Motivations
-
key obeservation
-
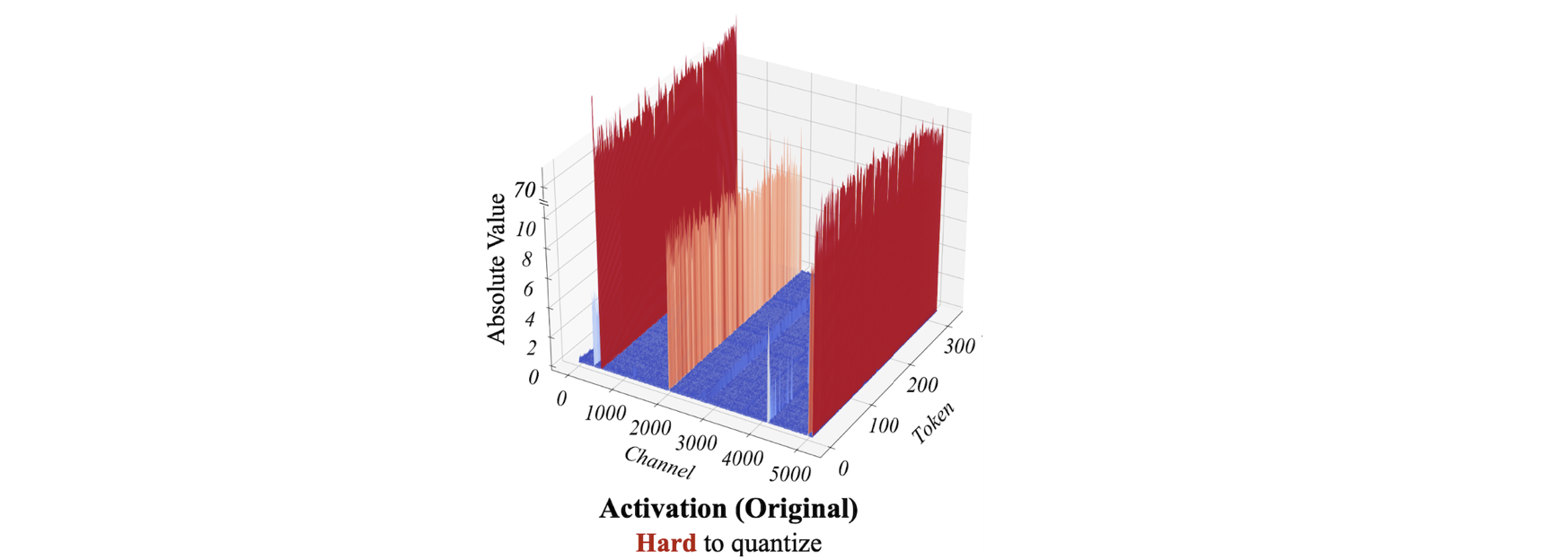
1️⃣ LLMs는 outliers로 인해 activation Q가 어렵다.
-
2️⃣ outlier들은 여러 channel들 중 적은 수의 fixed channel에만 존재한다.
-
3️⃣ 그런데, activation에서 서로 다른 각 token들이 channel-wise(각 channel 별)로는 분산이 비슷한 특징을 갖는다.
- per-channel Q 한다면, per-tensor Q에 비해 Q error를 더 줄일 수 있다.
- 하지만, per-channel Q는 GEMM kernel들과 호환성이 낮아, 이전 LLM.int8(), ZeroQuant에서는 per-token Q를 사용했다.
-
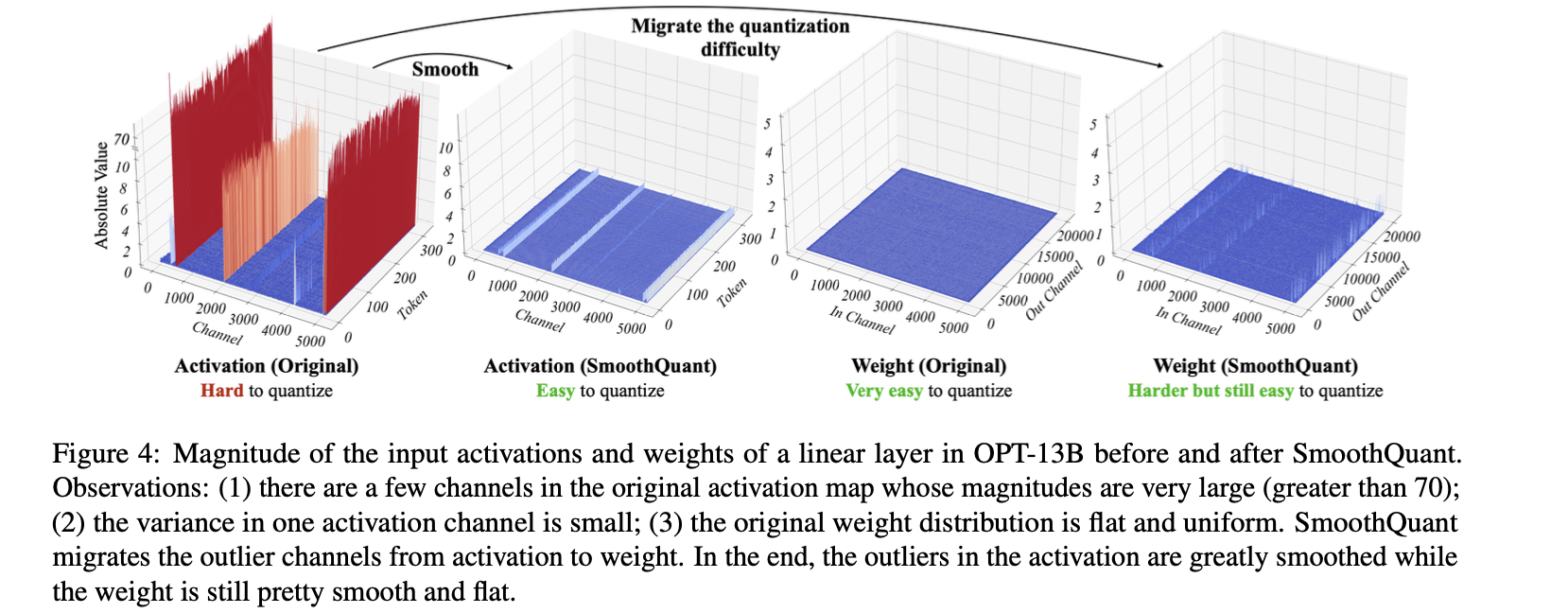
SmoothQuant
-
smoothing factor 도입해서, activation Q 어려움을 weight로 migration
-
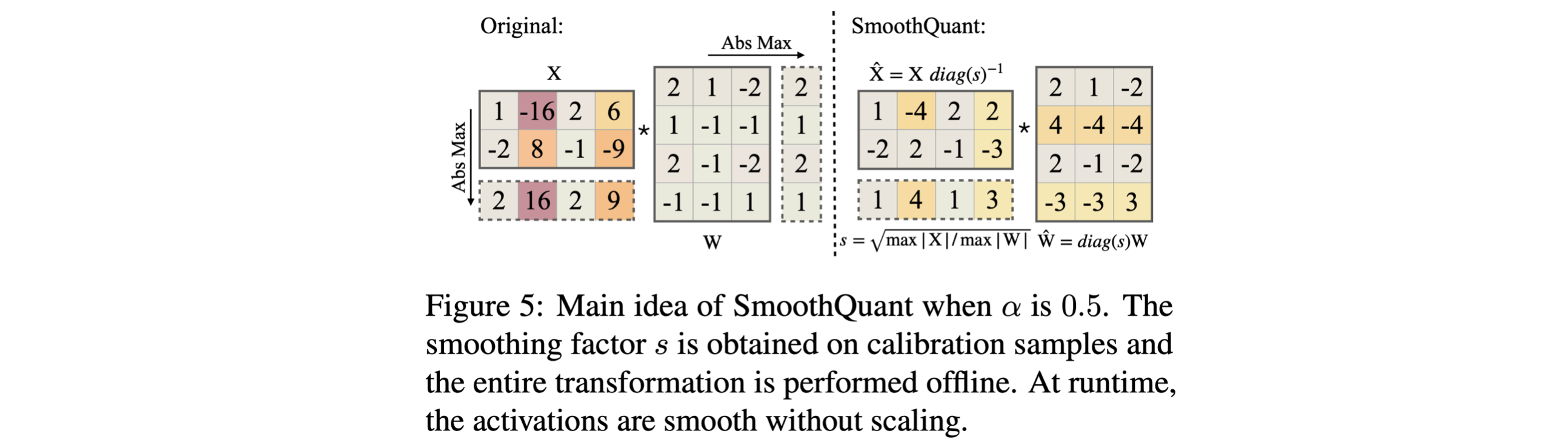
per-channel activation Q 대신, input activation을 per-channel smoothing factor 로 나누어 "smooth"하는 방법을 제안한다.
-
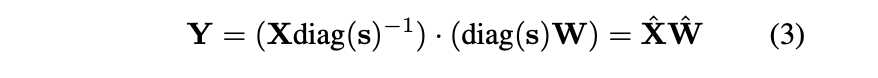
-
linear layer의 mathematical equivalence를 유지하기 위해서, (반대 방향으로) weights를 scaling 해준다.
-
-
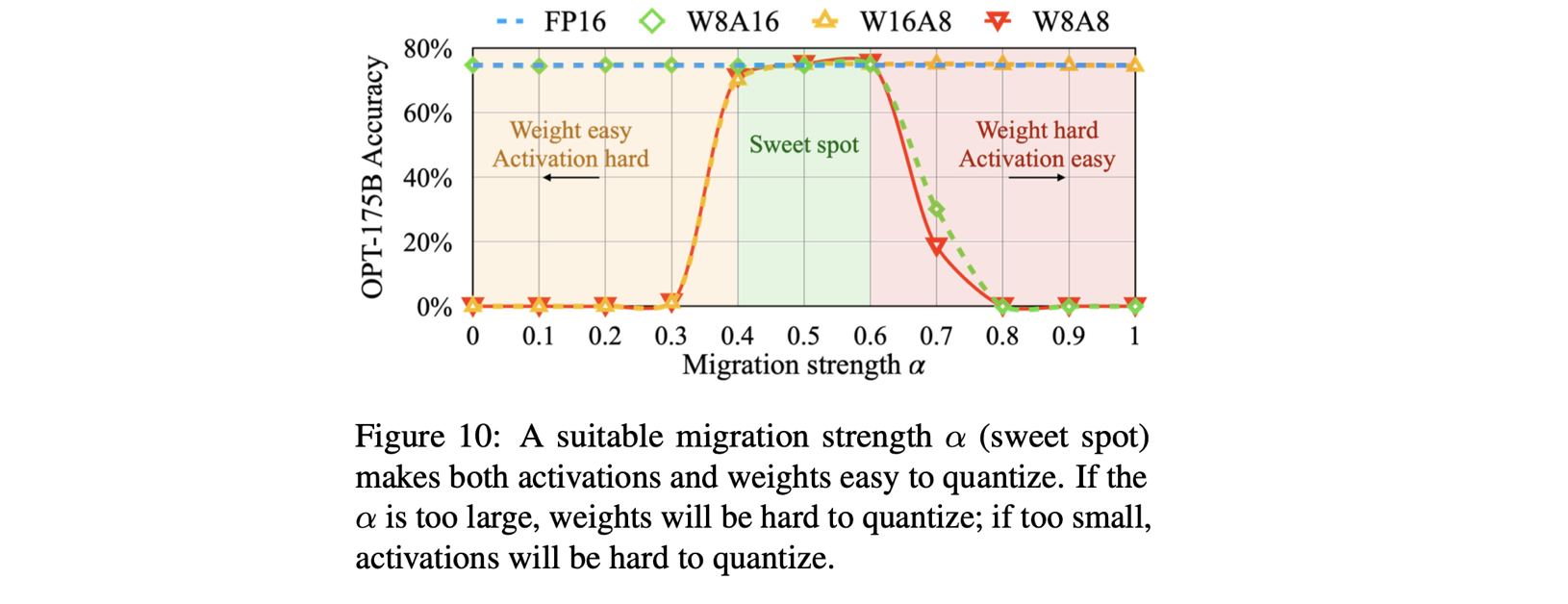
weight Q difficulty 와 activation Q difficulty 사이의 균형
-
migration strength 를 hyper-parameter로 도입해서, 얼마나 activation Q difficulty를 weight로 migration할지 결정한다.
-
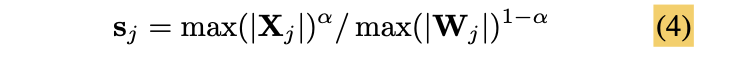
-
대응되는 weight row와 activation channel에서 유사한 maximum value를 공유하여, Q difficutly를 공유하도록 한다.
-
저자는 OPT, BLOOM 모델에 대해, 특히 weights와 activations에 동일한 quantizer(e.g. per-tensor, static Q)를 사용할 때, 가 균형잡힌 point임을 발견했다.
-
-
-
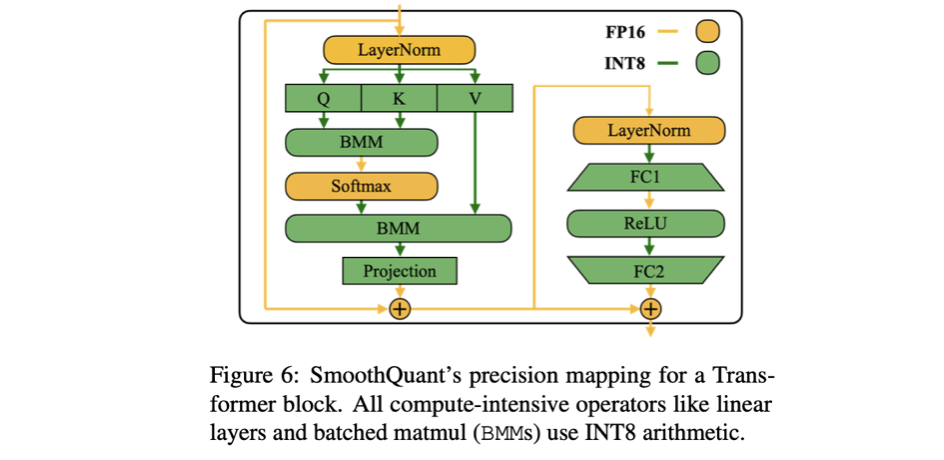
Transformer blocks에 적용
-
LLMs의 linear layer는 대부분의 parameter와 연산량을 차지한다.
-
compute-heavy-operators(linear layers, attention layers의 BMM)의 input과 weight를 INT8로 Q.
-
lightweight element-wise operations(ReLU, Softmax, Layer-Norm)의 activation은 FP16으로 유지.
-