
Sample Size
- a part of population that is representative of the population
- ex. when you have to use data that is just way too broad
- the goal is to get enough information from a small group within a population to make predictions or conclusions about the whole population
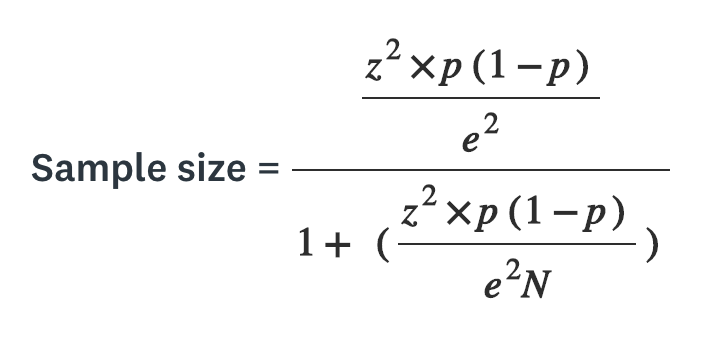
N = population size e = margin of error (percentage in decimal form) z = z-score
z-score is the number of standard deviations a given proportion is away from the mean
Random Sample
- a way of selecting a sample from a population so that every possible type of the sample has an equal chance of being chosen
- this will reduce the sampling bias
Statistical Power
- the probability of getting meaningful results from a test
Hypothesis Testing
- a way to see if a survey or experiment has meaningful results
Margin of Error
-
maximum amount that the sample reuslts are expected to differ from those of the actual population
-
to calculate the margin of error you need:
- population size
- sample size
- confidence level
-
when executing A/B test, it is important to know about margin error
- if a returns 5% and b returns 3%, yet the margin of error is 2%, a overlaps the result of the b, therefore, the result is not statistically significant
