👨🏫학습목표
오늘은 DPG와 DDPG의 개념에 대해 배워볼 예정이다.
1️⃣ Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient
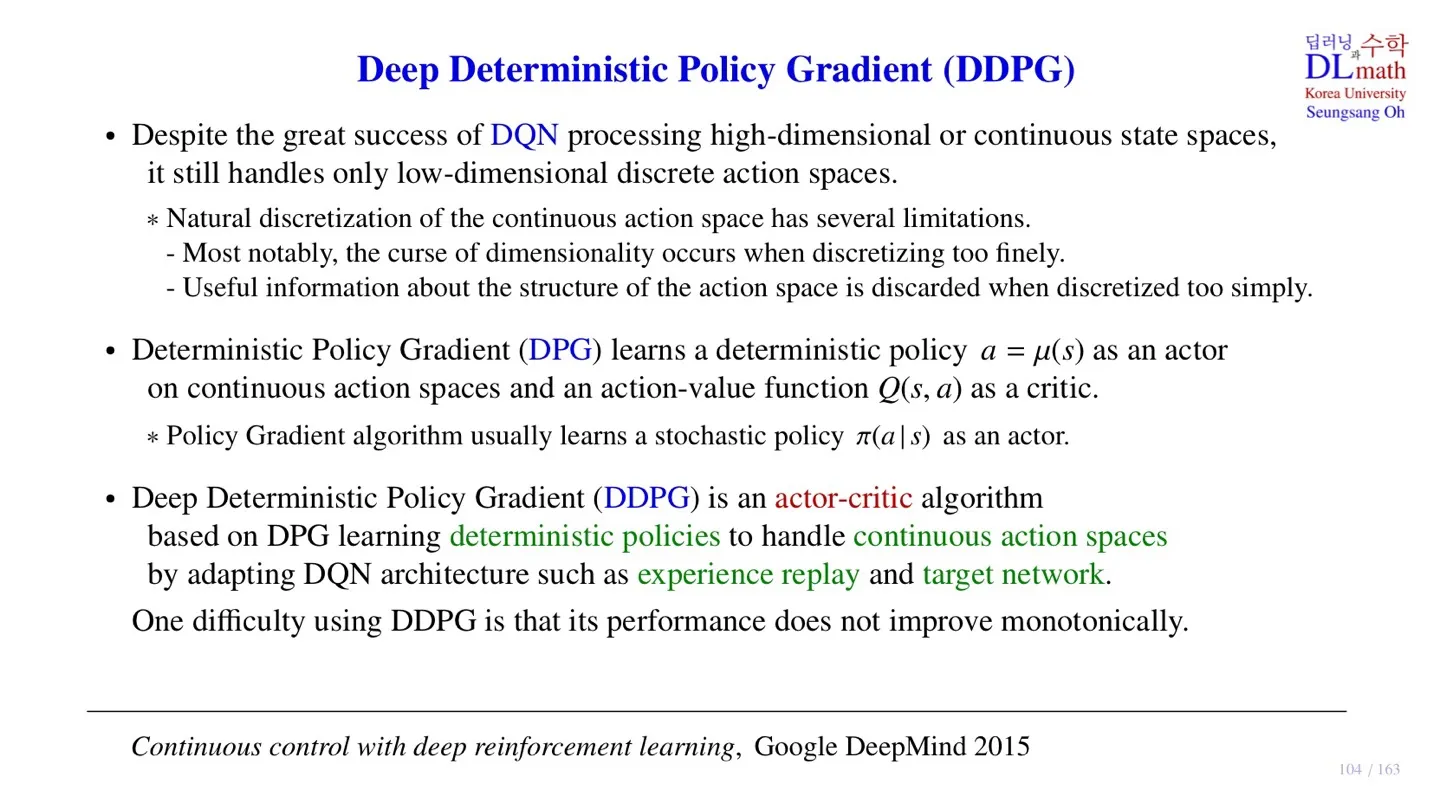
🔷 기존의 모델
🔻 DQN
- 크고 continuous한 state space를 입력으로 처리할 수 있다.
- 하지만 출력으로는 작고 discrete한 action space만 처리할 수 있어서 로보틱스에 적용하기 힘들었다.
🔻 A3C
- Policy를 직접 approximation하기 때문에 Continuous action space를 처리할 수 있다.
지금까지 다루었던 Stochastic policy π(a∣s) 는 random한 성질이 반영되었다.
오늘은 다른 방법으로 continuous action space를 처리할 수 있는 모델을 다뤄보려 한다.
🔷 Deterministic Policy Gradient (DPG)
- Deterministic policy a=μ(s) 를 배운다.
- Deterministic policy는 입력 state가 주어지면 action이 결정된다.
- Actor : deterministic policy a=μ(s)
- Critic : action-value function Q(s,a)
🔷 Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient (DDPG)
- DPG를 기반으로 한 Actor-critic algorithm
- Deterministic policy를 학습한다.
- Q(s,a)를 구하기 위해 DQN을 사용한다.
- DQN을 사용하기 때문에 DQN의 핵심 구조인 experience ereplay와 target network 역시 사용한다.
- 다만 학습이 진행됨에 따라 반드시 Object function이 개선되지는 않는다는 한계가 존재한다.
2️⃣ Deterministic Policy Gradient
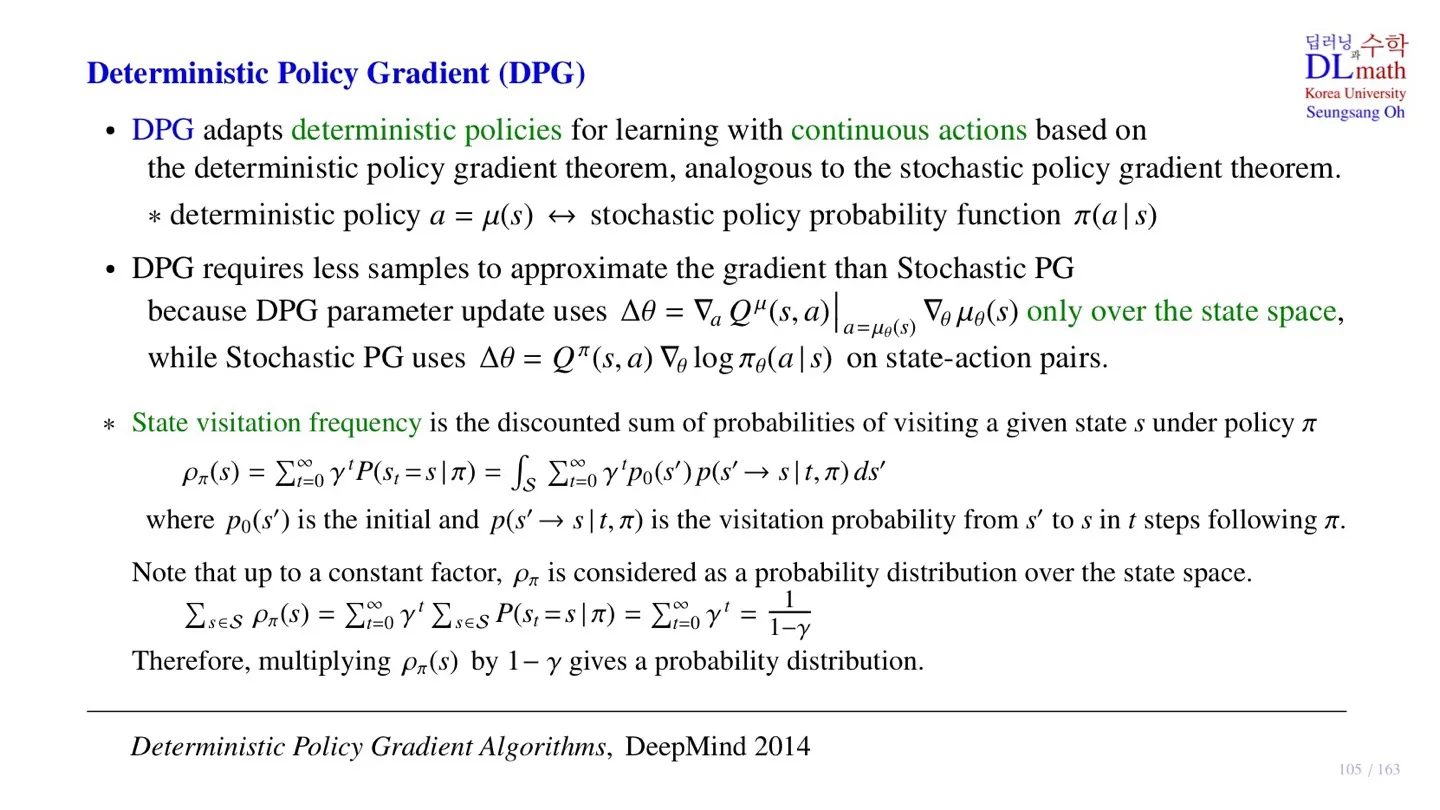
🔷 DPG
- Continous action space를 처리하기 위해 deterministic policy를 사용한다.
- Deterministic policy a=μ(s)
🔻 DPG의 gradient
Δθ=∇aQμ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)∇θμθ(s)
- State에 대해 action이 deterministic하게 결정되기 때문에 state만 고려하면 된다.
- 즉 훨씬 더 적은 데이터로 학습이 가능하다.
🔻 State visitation frequency
- 주어진 Policy에서 특정한 state를 얼마나 자주 방문하는지 알려주는 값이다.
ρπ(s)=t=0∑∞γtP(St=s∣π)=∫St=0∑∞γtp0(s′)p(s′→s∣t,π)ds′
- ρπ(s): 주어진 policy에서 해당 state의 state visitation frequency
- 주어진 policy에서 특정 state가 발생할 확률을 discount factor로 가중합한 값이다.
- 모든 시점 t에서 해당 특정 state가 발생할 확률을 더한다.
- p0(s′): s′ 에서 시작할 확률
- p(s′→s∣t,π): 시점 t에서 s에 도달할 확률
- ∫Sds′: 모든 state가 시작 state s′가 될 수 있고 state space가 continuous하기 때문에 적분한다.
s∈S∑ρπ(s)=t=0∑∞γts∈S∑P(St=s∣π)=t=0∑∞γt=1−γ1
- ∑t=0∞,∑s∈S의 순서를 바꾸어도 식은 성립한다.
- ∑s∈SP(St=s∣π)=1 이므로 두번째 등호가 성립한다.
- ∑s∈Sρπ(s)=1−γ1 이므로 ρπ(s)에 1−γ를 곱하면 확률로 만들 수 있다.
3️⃣ Stochastic VS Deterministic
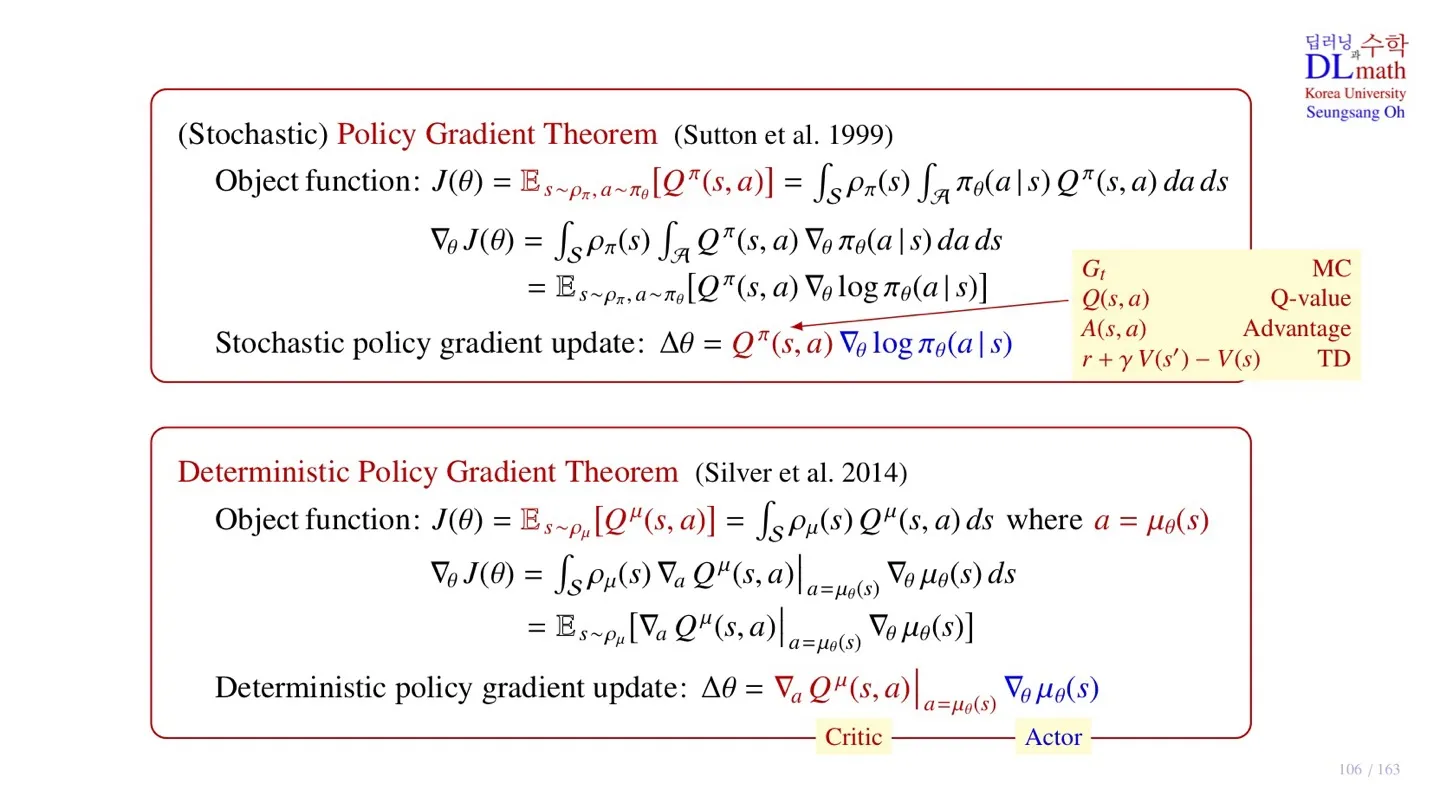
🔷 Stochactic Policy Gradient Theorem
🔻 Object function
J(θ)=Es∼ρπ,a∼πθ[Qπ(s,a)]=∫Sρπ(s)∫Aπθ(a∣s)Qπ(s,a)dads
- Q-function의 기대값을 object function으로 사용한다.
- s∼ρπ: State는 state visitation frequency를 따른다.
- a∼πθ: Action은 policy를 따른다.
- Es∼ρπ,a∼πθ[...]: State와 Action에 대해 둘다 기대값을 적용해야 하기 때문에 ∫S∫A...dads 를 적용한다.
🔻 Gradient
∇θJ(θ)=∫Sρπ(s)∫AQπ(s,a)∇θπθ(a∣s)dads
=Es∼ρπ,a∼πθ[Qπ(s,a)∇θlogπθ(a∣s)]
🔻 Stochastic policy gradient update
Δθ=Qπ(s,a)∇θlogπθ(a∣s)
- Critic : Qπ(s,a)
- Actor : ∇θlogπθ(a∣s)
🔷 Deterministic Policy Gradient Theorem
🔻 Object function
J(θ)=Es∼ρμ[Qμ(s,a)]=∫Sρμ(s)Qμ(s,a)dswhere a=μθ(s)
- Q-function의 기대값을 object function으로 사용한다.
- s∼ρπ: State는 state visitation frequency를 따른다.
- a=μθ(s): Action은 state에 따라 deteministic하게 결정된다.
- Es∼ρπ[...]: State에 대해 기대값을 적용해야 하기 때문에 ∫S...ds 를 적용한다.
🔻 Gradient
∇θJ(θ)=∫Sρμ(s)∇aQμ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)∇θμθ(s)ds
=Es∼ρμ[∇aQμ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)∇θμθ(s)]
🔻 Deterministic policy gradient update
Δθ=∇aQμ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)∇θμθ(s)
- Critic : ∇aQμ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)
- Actor : ∇θμθ(s)
4️⃣ Deep Deterministic Policy Gradient
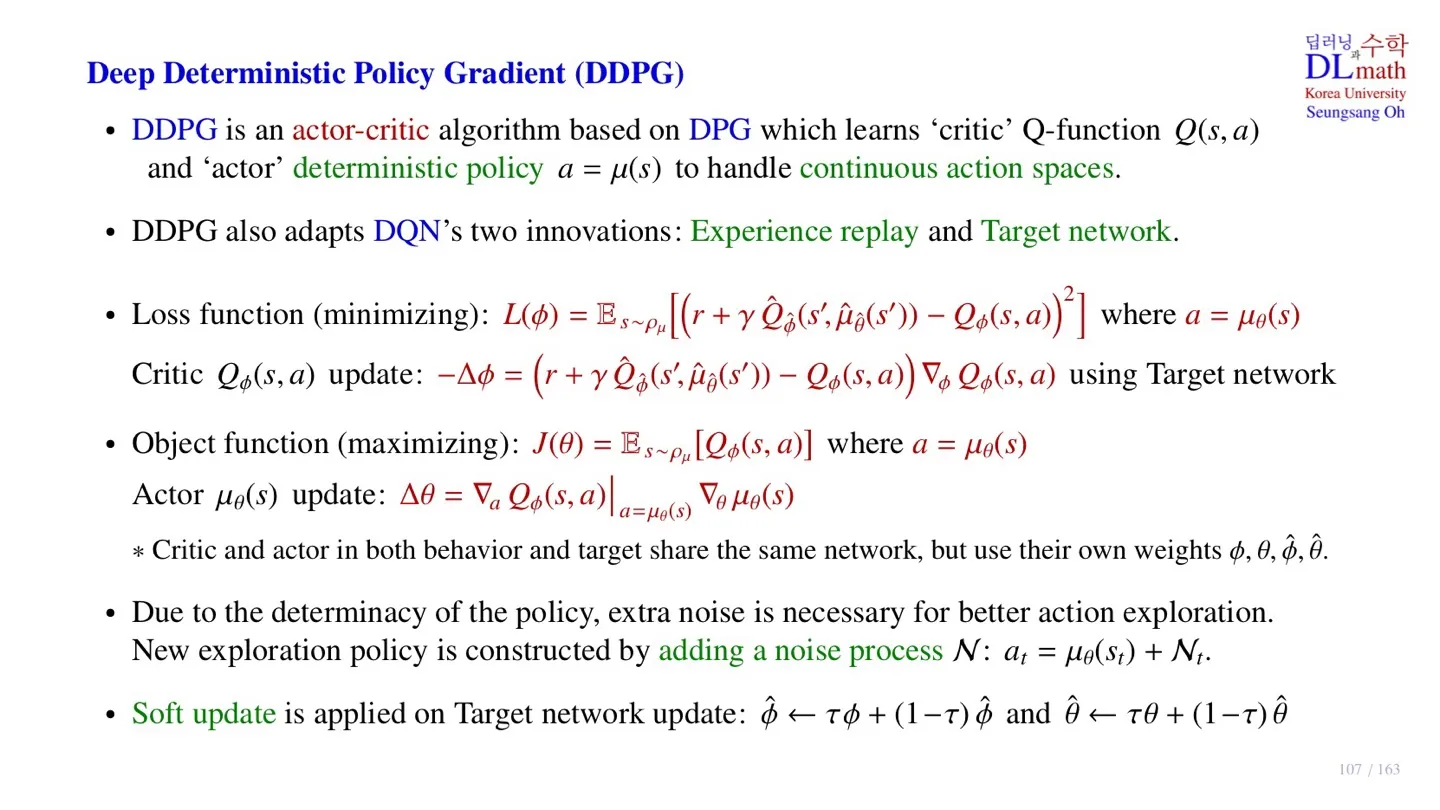
🔷 DDPG
- DPG를 기반으로 한 actor-critic algorithm이다.
- Critic으로는 Q-function Q(s,a)를 학습한다.
- Actor로는 deterministic policy a=μ(s)를 학습한다.
- Critic Network로는 DQN을 사용하며, 따라서 DQN의 experience replay와 Target Network 구조 역시 사용한다.
🔻 Critic Network의 Loss function
L(ϕ)=Es∼ρμ[[r+γQ^ϕ^(s′,μ^θ^(s′))−Qϕ(s,a)]2] where a=μθ(s)
- DQN과 동일한 Loss을 적용한다.
- Temporal Difference error를 사용한다.
- Target Network와 behavior Network가 구분되어 있는 Off-policy이다.
- 단, Action은 actor Network에서 deterministic하게 결정된다.
🔻 Critic Network 업데이트
−Δϕ=(r+γQ^ϕ^(s′,μ^θ^(s′))−Qϕ(s,a))∇ϕQϕ(s,a)
- Gradient descent 방식으로 업데이트한다.
🔻 Actor Network의 Object function
J(θ)=Es∼ρμ[Qϕ(s,a)] where a=μθ(s)
🔻 Actor Network 업데이트
Δθ=∇aQϕ(s,a)∣a=μθ(s)∇θμθ(s)
- Gradient ascent 방식으로 업데이트한다.
🔷 학습 파라미터
- ϕ,θ,ϕ^,θ^ 총 4개를 사용한다.
- Action이 deterministic하기 때문에 exploration이 부족하다는 한계가 존재한다.
- 이를 위해 출력된 action에 noise를 더하는 방법을 사용한다.
N:at=μθ(st)+Nt
- 각 step마다 다른 noise를 부여하기 위해 Noise squence를 만든다.
- 그리고 해당 step t에 맞는 noise Nt 를 더한다.
🔻 Target Network의 soft update
ϕ^←τϕ+(1−τ)ϕ^ and θ^←τθ+(1−τ)θ^
- 기존의 DQN은 일정 step 후 target Network를 behavior Network로 업데이트한다.
- 일정 step마다 parameter를 조금씩 업데이트한다.
5️⃣ DDPG의 pseudo code

🔷 초기 설정
🔻 파라미터 초기화
- Critic Network Q(s,a;ϕ)와 Actor Network μ(s;θ)를 초기화한다.
- Target Network ϕ^=ϕ,θ^=θ로 초기화한다.
- Replay Buffer R 을 정의한다.
🔷 업데이트 진행
🔻 Noise sequence, 시작 state 초기화
- Initial state s1 설정
- Noise sequence N 초기화
🔻 Sample data 수집
- Deterministic policy μ(st;θ)을 통해 action 선정
- at=μ(st;θ)+Nt noise를 추가하여 action 변형
- Action at를 통해 immediate reward rt+1과 next state st+1 수집
- (st,at,rt+1,st+1)을 replay buffer R에 저장한다.
🔻 파라미터 업데이트
- Replay buffer R 에서 minibatch B 만큼 sample data를 추출한다.
- Sample data를 통해 target yi=ri+1+γQ^(si+1,μ^(si+1;θ^);ϕ^)를 구한다.
L=B1i∑(yi−Q(si,ai;ϕ))2
- Target을 통해 critic Network를 업데이트한다.
∇θJ≈B1i∑∇aQ(si,a;ϕ)∣a=μ(si;θ)∇θμ(si;θ)
- Deterministic policy gradient를 사용하여 Actor Network도 업데이트한다.
ϕ^←τϕ+(1−τ)ϕ^ and θ^←τθ+(1−τ)θ^
- 일정 step이 지난 후 target Network를 soft update를 진행한다.
6️⃣ 정리
🔷 26강에서 배운 내용은 아래와 같다.
- DPG는 deterministic policy를 사용한다.
- DDPG는 DPG를 기반으로 한 actor-acritic algorithm이다.
- DDPG는 Replay Buffer를 사용한다.
- DDPG는 target Network와 behavior Network가 분리되어 있는 off-policy이다.
- DDPG는 target Network를 업데이트할 때, soft updata를 진행한다.