[2022 ICML] Iterative Bilinear Temporal-Spectral Fusion for Unsupervised Representation Learning in Time Series (23회 인용)
Paper review
Abstract
다변량 시계열 데이터를 위한 비지도 표현학습은 어려움
1. Complex Dynamics
2. Sparse Annotations그래서 보통 data augmentation을 활용해 positive/negative sample을 만들고 contrastive learning 진행함
그러나 이러한 Representation Learning도 2가지 결점이 존재함
1. Time Slicing을 사용하는데 이는 sampling bias와 incorrect optimization를 가져옴
2. Spectral information과 temporal-spectral relations을 고려하지 않음
- 따라서 본 논문에서는 Bilinear Temporal-Spectral Fusion(BTSF)를 제안함.
1. Segment-level augmentation 대신 Instance-level augmentation을 이용함. (global context와 long-term dependencies를 제공하기 위해 전체 시계열에 단순 dropout을 적용함)
2. Cross-domain관계로 시계열 표현을 반복적으로 수정함.(time-frequency pairs를 인코딩하고 S2T와 T2S Aggregation module을 적용함)
3. Allignment와 Uniformity 평가를 추가적으로 진행함.
4. 실제 적용 능력을 파악하기 위해 Classification, Forecasting, Anomlay Detection을 진행함.
1. Introduction
- 시계열 분석은 많은 분야에서 사용되지만, 충분한 라벨이 없는 경우가 많음.
- 따라서, 시계열의 비지도 표현학습이 많이 연구되고 있음 (학습한 representation을 downstream task와 연결해서 활용함)
- Scalable Representation Learning(SRL)
- Contrastive Predictive Coding(CPC)
- Temporal and Contextual Contrasting(TS-TCC)
- Temporal Neighborhood Coding(TNC)
- 위 모델들의 주된 차이점은 contrastive pairs를 고를 때, time slicing 기반으로 서로 다른 sampling 정책을 사용한다는 것임
- 하지만, 위 정책들은 global semantical 정보가 없기 때문에 false negatives에 영향 받기 쉽고 long-term dependency를 포착하기 힘듦.
- 또한 temporal feature만 추출하고 spectral feature와 temporal-spectral relations를 무시함.
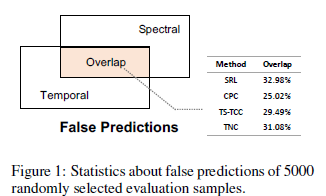
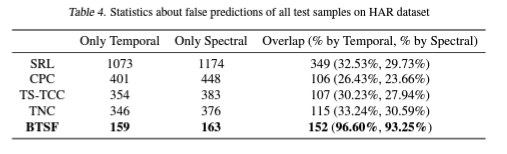
-> 기존 모델들의 temporal&Spectral 관점에서 false prediction의 겹치는 부분을 살펴본 결과, 30% 내외의 결과를 도출함
-> 이러한 실험 결과를 통해, 기존 모델들이 temporal과 spectral representation을 독립적으로 학습함을 알 수 있고, 둘의 관계를 동시에 학습하면 더 좋은 representation이 될 것임.
[제안 모델]
unsupervised representation learning framework for multivariate time series
Bilinear Temporal Spectral Fusion (BTSF)
1. global temporal information and long-term dependencies of time series
: 전체 시계열을 input을 대상으로 intance-level augmentation을 하기 위해 standard dropout 사용함.
2. iterative bilinear fusion between temporal and spectral features
3. cross-domain interaction with Spectrum-to-Time and Time-to-Spectrum Aggregation modules
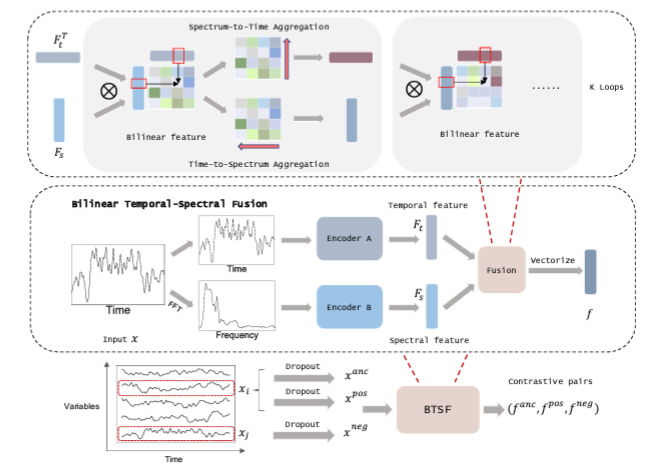
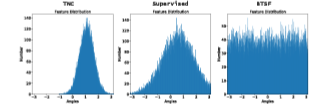
3. Method
3-1. Instance-level Augmentation
- 본 연구에서는 global temporal information을 보존하고, time series의 original 특성을 변화시키지 않기 위해, standard dropout을 적용함.
- 하나의 변수 x_i에서 x^anc와 x^pos를 만들고, 랜덤하게 선택된 다른 변수에서 x^neg 만듦.
- 실제 실험에서는. anchor를 만든 변수를 제외한 나머지 모든 변수에서 negative pair를 만듦.
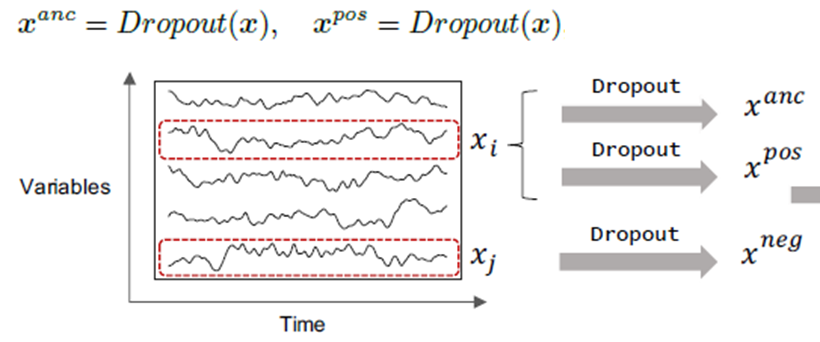
[장점] - Augmentation method의 특성 때문에 좀 더 일반적이고 시계열 상태에 독립적임.
(non-stationary, periodic time series에도 적용 가능함)
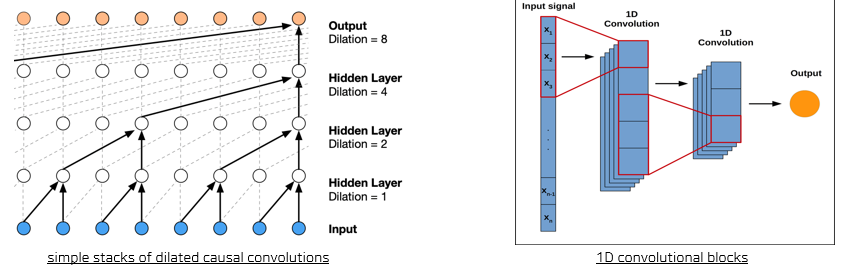
3-2. Temporal-Spectral Fusion
- 본 연구에서는 temporal features뿐만 아니라, spectral features를 활용함
- augmented time series x_t와 FFT로 변환된 spectral signal x_s를 각 encoding network를 통과시킴.
- Encoder_A(simple stacks of dilated causal convolutions) + max pooling
- Enocder_B(1D convolutional blocks) + max pooling
3-3. bilinear Feature
- 각 domain의 feature사이의 channel-wise interaction을 통해 time-frequency를 도출함.
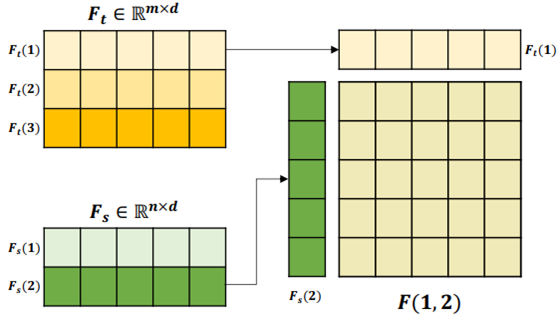
- Time frequency들의 합을 최종 F_bilinear로 사용함
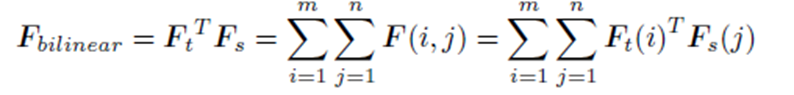
3-4. S2T & T2S Aggregation
- time-frequency 관련성을 더 잘 표현하기 위해 bilinear feature로부터 cross-domain dependency 도출함.
- Spectrum-to-Time Aggregation (S2T)
: F_t = BiCausal(Conv(F_bilinear))
- Time-to-Spectrum Aggregation (T2S)
: F_s = Conv(BiCausal(F_bilinear))
(Conv는 normal convolutional block이고, Bicausal은 bi-directional casual convolutional blocks)
3-5. Iterative Bilinear Fusion
- S2T와 T2S를 통해 정제된 temporal/spectral feature로 다시 bilinear feature를 도출하는 과정을 반복하여 최종 bilinear feature 도출함.
기타
-
Memory efficiency
- Quadratic expansiion으로 고차원의 feature가 저장되고 있음
- 따라서 메모리 효율을 높이기 위해, final bilinear feature를 low-rank로 변환함.
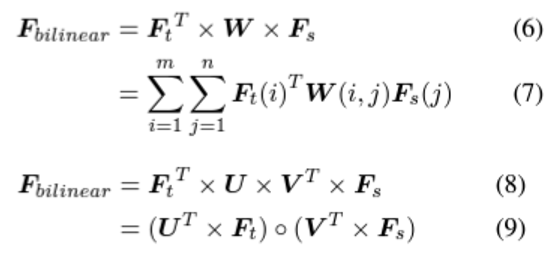
-
Final joint feature representation
- Original temporal and spectral information을 잊지 않기 위해, initial feature를 더함.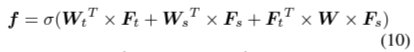
-
Loss function
- Contrastive learing에서 positive pair와의 거리는 가깝게, negative pair와의 거리는 멀게 학습함.
- 따라서, contrastive tuple에 대한 feature representation들로 loss function을 구성함.
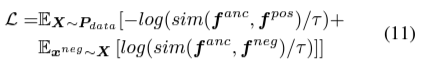
4. Experiments
비교모델
(공정한 비교를 위해 same encoding architecture와 비슷한 computational compexity와 parameters를 설정함)
- Contrastive Predictive Coding (CPC)
- Scalable Representation Learning (SRL)
- Temporal and Contextual Contrasting (TS-TCC)
- Temporal Neighborhood Coding (TNC)
Major tasks
- Classification
- Prediction
- Anomaly Detection
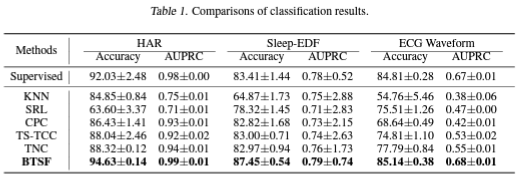
1. Time Series Classification
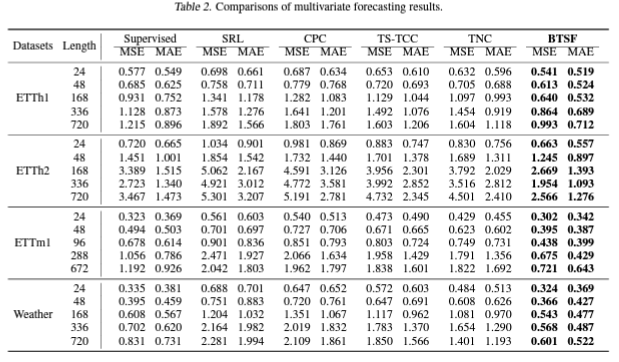
2. Time Series Forecasting
3. Time Series Anomaly Detection

4. Analysis
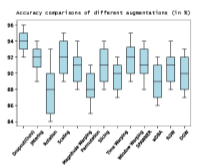
- Augmentation comparisons
- Impact of iterative bilinear fusion
-
Alignment

-
Uniformity