 input_string에 접근해 calculator_text.text에 저장된 값을 대입
Calculator.input_string = calculator_text.text
// 2. C++에서 input_string에 저장된 text를 통해 연산 진행 후
// calculate() 함수의 return 값을 result에 저장
Calculator.result = Calculator.calculate()
// 3. result를 calculator_text.text에 저장
// 4. 최종적으로 그 값을 text에 출력
calculator_text.text = Calculator.result
}
} [Calculator.cpp]
int Calculator::calculate() {
// QML에서 전달된 QStirng 자료형인 input_string 데이터를 string으로 형변환
string input_exp = input_string.toString().toStdString();
...
}
2) Q_INVOKABLE
Q_INVOKABLE
Q_INVOKABLE 함수
- QML에서 C++ 함수에 직접 접근 가능하도록 하는 매크로
// QML에서 C++의 calculate() 함수에 접근하기 위함
Q_INVOKABLE int calculate();4. 예외처리
C++ 계산기 코드 의 예외처리 항목 (적용 : ⭕, 미적용 : ❌)
1. 입력 문자열이 12자를 초과하는 경우 ⭕
2. 정수가 아닌 문자를 입력하는 경우 ❌ => 버튼 입력이기 때문에 어차피 불가능
3. 정수와 문자를 함께 입력하는 경우 ❌ => 버튼 입력이기 때문에 어차피 불가능
4. 사칙연산자가 아닌 다른 기호를 입력한 경우 ❌ => 버튼 입력이기 때문에 어차피 불가능
5. num2의 뒤에 연산자가 있는 경우 EX) 1-1- ⭕
6. 맨 앞에 연산기호가 붙는 경우 ('-' 제외) EX) +1+1 ⭕
7. 연산자를 두 개 붙여 입력하는 경우('-' 제외) EX) 1++1 ⭕
8. 세 개 이상의 정수를 입력하는 경우 EX) 1+1+1 ⭕
9. '/' 연산 때, 분자 혹은 분모에 '0' 입력 시, 다시 입력 요구하기 ⭕
➕ num1 혹은 num2 미입력하는 경우 ⭕int Calculator::calculate() {
// QML에서 가져온 input_string를 QVariant -> String 으로 형변환
string input_exp = input_string.toString().toStdString();
int num1, num2;
char sign;
stringstream stream(input_exp);
stream >> num1;
stream >> sign;
stream >> num2;
// 2번 예외 상황을 처리하기 위해 num1, num2를 0으로 초기화
num1 = 0; num2 = 0;
int len = input_exp.length(); // 입력받은 문자열 길이 구하기
int sign_index = input_exp.find(sign); // sign 인덱스
int sign_subtract = input_exp.find('-',sign_index+2); // 예외 상황 중 '-'제외에 활용할 '-' 인덱스
// 1. 입력한 문자열이 길이가 12 이하인지 판단
if(len > 12) {
return 0;
}
// 2. num1 혹은 num2 가 비어있는지 판단
if(num1 == 0 || num2 == 0) {
return 0;
}
char ch[] = {'+', 'X', '/'}; // 입력된 연산자와 비교하기 위한 연산자 배열 선언
char sign_arr;
// '-'를 제외한 기호들을 for문을 활용해 하나씩 추출해 3, 4번에 적용
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sign_arr = ch[i];
int sign_temp = input_exp.find(sign_arr,sign_index+1); // num2 이후에 또 sign이 입력되면, 그 sign의 인덱스를 저장
int first = input_exp.find_first_of(sign_arr,0); // 입력된 연산자 중 가장 앞 쪽에 놓인 sign의 인덱스
int last = input_exp.find_last_of(sign_arr,len-1); // 입력된 연산자 중 가장 뒤 쪽에 놓인 sign의 인덱스
// 앞에서부터 찾은 연산자 인덱스,뒤에서부터 찾은 연산자 인덱스 비교
if(first == last){
// 3. '-'를 맨 앞 혹은 num2 앞에 입력했는지 판단
if(input_exp.find('-') == 0 || input_exp.find('-') == sign_index+1) {
return 0;
}
}
else{
return 0;
}
// 4. 입력 정수가 3개 이상인지 판단
if(sign_temp != string::npos || sign_subtract != string::npos) {
return 0;
}
}5. 결과
[정상 결과]

[예외상황]
모든 예외상황 결과는 "0" 을 출력
🔗 아래 최종 소스코드 중 main.qml에 QML 추가 게시물 의 QML 소스코드를 적용하면, 또 다른 버튼 클릭 이벤트를 확인 가능!
👩💻 최종 소스코드
[main.cpp]
#include <QGuiApplication>
#include <QQmlApplicationEngine>
#include <QQmlContext>
#include <calculator.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
QCoreApplication::setAttribute(Qt::AA_EnableHighDpiScaling);
QGuiApplication app(argc, argv);
QQmlApplicationEngine engine;
engine.load(QUrl(QStringLiteral("qrc:/main.qml")));
Calculator *ca = new Calculator();
engine.rootContext()->setContextProperty("Calculator", ca);
return app.exec();
}[main.qml]
import QtQuick 2.10
import QtQuick.Window 2.10
import QtQuick.Layouts 1.3
import QtQuick.Controls 2.3
Window {
id: window
visible: true
width: 360
height: 480
title: qsTr("Calculator")
Text {
id: calculator_text
width: parent.width
height: parent.height - parent.width
Layout.fillWidth: true
Layout.fillHeight: true
verticalAlignment: Text.AlignVCenter
horizontalAlignment: Text.AlignRight
font.pixelSize: 25
rightPadding: 20
anchors.top: parent.top
}
GridLayout {
id: gridLayout
width: parent.width
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
rows: 4
columns: 4
anchors.top: calculator_text.bottom
anchors.bottom: parent.bottom
Button {
id: button_7
text: qsTr("7")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "7"
}
}
Button {
id: button_8
text: qsTr("8")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "8"
}
}
Button {
id: button_9
text: qsTr("9")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "9"
}
}
Button {
id: button_add
text: qsTr("+")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "+"
}
}
Button {
id: button_4
text: qsTr("4")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "4"
}
}
Button {
id: button_5
text: qsTr("5")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "5"
}
}
Button {
id: button_6
text: qsTr("6")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "6"
}
}
Button {
id: button_subtract
text: qsTr("-")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "-"
}
}
Button {
id: button_1
text: qsTr("1")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "1"
}
}
Button {
id: button_2
text: qsTr("2")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "2"
}
}
Button {
id: button_3
text: qsTr("3")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "3"
}
}
Button {
id: button_multiply
text: qsTr("X")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "X"
}
}
Button {
id: button_clear
text: qsTr("clear")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text = ""
}
}
Button {
id: button_0
text: qsTr("0")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "0"
}
}
Button {
id: button_equal
text: qsTr("=")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
Calculator.input_string = calculator_text.text
Calculator.result = Calculator.calculate()
calculator_text.text = Calculator.result
}
}
Button {
id: button_divide
text: qsTr("/")
Layout.fillHeight: true
Layout.fillWidth: true
onClicked: {
calculator_text.text += "/"
}
}
}
}[Calculator.h]
#ifndef CALCULATOR_H
#define CALCULATOR_H
#include <QObject>
#include <iostream>
#include <QVariant>
#include <iostream>
class Calculator : public QObject
{
Q_OBJECT
Q_PROPERTY(double result READ getResult WRITE setResult NOTIFY resultChanged)
Q_PROPERTY(QVariant input_string READ getInput_string WRITE setInput_string NOTIFY input_stringChanged)
public:
Calculator();
~Calculator();
private:
int num1;
int num2;
double result;
QVariant input_string;
protected:
void setResult(double result) { this->result = result; emit resultChanged(); }
int getNum1() { return num1; }
int getNum2() { return num2; }
//Q_INVOKABLE void calculate(); // 순수 가상함수
public:
void setNumber(int num1, int num2) { this->num1 = num1; this->num2 = num2; }
double getResult() { return result; }
//Q_INVOKABLE double getResult() { calculate(); return result; }
void setInput_string(QVariant input_string) { this->input_string = input_string; emit input_stringChanged(); }
QVariant getInput_string() { return input_string; }
int add();
int subtract();
int multiply();
int divide();
Q_INVOKABLE int calculate();
signals:
void input_stringChanged();
void resultChanged();
};
#endif // CALCULATOR_H[Calculator.cpp]
#include "calculator.h"
#include <QDebug>
#include <QVariant>
#include <iostream>
#include <string>
#include <sstream> // stringstream 라이브러리
#include <iomanip> // fixed 라이브러리
#include <cmath> // setprecision 라이브러리
using namespace std;
Calculator::Calculator(){}
Calculator::~Calculator(){}
int Calculator::calculate() {
// qml에서 가져온 input_string를 QVariant -> String 으로 형변환
string input_exp = input_string.toString().toStdString();
int num1, num2;
char sign;
// 2번을 예외상황을 처리하기 위해 num1, num2 초기화
num1 = 0; num2 = 0;
stringstream stream(input_exp);
stream >> num1;
stream >> sign;
stream >> num2;
int len = input_exp.length(); // 입력받은 문자열 길이 구하기
int sign_index = input_exp.find(sign); // sign 인덱스
int sign_subtract = input_exp.find('-',sign_index+2); // 예외 상황 중 '-'제외에 활용할 '-' 인덱스
// 1. 입력한 문자열이 길이가 12 이하인지 판단
if(len > 12) {
return 0;
}
// 2. num1 혹은 num2 가 비었는지 판단
if(num1 == 0 || num2 == 0) {
return 0;
}
char ch[] = {'+', 'X', '/'}; // 입력된 연산자와 비교하기 위한 연산자 배열 선언
char sign_arr;
// '-'를 제외한 기호들을 for문을 활용해 하나씩 추출해 3, 4번에 적용
for(int i = 0; i < 3; i++) {
sign_arr = ch[i];
int sign_temp = input_exp.find(sign_arr,sign_index+1); // num2 이후에 또 sign이 입력되면, 그 sign의 인덱스를 저장
int first = input_exp.find_first_of(sign_arr,0); // 입력된 연산자 중 가장 앞 쪽에 놓인 sign의 인덱스
int last = input_exp.find_last_of(sign_arr,len-1); // 입력된 연산자 중 가장 뒤 쪽에 놓인 sign의 인덱스
// 2. 앞에서부터 찾은 연산자 인덱스,뒤에서부터 찾은 연산자 인덱스 비교
if(first == last){
// 4. '-'를 맨 앞 혹은 num2 앞에 입력했는지 판단
if(input_exp.find('-') == 0 || input_exp.find('-') == sign_index+1) {
return 0;
}
}
else{
return 0;
}
// 3. 입력 정수가 3개 이상인지 판단
if(sign_temp != string::npos || sign_subtract != string::npos) {
return 0;
}
}
switch (sign) {
case '+':
setNumber(num1, num2);
return add();
case '-':
setNumber(num1, num2);
return subtract();
case 'X':
setNumber(num1, num2);
return multiply();
case '/':
if(num1 != 0 && num2 != 0) {
setNumber(num1, num2);
return divide();
}
else {
return 0;
}
default:
break;
}
return 0;
}
int Calculator::add() {
return getNum1() + getNum2();
}
int Calculator::subtract() {
return getNum1() - getNum2();
}
int Calculator::multiply() {
return getNum1() * getNum2();
}
int Calculator::divide() {
return getNum1() / getNum2();
}