Fitting
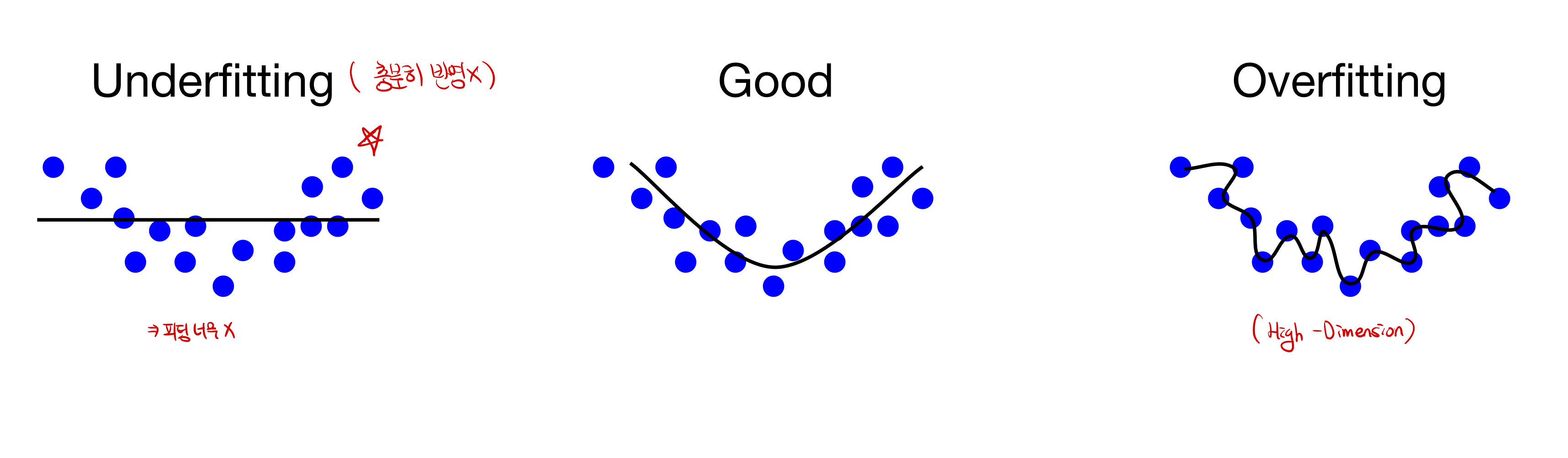
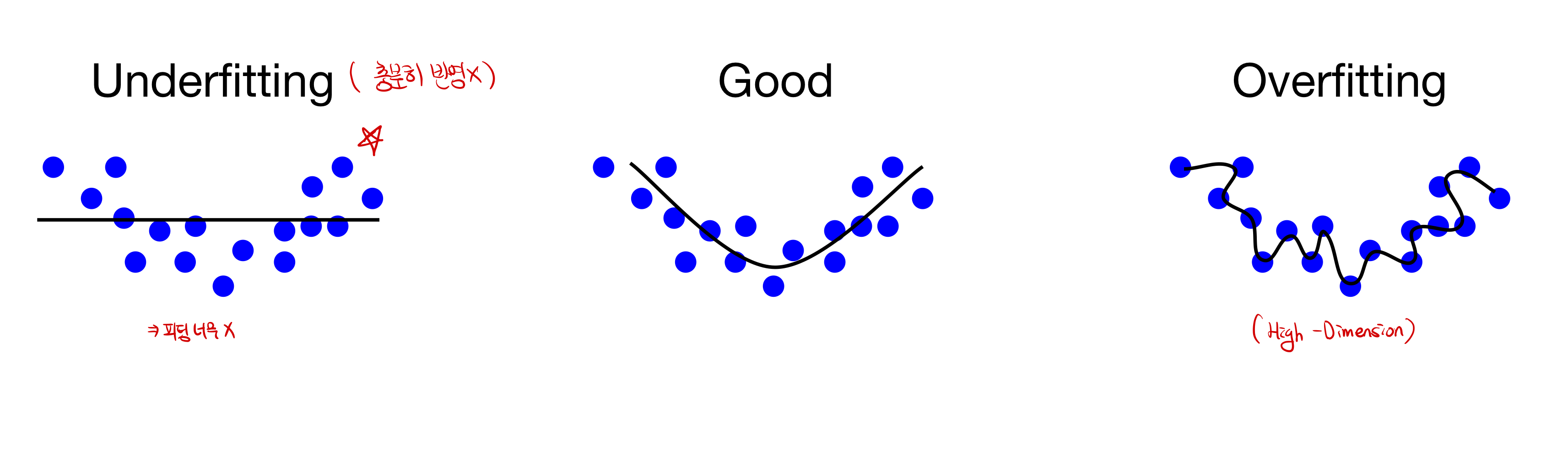
Fitting 이란? 모델의 학습 적합도를 의미한다. 충분한 학습이 되지 못해, 적합도가 떨어지는 모델을 Underfitting이 된 상태라고 의미하며, 너무 train dataset에 과적합되어있는 경우를 Overfitting이라고 한다.
- Overfitting의 문제점
Overfitting이 된경우, trainset에 과적합이 되어있어서, 새로운 test 데이터 set에 과적합된 모델을 적용할 경우, Good-fitting이 된 모델보다 손실값이 큰 값이 나오는 경우가 발생한다. 따라서 이러한 이유에서 overfitting을 막을 수 있는 모델이 필요하다.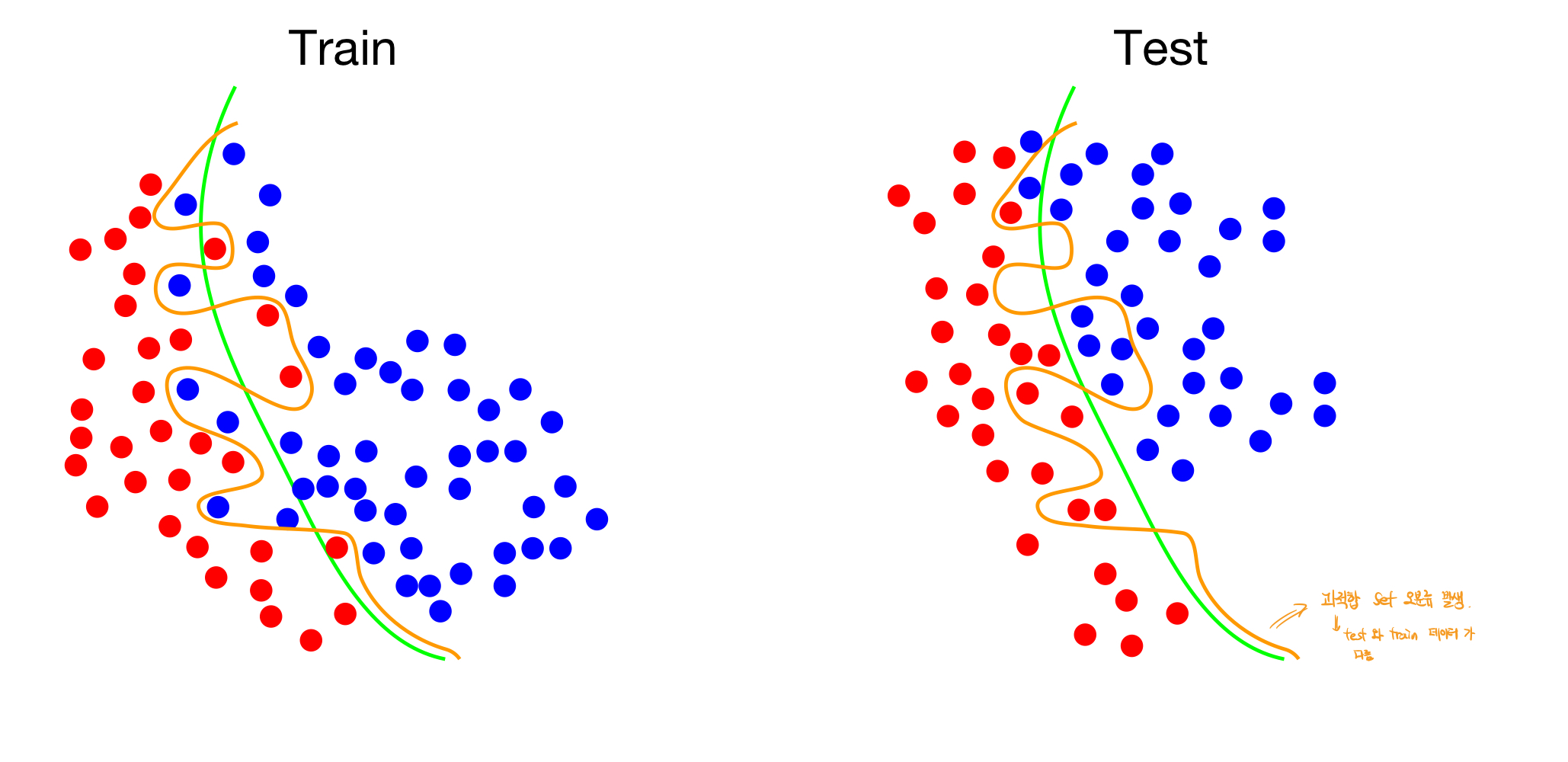
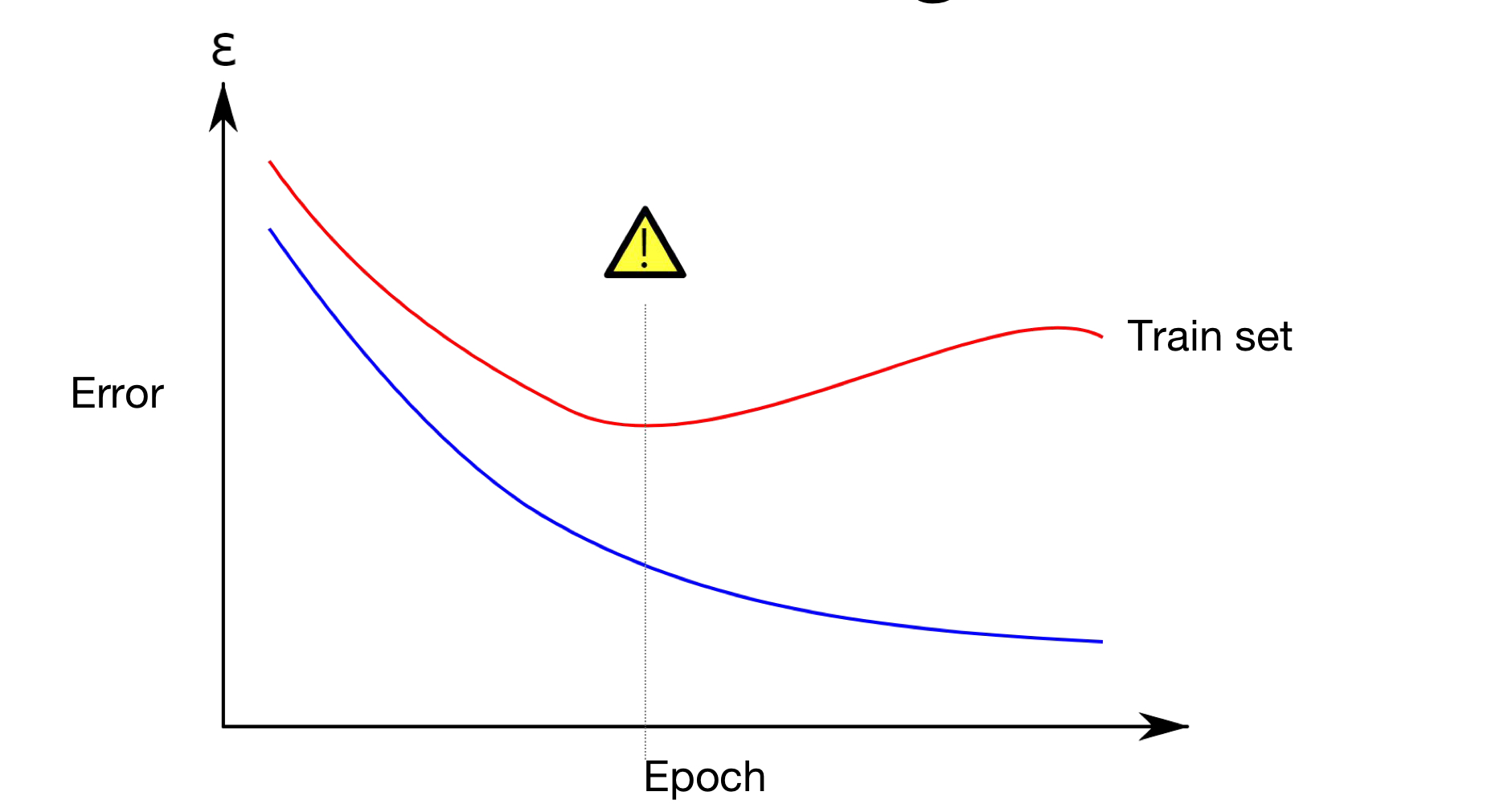
새로운 해결방안 :Dropout
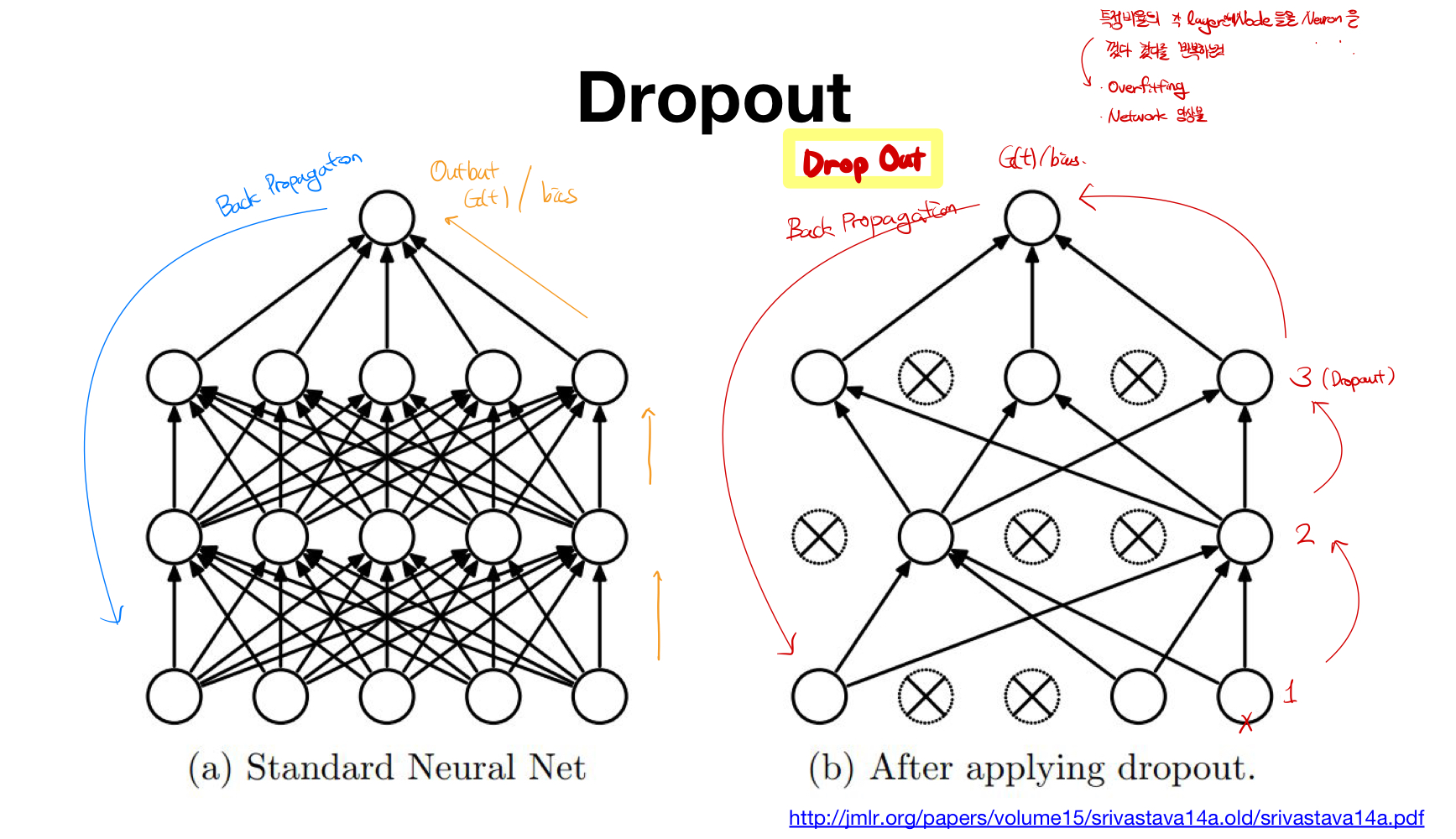
Dropout이란? 각 layer의 특정 비율 만큼 Node혹은 Neuron들을 껐다 켰다를 반복하면서 학습시키는 것을 의미한다.
- 장점:
- Overfitting을 방지할 수 있다.
- Network앙상블 효과를 만들어 낼 수 있다.
- 코드 구현
1.dropout = torch.nn.dropout(p=drop_prob)와 같이 선언해주고, drop_prob을 이용해서 dropout을 할 비율을 정해준다. Train 모델일 때는model.train()을 test를 할때에는model.eval()을 이용해준다. (test모델에서는 학습을 할 때 dropout이 일어나면 안된다.
# Lab 10 MNIST and softmax
import torch
import torchvision.datasets as dsets
import torchvision.transforms as transforms
import random
device = 'cuda' if torch.cuda.is_available() else 'cpu'
# for reproducibility
random.seed(777)
torch.manual_seed(777)
if device == 'cuda':
torch.cuda.manual_seed_all(777)
# parameters
learning_rate = 0.001
training_epochs = 15
batch_size = 100
drop_prob = 0.3
# MNIST dataset
mnist_train = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=True,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
mnist_test = dsets.MNIST(root='MNIST_data/',
train=False,
transform=transforms.ToTensor(),
download=True)
# dataset loader
data_loader = torch.utils.data.DataLoader(dataset=mnist_train,
batch_size=batch_size,
shuffle=True,
drop_last=True)
# nn layers
linear1 = torch.nn.Linear(784, 512, bias=True)
linear2 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 512, bias=True)
linear3 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 512, bias=True)
linear4 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 512, bias=True)
linear5 = torch.nn.Linear(512, 10, bias=True)
relu = torch.nn.ReLU()
dropout = torch.nn.Dropout(p=drop_prob)
# xavier initialization
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear1.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear2.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear3.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear4.weight)
torch.nn.init.xavier_uniform_(linear5.weight)
# model
model = torch.nn.Sequential(linear1, relu, dropout,
linear2, relu, dropout,
linear3, relu, dropout,
linear4, relu, dropout,
linear5).to(device)
# define cost/loss & optimizer
criterion = torch.nn.CrossEntropyLoss().to(device) # Softmax is internally computed.
optimizer = torch.optim.Adam(model.parameters(), lr=learning_rate)
total_batch = len(data_loader)
model.train() # set the model to train mode (dropout=True)
for epoch in range(training_epochs):
avg_cost = 0
for X, Y in data_loader:
# reshape input image into [batch_size by 784]
# label is not one-hot encoded
X = X.view(-1, 28 * 28).to(device)
Y = Y.to(device)
optimizer.zero_grad()
hypothesis = model(X)
cost = criterion(hypothesis, Y)
cost.backward()
optimizer.step()
avg_cost += cost / total_batch
print('Epoch:', '%04d' % (epoch + 1), 'cost =', '{:.9f}'.format(avg_cost))
print('Learning finished')
# Test model and check accuracy
with torch.no_grad():
model.eval() # set the model to evaluation mode (dropout=False)
# Test the model using test sets
X_test = mnist_test.test_data.view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_test = mnist_test.test_labels.to(device)
prediction = model(X_test)
correct_prediction = torch.argmax(prediction, 1) == Y_test
accuracy = correct_prediction.float().mean()
print('Accuracy:', accuracy.item())
# Get one and predict
r = random.randint(0, len(mnist_test) - 1)
X_single_data = mnist_test.test_data[r:r + 1].view(-1, 28 * 28).float().to(device)
Y_single_data = mnist_test.test_labels[r:r + 1].to(device)
print('Label: ', Y_single_data.item())
single_prediction = model(X_single_data)
print('Prediction: ', torch.argmax(single_prediction, 1).item())