INT8 Matrix Multiplication for feed-forward and attention projection layers in Transformers(175B parameter).
-
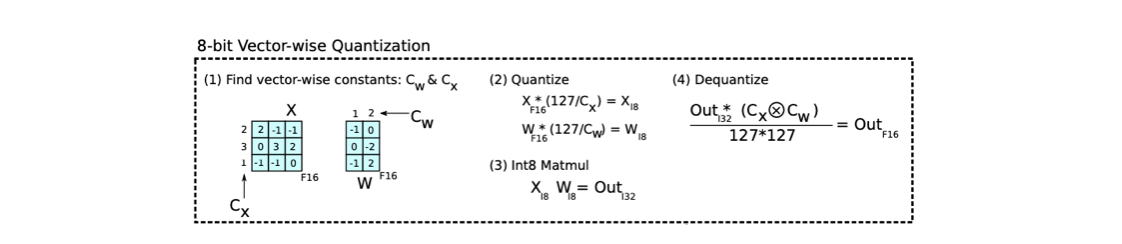
vector-wise Q with separate normalization constants for each inner product in the matrix multiplication.
-
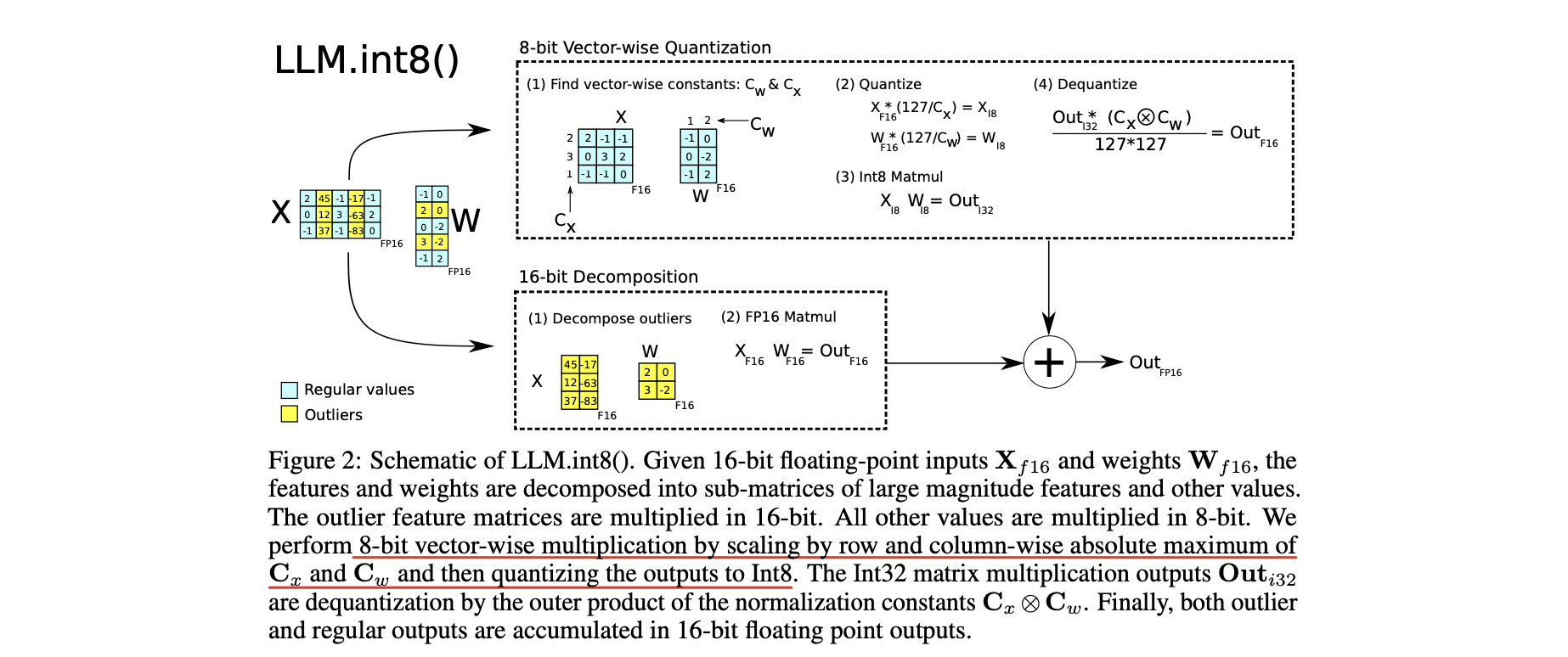
mixed-precision decomposition scheme
- 🟨 outlier feature dimensions ➡️ 16-bit matrix multiplication
- 🟨 other 99.9% dimensions ➡️ 8-bit matrix multiplication
Motivation
-
feed-forward and attention projection layers and their matrix multiplication operations are responsible for 95% of consued parameters and 65-85% of all computation
(Ilharco et al. 2020: High performance natural language processing) -
현재까지의 transformer를 위한 8-bit Q는 350M parameter보다 적은 model들에 대해 연구.
-
in transformer
-
다른 dimension들보다 20까지 큰 large feature는 모든 transformer에서 25% 정도 나타난다.
-
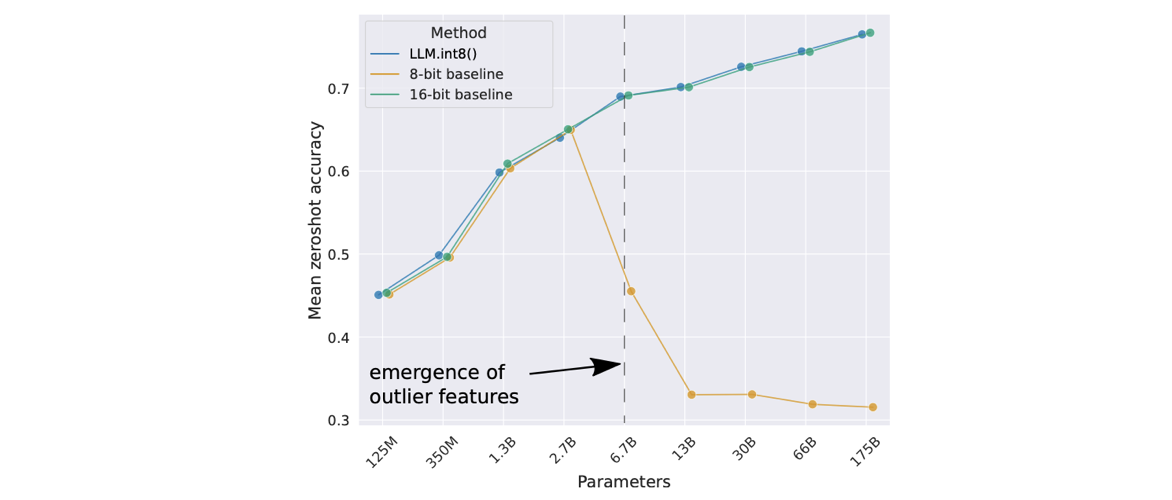
transformer를 6B parameter까지 scale하면, outlier는 다른 layer로 점진적으로 spread한다.
-
6.7B parameter에서는, 모든 transformer layer와 75%의 모든 sequence dimension이 extreme한 크기의 feature에 영향을 받는다.
-
6.7B scale에서, 150,000 outlier가 sequence마다 발생하는데, 전체 transformer를 통틀어 오직 6개의 feature dimension들에 집중되어 있다.
이 outlier feature demsnion을 제거하면(=zero로 만들면), top-1 attention softmax probability mass 가 20% 이상 감소하고, validation perplexity를 600-1000% 악화.
(모든 input feature에서 0.1% 밖에 차지 하지 않는데, 성능 악화에 큰 영향) -
이와 대조적으로, 같은 양의 random feature를 zero로 만들면 probability를 최대 0.3% 감소, perplexity는 0.1% 정도 악화.
-
Challenge
-
- the need for higher Q precision at scales beyond 175B parameters
-
- the need to explicitly represent the sparse byt systematic large magnitude outlier features that ruin Q precision once they emerege in all transformer layers starting at scales of 6.7B parameters
Methods
1. Vector-wise Q
(Vector-wise Q로 2.7B param scale 까지는 Q 이후에도 성능 유지 효과)
-
matrix multiplication(MM)이 독립적인 row와 column vector의 inner product로 구성.
-
multiple scaling constants
(single scaling constant per tensor ❌)- 각 inner product마다 독립적인 Q normalization constant (scaling constant)를 사용해서 Q 정확도 향상 가능.
- 의 각 row 마다 다른 scaling constant
- 의 각 column마다 다른 scaling constant
-
8-bit Q해서 MM하고, dequantization을 통해 16-bit로 복구.
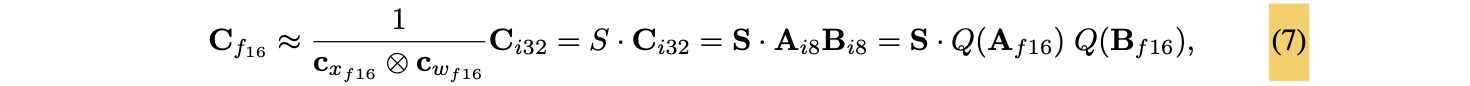
- 각 inner product 결과에 row와 column의 scaling constant의 outer product를 나눠서, dequantization 할 수 있음.
2. Mixed-precision Decomposition : Outlier는 FP16으로 처리, 나머지는 INT8로 처리
(6.7B param 이상에서도 성능 유지하려면 필요)
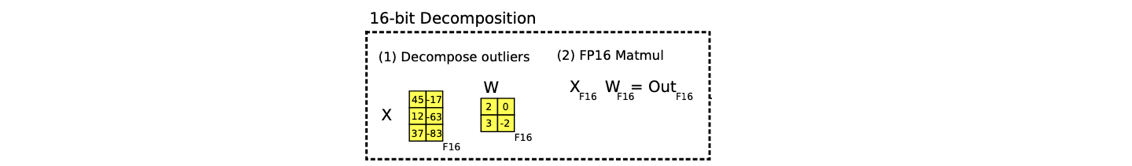
-
hidden state의 feature dimension에서의 extreme outlier를 이해하고 처리하는 것이 중요하다.
-
bilion-scale 8-bit transformer는 large magnitude features(columns)를 가진다.
-
input matrix 가 주어질 때, outlier가 발생한다면,
- 거의 모든 sequence(token) dimension (모든 row) 에 발생하지만
- 특정 feature(hidden) dimension (특정 column) 에서만 발생하는 특징을 갖는다.
-
그런데 vector-wise Q는 hidden state의 각 row를 Q하기 때문에, outlier feature에는 효율적이지 못하다.
-
럭키비키로, outlier feature는 모든 feature dimension(column)에서 0.1% 정도 만을 차지함을 관찰했다.
-
따라서 outlier dimension(column)만 high precision MM으로 처리하는 decomposition 테크닉을 제안했다.
-
최소 outlier를 하나 이상 가진 모든 dimension(column) 를 set 으로 분리한다.
-
-
Mixed precision for MM은 아래와 같이 정의된다.
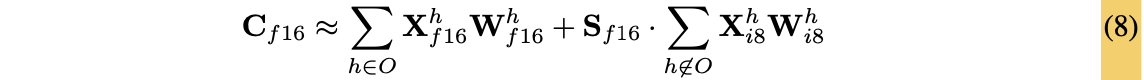
- 이렇게 99.9%의 weight는 8-bit로, outlier는 16-bit로 처리해서, memory-efficient MM을 할 수 있다.
- outlier magnitude threshold 으로 transformer 성능 하락을 0에 가깝게 할 수 있었다.
- 13B 이하의 transformer의 outlier feature dimension은 7개 이하이기 때문에, decomposition 연산은 0.1% 정도만의 additional memory를 사용한다.