
gather
(1) 2D tensor에서 대각선 요소 가져오기
import torch
A = torch.Tensor([[1, 2],
[3, 4]])
output = torch.gather(A, 0, torch.tensor([[0, 1]]))(2) 2*2*2 3D tensor에서 대각선 요소 가져오기
① 첫번째 시도. gather 두번 사용하기
import torch
A = torch.Tensor([
[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]
])
# torch.gather
index = torch.tensor([
[[0,1],
[0,1]],
[[0,1],
[0,1]]
])
output = torch.gather(A, 1, index)
print(output)
index = torch.tensor([
[[0,0],
[1,1]]
])
output = torch.gather(output, 0, index, out=None)
print(output)
② 두번째 시도. gather + view
# gather + view
import torch
A = torch.Tensor([
[[1, 2],
[3, 4]],
[[5, 6],
[7, 8]]
])
# torch.gather
index = torch.tensor([
[[0,0],
[1,1]],
[[0,0],
[1,1]]
])
# output = torch.gather(A, 2, index)
# print(output)
# (1) 각 행마다 대각 성분으로만 이루어진 행렬을 만든 후
# [[[1, 1],
# [4, 4]],
# [[5, 5],
# [8, 8]]]
# (2) dim 1 -> ([1,1,4,4,...])
# (3) 필요한 대각 성분만 slicing한 뒤 다시 reshape
output = torch.gather(A, 2, index).view(1,-1)[:,::2].view(2,2)
print(output)
(3) 임의의 크기의 3D tensor에서 대각선 요소 가져오기
import torch
# 3D tensor에서 대각선 요소 가져와 2D로 반환
def get_diag_element_3D(A):
C, H, W = A.size()
D = min(H, W) #
index = torch.tensor([[[i]*D for i in range(D)] for _ in range(C)])
# gather index의 경우,
# 2*3*4 -> 대각행렬은 한 row당 3*3
# 2*5*2 -> 한 row당 2*2 가 필요하므로 h, w의 min값을 활용한다.
output = torch.gather(A, 2, index).view(1,-1)[:,::D].view(-1,D)
return outputhook
Package 실행시, self.hooks에 등록된 함수가 있으면 실행한다.
tensor에 적용하는 hook
- register_hook - PyTorch 공식 문서
- register_backward_hook - PyTorch 공식 문서
- register_full_backward_hook - PyTorch 공식 문서
Module에 적용하는 hook
forward hook
module에만 적용되고, forward() 호출시 실행된다. 이때, forward_pre_hook는 forward 실행 전, forward_hook는 실행 후에 호출된다.
register_forward_pre_hook
import torch
from torch import nn
class Add(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
def forward(self, x1, x2):
output = torch.add(x1, x2)
return output
# 모델 생성
add = Add()
# answer = [x1, x2, output]
answer = []
# answer = [x1, x2]
def pre_hook(module, input):
# print('pre_hook : ', input[0], input[1])
answer.append(input[0])
answer.append(input[1])
return input[0], input[1]
add.register_forward_pre_hook(pre_hook)
# answer에 output 저장
def hook(module, input, output):
# print('hook : ', output)
answer.append(output)
return output
add.register_forward_hook(hook)
# answer.append(get_hook)
x1 = torch.rand(1)
x2 = torch.rand(1)
output = add(x1, x2)
print(answer)
backward hook
Module, tensor에 적용되고 backward() 호출시 실행된다.
(1) module 단위
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.W = Parameter(torch.Tensor([5]))
def forward(self, x1, x2):
output = x1 * x2
output = output * self.W
return output
# 모델 생성
model = Model()
# answer = [x1.grad, x2.grad, output.grad]
answer = []
# hook를 이용해서 answer에 x1.grad, x2.grad, output.grad 값을 저장하자
def module_hook(module, grad_input, grad_output):
answer.append(grad_input[0])
answer.append(grad_input[1])
answer.append(grad_output[0])
model.register_full_backward_hook(module_hook)
x1 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
x2 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
# print("answer : ",answer)
output = model(x1, x2)
output.retain_grad()
output.backward()
print("answer : ",answer)
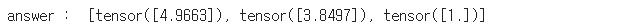
backward hook으로 gradient를 다뤄보자
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.W = Parameter(torch.Tensor([5]))
def forward(self, x1, x2):
output = x1 * x2
output = output * self.W
return output
# 모델 생성
model = Model()
# hook를 이용해서 module의 gradient 출력의 합이 1이 되게 만들어보자
# ex) (1.5, 0.5) -> (0.75, 0.25)
def module_hook(module, grad_input, grad_output):
print(grad_input)
total = 0
for grad in grad_input:
total+=grad
grad_input = torch.divide(grad_input[0],total), torch.divide(grad_input[1],total)
print(grad_input)
return grad_input
model.register_full_backward_hook(module_hook)
x1 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
x2 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
output = model(x1, x2)
output.backward()(2) tensor 단위
module 단위의 backward hook은, module 기준으로 input, output gradient 값만 가져와서 내부의 tensor의 gradient값은 알아낼 수 없다. 이 때는, tensor 단위의 hook를 사용한다.
import torch
from torch import nn
from torch.nn.parameter import Parameter
class Model(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.W = Parameter(torch.Tensor([5]))
def forward(self, x1, x2):
output = x1 * x2
output = output * self.W
return output
# 모델 생성
model = Model()
# Model의 Parameter W의 gradient 값을 저장하자
answer = []
def tensor_hook(grad):
answer.append(grad)
model.W.register_hook(tensor_hook)
x1 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
x2 = torch.rand(1, requires_grad=True)
output = model(x1, x2)
output.backward()
apply
입력으로 받는 모든 module을 순차적으로 처리한다.
(1) apply를 활용해 parameter(W)를 1로 초기화하는 함수를 구현해보자
model = Model()
# pply를 이용해 모든 Parameter 값을 1로 초기화
def weight_initialization(module):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
for param in module.parameters():
# param data를 update
param.data = torch.ones_like(param.data)
# apply는 apply가 적용된 module을 return 해준다
returned_module = model.apply(weight_initialization)(2) apply를 활용해 repr을 수정해보자
 ⬇
⬇

model = Model()
# apply를 이용해서 repr 출력을 수정
from functools import partial
def function_repr(self):
# print(self.name)
return f'name={self.name}'
def add_repr(module):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
try:
print(function_repr(module))
extra_repr = lambda repr:repr
module.extra_repr = partial(extra_repr, function_repr(module))
except:
pass
# apply 적용된 module을 return
returned_module = model.apply(add_repr)
model_repr = repr(model)
print("모델 출력 결과")
print("-" * 30)
print(model_repr)
print("-" * 30)
(3) apply를 활용해 function을 linear transformation처럼 동작하도록 수정하자
- Function_A :
x+W - Function_B :
x-W - Function_C :
x+W - Function_D :
x/W
➡ x @ W + b
model = Model()
from functools import partial
# Parameter b 추가
def add_bias(module):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
if module_name.split('_')[0] == "Function":
module.b = Parameter(torch.rand(2,1))
# 1로 초기화
def weight_initialization(module):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
add_bias(module)
if module_name.split('_')[0] == "Function":
module.W.data.fill_(1.0)
module.b.data.fill_(1.0)
# apply를 이용해 모든 Function을 linear transformation으로 바꾸자 (X @ W + b)
def hook(module, input, output):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
output = input[0] @ module.W.T
# output = torch.mul(input[0],module.W.T)
output = torch.add(output, module.b)
return output
def linear_transformation(module):
module_name = module.__class__.__name__
print(module_name)
if module_name.split('_')[0] == "Function":
module.register_forward_hook(hook)
returned_module = model.apply(add_bias)
returned_module = model.apply(weight_initialization)
returned_module = model.apply(linear_transformation)
# FriendLinearModel : nn.linear
class FriendLinearModel(nn.Module):
def __init__(self):
super().__init__()
self.linear = nn.Sequential(nn.Linear(2, 2),
nn.Linear(2, 2),
nn.Linear(2, 2),
nn.Linear(2, 2))
def forward(self, x):
return self.linear(x)
def friends_init_weights(m):
if type(m) == nn.Linear:
m.weight.data.fill_(1.0)
m.bias.data.fill_(1.0)
friend_model = FriendLinearModel()
friend_model.apply(friends_init_weights)
# nn.Linear 모델과 비교
grads = tester(model, friend_model)