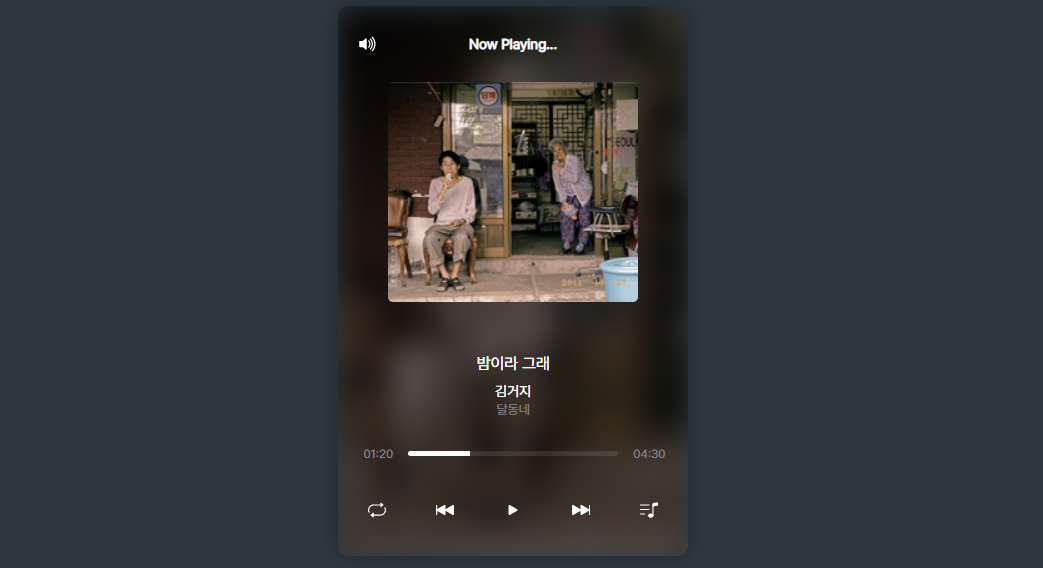
MusicPlayer🎵
사용언어 : React
데모사이트 : DEMO
🧡사용된 기술
✨reducer
재생중인 플레이어의 상태를 저장하는 객체 생성
const initialState = {
playlist,
currentMusicId: playlist[randomIdx].id,
currentIdx: randomIdx,
playing: false,
repeat: 'ALL', // ONE SHUFFLE
}reducer로 관련 기능을 관리하고, 파일을 따로 분리하여 관리
function musicPlayerReducer(state = initialState, action){
switch(action.type) {
case 'PLAY':
return {
...state,
playing: true
}
case 'PAUSE':
return {
...state,
playing: false
}
case 'NEXT':
const nextIdx = state.repeat === 'SHUFFLE' ?
getRandomNum(state.currentIdx)
: (state.currentIdx + 1) % state.playlist.length
return {
...state,
currentIdx: nextIdx,
currentMusicId: playlist[nextIdx].id
}
.
.
.✨context
전역에서 사용되는 데이터를 context로 관리
export const RefContext = createContext(null);
function App() {
const [showPlayList, setShowPlayList] = useState(false)
const audioRef = useRef();
return (
<RefContext.Provider value={{audioRef, showPlayList, setShowPlayList}}>
<Player />
<PlayList />
</RefContext.Provider>
)
}✨styled components
import styled, { css } from 'styled-components'
export const Header = styled.div `
display: flex;
justify-content: space-between;
align-items: center;
padding: 10px;
${({type}) => type === 'playlist' && css`
position: sticky;
top: 0;
background-color: #191825;
`}
.
.
.✨framer-motion
framer-motion를 활용하여 playlist의 모션제어
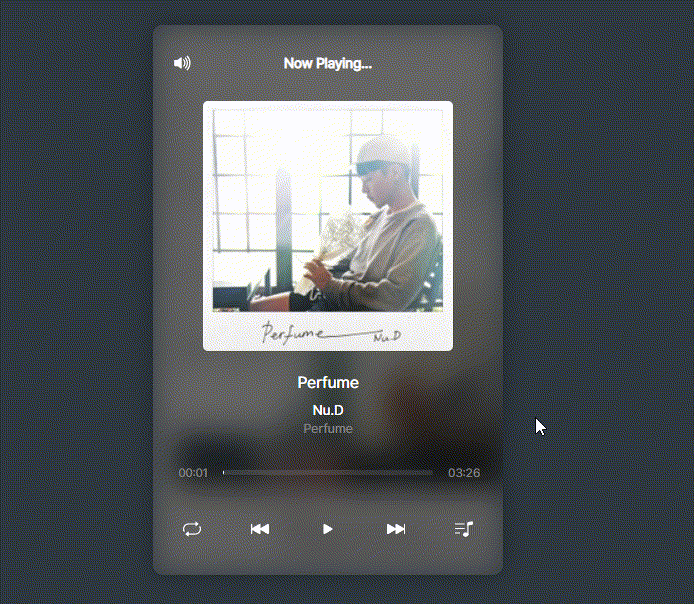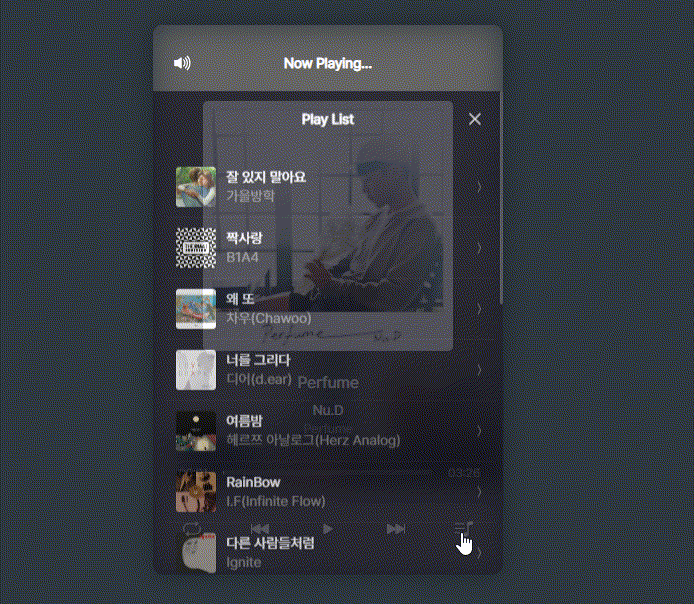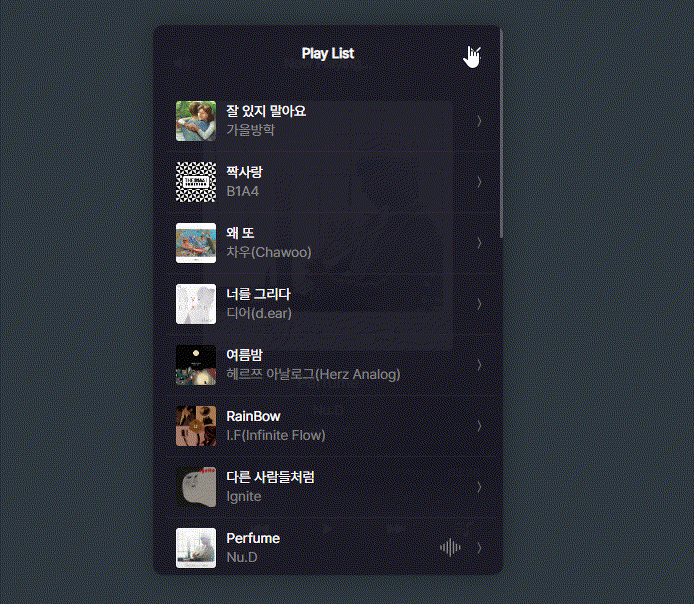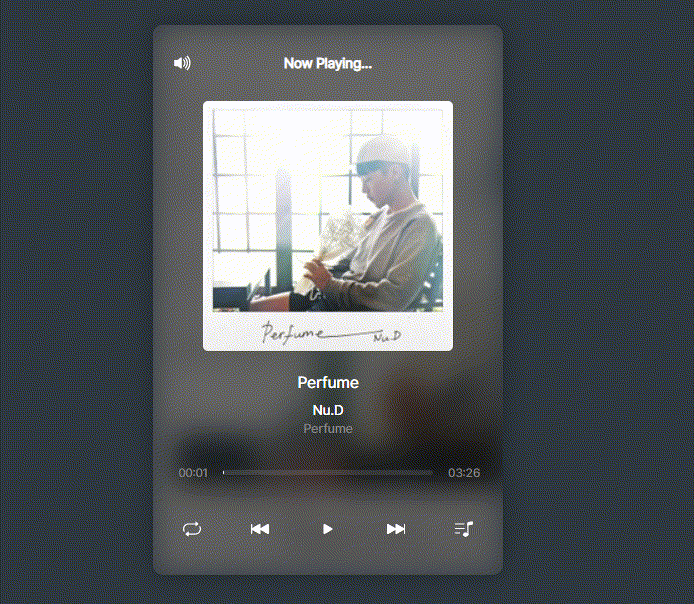
function PlayList() {
const showVariants = {
hidden: {y: innerHeight, opacity: 0},
visible: {y: 0, opacity: 0.95},
}
const hiddenVariants = {
hidden: {y: 0, opacity: 0.95},
visible: {y: innerHeight, opacity: 0},
}
return (
<S.PlayList
initial="hidden"
animate="visible"
variants={showPlayList ? showVariants : hiddenVariants}
transition={{ type: "tween", duration: 0.3 }}
>
.
.
.
</S.PlayList>
)
}
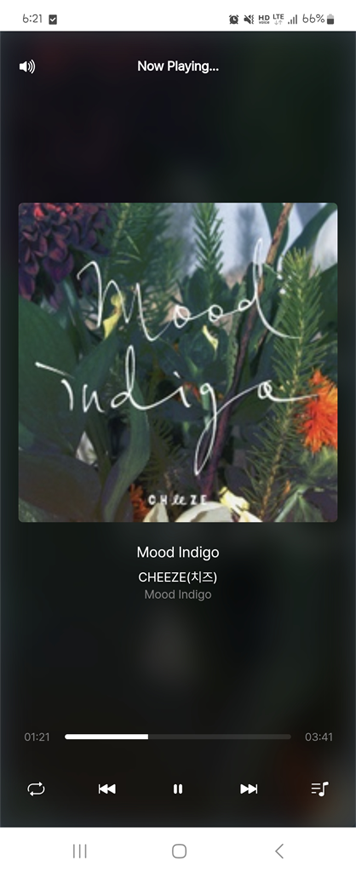
🧡반응형 레이아웃
- 반응형 레이아웃을 적용하여 모바일 환경에도 최적화
마치며🙌
audio객체를 본격적으로 다뤄본적도 처음이였고.. reducer사용도, react도 많이 익숙치 않은 상황에서 만들다보니 생각보다 복잡하고 어려웠다 @.@... 그래도 덕분에 reducer랑 드디어 제법 친해진 느낌이 든다!!
